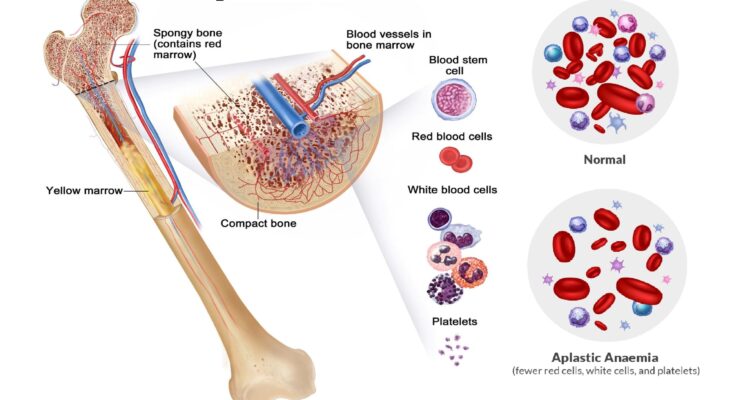
Aplastic Anemia Treatment: Aplastic anemia is a rare but serious condition characterized by the inability of the bone marrow to produce sufficient new cells to replenish blood cells.
The condition can occur at any age, affecting both children and adults, and presents significant challenges in diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Aplastic Anemia
What is Aplastic Anemia?
Aplastic anemia is a rare but serious blood disorder characterized by the bone marrow’s inability to produce sufficient new blood cells. This condition leads to a deficit in all three types of blood cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Understanding aplastic anemia is crucial because it significantly impacts the body’s ability to carry oxygen, fight infections, and control bleeding.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of aplastic anemia can be challenging to determine, several key factors are known to contribute to its development:
- Autoimmune Disorders: The immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the bone marrow.
- Exposure to Toxic Chemicals: Chemicals like benzene or certain drugs, including chemotherapy, can harm bone marrow.
- Viral Infections: Certain viruses, like hepatitis, Epstein-Barr, or HIV, can trigger this condition.
- Genetic Factors: In some cases, aplastic anemia can be linked to genetic syndromes like Fanconi anemia.
Understanding these causes and risk factors can help in early diagnosis and effective management of the condition.
Statistics and Prevalence
Aplastic anemia is considered a rare disease. Globally, it affects approximately 2 out of every 1 million people annually. However, the prevalence rate may vary based on geographic regions and specific population groups. Despite its rarity, the impact of aplastic anemia is significant, making awareness and research into this condition vitally important.
Symptoms and Early Signs of Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia, a condition where the body fails to produce enough new blood cells, presents with several common symptoms that should not be overlooked. These symptoms can vary in intensity but typically include:
- Fatigue and Weakness: A general feeling of tiredness and a notable decrease in energy levels can be a primary indicator.
- Shortness of Breath: Even during mild physical activities, experiencing breathlessness is a common symptom.
- Pale Skin: A noticeable paleness or a washed-out appearance can be a sign of reduced red blood cells.
- Frequent Infections: Due to a decrease in white blood cells, there’s an increased susceptibility to infections.
- Unexplained Bruising or Bleeding: Easy or excessive bruising or bleeding, such as frequent nosebleeds or bleeding gums, can be indicative of a low platelet count.
Importance of Recognizing Early Signs
Early detection of aplastic anemia is crucial. Recognizing the early signs can lead to timely diagnosis and treatment, potentially preventing the progression to more severe stages. Early intervention can significantly improve the prognosis and quality of life for those affected. Understanding and being vigilant about the early symptoms can make a substantial difference in managing the condition effectively.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you or someone you know is experiencing a combination of these symptoms, especially if they persist or worsen over time, it’s essential to seek medical advice. It’s particularly important to consult a healthcare professional if:
- Symptoms such as fatigue, breathlessness, or paleness develop without a clear reason.
- There’s an increase in the frequency or severity of infections.
- Unusual bleeding or bruising occurs frequently and without apparent cause.
However, being aware of the symptoms and early signs of aplastic anemia is vital for prompt and effective treatment. If you have concerns about any of these symptoms, consulting with a healthcare provider as soon as possible is the best course of action. Early detection and intervention can lead to better outcomes and help manage the condition more effectively.
Diagnosis of Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia, a rare and serious condition, requires a careful diagnostic approach to confirm its presence and understand its severity. This article will guide you through the essential steps involved in diagnosing aplastic anemia, outlining the importance of each diagnostic procedure.
Initial Assessment and Medical History
The journey to diagnosing aplastic anemia often begins with a comprehensive initial assessment. This includes a thorough medical history review and a physical examination. Doctors will inquire about symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, or frequent infections, which are common in aplastic anemia. They will also ask about the patient’s medical history, including any exposure to toxins, use of certain medications, or a history of autoimmune diseases, all of which can contribute to the development of this condition.
Blood Tests and Their Significance
Blood tests play a pivotal role in diagnosing aplastic anemia. The most common tests include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test measures the levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. In aplastic anemia, these levels are usually lower than normal.
- Reticulocyte Count: Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells. A low count suggests that the bone marrow isn’t producing enough of these cells.
- Peripheral Blood Smear: This test examines the appearance of blood cells under a microscope. It helps in ruling out other blood disorders.
These tests not only help in diagnosing aplastic anemia but also in assessing its severity, which is crucial for determining the treatment approach.
Bone Marrow Biopsy and Other Diagnostic Procedures
If blood tests indicate aplastic anemia, the next step is usually a bone marrow biopsy. This procedure involves taking a small sample of bone marrow, typically from the hip bone, and examining it under a microscope. In aplastic anemia, the bone marrow is usually empty (hypocellular), confirming the diagnosis.
Other diagnostic procedures may include:
- Chest X-ray or CT scans: To check for infections or abnormalities in the chest.
- Viral Studies: Certain viruses can cause aplastic anemia, so doctors might test for them.
- Immune Function Tests: Since aplastic anemia can be immune-mediated, these tests can provide additional insights.
Each of these diagnostic steps is crucial in confirming the diagnosis of aplastic anemia and planning the appropriate treatment strategy. If you suspect you might have symptoms of aplastic anemia, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Aplastic Anemia
This article outlines the various treatment options available, helping patients and caregivers understand their choices and make informed decisions.
1. Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a common initial treatment for aplastic anemia. They help manage symptoms by providing red blood cells to alleviate anemia and platelets to reduce the risk of bleeding. However, transfusions are not a cure and may need to be repeated.
2. Immunosuppressive Therapy
Immunosuppressive therapy is often used when a bone marrow transplant isn’t an option. Medications like antithymocyte globulin (ATG) and cyclosporine help suppress the immune system, allowing the bone marrow to recover and increase blood cell production.
3. Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT)
A BMT is a potential cure for aplastic anemia, especially effective in younger patients and those with a matched sibling donor. This procedure replaces the damaged bone marrow with healthy marrow from a donor, offering a chance for a complete recovery.
4. Stem Cell Transplant
Similar to a bone marrow transplant, a stem cell transplant uses stem cells from a donor’s blood or bone marrow to rebuild the patient’s bone marrow. It’s particularly beneficial for patients who don’t have a fully matched bone marrow donor.
5. Growth Factors
Growth factors like erythropoietin or granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) can stimulate bone marrow to produce more blood cells. These are usually used in combination with other treatments.
6. Medication for Infections and Bleeding
Patients with aplastic anemia are prone to infections and bleeding. Medications to prevent and treat infections, along with drugs to help with clotting, are vital parts of the treatment plan.
7. Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alongside medical treatments, lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms. These include avoiding infections, eating a balanced diet, and maintaining good general health.
Aplastic anemia treatment is multifaceted, involving various medical interventions and lifestyle adaptations. Patients should work closely with their healthcare team to choose the best treatment plan for their specific condition.
Managing Aplastic Anemia
Living with aplastic anemia requires a comprehensive approach to manage the condition effectively. This section focuses on practical strategies for lifestyle adjustments, dietary recommendations, and coping with symptoms and side effects.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Care
- Prioritize Rest and Stress Reduction: Aplastic anemia can lead to fatigue and weakness. It’s essential to ensure adequate rest and reduce stress. Engage in relaxing activities like gentle yoga, meditation, or light walking.
- Maintain a Clean Environment: Due to the increased risk of infections, keep your living space clean and avoid crowded places. Regular hand washing and using hand sanitizers can prevent infections.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Stay up-to-date with your medical appointments. Regular blood tests and doctor visits are crucial for monitoring your condition and adjusting treatments.
- Support Networks: Joining support groups for aplastic anemia can provide emotional support and valuable information from others experiencing similar challenges.
Dietary Recommendations
- Balanced Nutrition: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. These foods provide essential nutrients that can help support your immune system and overall health.
- Iron-Rich Foods: Incorporating iron-rich foods like spinach, lentils, and fortified cereals can help manage anemia symptoms.
- Safe Food Practices: With a compromised immune system, it’s important to avoid raw or undercooked meats and eggs, unpasteurized dairy products, and unwashed fruits and vegetables to reduce the risk of infections.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is key. Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, to help your body function optimally.
Coping with Symptoms and Side Effects
- Manage Fatigue: Listen to your body and rest when needed. Short, frequent breaks throughout the day can help manage energy levels.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers can be used under the guidance of a doctor. Warm baths or heating pads may also provide relief from discomfort.
- Monitor for Infections: Be vigilant about symptoms like fever, chills, or unusual fatigue, which could indicate an infection. Seek medical attention promptly if these symptoms occur.
- Emotional Well-being: Living with a chronic illness can be challenging. Counseling or therapy can be beneficial in managing emotions and mental health.
By implementing these lifestyle and dietary changes and learning to effectively cope with symptoms and side effects, individuals with aplastic anemia can lead more comfortable and fulfilling lives. Regular consultation with healthcare providers is essential to ensure the best possible management of the condition.
Advancements in Aplastic Anemia Treatment
Recent Developments and Research in Aplastic Anemia Treatment
Aplastic anemia, a condition characterized by the body’s inability to produce sufficient blood cells, has seen significant advancements in treatment options, thanks to ongoing research and development. Understanding these developments is crucial for patients and healthcare professionals alike.
Innovative Treatment Approaches: Recent years have witnessed the emergence of novel treatment methods that focus on stimulating the bone marrow to produce blood cells. This has been a game-changer for many patients who previously had limited options.
Gene Therapy and Research: Gene therapy has shown promise in treating aplastic anemia. Scientists are exploring the potential of modifying genes to encourage healthy blood cell production, offering a ray of hope for a more effective and long-lasting solution.
Improvements in Bone Marrow Transplants: Bone marrow transplants have long been a cornerstone in treating aplastic anemia. Recent improvements in donor matching and post-transplant care have significantly increased success rates and reduced complications.
Emerging Therapies and Future Outlook in Aplastic Anemia Treatment
The future of aplastic anemia treatment is bright, with several emerging therapies on the horizon.
Immunosuppressive Therapy Enhancements: Advances in immunosuppressive therapy are making it more effective and less toxic, providing a safer option for patients who are not candidates for bone marrow transplants.
Stem Cell Research: Ongoing research in stem cell therapy offers exciting possibilities. The ability to grow blood cells in a lab and transplant them into patients could revolutionize treatment.
Personalized Medicine: The move towards personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the individual’s genetic makeup, is particularly promising in aplastic anemia treatment. This approach could lead to more effective and less invasive treatments.
With these advancements and the promise of future research, there is renewed hope for those suffering from aplastic anemia. Continuous research and development are key to unlocking even more effective treatments, potentially turning this once daunting diagnosis into a manageable condition.
Case Studies and Success Stories: Exploring Triumphs in Aplastic Anemia Treatment
Real-Life Examples of Successful Aplastic Anemia Treatment Outcomes
- Introduction to Aplastic Anemia: Aplastic anemia is a rare and serious condition where the bone marrow fails to produce enough new blood cells. Understanding the treatment journey through real-life examples can inspire and educate both patients and healthcare professionals.
- Success Story 1: A detailed account of a patient who recovered from severe aplastic anemia. This story will highlight the diagnosis process, treatment plan (like bone marrow transplant or immunosuppressive therapy), and the patient’s journey to recovery.
- Success Story 2: Focus on a pediatric case of aplastic anemia, showcasing the unique challenges and treatment strategies for children. Emphasize the role of family support and pediatric care specialists in the recovery process.
- Key Takeaways: Summarize the common factors in successful treatment outcomes, such as early diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and comprehensive care teams.
Lessons Learned from Challenging Cases
- Challenging Case Overview: Introduction to more complex cases of aplastic anemia, where standard treatment approaches faced obstacles or were less effective.
- Case Study 1: A deep dive into a case where the patient had a rare complication or an unusual response to treatment. Discuss the adjustments made in the treatment plan and the interdisciplinary approach taken.
- Case Study 2: Analyze a case that required innovative treatment methods or experimental therapies. Highlight how these approaches could pave the way for new treatment possibilities in aplastic anemia.
- Learnings and Improvements: Conclude with insights gained from these challenging cases, emphasizing the importance of research, adaptability in treatment plans, and the potential for future advancements in aplastic anemia care.
The use of real-life examples and case studies provides a relatable and educational perspective, enhancing the understanding of aplastic anemia treatment.
Conclusion
If you or someone you know exhibits symptoms that could suggest aplastic anemia, it’s imperative to seek medical attention promptly. Early intervention can significantly impact the effectiveness of the treatment and the overall prognosis. Don’t hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals for guidance and support.
Understanding aplastic anemia, its diagnosis, and treatment options empowers individuals to make informed health decisions. Remember, knowledge is the first step towards effective management and improved health outcomes.