Anal Fissure Symptoms: Anal fissures are a common yet often misunderstood condition, affecting a significant portion of the population at some point in their lives.
This condition can cause considerable discomfort and distress, but understanding its symptoms and causes can lead to effective management and relief.
Understanding Anal Fissures
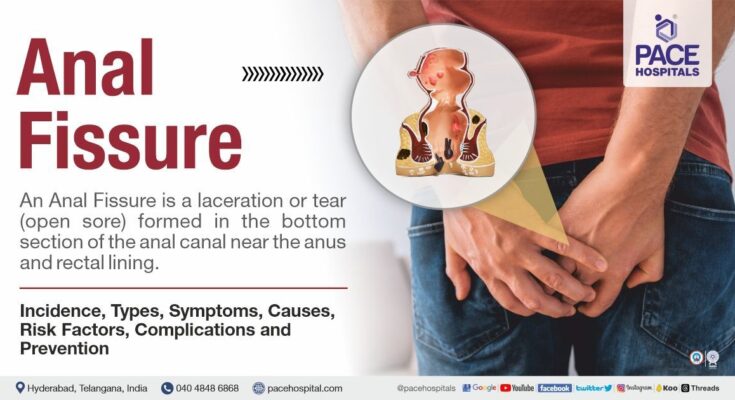
Anal fissures are small tears in the lining of the anal canal, a condition that can cause significant discomfort and distress. They are often mistaken for other conditions like hemorrhoids, but there are key differences that set them apart.
Definition and Explanation of Anal Fissures
An anal fissure is a small tear or cut in the thin, moist tissue (mucosa) that lines the anus. This condition can cause pain and bleeding during bowel movements. Anal fissures are commonly caused by passing hard or large stools, chronic constipation, or diarrhea. Symptoms typically include a sharp pain during bowel movements, followed by prolonged burning. There might also be bright red blood on the toilet paper or in the toilet bowl.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of anal fissures is crucial for effective treatment. These fissures are usually less than an inch in length, but they can cause significant pain.
Distinction Between Anal Fissures and Other Similar Conditions
While anal fissures and hemorrhoids both affect the same general area, they are distinctly different conditions. Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in your rectum or anus, whereas anal fissures are tears in the lining of the anus. The symptoms can be similar – pain and bleeding – but the causes and treatments differ. Hemorrhoids are often related to an increase in pressure in the lower rectum, which can be due to a variety of factors, including straining during bowel movements, obesity, or pregnancy.
In contrast, anal fissures are primarily caused by trauma to the inner lining of the anus, usually due to hard or bulky stools, or conditions that cause increased tension in the anal sphincter. Understanding these differences is key for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Symptoms of Anal Fissures
Detailed list of common symptoms associated with anal fissures, emphasizing key indicators and offering clarity on each symptom. Understanding these symptoms is crucial, as it guides when to seek medical advice.
Common Symptoms
- Sharp Anal Pain: The most prominent symptom of an anal fissure is a sharp, intense pain during bowel movements. This pain can linger for several hours, making it a significant discomfort factor.
- Bleeding: Look for bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl. This bleeding is typically mild but noticeable, distinguishing it from other potential causes.
- Burning Sensation: Post bowel movement, a burning sensation or discomfort can persist in the anal area, lasting for hours.
- Visible Tear or Crack: In some cases, the fissure can be seen as a small tear or crack near the anus, usually visible upon careful examination.
- Itching: Chronic anal fissures can lead to persistent itching in the affected area, which can be both uncomfortable and distressing.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It is essential to seek medical advice if you experience any of the following:
- Persistent symptoms lasting more than a few weeks.
- Recurrent episodes of symptoms.
- Significant bleeding or pain that interferes with daily activities.
- Accompanying symptoms like fever or unusual discharge, which might indicate an infection or more severe condition.
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and provide significant relief. Therefore, paying attention to these symptoms and consulting a healthcare professional is advisable if you suspect an anal fissure.
Primary Causes of Anal Fissures
Now, lets delves into the most common factors leading to the development of anal fissures and discusses how these causes are directly related to the symptoms experienced.
1. Chronic Constipation
Chronic constipation is a leading cause of anal fissures. Hard or large stools can stretch the anal canal beyond its capacity, leading to tears in the lining. The symptoms, including pain and bleeding during bowel movements, are direct results of this trauma.
2. Diarrhea
Frequent diarrhea can also contribute to the development of anal fissures. The constant irritation and inflammation from loose stools make the anal tissue more susceptible to tearing, which explains the associated discomfort and bleeding.
3. Childbirth
For women, childbirth is a common cause of anal fissures. The intense pressure and stretching during delivery can result in tears in the anal region. Postpartum women often report pain and bleeding, typical symptoms of fissures.
4. Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Conditions like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, categorized under inflammatory bowel diseases, can lead to anal fissures. Inflammation and ulceration in the bowel increase the risk of tears in the anal lining, contributing to the symptomatic pain and bleeding.
5. Excessive Straining
Excessive straining during bowel movements, often due to constipation, puts immense pressure on the anal canal, leading to fissures. This straining is directly linked to the symptomatic pain experienced during and after bowel movements.
6. Poor Hygiene
Poor anal hygiene can exacerbate the risk of developing fissures. It can lead to irritation and infection, worsening the condition and prolonging the healing process. Symptoms like itching and discomfort are often aggravated by inadequate hygiene.
7. Age-Related Changes
As individuals age, the skin and mucosa around the anus become less elastic and more prone to tearing. Elderly individuals often experience symptoms of anal fissures due to these age-related changes.
Understanding these primary causes and their relation to the symptoms helps in the prevention and management of anal fissures. Implementing lifestyle changes like a high-fiber diet, proper hydration, and maintaining good hygiene can significantly reduce the risk of developing this painful condition.
Risk Factors and Prevention of Anal Fissures
Understanding the risk factors and implementing preventive strategies is crucial in minimizing the likelihood of developing this condition. This section provides an overview of common risk factors and offers practical tips for prevention.
Risk Factors for Anal Fissures
- Constipation: Hard, dry bowel movements are a primary risk factor. They can cause straining and subsequently lead to tears in the anal lining.
- Diarrhea: Frequent loose stools can also irritate the anus, increasing the risk of fissures.
- Childbirth: Women may be at a higher risk post-delivery due to the strain and pressure involved in childbirth.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can make one more susceptible to anal fissures.
- Age: Older adults often have decreased blood flow to the area, making the anal tissue more prone to tearing.
- Anal Intercourse: This can cause significant strain and potential injury to the anal canal.
Prevention Strategies
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps to soften stools, reducing the strain during bowel movements.
- Fiber-Rich Diet: Consuming a diet high in fiber aids in smoother bowel movements. Include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps in maintaining regular bowel movements.
- Avoid Straining: Try not to strain during bowel movements, as this puts pressure on the anal area.
- Proper Bathroom Habits: Spend as little time as necessary on the toilet and avoid reading or using your phone, which can inadvertently prolong the time spent straining.
- Use Stool Softeners: If you’re prone to constipation, consider using over-the-counter stool softeners as recommended by a healthcare professional.
Incorporating these tips into your daily routine can significantly reduce the risk of developing anal fissures. If you are experiencing symptoms or have concerns, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options. Remember, early intervention can prevent complications and promote better health outcomes.
Diagnosis of Anal Fissures
Diagnostic process for anal fissures and emphasizes the importance of professional medical diagnosis.
Understanding the Symptoms
The first step in diagnosing an anal fissure involves recognizing its symptoms. Common signs include:
- Sharp pain during bowel movements
- Bleeding, typically noted as bright red blood on toilet paper or in the stool
- Itching or irritation around the anus
If you experience these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Medical Consultation
A healthcare provider will start with a detailed medical history and a physical examination. During the examination, the doctor may inspect the anal area for signs of a fissure. In some cases, they might perform a digital rectal exam (DRE) or use an anoscope, a small tube that allows them to see into the anus and rectum.
Differential Diagnosis
Since symptoms of anal fissures can be similar to other conditions like hemorrhoids or inflammatory bowel diseases, it’s essential for healthcare professionals to conduct a differential diagnosis. This process involves ruling out other conditions that could be causing the symptoms.
The Role of Additional Tests
In some cases, additional tests may be necessary, especially if the fissure is not readily visible or if there’s a suspicion of other underlying conditions. These tests can include:
- Anoscopy: A more detailed examination of the anal canal and lower rectum.
- Colonoscopy: Recommended if there’s a concern about diseases of the larger intestine.
- Sigmoidoscopy: Focuses on the lower part of the colon.
Why Professional Diagnosis Matters
Self-diagnosis of anal fissures is not advisable due to the similarity of symptoms with other anal and rectal conditions. A professional medical diagnosis ensures that the treatment is appropriate for the specific condition, thereby reducing the risk of complications and promoting faster healing.
However, recognizing the symptoms of an anal fissure and seeking prompt medical attention are key to an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Remember, a healthcare professional is the best resource for diagnosing and treating anal fissures.
Treatment Options for Anal Fissures
Understanding the available treatments and their relationship to the severity of symptoms is crucial for effective management.
1. Conservative Treatments:
- High-Fiber Diet & Fluids: A high-fiber diet and increased fluid intake can soften stools, reducing strain during bowel movements.
- Sitz Baths: Warm sitz baths, where one soaks the anal area in warm water, can provide relief and aid in healing.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Topical creams or ointments, such as those containing hydrocortisone, can reduce inflammation and pain.
2. Medication:
- Topical Nitroglycerin or Calcium Channel Blockers: These medications can relax the anal sphincter, improve blood flow, and promote healing.
- Stool Softeners: They help in easing bowel movements and reducing strain.
3. Botox Injections:
Botulinum Toxin: Used in more persistent cases, Botox injections into the anal sphincter can relax the muscles, easing pain and facilitating healing.
4. Surgery:
Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy: Reserved for severe or chronic fissures, this surgical procedure involves cutting a small portion of the anal sphincter muscle to reduce spasm and pain, promoting healing.
Severity and Treatment Correlation:
- Mild Symptoms: Typically respond well to conservative treatments and lifestyle changes.
- Moderate to Severe Symptoms: May require prescription medications or Botox injections.
- Chronic or Severe Cases: Surgery may be recommended when other treatments fail.
Key Takeaway: The choice of treatment for anal fissures depends on the severity of symptoms. Mild cases often improve with simple measures, while severe or chronic fissures might necessitate advanced interventions. It’s vital to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment plan.
Complications if Left Untreated
If left untreated, these fissures can lead to several complications, emphasizing the importance of early recognition and treatment.
Serious Complications from Neglect
- Chronic Pain and Discomfort: Persistent anal fissures can cause continuous pain and discomfort, especially during bowel movements, leading to a significant decline in quality of life.
- Infection Risk: Open wounds in the anal area can become infected, leading to further complications. This risk of infection can also extend to surrounding tissues, potentially causing more severe health issues.
- Anal Abscesses: Untreated fissures can lead to the development of abscesses. These are painful, pus-filled infections that can require surgical intervention.
- Fistula Formation: In some cases, a chronic fissure may lead to the formation of a fistula, an abnormal connection between the anal canal and the skin near the anus. This condition often necessitates surgical treatment.
- Bowel Movement Issues: Chronic pain and discomfort can lead to fear of having bowel movements, potentially causing constipation or exacerbating existing bowel disorders.
- Bleeding: Repeated trauma to an untreated fissure can result in recurrent bleeding, leading to anemia in severe cases.
The Importance of Early Detection
Recognizing the symptoms of anal fissures early is crucial for preventing these complications. Symptoms include pain during bowel movements, visible tears in the anal area, and slight bleeding. Early treatment typically involves lifestyle changes, such as increasing fiber intake and using topical treatments to promote healing and relieve pain. In more severe cases, surgical options may be considered.
By understanding the potential complications of untreated anal fissures and the importance of early symptom recognition, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining their health and avoiding more severe health issues.
Conclusion
If you’re experiencing any symptoms of an anal fissure, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. They can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend the most effective treatment plan. Remember, seeking medical advice is not just about alleviating current discomfort but also about preventing potential complications and ensuring your long-term well-being.
In summary, your awareness and proactive approach towards the symptoms and causes of anal fissures are key. Don’t hesitate to reach out to a medical professional for guidance and treatment. Your health and comfort are paramount, and with the right care, you can effectively manage and overcome the challenges of anal fissures.