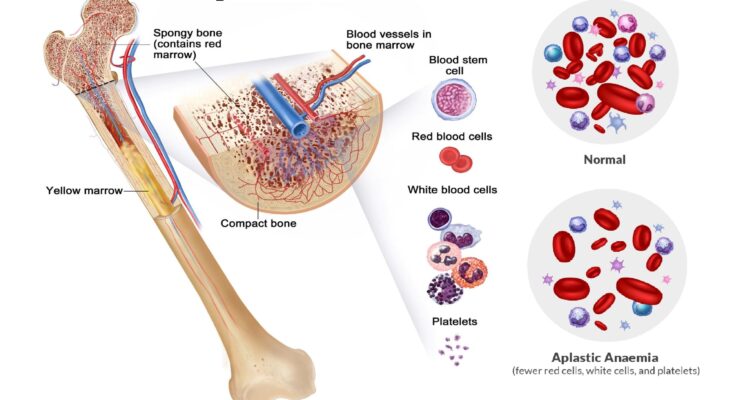
Aplastic Anemia Symptoms: Aplastic anemia is a rare, potentially life-threatening condition characterized by the bone marrow’s inability to produce sufficient blood cells.
This comprehensive guide delves into the symptoms and causes of aplastic anemia, offering essential information for individuals seeking to understand this complex condition.
What is Aplastic Anemia?
Aplastic anemia is a rare, serious blood disorder characterized by the bone marrow’s failure to produce sufficient new blood cells. This condition affects the body’s ability to regenerate and maintain a healthy supply of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Essentially, aplastic anemia results in a deficiency of all three types of blood cells, which can lead to a range of health complications.
Impact on the Body
The deficiency of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in aplastic anemia has significant effects on the body:
- Red Blood Cells: Their scarcity leads to fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath because of inadequate oxygen transport.
- White Blood Cells: A reduction in these cells compromises the immune system, increasing the risk of infections.
- Platelets: Low platelet counts can result in prolonged bleeding and bruising, as platelets are crucial for blood clotting.
Statistics and Demographics
Aplastic anemia is relatively rare, affecting fewer than 1,000 people each year in the United States. However, its incidence varies globally and can occur at any age. It’s slightly more common in teens and young adults, and again in those over 60. The condition does not show a significant gender bias but has been observed to be more prevalent in certain geographical regions, potentially due to environmental factors.
In terms of demographics, aplastic anemia is a concern for everyone, although certain genetic conditions or exposure to toxic substances can increase the risk. Timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the disease and improving the quality of life for those affected.
Symptoms of Aplastic Anemia
Understanding its symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. This article provides a detailed overview of the common symptoms of aplastic anemia, their implications, and how they differ from other forms of anemia.
Common Symptoms of Aplastic Anemia
- Fatigue and Weakness: These are primary symptoms, resulting from the reduced red blood cell count, which leads to decreased oxygen delivery to the body’s tissues.
- Shortness of Breath: This occurs due to the lack of sufficient red blood cells to carry oxygen, causing difficulty in breathing, especially during physical exertion.
- Pale Skin: The decrease in red blood cells often leads to a noticeable paleness of the skin.
- Frequent Infections: Due to the low white blood cell count, the body’s ability to fight infections is compromised, leading to increased susceptibility to illnesses.
- Unexplained Bruising or Bleeding: A reduced platelet count, responsible for blood clotting, can cause easy bruising, nosebleeds, or bleeding gums.
Explaining the Symptoms and Their Impact
Each symptom of aplastic anemia has a direct link to the bone marrow’s impaired ability to produce blood cells:
- Fatigue and Weakness: These symptoms significantly impact the quality of life, making daily activities challenging.
- Shortness of Breath: It can limit physical activity and may be distressing or frightening.
- Pale Skin: While often less directly impactful, it can be a visible sign prompting medical investigation.
- Frequent Infections: This can be dangerous, leading to severe illnesses that require immediate medical attention.
- Unexplained Bruising or Bleeding: These can be signs of potentially serious medical issues and may require prompt treatment to prevent severe complications.
Differentiating from Other Forms of Anemia
Aplastic anemia differs from other forms of anemia in several ways:
- Cause: Unlike other anemias often caused by nutritional deficiencies or chronic diseases, aplastic anemia is primarily due to bone marrow failure.
- Blood Cell Counts: In aplastic anemia, all three blood cell lines (red cells, white cells, and platelets) are typically reduced, which is not always the case in other forms of anemia.
- Treatment and Prognosis: The treatment approach and prognosis in aplastic anemia are significantly different, often involving bone marrow transplants and long-term immunosuppressive therapy.
However, recognizing the unique symptoms of aplastic anemia and understanding how they differ from other anemias are vital for effective diagnosis and management. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
Causes of Aplastic Anemia: Understanding the Triggers
Understanding its causes is crucial for both diagnosis and treatment. This article delves into the known causes, differentiating between congenital and acquired factors, and examines the role of environmental and genetic influences.
Exploring Known Causes
Aplastic anemia can stem from various sources. The condition is often idiopathic, meaning its exact cause remains unknown in many cases. However, several recognized factors contribute to its development:
- Autoimmune Disorders: The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys healthy bone marrow cells.
- Exposure to Toxic Chemicals: Certain chemicals, like benzene, are linked to the development of aplastic anemia.
- Medications: Some drugs, especially those used in chemotherapy, can harm bone marrow.
- Viral Infections: Infections such as hepatitis, Epstein-Barr, or HIV can trigger aplastic anemia.
- Radiation Therapy: Used primarily in cancer treatment, radiation can damage bone marrow.
Congenital vs. Acquired Causes
Aplastic anemia causes are classified into two categories:
- Congenital Aplastic Anemia: This form is present at birth and often linked to genetic syndromes like Fanconi anemia.
- Acquired Aplastic Anemia: Develops later in life due to factors like exposure to toxic chemicals, certain medications, radiation therapy, and autoimmune disorders.
The Role of Environmental Factors and Genetics
Environmental Influences: Prolonged exposure to toxic substances, radiation, and certain medications are significant environmental contributors. Lifestyle factors, such as exposure to hazardous chemicals in the workplace, also play a role.
Genetic Factors: While less common, genetic predisposition can be a factor, particularly in congenital aplastic anemia. Certain inherited conditions like Fanconi anemia directly influence the likelihood of developing aplastic anemia.
Aplastic anemia arises from a complex interplay of factors, with both environmental and genetic elements playing pivotal roles. Understanding these causes is vital for effective management and treatment strategies. Early diagnosis and identification of the specific cause can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Diagnosing Aplastic Anemia: A Comprehensive Guide
Early detection is crucial in managing this disease effectively. This guide outlines the diagnostic process, emphasizing symptom recognition, various tests, and the importance of early detection.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Aplastic Anemia
The first step in diagnosing aplastic anemia is symptom recognition. Common symptoms include fatigue, shortness of breath, irregular heart rate, pale skin, frequent infections, unexplained bruising, and prolonged bleeding. Awareness of these symptoms is essential, as they often mimic other health conditions, making early diagnosis challenging.
Diagnostic Tests and Examinations
Once symptoms are identified, healthcare professionals employ several tests and examinations to diagnose aplastic anemia:
- Blood Tests: Complete blood count (CBC) tests are crucial for measuring the levels of red and white blood cells and platelets. Low counts of these cells may indicate aplastic anemia.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: This is a definitive test where a sample of bone marrow is extracted for examination. It helps in determining the health of blood-forming cells.
- Viral Infection Tests: Since certain infections can lead to aplastic anemia, testing for viral infections is often part of the diagnostic process.
- Autoimmune Disorder Screening: Autoimmune disorders can cause aplastic anemia, so tests to rule out these conditions are common.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of aplastic anemia is vital for several reasons:
- Improves Treatment Efficacy: Early diagnosis allows for more effective treatment strategies, improving the patient’s prognosis.
- Prevents Complications: Timely diagnosis reduces the risk of complications such as infections and bleeding disorders.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Early intervention can significantly improve the quality of life for patients with aplastic anemia.
However, recognizing the symptoms of aplastic anemia, undergoing thorough testing, and understanding the importance of early detection are key components in managing this condition. Regular consultations with healthcare professionals and staying informed about the symptoms and tests can aid in timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
Treatment Options for Aplastic Anemia: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the various methods available is crucial for those affected by this condition. The primary treatments for aplastic anemia include:
- Blood Transfusions: These provide immediate relief by supplying red blood cells or platelets, improving symptoms such as fatigue and preventing bleeding.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy: Medications like antithymocyte globulin (ATG) and cyclosporine help suppress the immune system, which may be attacking the bone marrow, allowing for new blood cell production.
- Bone Marrow Transplants (BMT): Often considered for younger patients or those with a matched donor, BMT replaces damaged bone marrow with healthy marrow, offering a potential cure.
Tailoring Treatment Based on Symptoms and Severity
The approach to treating aplastic anemia varies greatly depending on the severity of the condition and the symptoms presented. For instance:
- Mild Cases: Observation and regular monitoring might be sufficient for those with less severe symptoms.
- Moderate to Severe Cases: More aggressive treatments, such as immunosuppressive therapy or bone marrow transplant, are often necessary.
- Associated Infections or Complications: Specialized treatment plans are formulated to address these additional challenges.
This personalized approach ensures that each patient receives the most effective and appropriate care for their specific condition.
Advances in Treatment and Research
The landscape of aplastic anemia treatment is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and advancements bringing new hope:
- Gene Therapy and Research: Exploratory treatments focusing on genetic factors and stem cell therapy are paving the way for innovative solutions.
- Improved Transplant Techniques: Advances in bone marrow transplant procedures are increasing success rates and reducing complications.
- New Medications: Research into novel drugs and treatment combinations is ongoing, aiming to enhance efficacy and reduce side effects.
This comprehensive guide to the treatment options for aplastic anemia underlines the importance of a tailored approach based on individual needs and the exciting potential of new research and advancements in this field. With ongoing developments, patients have access to increasingly effective and personalized treatment strategies.
Lifestyle Changes and Management Strategies
Managing aplastic anemia involves a holistic approach that encompasses medical treatments and lifestyle adjustments. Here are key strategies:
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Frequent visits to a hematologist are essential to monitor blood cell counts and adjust treatments.
- Infection Prevention: Due to a weakened immune system, it’s crucial to avoid infections. This includes practicing good hygiene, avoiding crowded places, and staying up-to-date with vaccinations.
- Balanced Diet: A nutritious diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall health and can aid in managing symptoms.
- Physical Activity: While strenuous exercise might be challenging, light activities like walking or yoga can enhance well-being.
- Avoiding Certain Medications: Some over-the-counter drugs can aggravate aplastic anemia. It’s important to consult with healthcare providers before taking new medications.
Impact of Symptoms on Daily Life
Aplastic anemia can affect various aspects of daily life:
- Fatigue: This is a common symptom, making it hard to perform routine activities. Energy-conserving strategies and rest periods can be helpful.
- Bleeding and Bruising: Due to low platelet counts, there’s an increased risk of bleeding and bruising, which requires careful attention to physical activities.
- Emotional Well-being: Dealing with a chronic illness can lead to feelings of anxiety and depression. It’s vital to acknowledge these emotions and seek professional help if needed.
Support Systems and Resources
Living with aplastic anemia doesn’t have to be a solitary journey. Various support systems and resources are available:
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have aplastic anemia can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Patient Advocacy Organizations: These organizations offer resources, education, and advocacy for those affected by aplastic anemia.
- Online Resources: Websites and online forums can be valuable sources of information and support.
- Mental Health Professionals: Counselors or therapists specialized in chronic illness can help in coping with the emotional challenges.
However, while aplastic anemia poses unique challenges, effective management through lifestyle changes, awareness of the impact on daily life, and utilization of available support systems can lead to a quality life. Adapting to these changes requires patience and perseverance, but it’s a journey worth undertaking for the sake of one’s health and well-being.
Prevention and Risk Reduction: Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia, a condition where the body stops producing enough new blood cells, can be daunting. However, by understanding the prevention and risk reduction strategies, you can significantly lower your chances of developing this condition. Here’s what you need to know:
1. Embrace Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Avoid Exposure to Toxic Chemicals: Chemicals like benzene, found in some workplaces and in cigarette smoke, can increase the risk. Minimize exposure to harmful chemicals and quit smoking.
- Practice Safe Medication Use: Some drugs, especially certain antibiotics and chemotherapy drugs, can trigger aplastic anemia. Always use medications as prescribed and discuss potential risks with your healthcare provider.
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall health, including bone marrow function. Incorporate foods high in iron, vitamin B12, and folate.
2. Understand Genetic and Environmental Factors
- Know Your Family History: If aplastic anemia runs in your family, you might be at a higher risk. Share your family health history with your doctor.
- Be Cautious with Radiation and Chemotherapy: These treatments can affect bone marrow. If you’re undergoing these therapies, work closely with your healthcare team to monitor your blood cell counts.
3. Regular Health Check-Ups and Symptom Awareness
- Regular Medical Check-Ups: Routine blood tests can detect early signs of aplastic anemia. Regular check-ups help catch potential problems before they become serious.
- Be Alert to Symptoms: Symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, unexplained bruising, or frequent infections should prompt a medical consultation. Early detection is key in managing aplastic anemia effectively.
4. Stay Informed and Prepared
- Educate Yourself: Understanding the condition and its triggers can help in prevention. Stay updated with the latest research and advancements in the treatment of aplastic anemia.
- Build a Support System: Having a strong support system of family, friends, and healthcare professionals can provide the necessary help and guidance.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can reduce the risk of developing aplastic anemia and maintain a healthier life. Remember, prevention starts with awareness and proactive health management. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
Preparing for your appointment
Make an appointment with your primary care provider if you have long-lasting fatigue or other symptoms that worry you. You might end up seeing a doctor who specializes in treating blood disorders, called a hematologist; the heart, called a cardiologist; or the digestive system, called a gastroenterologist.
Here’s some information to help you get ready for your appointment.
What you can do
Before your appointment, make a list of:
- Your symptoms and when they began.
- Key personal information, including major stresses, medical devices you have in your body, toxins or chemicals you’ve been around, and recent life changes.
- All medicines, vitamins and other supplements you take, including the doses.
- Questions to ask your health care provider.
For anemia, basic questions to ask include:
- What’s the most likely cause of my symptoms?
- Are there other possible causes?
- What tests do I need?
- Is my anemia likely short term or long lasting?
- What treatments are there, and which do you recommend?
- What side effects can I expect from treatment?
- I have other health conditions. How can I best manage them together?
- Do I need to change my diet?
- Do you have brochures or other printed materials I can have? What websites do you recommend?
What to expect from your doctor
Your health care provider is likely to ask you questions, such as:
- Do your symptoms come and go or are they constant?
- How bad are your symptoms?
- Does anything seem to make your symptoms better?
- What, if anything, appears to make your symptoms worse?
- Are you a vegetarian?
- How many servings of fruits and vegetables do you eat in a day?
- Do you drink alcohol? If so, how often, and how many drinks do you have?
- Are you a smoker?
- Have you recently donated blood more than once?
Conclusion
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms akin to those of aplastic anemia, it’s crucial to seek medical advice promptly. Timely diagnosis and treatment are key to managing this condition effectively. Remember, your health should always be a top priority.
Moreover, raising awareness and educating oneself about aplastic anemia is vital. Understanding this condition not only helps in early detection but also fosters empathy and support for those affected. By spreading the word, we can contribute to a more informed and health-conscious society.
Let’s take a step towards better health and awareness. If you found this information helpful, consider sharing it with your community. Together, we can shine a light on aplastic anemia, encouraging early detection and support for those in need. Remember, awareness is the first step towards change.