Anemia Treatment: Anemia, a common blood disorder affecting millions worldwide, is characterized by a deficiency in the number or quality of red blood cells (RBCs) or hemoglobin.
This condition leads to decreased oxygen transport, causing symptoms like fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment options for anemia is vital for effective management and improving patient outcomes.
Understanding Anemia
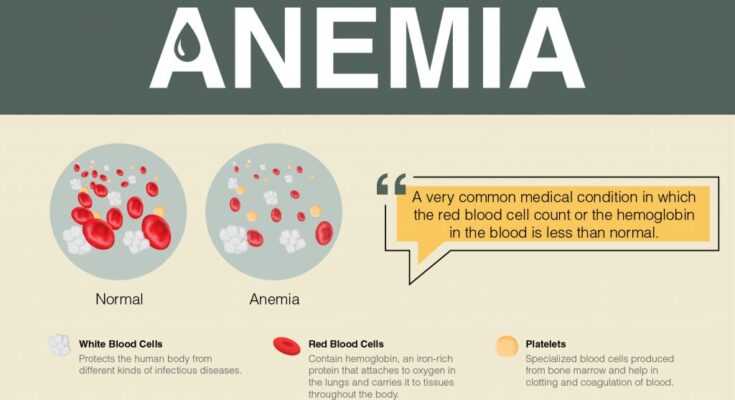
Anemia is a condition marked by a deficiency in the number or quality of red blood cells (RBCs) in the body, which impairs the blood’s ability to carry sufficient oxygen to the body’s tissues. This deficiency can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. The condition arises when the body either loses too many red blood cells, produces too few, or these cells don’t function as they should.
Types and Causes of Anemia
Anemia can be classified into several types, each with unique causes:
- Iron-Deficiency Anemia: This is the most common form of anemia, often resulting from a lack of iron in the diet. Iron is crucial for producing hemoglobin, the substance in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Without adequate iron, the body can’t produce enough hemoglobin, leading to reduced oxygen flow.
- Vitamin-Deficiency Anemia: Besides iron, the body also needs vitamin B12 and folate to produce red blood cells. A diet lacking in these nutrients, or conditions that affect nutrient absorption, can result in this type of anemia.
- Aplastic Anemia: This rare, but serious form, occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough red blood cells. Causes can include infections, certain medicines, autoimmune diseases, and exposure to toxic chemicals.
- Hemolytic Anemia: This type occurs when red blood cells are destroyed faster than they can be made. It can be inherited or develop later in life.
- Sickle Cell Anemia: A hereditary form of anemia, it’s caused by a defective form of hemoglobin that forces red blood cells to assume an abnormal, rigid, sickle shape. These irregular cells can get stuck in small blood vessels, blocking blood flow.
Global Prevalence and Statistics
Anemia is a global health issue, affecting people of all ages and ethnicities. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 1.62 billion people suffer from anemia worldwide, representing 24.8% of the population. The prevalence is highest among preschool-age children (47.4%) and lowest among men (12.7%). Women, especially those who are pregnant, are particularly susceptible due to increased iron demands.
Anemia’s impact is far-reaching, often exacerbating other health conditions and impacting quality of life. It is crucial for individuals, especially those at higher risk, to understand the importance of a balanced diet and regular health check-ups to detect and manage anemia effectively.
Symptoms of Anemia: Understanding the Signs
Recognizing these signs is crucial for early detection and treatment. This section aims to elucidate the common symptoms of anemia, how they differ across anemia types, and when it is essential to seek medical advice.
Common Symptoms of Anemia
Anemia typically presents a range of symptoms, which can vary in intensity:
- Fatigue: The most common and often the first noticeable symptom. It occurs due to insufficient oxygen reaching the body’s tissues.
- Pale Skin: Reduced hemoglobin can cause a noticeable paleness, particularly in the face, nails, and gums.
- Shortness of Breath and Dizziness: These symptoms occur because the body is working harder to supply oxygen.
- Heart Palpitations: An irregular or fast heartbeat can result from the heart pumping more vigorously to compensate for the low oxygen levels.
- Headaches and Concentration Problems: These are less common but can occur due to reduced oxygen supply to the brain.
Variations in Symptoms Depending on Anemia Type
Different types of anemia can cause specific symptoms:
- Iron Deficiency Anemia: Often marked by cravings for non-nutritive substances like ice or dirt (a condition known as pica), soreness of the mouth, and brittle nails.
- Vitamin Deficiency Anemia: Can cause numbness in the hands and feet, difficulties in maintaining balance, and cognitive disturbances.
- Chronic Disease-Related Anemia: Often accompanies chronic diseases like cancer or kidney disease, with symptoms being more related to the underlying illness.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It is imperative to consult a healthcare professional if you notice:
- Persistent fatigue and weakness
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats
- Shortness of breath with minimal exertion
- Unexplained paleness of the skin
Early consultation is vital, as some types of anemia can be indicative of serious underlying conditions.
Understanding the symptoms of anemia is key to prompt diagnosis and treatment. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned, especially those not typical for you, it’s advisable to seek medical guidance. Timely intervention can significantly improve the condition and overall quality of life.
Diagnosing Anemia: Understanding the Process
This process is crucial for determining the specific type of anemia and its underlying cause. The journey to a correct diagnosis begins with a thorough review of the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and a physical examination.
Common Tests and Procedures
- Blood Tests: The cornerstone of anemia diagnosis is blood testing. The most common is the Complete Blood Count (CBC), which provides detailed information about the levels and health of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. A CBC can indicate if anemia is present and suggest its potential cause.
- Hemoglobin Test: This test specifically measures the amount of hemoglobin, an essential protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. Low hemoglobin levels are a direct indicator of anemia.
- Bone Marrow Tests: In some cases, especially when more common tests don’t reveal clear causes, bone marrow tests are conducted. These tests help determine if the bone marrow is functioning correctly and producing enough red blood cells.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in diagnosing anemia. This includes general practitioners, hematologists, and sometimes gastroenterologists. They interpret test results, consider patient history, and sometimes, require additional tests to pinpoint the exact type and cause of anemia. Their expertise ensures a comprehensive approach, leading to an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
Anemia Treatment: Effective Strategies and Their Importance
Understanding General Treatment Approaches for Anemia
Anemia, a condition characterized by a lack of healthy red blood cells, demands a well-rounded treatment approach. The primary goal is to increase the number of healthy red blood cells, thereby improving oxygen transportation throughout the body. This is typically achieved through:
- Iron Supplementation: Since iron deficiency is a common cause of anemia, oral iron supplements can effectively restore iron levels in the body.
- Vitamin and Mineral Supplementation: Vitamins like B12 and folic acid are essential for red blood cell production. Supplements can help in cases where anemia is due to a deficiency of these nutrients.
- Medication Adjustments: If medications are the underlying cause, doctors might alter the prescription or dosage to mitigate anemia.
- Blood Transfusions: In severe cases, blood transfusions can be necessary to quickly increase red blood cell count.
- Dietary Modifications: Incorporating iron-rich foods, like leafy green vegetables, meat, and fortified cereals, can be a beneficial part of treatment.
The Importance of Treating the Underlying Cause of Anemia
It’s crucial to address the root cause of anemia for effective treatment. Anemia can stem from various issues like chronic diseases, nutritional deficiencies, or genetic disorders. Ignoring the underlying cause can lead to recurrent anemia and other complications. A comprehensive medical evaluation is essential for a targeted treatment plan that not only alleviates the symptoms of anemia but also tackles its source.
How Treatment Varies by Anemia Type
Anemia comes in different forms, each requiring a specific treatment approach:
- Iron-Deficiency Anemia: Treated primarily with iron supplements and dietary changes.
- Vitamin Deficiency Anemias: Requires supplementation of the deficient vitamin, such as B12 or folic acid.
- Anemia of Chronic Disease: Treatment involves managing the underlying chronic condition, like rheumatoid arthritis or cancer.
- Aplastic Anemia: This rare form may require medications, blood transfusions, or a bone marrow transplant.
- Hemolytic Anemia: Treatment focuses on controlling the destruction of red blood cells, which may involve medication or surgery.
Tailoring the treatment to the specific type of anemia ensures more effective management and better patient outcomes.
Specific Anemia Treatments
When it comes to treating anemia, the approach varies depending on the type. Here’s a closer look at specific treatments for different forms of anemia.
Iron-Deficiency Anemia
Iron-deficiency anemia is commonly treated with iron supplements. These supplements can effectively increase iron levels in your blood, alleviating the symptoms of anemia. Alongside supplements, making dietary changes is essential. Incorporating iron-rich foods like lean meats, beans, leafy green vegetables, and fortified cereals can make a significant difference.
Vitamin-Deficiency Anemia
For anemia caused by a lack of vitamins, particularly B12 or folate, the treatment involves B12 and folate supplements. These supplements help in restoring the body’s supply of these vital nutrients. Additionally, including vitamin B12 and folate-rich foods in your diet, such as eggs, dairy products, and leafy greens, can support the treatment process.
Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia requires more intensive treatment. Blood transfusions can temporarily relieve symptoms by providing your body with the blood cells it’s lacking. However, in some cases, a bone marrow transplant might be necessary. This procedure involves replacing your damaged bone marrow with healthy marrow from a donor.
Hemolytic Anemia
The treatment for hemolytic anemia focuses on managing the underlying causes. If it’s caused by an infection or a certain medication, addressing these issues is paramount. In some cases, medication to suppress the immune system or to treat an infection can be part of the treatment plan.
Each type of anemia requires a tailored approach to treatment. It’s crucial to work with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action based on your specific condition. Remember, early diagnosis and proper treatment can greatly improve the quality of life for those living with anemia.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies for Anemia
1. Dietary Changes and Nutrition Tips
Dealing with anemia requires a strategic approach to diet and nutrition. Here’s how you can make impactful changes:
- Iron-Rich Foods: Incorporate iron-rich foods such as lean meats, leafy green vegetables, beans, and nuts into your diet. These foods boost your iron intake, a key component in fighting anemia.
- Vitamin C for Iron Absorption: Vitamin C aids in the absorption of iron. Include citrus fruits, tomatoes, and bell peppers in your meals to enhance iron absorption.
- Whole Grains and Iron-Fortified Cereals: Opt for whole grains and cereals fortified with iron. They are an excellent way to supplement your iron levels, especially for vegetarians.
- Limit Iron Blockers: Certain foods and drinks like coffee, tea, and high-calcium foods can hinder iron absorption. Moderating their consumption can be beneficial.
2. Importance of Regular Medical Check-Ups
Regular check-ups are crucial in managing anemia effectively:
- Monitoring Blood Levels: Frequent blood tests are necessary to monitor iron levels and the overall effectiveness of your treatment plan.
- Medication Adjustments: Your doctor can adjust your medications or supplements based on your blood test results.
- Professional Dietary Advice: Healthcare professionals can provide personalized dietary recommendations based on your specific type of anemia.
3. Exercise and Lifestyle Adjustments to Manage Symptoms
Adjusting your lifestyle and exercise routine can help alleviate anemia symptoms:
- Moderate Exercise: Engage in moderate exercise to boost your energy levels. Activities like walking, yoga, or light aerobic exercises can be beneficial.
- Adequate Rest: Ensure you get enough rest. Anemia can lead to fatigue, so it’s important to listen to your body and rest when needed.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate anemia symptoms. Practice stress-relief techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies.
Managing anemia involves a comprehensive approach that includes dietary changes, regular medical check-ups, and lifestyle adjustments. By focusing on a nutrient-rich diet, staying on top of medical appointments, and balancing exercise with adequate rest, individuals can effectively manage anemia and improve their overall well-being.
Potential Complications and Risks of Anemia
It’s crucial to understand these potential risks to emphasize the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment. Untreated anemia may result in:
- Chronic Fatigue and Weakness: Without enough red blood cells to carry oxygen throughout the body, individuals may experience persistent tiredness and weakness, impacting daily life.
- Heart and Lung Complications: Anemia forces the heart to work harder to supply oxygen to your body, which can lead to an enlarged heart or heart failure. Lung function may also be compromised.
- Complications During Pregnancy: Anemia in pregnant women can lead to premature births and low birth weight in newborns.
- Increased Susceptibility to Infections: A decrease in red blood cells can weaken the immune system, making the body more vulnerable to infections.
Risks Associated with Anemia Treatment Methods
Various treatment methods for anemia, including dietary changes, supplements, medications, and in severe cases, blood transfusions, come with their own set of risks:
- Iron Supplements Side Effects: These can include constipation, nausea, and in rare cases, iron overload.
- Blood Transfusions Risks: Though relatively safe, they carry risks like allergic reactions and infections.
- Medication Reactions: Certain drugs used to treat anemia can have side effects or interact with other medications.
Long-term Outlook and Management
The long-term outlook for individuals with anemia largely depends on the cause and the effectiveness of the treatment plan. Proper management includes:
- Regular Monitoring: Keeping track of blood count levels and symptoms is crucial.
- Diet and Lifestyle Adjustments: A diet rich in iron, vitamin B12, and folate is essential. Avoiding substances that can worsen anemia, like alcohol and certain medications, is also important.
- Ongoing Treatment: For chronic conditions causing anemia, ongoing treatment may be necessary.
However, understanding the potential complications and risks associated with anemia and its treatments is vital for effective management and improving long-term health outcomes.
Recent Advances in Anemia Treatment
It’s a common ailment with various causes, ranging from nutritional deficiencies to chronic diseases. The recent advancements in anemia treatment are revolutionizing patient care, offering new hope and improved outcomes.
Breakthroughs in Research and Treatments
1. Gene Therapy:
Gene therapy has emerged as a groundbreaking approach, particularly for hereditary forms of anemia like thalassemia and sickle cell disease. This treatment involves modifying the patient’s own genes to correct the underlying genetic defects, offering a potential cure rather than just symptom management.
2. Iron Supplementation Innovations:
Iron deficiency is a major cause of anemia. Recent developments in iron supplementation, including more effective and easily absorbed oral formulations and safer intravenous options, are significant. These advancements reduce side effects and improve the treatment of iron-deficiency anemia.
3. Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents:
These agents, which stimulate red blood cell production, have been refined to offer more stable and sustained responses in patients with anemia due to chronic kidney disease or chemotherapy.
4. Targeted Drug Therapies:
For anemias associated with chronic diseases, targeted drug therapies have been developed. These drugs specifically target the pathways or factors causing anemia, such as inflammation, offering more effective and tailored treatments.
Future Prospects in Anemia Treatment and Management
Looking ahead, the future of anemia treatment is promising. Ongoing research focuses on:
- Personalized Medicine: Developing treatments tailored to individual genetic profiles and specific types of anemia.
- Advanced Diagnostic Tools: Utilizing cutting-edge technology for earlier and more accurate diagnosis of anemia’s underlying causes.
- Regenerative Medicine: Exploring the potential of stem cells and other regenerative techniques to treat or even cure certain types of anemia.
The landscape of anemia treatment is rapidly evolving, driven by scientific breakthroughs and a deeper understanding of the disease. These advancements not only promise more effective treatment options but also a better quality of life for those affected by this condition. The future holds great potential for further innovations and improved management of anemia.
FAQ Section: Understanding Anemia and Its Treatment
1. What is Anemia?
Anemia is a medical condition characterized by a lack of enough healthy red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen to your body’s tissues. This can lead to fatigue and various other symptoms.
2. What Causes Anemia?
Anemia can be caused by several factors, including iron deficiency, chronic diseases, vitamin deficiencies, and inherited conditions. Understanding the cause is crucial for effective treatment.
3. What Are the Symptoms of Anemia?
Common symptoms include fatigue, weakness, pale or yellowish skin, irregular heartbeats, shortness of breath, dizziness, and cold hands and feet. If you experience these symptoms, consult a healthcare provider.
4. How is Anemia Diagnosed?
Anemia is typically diagnosed through a complete blood count (CBC) test, which measures various blood components, including hemoglobin and red blood cells.
5. What Are the Treatment Options for Anemia?
Treatment depends on the cause. Iron supplements are common for iron-deficiency anemia, while vitamin B12 and folate supplements might be prescribed for vitamin-deficiency anemias. Always follow your healthcare provider’s advice.
6. Can Diet Help in Managing Anemia?
Yes, a diet rich in iron, vitamin B12, and folate can help. Foods like lean meats, beans, leafy greens, and fortified cereals are beneficial.
7. Is Anemia Preventable?
Some forms of anemia, like those caused by nutrient deficiencies, can be prevented with a balanced diet and proper nutrition. However, other forms, such as those due to genetic factors, might not be preventable.
8. When Should I See a Doctor for Anemia?
If you’re experiencing symptoms of anemia, or if you’re at risk due to a poor diet, chronic disease, or family history, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider.
9. Are There Any Risks if Anemia Goes Untreated?
Untreated anemia can lead to serious health problems, including heart and lung complications. It’s important to treat anemia early.
10. Can Anemia Recur After Treatment?
Anemia can recur, especially if the underlying cause, like a chronic disease or nutritional deficiency, isn’t adequately managed. Regular check-ups are essential.
Conclusion
Dealing with anemia can be challenging, but with the right approach, it’s manageable and often treatable. By understanding the condition, recognizing its signs, and seeking appropriate medical care, you can effectively manage anemia. Remember, a proactive attitude and adherence to prescribed treatments play a vital role in overcoming this condition.
As you move forward, keep in mind that managing anemia is not just about treating symptoms but also about enhancing your overall well-being. With the support of healthcare professionals and a focus on a healthy lifestyle, you can navigate this journey with confidence and optimism.