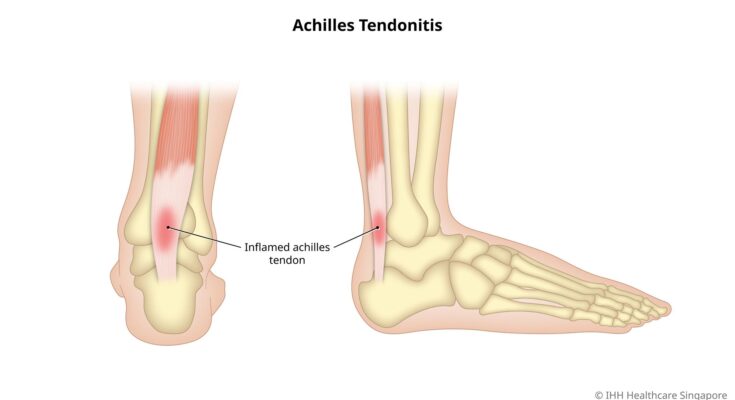
Achilles Tendinitis Treatment: The Achilles tendon, a critical part of our musculoskeletal system, often becomes the center of attention when it experiences inflammation, leading to a condition known as Achilles tendinitis.
Whether you’re an athlete, a weekend warrior, or someone facing the challenges of daily life, understanding this condition can be pivotal in ensuring you maintain optimal health and mobility.
In this article, we will delve deep into the diagnosis and treatment of Achilles tendinitis.
Understanding Achilles Tendinitis
a. Anatomy of the Achilles Tendon
The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the human body, connecting the calf muscles, specifically the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles, to the heel bone or calcaneus. It’s a strong, fibrous cord that allows us to point our toes and play an essential role in walking, running, and jumping.
b. Role of the Achilles Tendon in Daily Activities
Every day, the Achilles tendon plays a pivotal role in most of our movements. Whether you’re simply standing on your tiptoes to grab a book from a top shelf or running to catch the bus, the Achilles tendon is actively working. It provides the force needed to push off the ground, which is crucial for walking, climbing stairs, running, or even dancing. Its strength and flexibility are key to maintaining balance and stability in many physical activities.
c. Causes and Risk Factors of Achilles Tendinitis
Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury of the Achilles tendon. The most common causes include:
1. Intense Physical Activity: Suddenly increasing the intensity or duration of physical activities can strain the tendon.
2. Improper Footwear: Shoes that don’t offer proper support or have worn out soles can place extra stress on the Achilles tendon.
3. Underlying Foot Issues: Conditions such as flat feet or high arches can affect the way weight is distributed, leading to extra strain on the tendon.
4. Age: As we get older, our tendons can become less flexible and more prone to injury.
Risk factors further include participating in sports that involve repetitive jumping, running, or sudden starts and stops. An understanding of these causes and risk factors can help in prevention and early treatment.
Symptoms and Signs of Achilles Tendinitis
Recognizing the symptoms can be the first step in getting the necessary treatment.
a. Primary Symptoms of Achilles Tendinitis
The primary indicators of Achilles tendinitis include:
1. Pain and Stiffness: Often, the pain is mild at first and gradually worsens. You might feel it most when you wake up in the morning or after prolonged activity.
2. Swelling: The area around the tendon may become swollen, and this might be accompanied by warmth or redness.
3. Tenderness: Pressing along the tendon or its surrounding area might produce a tender feeling.
4. Limited Range of Motion: As the condition progresses, it may become more difficult to flex your foot or point your toes without pain.
b. How Symptoms Vary from Mild to Severe Cases
In mild cases of Achilles tendinitis, you might only experience a subtle ache in the back of your leg or near your heel after running or engaging in other sports. It’s easy to dismiss this as regular post-exercise soreness. However, if left untreated, these symptoms can intensify.
In severe cases, the pain associated with Achilles tendinitis can be sharp and debilitating, making it hard to walk, let alone engage in athletic activities. Swelling can become pronounced, and in some cases, you might even hear a creaking sound when moving your ankle or pressing on the tendon.
c. Importance of Early Detection
Spotting the symptoms of Achilles tendinitis early is crucial. Early detection:
1. Prevents Further Injury: Addressing the issue promptly can prevent the condition from worsening, which might lead to more severe injuries like tendon tears or ruptures.
2. Speeds Up Recovery: Treatment in the initial stages is often simpler and more effective, allowing for a quicker return to regular activities.
3. Minimizes Treatment Complexity: Ignoring symptoms can lead to chronic tendinitis, which might require more intensive treatments, including surgery.
However, if you suspect you might have Achilles tendinitis, it’s essential to pay attention to the symptoms and seek professional advice. An early intervention can pave the way for a smoother and swifter recovery.
Diagnosis of Achilles Tendinitis
Achilles tendinitis is a common condition affecting the tendon connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone. Accurate diagnosis is crucial to ensure appropriate treatment and faster recovery. Here’s how medical professionals typically diagnose Achilles tendinitis:
a. Clinical Evaluation: History and Physical Examination
History: The first step often involves obtaining a detailed medical history. Patients might describe symptoms like pain, stiffness, or swelling in the back of the heel, especially after periods of activity or upon waking up in the morning. They may also discuss any recent changes in physical activity or incidents that might have caused strain on the tendon.
Physical Examination: A physician typically palpates (touches) the affected area to identify swelling, warmth, or tenderness. Range of motion tests can also help in determining the extent of injury. By asking the patient to flex, point, or rotate the foot, the doctor can gauge the severity of the pain and its exact location.
b. Imaging Tests:
Ultrasound: This imaging technique uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures inside the body. For Achilles tendinitis, an ultrasound can display inflammation, thickening, or small tears in the tendon.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): An MRI provides a more detailed image of soft tissues than an ultrasound. This test can be particularly useful if the diagnosis is uncertain or if the condition doesn’t improve with conservative treatments. It can detect both partial and complete tears of the tendon, as well as any inflammation.
c. Differential Diagnosis: Other Conditions That Mimic Achilles Tendinitis
It’s essential to distinguish Achilles tendinitis from other conditions that exhibit similar symptoms. These may include:
1. Achilles Tendon Rupture: A complete or partial tear of the tendon, often accompanied by a “snapping” sensation and immediate severe pain.
2. Haglund’s Deformity: A bony enlargement on the back of the heel that can irritate the Achilles tendon.
3. Posterior Ankle Impingement: Pain at the back of the ankle due to compression of soft tissues.
4. Bursitis: Inflammation of the small sac of fluid (bursa) located between the Achilles tendon and the heel bone.
However, a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging tests ensures an accurate diagnosis of Achilles tendinitis. Recognizing other conditions with similar symptoms is vital for recommending the right course of treatment.
Conservative Achilles Tendinitis Treatment Options
Achilles tendinitis can be a painful and limiting condition. Before jumping to surgical interventions, many people prefer to start with conservative treatments. These methods are not only less invasive but can also be very effective in managing pain and promoting healing. Below, we explore the commonly recommended conservative treatments for Achilles tendinitis.
a. RICE Method: Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation
The RICE method is a go-to first aid response for many soft tissue injuries, and Achilles tendinitis is no exception.
1. Rest: Give your Achilles tendon a break. Avoid activities that cause pain or could further strain the tendon.
2. Ice: Applying ice can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain. Use a cold pack for 15-20 minutes every 1-2 hours during the first 48 hours after onset.
3. Compression: Wearing a compression bandage can help control swelling and support the injured area.
4. Elevation: Prop your leg up to help decrease swelling. Ideally, try to elevate your foot above the level of your heart.
b. Physical Therapy and Exercises
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of Achilles tendinitis treatment. A trained therapist can guide you through exercises to strengthen the calf muscles and improve flexibility of the Achilles tendon. Not only does this aid in recovery, but it can also help prevent future injuries. Regular stretches and low-impact exercises, when done correctly, can make a world of difference.
c. Medications: Pain Relievers and Anti-inflammatories
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen can be instrumental in managing pain and reducing inflammation. Always follow dosing instructions and consider potential interactions with other medications. Consult with a healthcare professional if unsure.
d. Use of Orthotics and Shoe Modifications
Sometimes, the way you walk or the shoes you wear can exacerbate Achilles tendinitis. Custom orthotics can help distribute pressure more evenly when walking or running. Similarly, shoe modifications, like heel lifts, can reduce strain on the tendon. Consult with a podiatrist or orthopedic specialist to determine the best options for your specific needs.
However, if you’re grappling with Achilles tendinitis, these conservative treatment options can serve as an effective starting point. Always consult with a medical professional before starting any treatment to ensure it’s appropriate for your specific condition and needs.
Advanced Achilles Tendinitis Treatment Methods
When initial treatments like rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relievers don’t bring relief, it might be time to consider advanced treatment options. As Achilles tendinitis can significantly affect one’s mobility and quality of life, understanding these advanced treatments can be a game-changer for many. Let’s dive into some of the most effective methods:
a. Shockwave Therapy
What is it? Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses acoustic waves to promote healing in the injured area.
Benefits:
- Pain Reduction: The therapy helps decrease pain by stimulating blood flow and accelerating the healing process.
- Mobility Improvement: Patients often report improved function and mobility after a few sessions.
How it Works: A device is used to send acoustic shockwaves into the Achilles tendon. This stimulates blood flow, encourages cellular repair, and can help break down scar tissue.
b. Platelet-rich Plasma (PRP) Injections
What is it? PRP therapy involves drawing a patient’s own blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting it into the injured area.
Benefits:
- Natural Healing: As PRP uses the patient’s own blood, it reduces the risk of allergic reactions or infections.
- Accelerated Repair: PRP releases growth factors that speed up tissue repair and regeneration.
Procedure: After drawing a small amount of blood, it’s placed in a centrifuge to separate the platelet-rich plasma. This concentrated plasma is then injected directly into the Achilles tendon area.
c. Surgery: Indications, Procedure, and Recovery
When is Surgery Required? Surgery is usually considered the last resort, often recommended when:
- The tendon has a significant tear or rupture.
- Pain persists even after trying other treatments for several months.
Procedure: During surgery, the damaged portion of the Achilles tendon is removed or repaired. Depending on the extent of the injury, the tendon may be reinforced with other tendons.
Recovery:
- Immediate Aftercare: The foot is typically immobilized in a cast or walking boot, allowing the tendon to heal.
- Physical Therapy: Post-surgery rehabilitation is crucial. Physical therapy exercises help restore strength and mobility.
- Duration: Full recovery can take anywhere from a few months to a year, depending on the severity of the injury and individual healing rates.
When facing Achilles tendinitis, it’s crucial to consult with a medical professional who can guide you on the best treatment path tailored to your needs.
Prevention and Management of Achilles Tendinitis
Here, we delve into the significance of preventive strategies and suitable management techniques, ensuring that your Achilles tendon remains healthy and robust.
a. Tips to Prevent Achilles Tendinitis
1. Gradual Progression: Avoid overburdening your tendon. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercises, especially when taking on new physical activities.
2. Stay Active: Engage in regular low-impact exercises to keep the Achilles tendon flexible and strong.
3. Warm-Up: Always start with a good warm-up routine before any strenuous activities. This prepares the tendon for the workload ahead.
4. Cross-Training: Incorporate a variety of exercises into your routine, like swimming or cycling, to ensure that the tendon isn’t being repetitively stressed in the same way.
5. Listen to Your Body: If you feel pain or discomfort in the Achilles area, it’s essential to rest and not push through the pain.
b. The Importance of Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
1. Flexibility is Key: Regular stretching of the calf muscles and the Achilles tendon increases its flexibility. This reduces the risk of the tendon becoming too tight and prone to injuries.
2. Strength Reduces Strain: Strengthening exercises, especially for the calf muscles, can mitigate the strain on the Achilles tendon. A strong calf muscle can better support and protect the tendon.
3. Consistency: Incorporate stretching and strengthening into your daily routine for maximum benefits. A consistent regimen promotes long-term tendon health.
c. Proper Footwear Selection
1. Right Fit: Always select shoes that fit well. Shoes that are too tight or too loose can place undue stress on the Achilles tendon.
2. Adequate Support: Invest in shoes with proper arch support. They help distribute pressure evenly across your foot and lessen the load on the tendon.
3. Avoid High Heels: Frequently wearing high heels can shorten the calf muscles over time, placing additional strain on the Achilles tendon.
4. Replace Worn-Out Shoes: Over time, shoes lose their cushioning and support. Regularly replacing or repairing worn-out shoes can prevent unnecessary strain.
However, a combined approach of preventive measures, regular stretching and strengthening, and making informed footwear choices can play a pivotal role in ensuring that Achilles tendinitis remains at bay. Adopt these measures today for a pain-free and active tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions on Achilles tendinitis
What is Achilles tendinitis?
Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury of the Achilles tendon, the band of tissue connecting calf muscles at the back of the lower leg to your heel bone.
What causes Achilles tendinitis?
This condition often arises due to repetitive stress on the Achilles tendon. Common causes include increased activity levels, wearing inappropriate footwear, or failing to stretch before physical activities.
How can I recognize Achilles tendinitis?
Symptoms often include pain and swelling around the heel, stiffness in the tendon, especially in the morning, and increased pain after physical activity.
How is Achilles tendinitis treated?
Treatment often involves rest, ice, over-the-counter pain relievers, and physical therapy. In severe cases, surgery might be necessary.
Can I prevent Achilles tendinitis?
Yes. Regularly stretch your Achilles tendon, gradually increase activity levels, and wear appropriate footwear to reduce your risk.
How long does recovery typically take?
Most people recover within a few months with proper treatment. However, severe cases may take longer.
Remember, if you’re experiencing symptoms of Achilles tendinitis, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
In wrapping up, it’s paramount to underscore the significance of comprehending, diagnosing, and addressing Achilles tendinitis. This condition isn’t just a mere foot problem; it’s an issue that, if left unchecked, can profoundly impact your quality of life and overall mobility. Proper understanding and early diagnosis are crucial to ensuring that you remain active and pain-free.
If you believe you’re experiencing symptoms of Achilles tendinitis or have concerns about your foot health, don’t hesitate. Seek professional advice. Your feet are the foundation upon which you stand, move, and explore the world. Prioritize their care and, by extension, your overall well-being. Remember, it’s always better to be proactive rather than reactive when it comes to health matters.