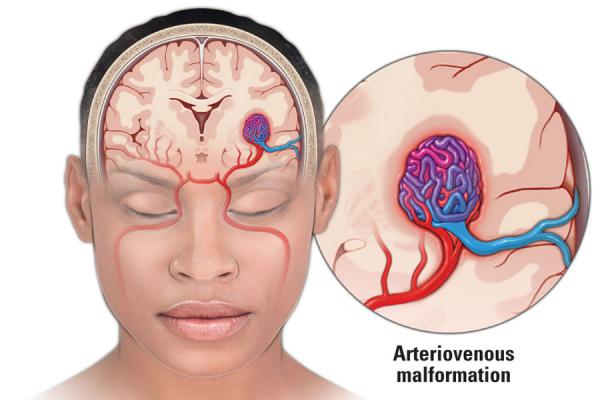
Arteriovenous Malformation Symptoms: Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) is a complex and often misunderstood medical condition, involving an abnormal connection between arteries and veins.
This connection disrupts the normal flow of blood and can have significant health implications. Understanding the symptoms and causes of AVM is crucial for early detection and effective management.
What is Arteriovenous Malformation?
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) is a complex, yet intriguing medical condition that requires a nuanced understanding. In essence, AVM is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. This medical anomaly is typically found in the brain or spine but can occur anywhere in the body.
To understand how AVM affects the body, it’s essential to grasp the role of arteries and veins. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to various parts of the body, while veins return oxygen-depleted blood back to the heart. Normally, blood flows from arteries to veins through a network of tiny vessels called capillaries. Here, oxygen and nutrients are exchanged for waste products.
In AVM, this orderly process is disrupted. The abnormal connection means blood flows directly from arteries to veins, skipping the crucial capillary stage. This can lead to multiple issues:
- High Pressure and Damage: The direct artery-to-vein connection subjects veins, which are not designed for high pressure, to arterial blood pressure. Over time, this can weaken the veins, leading to their potential rupture and bleeding.
- Reduced Oxygen Delivery: Since blood bypasses capillaries, there’s less efficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the surrounding tissues. This can lead to tissue damage and a range of symptoms, depending on the AVM’s location.
- Risk of Hemorrhage: The most significant risk associated with AVM is bleeding or hemorrhage. This is particularly concerning when the AVM is located in the brain, as a bleed here can lead to stroke-like symptoms or even life-threatening complications.
Understanding AVM is crucial for timely diagnosis and management. While some individuals with AVM may experience minimal symptoms, others might face significant health challenges. The key is to detect and monitor AVM to prevent or minimize complications.
Symptoms of Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
Recognizing the common symptoms associated with AVM is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
- Headaches and Seizures: One of the most prevalent symptoms of AVM, particularly when it occurs in the brain, is recurrent headaches. These are often accompanied by seizures, which may range from minor to severe.
- Neurological Issues: Depending on the AVM’s specific brain location, patients might experience a range of neurological symptoms. These can include muscle weakness, difficulty speaking, vision problems, and even severe neurological deficits.
- Bleeding: In some cases, AVMs can lead to bleeding, which is particularly dangerous when it occurs in the brain. This can result in a sudden, severe headache, often described as the worst headache of a person’s life.
- Pulsing Sound in the Ears: A less common but notable symptom is a pulsing sound in the ears, known as pulsatile tinnitus. This occurs when the AVM affects blood vessels near the auditory nerves.
Variability of Symptoms Based on AVM Location
The symptoms of AVM can vary significantly depending on its location:
- Brain AVMs: These often present with headaches, seizures, and neurological deficits. The risk of bleeding is a major concern, potentially leading to a stroke or brain damage.
- Spinal AVMs: When AVMs occur in the spinal cord, they can cause symptoms like back pain, muscle weakness, and loss of sensation in various body parts.
- Extremity AVMs: AVMs in arms or legs can lead to pain, swelling, and issues with blood flow to the affected limb.
Case Examples to Illustrate AVM Symptoms
To better understand how AVM symptoms manifest, consider these anecdotal cases:
- Case 1: A young woman presented with recurrent, unexplained headaches and was eventually diagnosed with a brain AVM after experiencing a seizure.
- Case 2: An older man developed sudden weakness in his legs. Medical evaluation revealed a spinal AVM, which was causing the neurological symptoms.
- Case 3: A child was noted to have a swollen, painful arm. Diagnostic tests showed an AVM in the upper limb, affecting blood circulation and nerve function.
However, being aware of the diverse symptoms of Arteriovenous Malformation and understanding how they vary based on the AVM’s location can aid in prompt diagnosis and treatment, mitigating potential complications.
Causes of Arteriovenous Malformation
Understanding the causes of AVM is critical for both patients and medical professionals. This article delves into the known causes and risk factors, examining both genetic and environmental aspects, and highlights the latest research findings in this field.
Known Causes and Risk Factors of AVM
While the exact cause of AVM remains a mystery in many cases, research has identified several factors that may contribute to its development. These factors range from genetic predispositions to environmental influences, painting a multifaceted picture of AVM etiology.
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in the development of AVM. Certain genetic conditions, such as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, have been linked to an increased risk of AVM. However, not all cases are hereditary, indicating that genetics is just one piece of the puzzle.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, although less understood, are also considered in AVM research. These may include prenatal exposure to certain substances or conditions that could potentially disrupt vascular development. The exact nature and impact of these environmental factors are still under investigation.
Current Research on AVM Causes
Recent studies have made significant strides in uncovering the complexities of AVM. Advanced imaging techniques and molecular biology have opened new avenues for understanding the underlying mechanisms of this condition. Current research is focused on identifying specific genetic mutations and environmental triggers that might contribute to the development of AVM, offering hope for more targeted treatments and prevention strategies in the future.
Understanding the causes of AVM is crucial for developing effective treatments and preventive measures. As research continues to evolve, it offers new insights into this challenging condition, bringing hope to those affected by AVM and expanding our knowledge of vascular diseases as a whole.
Diagnosing Arteriovenous Malformation
Diagnosing arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is a critical process that utilizes various advanced methods to identify this complex condition. Early detection is vital in managing AVM effectively, and understanding the role of symptoms in its diagnosis is crucial. This article delves into the methods used for diagnosing AVM, highlights the importance of early detection, and discusses the recent advances in diagnostic technology.
Methods Used for Diagnosing AVM
Diagnosing AVM involves a series of specialized tests and procedures. The most common methods include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI scans provide detailed images of the brain and spinal cord, helping to identify abnormal blood vessel structures characteristic of AVM.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: CT scans are used to detect bleeding in the brain and to visualize the structure of an AVM.
- Cerebral Angiography: This procedure involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels of the brain to make them visible under X-ray imaging. It’s the most accurate method for diagnosing AVM.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of AVM is crucial for several reasons:
- Preventing Hemorrhage: Undiagnosed AVMs can rupture, leading to brain hemorrhages. Early detection reduces this risk.
- Effective Treatment Planning: Detecting AVM early allows for more effective treatment planning, potentially including surgery or other interventions.
- Reducing Symptoms and Complications: Early diagnosis can help manage symptoms like headaches or seizures and prevent further complications.
Role of Symptoms in Diagnosis
Symptoms play a significant role in prompting the diagnosis of AVM. Common symptoms include:
- Headaches
- Seizures
- Muscle weakness or numbness
- Problems with speech or vision
- Unexplained noise in the ears
Recognizing these symptoms can lead to timely medical consultation and diagnosis.
Advances in Diagnostic Technology
Recent advances in diagnostic technology have significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of AVM diagnosis:
- High-Resolution Imaging: Improved MRI and CT scan technologies offer clearer, more detailed images.
- Functional MRI (fMRI): This advanced MRI technique maps brain activity and can show areas affected by the AVM.
- Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA): DSA provides more detailed images of blood vessels compared to traditional angiography.
However, diagnosing AVM involves a combination of advanced imaging techniques, awareness of symptoms, and an understanding of the importance of early detection. As technology advances, the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosing AVM continue to improve, enhancing patient outcomes.
Complications Arising from Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
Understanding the potential complications of arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is crucial for anyone dealing with this condition. When left untreated, AVM can lead to a range of health risks and challenges, each requiring immediate attention and care.
1. Increased Risk of Hemorrhage
One of the most severe complications of untreated AVM is the risk of hemorrhage or bleeding in the brain. This can occur when the abnormal blood vessels in the AVM rupture. Symptoms of a brain hemorrhage include severe headaches, nausea, vomiting, and sudden weakness or numbness, especially on one side of the body. It’s vital to seek immediate medical attention if these symptoms occur, as a brain hemorrhage can be life-threatening.
2. Progression of Neurological Symptoms
AVM can progressively worsen over time, leading to a variety of neurological symptoms. These may include seizures, which are sudden bursts of electrical activity in the brain causing convulsions or changes in behavior. There’s also the risk of progressive neurological decline, manifested as difficulties in speech, memory, or movement coordination, severely impacting daily life.
3. Increased Intracranial Pressure
Another potential complication of AVM is increased intracranial pressure. This happens when the abnormal blood flow caused by AVM leads to increased pressure within the skull. Symptoms can include headaches, blurred vision, and changes in consciousness. Over time, this increased pressure can cause significant damage to the brain tissue.
4. Stroke-Like Symptoms
In some cases, AVM can lead to symptoms similar to those of a stroke. These include sudden weakness, difficulty speaking, and loss of vision. These symptoms occur due to the abnormal blood flow in the brain, which can deprive certain areas of the oxygen and nutrients they need to function properly.
5. Cardiovascular Strain
AVM can also put extra strain on the heart. The abnormal connections between arteries and veins in an AVM can cause the heart to work harder to pump blood, potentially leading to heart-related complications.
However, untreated AVM poses several health risks, each with its own set of symptoms and potential outcomes. Recognizing these symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical care is essential for managing AVM and preventing these serious complications. Regular check-ups and following a treatment plan tailored by healthcare professionals can significantly reduce the risks associated with AVM.
Treatment Options for Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM): An In-Depth Guide
This guide offers a comprehensive overview of current treatment methods, considerations based on symptoms and severity, and a look at future trends in AVM treatment.
Current Treatment Methods for AVM
Surgical Interventions
- Microsurgical Resection: This involves the surgical removal of the AVM. It’s most effective when the AVM is accessible and not deeply embedded in the brain.
- Endovascular Embolization: Through this minimally invasive procedure, a glue-like substance is injected to block the abnormal blood vessels, reducing the risk of bleeding.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery: This non-invasive technique uses focused radiation to shrink the AVM over time.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Medication: While medications can’t cure AVM, they can help manage symptoms like headaches and seizures.
- Observation and Monitoring: In cases where AVMs present a low risk, regular monitoring through imaging tests may be recommended.
Treatment Based on Symptoms and Severity
- Mild AVMs: Often managed with medication and regular monitoring.
- Moderate to Severe AVMs: These usually require interventional therapies like embolization or surgery, especially if there is a risk of bleeding or stroke.
- Symptomatic AVMs: If AVMs cause symptoms like seizures or headaches, targeted treatments to alleviate these symptoms are essential.
Future Trends in AVM Treatment
- Advanced Imaging Techniques: Enhanced imaging technologies may provide better mapping of AVMs, aiding in more precise treatments.
- Genetic Research: Understanding the genetic factors that cause AVMs could lead to targeted therapies.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Ongoing research aims to improve minimally invasive procedures, reducing recovery times and risks.
The treatment of Arteriovenous Malformation requires a tailored approach, considering the individual’s symptoms and the severity of the condition. With ongoing research and advancements in medical technology, the future holds promise for more effective and less invasive treatment options.
Living with Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM): Navigating Lifestyle Adjustments and Gaining Insights Through Patient Stories
Living with an arteriovenous malformation (AVM) can be a challenging journey, requiring significant lifestyle adjustments and a deep understanding of the condition. This comprehensive guide aims to provide valuable insights into managing life with AVM, enriched by real-life stories and experiences from patients who have navigated this path.
Lifestyle Adjustments for AVM Patients
Living with AVM often means adapting your lifestyle to accommodate the condition and mitigate risks. Key adjustments might include:
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Staying in close contact with healthcare providers for ongoing monitoring of the AVM.
- Managing Symptoms: Learning to recognize and respond to symptoms like headaches or seizures, which could indicate changes in the AVM.
- Physical Activity Considerations: Tailoring exercise routines to avoid high-impact or strenuous activities that might exacerbate the condition.
- Diet and Nutrition: Adopting a balanced diet that supports overall health and well-being.
- Stress Management: Developing strategies to manage stress, as emotional well-being plays a significant role in physical health.
Patient Stories: The Heart of Living with AVM
Patient stories offer a unique and personal perspective on living with arteriovenous malformation. These narratives provide not only a glimpse into the daily challenges and triumphs but also serve as a source of inspiration and support for others in similar situations. Interviews with AVM patients can reveal:
- Personal Coping Strategies: How individuals have adapted their lives to manage AVM, including changes in work, hobbies, and family life.
- Emotional Impact: The psychological aspects of dealing with a chronic condition and how patients maintain mental health.
- Community and Support: The importance of finding support groups or communities of others living with AVM.
- Treatment Experiences: Personal experiences with different treatments, including surgery, medication, or other therapies.
Living with arteriovenous malformation presents unique challenges, but with the right knowledge, lifestyle adjustments, and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Patient stories are a vital component, offering real-world insights and encouragement. By understanding and adapting to the condition, those affected by AVM can navigate their journey with resilience and hope.
Prevention and Awareness of Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
Strategies for Prevention
Although the prevention of Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) can be challenging due to its often congenital nature, certain strategies can be instrumental in minimizing risks. These strategies focus primarily on mitigating factors that could potentially exacerbate an existing AVM or increase the risk of complications.
- Regular Medical Check-Ups: Early detection through routine medical examinations can be crucial. Individuals with a family history of AVM or related conditions should consider regular check-ups.
- Management of Associated Conditions: Proper management of conditions like high blood pressure and vascular disorders can reduce the strain on blood vessels, potentially lowering the risk of complications from AVM.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoidance of smoking, can improve overall vascular health.
- Avoiding High-Impact Activities: Individuals diagnosed with AVM may be advised to avoid activities that significantly increase blood pressure or pose a risk of head trauma.
Importance of Awareness and Education
Awareness and education about AVM are vital for several reasons:
- Early Detection: Educating the public about the symptoms and risks associated with AVM can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment, potentially reducing the risk of life-threatening complications.
- Understanding Risks: Awareness programs can help individuals understand the potential risks and complications associated with AVM, such as hemorrhage or neurological deficits.
- Empowering Patients: Knowledge about AVM empowers patients and their families to make informed decisions regarding treatment options and lifestyle modifications.
- Promoting Research and Support: Increased awareness can lead to more research funding and the development of support networks for those affected by AVM.
- Removing Stigma: Educating the broader community helps in destigmatizing the condition, fostering a more supportive environment for individuals dealing with AVM.
However, while prevention of AVM may not always be possible, adopting precautionary measures, staying informed, and seeking regular medical advice can play a significant role in managing the condition. Moreover, widespread awareness and education are crucial in enhancing early detection, supporting research, and providing a better quality of life for those affected.
Conclusion
As we conclude, it’s essential to remember that while this article provides valuable information about AVM, it cannot substitute for professional medical advice. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms suggestive of AVM, it’s imperative to seek professional medical advice promptly. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are key to managing AVM effectively and reducing the risk of complications.
Your health and well-being are paramount. Don’t hesitate to consult healthcare professionals for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized medical guidance. Remember, timely intervention can make a significant difference in the outcome of AVM treatment.