Anaphylaxis Treatment: Anaphylaxis is a severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction that can occur rapidly, demanding immediate attention and intervention.
This article provides a detailed exploration of the diagnosis and treatment of anaphylaxis, offering valuable insights for healthcare professionals, patients, and caregivers.
Understanding Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction that can occur rapidly after exposure to an allergen. It’s essential to understand what anaphylaxis is, its common causes, and its impact on individuals and society. This understanding is critical for anyone prone to allergic reactions or those caring for such individuals.
What is Anaphylaxis?
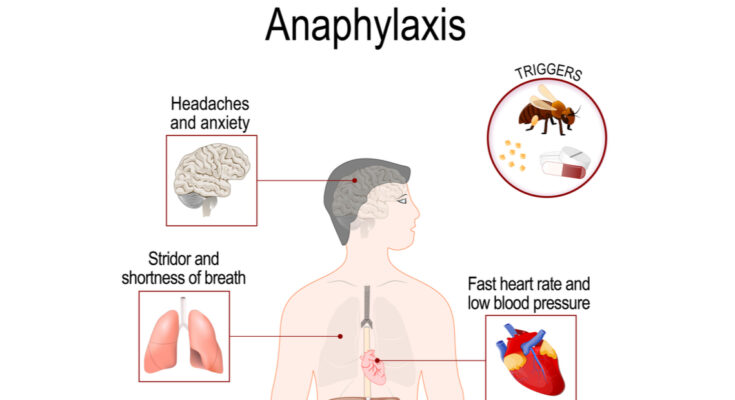
Anaphylaxis is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. It typically involves a range of symptoms that can quickly escalate, affecting multiple body systems. These symptoms may include skin reactions like hives, itching, flushed or pale skin, as well as difficulty breathing, a sudden drop in blood pressure, dizziness, fainting, and severe swelling of the face, lips, and throat. The rapid onset and severity of these symptoms distinguish anaphylaxis from less severe allergic reactions.
Common Causes and Triggers of Anaphylaxis
Several allergens can trigger anaphylaxis. The most common include:
- Foods: Peanuts, tree nuts, fish, shellfish, milk, and eggs are frequent culprits.
- Insect Stings: Bee, wasp, and hornet stings are notable triggers.
- Medications: Certain drugs, like antibiotics or aspirin, can induce anaphylaxis in susceptible individuals.
- Latex: Some people react to natural rubber latex found in medical gloves, balloons, and other products.
Understanding these triggers is vital for prevention and preparedness, especially for those at risk.
Statistics Highlighting Prevalence and Impact
Anaphylaxis remains a significant health concern globally. Here are some key statistics:
- Prevalence: The exact prevalence of anaphylaxis is challenging to determine due to underreporting, but it’s estimated that up to 2% of the population could be at risk.
- Hospitalizations: Anaphylaxis results in numerous hospital admissions annually, with food allergies being a leading cause in children.
- Fatalities: While fatalities are rare, they highlight the critical need for prompt and effective treatment.
- Economic Impact: The condition not only affects health but also imposes economic burdens due to medical care costs and lost productivity.
By understanding anaphylaxis, its causes, and its impact, individuals and healthcare providers can better prepare and respond to these emergencies, potentially saving lives and reducing the overall burden of this condition.
Symptoms of Anaphylaxis
This article aims to provide a detailed overview of anaphylaxis symptoms, their progression, and how they differ from other allergic reactions.
Key Symptoms to Watch For
Anaphylaxis symptoms can affect various body systems and often develop quickly. Key symptoms include:
- Skin Reactions: Hives, itching, and flushed or pale skin.
- Breathing Difficulties: Wheezing, shortness of breath, throat tightness, cough, and hoarseness.
- Circulatory Symptoms: A rapid, weak pulse, low blood pressure, dizziness, or fainting.
- Gastrointestinal Complaints: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
- Severe Symptoms: A feeling of impending doom, confusion, or a severe headache.
Progression of Symptoms
The progression of anaphylaxis symptoms can be swift and unpredictable. Initially, mild symptoms like skin rash or a feeling of unease may appear, but these can quickly escalate to more severe symptoms like breathing difficulties and circulatory issues. The speed of this progression underscores the importance of immediate medical attention.
Quick Identification: A Lifesaver
Quick identification of anaphylaxis is vital. If any combination of the above symptoms, especially after exposure to a known allergen, is observed, it’s imperative to seek emergency medical help immediately. Delay in treatment can lead to more severe complications, including anaphylactic shock, which is a medical emergency.
Differentiating Anaphylaxis from Other Allergic Reactions
Anaphylaxis is often confused with less severe allergic reactions. However, the key difference lies in the severity and the multi-system involvement. Anaphylaxis typically involves more than one body system (e.g., skin, respiratory, gastrointestinal), whereas a standard allergic reaction might only affect one area, like hives on the skin. Also, anaphylactic reactions are rapid in onset and progression, which is less common in other types of allergic reactions.
Understanding the symptoms of anaphylaxis and differentiating them from other allergic reactions is essential for timely and effective treatment. Always err on the side of caution and seek medical help if anaphylaxis is suspected. Remember, in the case of anaphylaxis, every second counts.
Diagnosing Anaphylaxis: Key Steps and Considerations
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and management. This article outlines the key steps and considerations in diagnosing anaphylaxis, focusing on medical history, and diagnostic tests.
Taking a Detailed Medical History
A thorough medical history helps in identifying potential allergic triggers. Key points include:
- Previous Allergic Reactions: History of allergies or previous anaphylactic episodes.
- Family History: Any family members with allergies or anaphylaxis.
- Recent Exposure: Foods, medications, insect stings, or other triggers prior to the onset of symptoms.
Diagnostic Tests
While the diagnosis of anaphylaxis is primarily clinical, based on symptoms and history, certain tests can support the diagnosis:
- Blood Tests: To check tryptase levels, which may rise during anaphylaxis.
- Skin Tests: To identify specific allergens, performed after the anaphylactic episode has resolved.
Immediate Actions and Referral
If anaphylaxis is suspected:
- Immediate Medical Attention: Seek emergency medical care.
- Use of Epinephrine: Administer an epinephrine auto-injector if available.
- Follow-Up Care: Referral to an allergist for further evaluation and management.
Anaphylaxis is a medical emergency requiring prompt recognition and treatment. Understanding the symptoms, taking a detailed medical history, and conducting appropriate tests are key to diagnosing this condition. Always seek immediate medical attention if anaphylaxis is suspected.
Anaphylaxis Treatment and Management
Immediate Steps During an Anaphylactic Reaction
Anaphylaxis is a severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction that requires immediate action. The first step in managing an anaphylactic reaction is to recognize the symptoms, which may include difficulty breathing, swelling, hives, and a drop in blood pressure. If these symptoms are observed, it is crucial to act fast.
- Call Emergency Services: The first and most important step is to call for emergency medical help. Anaphylaxis is a medical emergency that requires immediate professional attention.
- Use an Epinephrine Auto-Injector: If the individual has a prescribed epinephrine auto-injector, use it immediately as directed. Epinephrine is the first-line treatment for anaphylaxis and can be life-saving.
- Lie Down and Raise Legs: Have the person lie flat on their back and raise their legs. This position helps maintain blood flow and can prevent shock.
- Administer CPR if Necessary: If the person is not breathing or their heart stops, administer CPR if you are trained to do so.
Medical Treatments for Anaphylaxis
Epinephrine is the primary treatment for anaphylaxis. However, additional medical treatments may be administered by healthcare professionals:
- Additional Doses of Epinephrine: In some cases, more than one dose of epinephrine may be necessary.
- Oxygen Therapy: To assist with breathing difficulties, oxygen may be provided.
- Intravenous Fluids: These may be administered to maintain blood pressure and treat shock.
- Antihistamines and Steroids: These can help manage and reduce allergic reaction symptoms.
Living with Anaphylaxis
Living with anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction, requires careful planning and lifestyle adaptations. This guide provides essential insights for individuals managing severe allergies, emphasizing the importance of emergency action plans, and exploring the available support systems and resources.
Adapting Your Lifestyle with Severe Allergies
Living with severe allergies means making mindful adjustments in daily routines. Here are key areas to focus on:
- Dietary Changes: Understand your allergens and read labels meticulously. It’s crucial to avoid foods that trigger allergic reactions and to be aware of cross-contamination risks.
- Environment Control: Create a safe space at home by reducing exposure to allergens. This might involve using air purifiers, avoiding certain pets, or using hypoallergenic bedding.
- Educating Others: Inform friends, family, and coworkers about your allergies. Teach them about the signs of anaphylaxis and how they can help in an emergency.
- Self-Care Routines: Incorporate stress-reduction techniques and regular health check-ups into your routine. Managing stress is vital as it can sometimes exacerbate allergic reactions.
Emergency Action Plans: Your Safety Net
An emergency action plan is a lifesaver for anyone with severe allergies. This plan should include:
- Clear Instructions: Outline the steps to take during an allergic reaction, including when and how to use an epinephrine auto-injector.
- Emergency Contacts: Keep a list of emergency contacts, including family members and healthcare providers.
- Medication Readiness: Always carry your emergency medication, such as epinephrine auto-injectors, and ensure they are within their expiration date.
Building a Support System and Accessing Resources
No one should manage anaphylaxis alone. Building a support network is essential:
- Join Support Groups: Connect with others who have similar experiences. This can be an invaluable source of emotional support and practical advice.
- Utilize Online Resources: Leverage online platforms for the latest information, tips, and guidance on living with severe allergies.
- Professional Help: Regular consultations with an allergist or immunologist can help manage your condition effectively.
- Educational Resources: Utilize resources like the Anaphylaxis Campaign or the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology for information and advocacy.
Living with anaphylaxis can be challenging, but with the right adaptations, emergency plans, and support systems, individuals with severe allergies can lead safe, fulfilling lives. Remember, knowledge and preparedness are your best tools in managing this condition.
FAQ Section: Understanding Anaphylaxis and Its Treatment
1. What is anaphylaxis?
Anaphylaxis is a severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction. It can occur within seconds or minutes of exposure to something you’re allergic to, such as peanuts or bee stings.
2. What are the symptoms of anaphylaxis?
Symptoms may include a rapid, weak pulse, skin rash, nausea, and vomiting. Severe cases can lead to a sudden drop in blood pressure, trouble breathing, and loss of consciousness.
3. How is anaphylaxis treated?
The primary treatment for anaphylaxis is epinephrine (adrenaline), typically administered through an auto-injector. It is crucial to administer epinephrine as soon as anaphylaxis is suspected.
4. Can anaphylaxis be prevented?
While it’s not always possible to prevent anaphylaxis, avoiding known allergens and carrying an epinephrine auto-injector can significantly reduce the risk.
5. What should I do if someone is experiencing anaphylaxis?
Immediately administer an epinephrine injection and call emergency services. Lay the person flat, elevate their legs, and ensure they’re kept warm. Do not give them anything to drink.
6. Is anaphylaxis common?
Anaphylaxis is rare, but its incidence is increasing, especially among children and young adults.
7. Can anaphylaxis occur more than once?
Yes, if you have experienced anaphylaxis once, you’re at increased risk of another episode. It’s important to identify and avoid your allergens.
8. Are there any long-term effects of anaphylaxis?
Most people recover completely with prompt treatment, but it’s important to follow up with a healthcare professional as it can recur.
9. Can children outgrow their allergies causing anaphylaxis?
Some children may outgrow certain food allergies, but life-threatening allergies, especially to insect stings and medications, often persist.
10. Where can I find more information about anaphylaxis?
Consult healthcare providers, allergy specialists, and reputable websites for current information on anaphylaxis management and treatment.
Conclusion
In summary, recognizing, diagnosing, and effectively treating anaphylaxis is a critical health priority. By fostering awareness and preparedness across various sectors of society, we can improve response times, ensure accurate diagnoses, and provide life-saving treatments promptly. It’s a collective responsibility that we must all embrace for the safety and well-being of our communities.