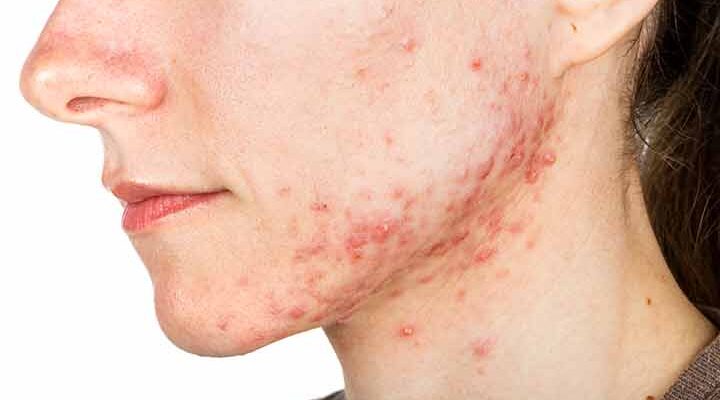
Acne Treatment: Acne is a prevalent skin ailment that affects millions globally. Characterized by pimples, blackheads, and sometimes deeper lumps known as cysts or nodules, it primarily appears on the face, neck, chest, back, and shoulders.
Accurate diagnosis is paramount. Not all skin blemishes are acne, and misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective or even counterproductive treatments. Once correctly identified, effective acne treatment is crucial. Not only does the right treatment alleviate physical symptoms, but it also boosts self-esteem and confidence, allowing individuals to put their best face forward in every life endeavor.
Embracing a comprehensive approach to acne – from understanding its roots to seeking the right remedies – is the cornerstone to achieving clear, radiant skin.
Understanding Acne
What is Acne?
Acne is a prevalent skin condition characterized by the appearance of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and, in severe cases, deep lumps or cysts. It primarily affects areas of the skin with a significant number of oil glands, such as the face, chest, and back. The condition arises when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. While often associated with adolescence, acne can occur at any age and can cause emotional distress and skin scarring.
Causes of Acne
There are several factors that contribute to the development of acne:
1. Hormones: Changes in hormonal levels, especially during puberty, can cause the skin’s oil glands to enlarge and produce more oil, leading to acne. Women may also experience hormonal acne around menstruation, during pregnancy, or due to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
2. Bacteria: Once a pore becomes clogged, bacteria can flourish, leading to redness and inflammation.
3. Excess Oil Production: Overactive oil glands can produce excessive oil, which can trap dead skin cells and bacteria in pores.
4. Diet and Lifestyle: Certain foods and habits may exacerbate acne for some individuals, though this is subject to ongoing research.
5. Medications: Some medications can trigger or aggravate acne. It’s essential to discuss potential side effects with a healthcare professional.
Different Types of Acne
Acne can manifest in various forms, including:
1. Blackheads (Open Comedones): Visible on the skin’s surface, blackheads are pores clogged with oil and dead skin cells, appearing black at the tip due to oxidation.
2. Whiteheads (Closed Comedones): These are similar to blackheads but are enclosed by a layer of skin, giving them a white or flesh-colored appearance.
3. Papules: Small, red, raised bumps on the skin caused by inflammation or infection of hair follicles.
4. Pustules: Similar to papules but filled with pus. They appear as red bumps with a white or yellow center.
5. Nodules: Larger, painful lumps beneath the skin’s surface. These are caused by clogged, swollen hair follicles.
6. Cysts: Painful, pus-filled lumps beneath the skin’s surface, larger than pustules. They can cause scarring if not treated appropriately.
Understanding the different types and causes of acne can aid in effective treatment and prevention. If acne persists or is severe, seeking advice from a dermatologist or healthcare professional is recommended.
Diagnosing Acne
For a clear and comprehensive understanding, here’s a dive into the process of diagnosing acne, from recognizing when it’s time to see a specialist to understanding the severity of your acne.
When to See a Dermatologist
While acne is a widespread issue, it isn’t always necessary to visit a doctor right away. Over-the-counter (OTC) treatments, which encompass creams, gels, and washes, can effectively address many mild acne cases. However, if you notice the following signs, it may be time to consult a dermatologist:
1. Persistence: Your acne doesn’t improve after 6-8 weeks of OTC treatments.
2. Severe Forms: Presence of large, painful cysts or nodules.
3. Scarring: You’re developing scars or dark spots from your acne.
4. Uncertainty: You’re not sure if it’s acne or another skin condition.
Remember, a dermatologist can offer potent treatments not available OTC, providing quicker and more effective results.
Clinical Examination
Once you decide to visit a dermatologist, you might wonder about the proceedings of the consultation. Here’s what you can expect:
1. Discussion: The dermatologist will begin by discussing your skin concerns, medical history, and any treatments you’ve tried in the past.
2. Physical Examination: A close-up inspection of your skin to determine acne type, severity, and any potential complications.
3. Recommendations: Post-examination, the doctor will suggest appropriate treatments or tests. This could include prescription creams, oral medications, or even certain procedures.
4. Skin Care Guidance: Apart from specific treatments, you’ll get advice on the right skincare regime to help manage and prevent future breakouts.
Understanding the Severity
Acne isn’t a one-size-fits-all condition. Its severity varies, and recognizing this can help in obtaining the right treatment. Broadly, acne can be classified into:
1. Mild Acne: This involves a few whiteheads, blackheads, or small pimples. They aren’t inflammatory and usually respond well to OTC treatments.
2. Moderate Acne: Characterized by multiple pustules and papules, which are inflamed and can be painful. They are typically deep-seated and may require prescription treatments.
3. Severe Acne: This encompasses cysts and nodules, which are large, painful, and deep-seated. They often lead to scarring and require more aggressive treatment from a dermatologist.
However, understanding acne, its severity, and when to seek professional help is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. Your skin is a reflection of your health, so it’s essential to give it the care it deserves.
Acne Treatment Options
While it’s essential to understand the cause of your acne, choosing the right treatment can alleviate the symptoms and improve the skin’s appearance. Below is a guide to various acne treatment options.
4.1. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Solutions
Over-the-counter solutions are readily available in most pharmacies and can be an effective first line of defense against mild to moderate acne. Some of the popular OTC acne treatments include:
1. Salicylic Acid: Works by exfoliating the skin and unclogging the pores.
2. Benzoyl Peroxide: An antibacterial agent that kills acne-causing bacteria and reduces inflammation.
3. Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): Derived from fruits and milk, they help in removing dead skin cells.
4. Sulfur: Often combined with other ingredients, sulfur helps reduce oiliness and unclog pores.
Prescription Medications
For those with moderate to severe acne, or for individuals who don’t respond to OTC solutions, a dermatologist can prescribe stronger treatments. These include:
1. Topical Antibiotics: Like clindamycin, they target the bacteria that contribute to acne.
2. Retinoids: Such as tretinoin, they’re derived from Vitamin A and are effective in unclogging pores.
3. Oral Antibiotics: Minocycline and doxycycline, among others, can be prescribed to reduce bacteria and inflammation.
4. Oral Contraceptives: For women, certain birth control pills can regulate hormones that trigger acne.
Advanced Therapies
If conventional treatments prove ineffective, there are more advanced therapies that can address stubborn acne:
1. Light and Laser Therapy: Target the deep layers of skin without harming the surface. They can reduce oil production and kill acne-causing bacteria.
2. Chemical Peels: Involve applying a strong chemical solution to remove the top layer of skin, promoting new skin growth.
3. Drainage and Extraction Procedures: Dermatologists can use special tools to remove cysts and whiteheads, providing relief from larger blemishes.
Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
Apart from medical treatments, lifestyle changes and natural remedies can also play a pivotal role in managing acne:
1. Dietary Changes: Limiting dairy and high-glycemic foods might improve acne for some people.
2. Herbal Remedies: Tea tree oil and green tea extracts have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
3. Skincare Practices: Keeping the skin clean, moisturized, and protected from the sun can prevent and alleviate acne symptoms.
Remember, while all these options can be effective, it’s essential to consult with a dermatologist or skincare professional to find the best treatment tailored to your skin type and acne severity.
Tips for Managing Acne
By understanding some fundamental tips and integrating them into your daily life, you can reduce breakouts and improve your skin’s overall health. Below, we provide insights to make your acne management more effective.
1. Establish a Proper Skincare Routine
1. Cleanse: Choose a gentle cleanser suited for acne-prone skin. Cleansing twice daily can help remove dirt, oil, and bacteria.
2. Exfoliate: Use a mild exfoliator once or twice a week to remove dead skin cells, ensuring pores remain unclogged. Avoid over-exfoliating, which can irritate the skin.
3. Moisturize: Even if your skin is oily, it’s essential to hydrate. Select a lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep your skin balanced.
4. Treat: Consider using over-the-counter treatments containing ingredients like salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide, which target acne-causing bacteria.
2. Avoid Picking or Popping Pimples
Picking can lead to scarring and spread bacteria, worsening acne. Instead, if a pimple comes to a head, use a sterile needle or pimple patch to safely address it.
3. Stress Less
Elevated stress levels can exacerbate acne. Incorporate relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or exercise to manage stress effectively.
4. Understand the Importance of Sunscreen
Sun exposure can darken acne scars and increase inflammation. Protect your skin daily with a broad-spectrum SPF, ideally one that’s oil-free or designed for acne-prone skin.
5. The Role of Makeup
Makeup can be both a friend and foe. While it’s tempting to cover up blemishes, some products can clog pores. Opt for non-comedogenic and mineral-based makeup products. Always ensure you remove your makeup thoroughly before bedtime.
Incorporating these tips into your routine can go a long way in managing and reducing acne. Remember, everyone’s skin is unique, so it may take some experimentation to find what works best for you. Don’t hesitate to consult a dermatologist for personalized advice.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Acne Treatments
Acne treatments, whether they are over-the-counter (OTC) products, prescription medications, or more advanced procedures, come with their own set of potential side effects and risks. It’s crucial for individuals considering these treatments to be well-informed, ensuring that they can make the best decision for their skin health.
1. Common Side Effects of OTC Products and Prescription Medications:
1. Dryness and Peeling: One of the most common side effects of many acne products is skin dryness and peeling. This is often due to ingredients such as benzoyl peroxide and salicylic acid.
2. Redness and Irritation: The skin might become red, irritated, or inflamed, especially when starting a new product. It’s vital to monitor this, as some minor irritation can be normal, but persistent redness can indicate a reaction.
3. Increased Sensitivity to Sunlight: Some acne treatments can make the skin more sensitive to UV rays, increasing the risk of sunburn. Hence, using sunscreen and avoiding prolonged sun exposure is recommended.
4. Allergic Reactions: Ingredients in OTC or prescription acne products might trigger allergic reactions in some people. Symptoms could include itching, swelling, hives, or more severe reactions in rare cases.
2. Risks Associated with More Advanced Acne Treatment Procedures:
1. Laser Treatments: While effective, laser treatments can sometimes cause skin discoloration, burns, or scars if not done correctly.
2. Chemical Peels: These can lead to scarring, persistent redness, or, rarely, infection if not applied appropriately.
3. Drainage and Extraction: Carried out to remove large cysts, this procedure might leave scars or can lead to an infection if not done in a sterile environment.
4. Isotretinoin (commonly known as Accutane): This potent prescription medication is effective against severe acne but comes with a list of potential side effects, including birth defects if taken during pregnancy, depression, and liver problems.
However, while many acne treatments are effective, it’s essential to understand their potential side effects and risks. Always consult with a dermatologist or skincare professional before starting any new treatment to ensure it’s the right fit for your individual needs. Remember, everyone’s skin is unique, and what works for one person might not work for another.
FAQs on Acne Treatment
Navigating the world of acne diagnosis and treatment can be overwhelming. Below are some of the most frequently asked questions on the topic, answered in an SEO and readability-friendly manner for your ease.
1. What causes acne?
Acne is primarily caused by overactive oil glands, blocked pores, and the growth of bacteria. Factors such as hormones, diet, stress, and genetics can also contribute to its development.
2. Are there different types of acne?
Yes, acne can be categorized into a few types: blackheads, whiteheads, papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts. Each has its unique appearance and can require different treatment approaches.
3. Does diet affect acne?
Diet can play a role in acne for some people. Foods high in sugar or dairy products might trigger breakouts for certain individuals, though the link between diet and acne is still under research.
4. How can I prevent acne breakouts?
Maintaining a consistent skincare routine, keeping your skin clean, and avoiding pore-clogging products can help. It’s also essential to manage stress and eat a balanced diet.
5. Are over-the-counter treatments effective?
Over-the-counter treatments can be effective for mild to moderate acne. They often contain ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or alpha hydroxy acids. However, severe cases may require prescription treatments.
6. When should I see a dermatologist for my acne?
If your acne is causing distress, is painful, or doesn’t improve with over-the-counter treatments, it’s a good idea to consult a dermatologist. They can offer more specialized treatments and advice.
7. Are there natural remedies for acne?
Some natural remedies, such as tea tree oil and aloe vera, have been found to help with mild acne. However, their effectiveness varies from person to person, and they might not be suitable for severe cases.
8. Will acne scars fade over time?
Some acne scars may fade over time, but others can be permanent. There are treatments available, like laser therapy and chemical peels, that can help reduce the appearance of scars.
We hope these answers shed some light on your acne-related concerns. If you have more questions, it’s always best to consult with a dermatologist or skincare professional.
Conclusion
In wrapping up, the significance of accurate diagnosis in the realm of acne treatment cannot be overstated. It’s the bedrock upon which effective and lasting solutions are built. Remember, treating acne is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Just as each individual is unique, so is their skin and the challenges it presents.
If you or someone you know is grappling with persistent acne issues, it’s paramount to seek guidance from a professional. Their expertise can help pinpoint the exact cause and offer tailor-made treatments that can make a world of difference. Don’t hesitate; prioritize your skin’s health and radiance today.