Alcoholic Hepatitis Treatment: Alcoholic hepatitis is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition resulting from prolonged alcohol abuse.
This inflammatory condition of the liver is characterized by liver damage, which impedes its ability to function effectively.
Understanding the nuances of its diagnosis and treatment is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Understanding Alcoholic Hepatitis
Alcoholic hepatitis develops as a result of extended, excessive alcohol consumption. The liver, tasked with processing alcohol, becomes overwhelmed and damaged over time. This disease is not limited to heavy drinkers; even those with a history of moderate drinking can develop alcoholic hepatitis under certain conditions.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of alcoholic hepatitis is the chronic consumption of alcohol. The risk increases significantly for individuals who consume large amounts of alcohol over many years. Factors that may influence the development of alcoholic hepatitis include:
- Genetic predisposition: Some individuals have a genetic makeup that makes them more susceptible to liver damage from alcohol.
- Gender: Women may be at a higher risk due to differences in how their bodies process alcohol.
- Other liver conditions: Pre-existing liver conditions, such as fatty liver disease, can exacerbate the risk.
- Nutritional status: Poor nutrition can worsen liver damage from alcohol.
- Binge drinking: Episodes of heavy drinking can cause sudden and severe liver inflammation.
Statistics on Prevalence and Demographics Affected
Alcoholic hepatitis is a global health concern, with its prevalence varying across different regions and demographics:
- Age group: It’s most commonly diagnosed in individuals between 40 and 60 years old.
- Gender distribution: Although both men and women are affected, men are generally more prone to developing this condition due to higher rates of alcohol consumption.
- Geographical variation: Prevalence rates are higher in regions where alcohol consumption is more widespread and culturally accepted.
- Co-occurrence with other conditions: A significant number of individuals with alcoholic hepatitis also suffer from other alcohol-related disorders.
Understanding alcoholic hepatitis is crucial for both prevention and early intervention. Reducing alcohol intake, maintaining a healthy diet, and regular medical check-ups can significantly lower the risk of developing this serious condition. If you or someone you know is struggling with alcohol dependency, seeking professional help is a critical first step towards recovery and maintaining liver health.
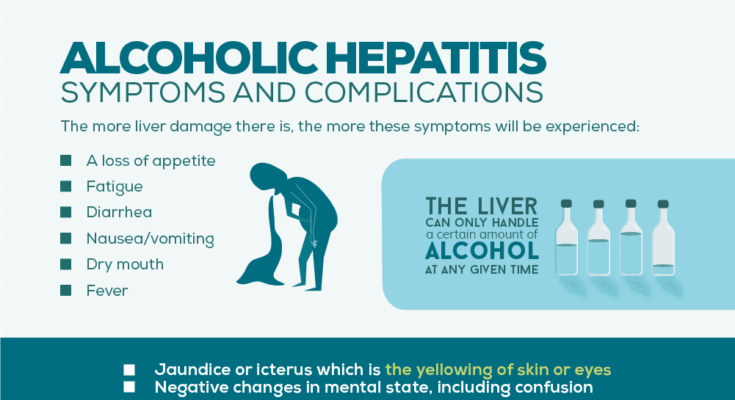
Symptoms of Alcoholic Hepatitis
Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment, which can significantly improve outcomes.
Common Symptoms of Alcoholic Hepatitis
- Jaundice: This is one of the most noticeable signs. It’s characterized by a yellowing of the skin and eyes, indicating liver dysfunction.
- Abdominal Pain and Swelling: The liver’s swelling can cause discomfort or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. Sometimes, fluid accumulation in the abdomen (ascites) occurs, causing noticeable swelling.
- Nausea and Vomiting: A disturbed liver function can lead to persistent nausea, often accompanied by vomiting.
- Loss of Appetite: This symptom can lead to unintentional weight loss, further weakening the body.
- Fatigue and Weakness: These symptoms are common in liver diseases, reflecting the body’s struggle to cope with the impaired liver function.
- Fever: A mild fever can sometimes accompany alcoholic hepatitis, indicating inflammation or infection in the body.
Differentiating Alcoholic Hepatitis from Other Liver Diseases
While some symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis are similar to other liver conditions, certain factors are indicative of this specific disease:
- History of Alcohol Use: A key differentiator is a history of heavy alcohol use. This history is often absent in other liver diseases like viral hepatitis or fatty liver disease unrelated to alcohol.
- Rapid Onset: Symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis can appear more abruptly compared to other liver diseases, which often develop slowly over time.
Importance of Early Recognition
Recognizing these symptoms early is vital. Alcoholic hepatitis can progress to more severe liver damage or cirrhosis if left untreated. Early intervention can halt or even reverse some of the damage, emphasizing the need for awareness and prompt medical attention.
However, identifying the symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis promptly can be a life-saving measure. It is essential for individuals with a history of heavy alcohol use to be particularly vigilant and seek medical advice if these symptoms appear. Early diagnosis and treatment significantly improve the prognosis and can prevent the progression to more serious liver conditions.
Diagnosing Alcoholic Hepatitis
Here will guide you through the common diagnostic methods and tests, emphasizing the role of medical history and physical examination, and highlighting the importance of early and accurate diagnosis.
Common Diagnostic Methods and Tests
When suspecting alcoholic hepatitis, healthcare professionals utilize a variety of diagnostic tests. These typically include:
- Blood Tests: These are essential to check for elevated liver enzymes, which indicate liver damage. Complete blood counts and tests for liver function are standard.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI can be used to visualize the liver and assess the extent of damage.
- Liver Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy is performed to confirm the diagnosis, where a small tissue sample from the liver is examined under a microscope.
Understanding these tests helps patients and their families comprehend the diagnostic process and prepares them for discussions with their healthcare providers.
The Role of Medical History and Physical Examination
A thorough medical history and physical examination are foundational in diagnosing alcoholic hepatitis. During this process, doctors will:
- Inquire about alcohol consumption habits to understand the potential cause of liver damage.
- Look for physical signs of liver disease, such as jaundice, enlarged liver, or fluid accumulation in the abdomen.
This comprehensive evaluation aids in ruling out other causes of liver disease and tailoring the most appropriate treatment plan.
Importance of Early and Accurate Diagnosis
Early and accurate diagnosis of alcoholic hepatitis is critical for several reasons:
- Prevents Progression: Early detection can prevent the disease from progressing to more severe stages like cirrhosis or liver failure.
- Guides Treatment: A timely and precise diagnosis allows for the implementation of effective treatment strategies, including lifestyle changes and medical interventions.
- Improves Prognosis: The sooner alcoholic hepatitis is diagnosed and treated, the better the chances of recovery and the lower the risk of complications.
In summary, diagnosing alcoholic hepatitis involves a combination of blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes liver biopsy, underpinned by a thorough medical history and physical examination. Recognizing the importance of early and accurate diagnosis is key to managing this condition and improving patient outcomes.
By understanding these aspects, patients can engage more effectively in their healthcare and make informed decisions about their treatment and lifestyle modifications.
Treatment and Management of Alcoholic Hepatitis
The treatment and management of this condition require a multifaceted approach, focusing on both immediate medical intervention and long-term lifestyle modifications. Below are the key strategies for treating and managing alcoholic hepatitis:
Abstinence from Alcohol: The most crucial step in treating alcoholic hepatitis is the complete cessation of alcohol intake. This single action can significantly reduce liver inflammation and prevent further damage.
Nutritional Support: Patients with alcoholic hepatitis often suffer from malnutrition. A balanced diet, possibly supplemented with vitamins, particularly B vitamins, is essential for recovery and liver repair.
Medical Treatments: Depending on the severity, medications may be prescribed. These can include corticosteroids to reduce liver inflammation or pentoxifylline for severe cases.
Monitoring and Managing Complications: Regular monitoring for complications such as liver cirrhosis or failure is essential. In severe cases, a liver transplant may be considered.
Lifestyle Changes and Support: Long-term lifestyle changes, including maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding alcohol, are vital. Support groups and counseling can also be beneficial in managing alcohol dependency.
Regular Medical Check-ups: Ongoing medical supervision is crucial to monitor liver function and overall health status, adjusting treatments as needed.
By implementing these strategies, individuals with alcoholic hepatitis can significantly improve their liver health and overall well-being. It’s essential to seek medical advice promptly if you suspect you or someone you know is suffering from this condition.
Prevention of Alcoholic Hepatitis
Alcoholic hepatitis is a serious liver condition caused by excessive alcohol consumption. Preventing it is crucial for maintaining liver health and overall well-being. Here’s a concise guide:
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: The most effective way to prevent alcoholic hepatitis is to limit or avoid alcohol. For those who drink, following recommended guidelines and reducing intake can significantly lower the risk.
- Healthy Diet and Exercise: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, along with regular exercise, supports liver health and reduces the risk of liver diseases.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups help in early detection of any liver-related issues. This is particularly important for individuals with a history of alcohol use.
- Avoiding Risky Behaviors: Risky behaviors, like binge drinking or mixing alcohol with medications, can increase the likelihood of developing alcoholic hepatitis. Awareness and avoidance of these behaviors are crucial.
- Education and Support: Understanding the risks associated with excessive alcohol use, and seeking support from friends, family, or support groups can help in making healthier lifestyle choices.
- Vaccinations and Medications: In some cases, doctors may recommend vaccinations or medications to protect the liver from other potential harms.
By incorporating these strategies, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing alcoholic hepatitis. Remember, prevention is key to maintaining a healthy liver and overall health.
Preparing for your appointment
You might be referred to a digestive disease specialist, called a gastroenterologist.
What you can do
When you make the appointment, ask if there’s anything you need to do before certain tests, such as not eating or drinking.
Make a list of:
- Your symptoms, including any that don’t seem linked to the reason you made the appointment, and when they began.
- All medicines, vitamins and supplements you take, including doses.
- Key medical information, including other conditions you have.
- Key personal information, including recent changes or stressors in your life. Keep track of how much alcohol you drink for a few days for your healthcare professional.
- Questions to ask your healthcare professional.
Have a relative or friend go with you, if possible, to help you remember the information you’re given.
Questions to ask your doctor
- What’s the most likely cause of my symptoms? Are there other possible causes?
- Do I have any other liver disease?
- Is there scarring of my liver?
- What tests do I need? How do I prepare for them?
- Is my condition likely to go away or be long-lasting?
- What treatment do you suggest?
- I have other health problems. How can I best manage these conditions together?
Be sure to ask all the questions you have about your condition.
What to expect from your doctor
Your healthcare professional is likely to ask you questions, including:
- How bad are your symptoms? Do they come and go, or do you have them all the time?
- Does anything improve your symptoms or make them worse?
- Have you had hepatitis or yellowing of the skin or whites of your eyes?
- Do you use illicit drugs?
- Have you ever felt you should cut down on drinking or felt guilty or bad about your drinking?
- Are your family members or friends worried about your drinking? Have you been arrested or had other problems because of your drinking?
- Do you get angry or upset when anyone talks about your drinking?
- Do you feel guilty about drinking?
- Do you drink in the morning?
Conclusion
Alcoholic hepatitis is a severe condition that requires immediate attention. Early diagnosis and treatment, coupled with lifestyle changes, are key to managing and potentially reversing the effects of this disease. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, and abstaining from alcohol is the most effective way to prevent alcoholic hepatitis.