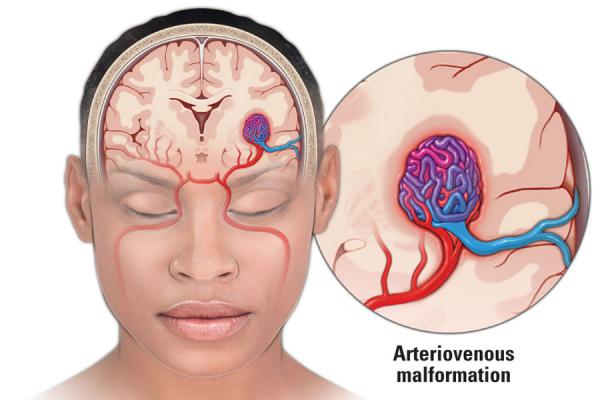
Arteriovenous Malformation Treatment: Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) is a complex, neurological condition characterized by an abnormal connection between arteries and veins.
This disorder can occur anywhere in the body but is most commonly found in the brain or spine. Understanding AVM is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
What is Arteriovenous Malformation?
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) is a complex medical condition involving an abnormal tangle of blood vessels. This condition arises when arteries and veins in the body connect improperly, bypassing the capillary system. This atypical connection can lead to various complications, as the high-pressure flow of blood from the arteries directly into the veins puts stress on the vascular system.
Types of AVMs
AVMs can occur in various parts of the body, but they are most commonly found in the brain and spine. The types of AVMs are generally classified based on their location and the characteristics of the abnormal vessels. Some common types include:
- Brain AVMs: Located in the brain, these are the most serious due to the potential for brain damage.
- Spinal AVMs: These occur along the spinal cord and can affect spinal function.
- Peripheral AVMs: Found in other parts of the body, such as the limbs, lungs, or kidneys.
Each type of AVM may present different symptoms and require distinct approaches to treatment.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
AVMs are relatively rare, affecting less than 1% of the population. They can occur in any age group but are most often diagnosed in people between the ages of 20 and 40. The exact cause of AVMs is not well understood, but they are generally believed to arise during fetal development.
Risk factors for developing an AVM are not clearly defined, but certain genetic conditions may increase the likelihood of having an AVM. It’s also observed that males are slightly more prone to this condition than females. There is no known way to prevent an AVM from forming, but understanding the risk factors and early detection can play a crucial role in managing the condition effectively.
Symptoms and Early Detection of Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
Understanding the symptoms and recognizing the need for prompt medical attention are crucial steps in managing this condition effectively.
Common Symptoms Associated with Arteriovenous Malformation
The symptoms of AVM can vary greatly depending on the location and size of the malformation. However, some common symptoms include:
- Headaches: Often the first and most common symptom, these can range from mild to severe.
- Seizures: Uncontrolled electrical disturbances in the brain can manifest as seizures in individuals with AVM.
- Muscle Weakness or Numbness: This can occur, particularly on one side of the body.
- Difficulty Speaking or Understanding Speech: AVM can affect areas of the brain responsible for language.
- Vision Problems: Some individuals may experience a loss of vision or other vision disturbances.
- Unexplained Dizziness or Balance Issues: These can occur if the AVM affects certain parts of the brain.
Importance of Recognizing Symptoms for Early Diagnosis
Early detection of AVM is critical. Recognizing the symptoms promptly can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment, potentially preventing more serious complications like brain damage or stroke. Early diagnosis often results in more effective treatment outcomes and can significantly reduce the risks associated with this condition.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is essential to seek medical attention if you or someone you know experiences any of the symptoms mentioned above, especially if they are sudden or severe. Consulting a healthcare professional is vital for a proper diagnosis. Remember, not all symptoms may be present, and they can vary in intensity. Therefore, any unusual or persistent symptoms should be evaluated by a medical expert.
However, being aware of the symptoms of Arteriovenous Malformation and understanding the importance of early detection are key. Prompt medical consultation can make a significant difference in the management and outcome of AVM treatment.
Diagnosing Arteriovenous Malformation
Diagnosing an arteriovenous malformation (AVM) involves a combination of sophisticated techniques and specialized medical expertise. This process is crucial for accurately identifying AVMs, which are abnormal connections between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. Here’s a detailed look at how AVMs are diagnosed:
Understanding Diagnostic Procedures for AVM
1. Initial Evaluation
The diagnostic journey begins with a thorough patient evaluation. Doctors look for symptoms like headaches, seizures, or neurological deficits, which might suggest the presence of an AVM. A detailed medical history is taken, focusing on risk factors and family history.
2. Imaging Techniques
Imaging plays a pivotal role in diagnosing AVMs:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This technique provides detailed images of the brain and blood vessels. It helps in identifying the location and size of the AVM. MRI is especially useful for understanding the relationship of the AVM with surrounding brain structures.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): A CT scan can quickly visualize the brain and is often the first imaging test performed, especially if bleeding is suspected. It can detect hemorrhages, which are a common complication of AVMs.
- Angiography: This is a critical diagnostic tool for AVM. It involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels and taking X-ray images. Angiography offers a detailed view of the blood flow in the arteries and veins, helping to delineate the structure of the AVM.
3. Confirming the Diagnosis
After initial imaging, if an AVM is suspected, further detailed angiographic studies are usually conducted. This helps in confirming the diagnosis and planning for potential treatment. The process involves mapping the AVM’s specific architecture, which is vital for any surgical or interventional procedures.
Role of Multidisciplinary Team
A multidisciplinary team, including neurologists, neurosurgeons, and radiologists, collaborates to interpret the results of these diagnostic tests. Their combined expertise ensures a comprehensive evaluation and an accurate diagnosis, which is crucial for effective management of AVM.
The diagnosis of arteriovenous malformation is a meticulous process, heavily reliant on advanced imaging techniques. Understanding the nuances of these procedures helps patients and their families in comprehending the condition and the importance of accurate diagnosis for effective treatment planning.
Treatment Options for Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
Understanding the array of available options is crucial for patients and healthcare providers. This comprehensive overview dives into the latest and most effective treatments for AVM, covering both surgical and non-surgical approaches, as well as highlighting innovative advancements in the field.
Surgical Treatments for AVM
- Resection: This surgical procedure involves the direct removal of the AVM from the brain or spinal cord. It’s often considered for AVMs that are accessible and not deeply embedded in critical brain areas. The success of resection largely depends on the location and size of the AVM.
- Endovascular Embolization: This less invasive method involves inserting a catheter into the arteries and guiding it to the AVM. Once in place, a substance is released to block the blood flow to the AVM, reducing the risk of bleeding. Endovascular embolization can be a stand-alone treatment or used in conjunction with other procedures to make surgery safer.
Non-Surgical Treatments for AVM
Radiosurgery: A non-invasive alternative, radiosurgery uses focused radiation to damage the blood vessels in the AVM, causing them to close over time. This method is particularly useful for smaller AVMs or those located in difficult-to-reach areas. The effects of radiosurgery develop gradually, and it may take several years to fully realize the benefits.
Innovations in AVM Treatment
The field of AVM treatment is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and technological advancements. Innovations include improved imaging techniques for precise AVM localization, advancements in endovascular materials, and the development of more targeted radiation therapies. These advancements promise to increase the efficacy, safety, and accessibility of treatments for AVM patients.
However, the treatment of Arteriovenous Malformation is multifaceted, offering various surgical and non-surgical options. The choice of treatment depends on the AVM’s characteristics and the patient’s overall health. With ongoing research and innovations, the future of AVM treatment looks promising, potentially offering more effective and less invasive options for patients.
Managing Risks and Complications of Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
Here, we delve into the potential complications of AVM and its treatments, explore strategies for effective risk management, and discuss the long-term outlook for patients with AVM.
Potential Complications of AVM and Its Treatments
AVM can lead to a range of complications, primarily due to the abnormal blood flow and the risk of bleeding in the brain. The most significant complications include:
- Hemorrhage: Bleeding in the brain, which can cause stroke-like symptoms or more severe outcomes.
- Seizures: Resulting from irritation of the brain tissue surrounding the AVM.
- Headaches: Often similar to migraines, these can be persistent and debilitating.
- Neurological Problems: Depending on the location of the AVM, various neurological issues such as muscle weakness, numbness, or difficulties with speech and vision can occur.
Treatment options, including surgery, endovascular embolization, and radiosurgery, also carry risks. These can range from general surgical risks like infection to specific issues like neurological damage or recurrence of the AVM.
Strategies for Risk Management
Effective management of AVM involves a multidisciplinary approach, tailored to the individual’s condition and overall health. Key strategies include:
- Regular Monitoring: Routine check-ups and imaging tests to monitor the AVM’s size and blood flow.
- Medication Management: To control symptoms like headaches and seizures.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Including stress management and avoiding activities that may strain the cardiovascular system.
- Informed Decision-Making: Understanding the benefits and risks of different treatment options.
Patients should maintain open communication with their healthcare team, ensuring any symptoms or changes in their condition are promptly addressed.
Long-Term Outlook for Patients with AVM
The prognosis for AVM patients varies widely based on the size, location, and nature of the malformation, as well as the individual’s overall health. With advancements in medical treatments and surgical techniques, many patients can manage their condition effectively and maintain a good quality of life. Early detection and treatment are crucial in minimizing the risk of serious complications.
Regular follow-ups and a personalized treatment plan play a pivotal role in the long-term management of AVM. While some risks persist, ongoing research and evolving medical practices continue to improve outcomes for AVM patients.
Living with Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM): A Guide to Management and Support
Understanding how to effectively manage and live with AVM is crucial for maintaining a good quality of life. This guide provides insights into lifestyle adjustments, support systems, and the importance of ongoing care and monitoring for individuals living with AVM.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Managing AVM
Living with AVM requires certain lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms and reduce risks. These include:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in light to moderate exercise can improve overall health. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to identify safe activities.
- Dietary Considerations: A balanced diet, possibly with specific nutritional guidelines tailored to your condition, can play a significant role in managing AVM.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or other relaxation practices can help in managing stress, which is crucial for AVM patients.
- Avoiding Certain Activities: Activities that significantly increase blood pressure or pose a risk of head injury should be avoided.
Support Systems: Counseling and Patient Support Groups
Dealing with AVM can be emotionally challenging. Accessing a strong support system is vital:
- Professional Counseling: Talking to a mental health professional can help in coping with the emotional aspects of living with AVM.
- Patient Support Groups: Joining AVM support groups allows for sharing experiences and tips with others who understand your situation.
Ongoing Care and Monitoring
Regular medical check-ups and monitoring are crucial for AVM patients:
- Routine Medical Appointments: Regular visits to your healthcare provider are necessary for monitoring the condition and making any necessary adjustments to treatment.
- Monitoring Symptoms: Being aware of new or worsening symptoms and reporting them to your doctor promptly is vital.
- Staying Informed: Keeping up-to-date with the latest AVM research and treatments can empower patients and help in making informed decisions about their care.
However, living with Arteriovenous Malformation requires a multifaceted approach involving lifestyle adjustments, emotional support, and consistent medical care. By embracing these strategies, individuals with AVM can lead fulfilling and healthy lives.
Advancements in Arteriovenous Malformation Treatment
The field of arteriovenous malformation (AVM) treatment has witnessed significant progress in recent years, marked by groundbreaking research and innovations. This article delves into the latest advancements and looks ahead to the future of treatment methods.
Recent Research and Developments in AVM Treatment
Recent advancements in AVM treatment have been transformative, offering new hope to patients. Key developments include:
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Surgeons are increasingly adopting less invasive procedures, which reduce recovery time and complications.
- Improved Imaging Technologies: Advanced imaging methods, like 3D angiography, provide detailed views of blood vessels, aiding in precise treatment planning.
- Targeted Drug Therapies: New pharmacological treatments focus on reducing the size of AVMs or controlling symptoms, offering alternatives to surgery.
- Radiosurgery Innovations: Enhanced radiosurgery techniques, like Gamma Knife and CyberKnife, offer precise treatment with fewer side effects.
These breakthroughs not only improve survival rates but also enhance the quality of life for AVM patients.
Future Prospects in Treatment Methods
Looking to the future, the field of AVM treatment is poised for further exciting developments:
- Gene Therapy: Research is exploring the potential of gene therapy to treat or even prevent AVMs.
- Regenerative Medicine: Stem cell research could lead to new ways to repair damaged blood vessels.
- Artificial Intelligence in Diagnosis: AI and machine learning algorithms are being developed to predict AVM risks and personalize treatment plans.
- Nanotechnology: The use of nanotechnology in drug delivery could revolutionize the way medications are administered to AVM patients.
The continuous evolution of AVM treatment methods promises more effective and personalized care for patients in the future. As research progresses, the hope is that these innovations will lead to a world where AVM is no longer a life-altering diagnosis.
FAQs: Understanding AVM and Its Treatment
Navigating through the complexities of Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) and its treatment can be challenging. This FAQ section aims to address common questions, offering clear and concise information to enhance your understanding.
What is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) is a vascular disorder where there’s an abnormal connection between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. This condition can occur anywhere in the body but is most commonly found in the brain or spine.
How is AVM diagnosed?
AVM diagnosis often involves imaging tests such as MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), MRA (Magnetic Resonance Angiography), or CT (Computed Tomography) scans. These tests help in providing detailed images of the blood vessels and identifying any abnormalities.
What are the symptoms of AVM?
Symptoms of AVM can vary based on its location and size. Common symptoms include headaches, seizures, weakness, numbness, or difficulty speaking. However, some individuals with AVM may not experience any symptoms.
What are the treatment options for AVM?
Treatment for AVM depends on several factors, including its size, location, and the patient’s overall health. Options include surgical removal, endovascular embolization (blocking the AVM with glue or other materials), and radiosurgery.
Is AVM treatment always necessary?
Not all AVMs require immediate treatment. Small, asymptomatic AVMs might be monitored over time. The decision to treat is based on the potential risks of bleeding versus the risks of the treatment procedure.
Can AVM lead to other health issues?
Yes, AVM can lead to serious health issues, including hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding in the brain), which is a life-threatening condition. Regular monitoring and appropriate treatment are crucial in managing these risks.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage AVM?
While lifestyle changes alone cannot cure AVM, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding high blood pressure, and regular check-ups can help manage the condition and reduce risks.
Can AVM recur after treatment?
There is a possibility of AVM recurrence, especially in younger patients or in cases of partial treatment. Regular follow-up is important to monitor for any signs of recurrence.
For more detailed information or specific concerns, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional experienced in treating AVM. Understanding your condition and treatment options is a vital step towards effective management and improved health outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, comprehending the nuances of arteriovenous malformation treatment is vital. It not only empowers patients and their families but also plays a significant role in making informed healthcare decisions.
Remember, knowledge is a powerful tool in the journey towards effective treatment and management of AVMs.