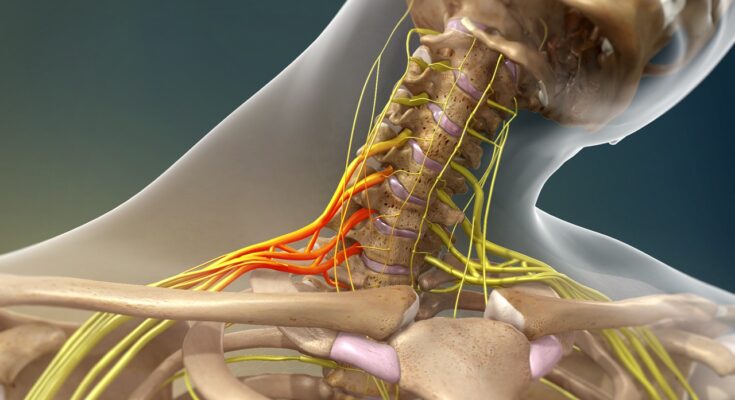
Brachial Plexus Injury Treatment: The brachial plexus is a critical network of nerves that originates from the spinal cord in the neck and extends through the armpits, supplying movement and sensation to the shoulder, arm, and hand.
A Brachial Plexus Injury (BPI), often caused by trauma such as motor vehicle accidents or sports injuries, can lead to varying degrees of paralysis and sensory loss in the upper limb.
Understanding the nuances of diagnosis and treatment of this complex injury is paramount for effective recovery and rehabilitation.
What is a Brachial Plexus Injury?
A brachial plexus injury refers to damage to the brachial plexus, a complex network of nerves located between the neck and shoulders. These nerves are responsible for transmitting signals from your spinal cord to your shoulder, arm, and hand. An injury to this network can cause varying degrees of pain, weakness, and loss of function in the upper limbs.
Common Causes of Brachial Plexus Injuries
Brachial plexus injuries are often caused by:
1. Trauma: This is the most common cause, including car or motorcycle accidents, sports injuries, or falls.
2. Birth Injuries: During childbirth, particularly in difficult or breech deliveries.
3. Compression: Prolonged pressure on the nerve, often from repetitive motions or improper posture, can lead to injury.
4. Tumors: Abnormal growths can compress and damage the nerves.
Types of Brachial Plexus Injuries
Brachial plexus injuries are categorized based on the type and severity of the nerve damage:
1. Avulsion: The most severe type, where the nerve is torn away from the spine.
2. Rupture: The nerve is torn, but not at the spinal attachment.
3. Neuroma: Scar tissue forms as the nerve tries to heal, putting pressure on the injured nerve and preventing signals from passing through effectively.
4. Neuropraxia: The mildest form, involving a temporary loss of nerve function due to compression or stretch without tearing.
Each type of injury requires a different approach to treatment and management. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve the prognosis for individuals with brachial plexus injuries.
Symptoms of Brachial Plexus Injury
Brachial Plexus Injuries (BPI) manifest through a variety of symptoms, which are crucial to recognize for timely intervention. The primary indicators include:
Weakness in the Arm: Individuals may experience a noticeable decline in arm strength, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks.
Numbness or Tingling: There’s often a sensation of pins and needles or numbness, particularly in the hands and fingers.
Pain: This can range from a dull ache to sharp, shooting pains, typically originating from the shoulder and extending down the arm.
Limited Movement: The range of motion in the shoulder, arm, or hand might be significantly reduced, impacting daily activities.
The Importance of Early Detection
Identifying these symptoms promptly is vital. Early detection of BPI can lead to more effective treatments, potentially preventing long-term damage and disability. It’s essential for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek medical advice as soon as possible.
Real-Life Insights: Case Studies and Anecdotes
Incorporating case studies or personal anecdotes can provide deeper understanding and relatability. For instance, a patient who sought early intervention after experiencing arm weakness and numbness could share their journey of recovery, highlighting the importance of recognizing these symptoms. While individual experiences vary, such stories underscore the significance of prompt medical attention in the case of Brachial Plexus injuries.
Diagnostic Procedures: A Comprehensive Overview
Let’s delves into the various diagnostic methods, emphasizing the significance of physical examination and the necessity of timely and precise diagnosis.
List of Diagnostic Techniques
Blood Tests: Vital for assessing organ function and detecting diseases.
Imaging Techniques: Such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, crucial for visualizing internal body structures.
Biopsy: Involves sampling tissue for closer examination, often used to diagnose cancer.
Endoscopy: A procedure using a camera to visualize internal organs directly.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): Essential for evaluating heart rhythm and function.
Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of internal body structures, commonly used in pregnancy and diagnosing soft tissue conditions.
Genetic Testing: Helps in identifying genetic disorders and predispositions.
Urinalysis: Analyzes urine for signs of disease, particularly in the kidneys and urinary tract.
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs): Assess lung function and breathing.
Allergy Testing: Identifies specific allergic triggers.
The Role of Physical Examination in Diagnosis
Physical examination remains a cornerstone in the diagnostic process. It involves a hands-on assessment by a healthcare professional to check for signs of illness. A thorough physical exam can reveal a lot about a person’s general health, detect potential diseases, and guide further diagnostic testing.
Key elements include:
- Inspection: Observing the body for signs of conditions.
- Palpation: Feeling the body with hands to detect abnormalities.
- Auscultation: Listening to sounds from organs (heart, lungs) using a stethoscope.
- Percussion: Tapping on the body surface to identify problems with organs underneath.
Importance of Accurate and Prompt Diagnosis
Prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial for several reasons:
Early Intervention: Timely diagnosis allows for early treatment, potentially preventing complications or more severe disease progression.
Improved Outcomes: Accurate diagnosis leads to more effective treatment plans, improving patient outcomes.
Cost-Effective: Early detection can reduce healthcare costs by avoiding more extensive and expensive treatments later.
Patient Confidence: Accurate and timely diagnosis can increase patient trust and confidence in their healthcare providers.
However, diagnostic procedures are essential tools in modern medicine. They range from basic physical examinations to advanced technological tests. The effectiveness of these methods lies not just in their ability to detect diseases but also in their application in a timely and accurate manner. As medical technology advances, these diagnostic tools continually evolve, offering more precision and less invasiveness, thereby enhancing patient care and treatment outcomes.
Treatment Options for Brachial Plexus Injury
The modalities encompass both surgical and non-surgical options, tailored to the severity and nature of the injury. Understanding these options is crucial for effective management and recovery.
Surgical Treatments
Surgical interventions are often considered when there is a severe injury or when non-surgical methods have not yielded satisfactory results. The primary surgical treatments include:
Nerve Grafts: This procedure involves replacing damaged sections of the nerves with segments of nerves harvested from other parts of the patient’s body. This technique helps to restore nerve function over time.
Nerve Transfers: In cases where nerve grafts are not viable, nerve transfers are performed. This involves rerouting a less important nerve in the arm or leg to replace the damaged nerve in the brachial plexus.
Other Surgical Procedures: Depending on the specifics of the injury, other surgeries like neurolysis or tendon transfer might be recommended.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments are typically the first line of defense, especially in less severe cases. They include:
Physical Therapy: A cornerstone of brachial plexus injury treatment, physical therapy helps maintain joint flexibility, improve muscle strength, and reduce pain.
Medications: Pain management often involves medications, such as anti-inflammatory drugs, pain relievers, and sometimes muscle relaxants.
Occupational Therapy: This focuses on improving the patient’s ability to perform daily activities through specialized exercises and the use of adaptive devices.
Emerging Treatments and Research
The field of brachial plexus injury treatment is constantly evolving, with ongoing research into new and more effective treatment methods. Emerging therapies include:
Regenerative Medicine: Techniques like nerve growth factor therapies and stem cell therapy are under investigation for their potential to regenerate damaged nerves.
Robotic-Assisted Rehabilitation: This innovative approach uses robotic devices to assist in repetitive and intensive rehabilitation exercises, enhancing recovery prospects.
Neuromodulation Techniques: These involve electrical or magnetic stimulation of the nervous system and are being studied for their potential in improving nerve function and pain management.
However, brachial plexus injury treatment is a dynamic and evolving field. The choice of treatment depends on various factors including the severity of the injury, patient’s health status, and the recovery goals. Consulting with a specialized medical professional is essential for a tailored and effective treatment plan.
Rehabilitation and Recovery of Brachial Plexus Injury
1. Role of Physical Therapy in Recovery
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation process of a Brachial Plexus injury. Customized physical therapy programs are designed to restore strength, improve flexibility, and enhance the overall function of the affected limb. The involvement of skilled physical therapists ensures a comprehensive approach towards recovery, focusing on exercises that target muscle re-education, range of motion, and pain management.
2. Expected Timeline for Recovery and Rehabilitation
The recovery timeline for a Brachial Plexus injury varies significantly based on the severity of the injury and the patient’s overall health. Generally, patients may observe noticeable improvements within weeks of consistent therapy, but complete recovery can take several months to years. It’s important to note that early intervention and adherence to therapy protocols substantially improve outcomes.
3. Patient Success Stories or Testimonials
Hearing from patients who have successfully navigated their recovery journey can be incredibly motivating for individuals facing a similar challenge. While individual experiences may vary, testimonials often highlight the positive impact of dedicated physical therapy and the importance of persistence and patience during the rehabilitation process. These success stories serve as powerful examples of resilience and the possibility of regaining functionality and quality of life post-injury.
Complications and Management of Brachial Plexus Injuries
Understanding these potential complications is crucial for patients and caregivers alike.
1. Chronic Pain: One of the most common complications of a brachial plexus injury is persistent pain. This pain can range from mild to severe and may not always correlate with the severity of the injury.
2. Muscle Weakness and Atrophy: Due to nerve damage, affected muscles may become weak. Over time, without proper use, these muscles can atrophy, leading to further disability.
3. Loss of Sensation: Nerve damage can also cause a loss of sensation in the arm or hand, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks.
4. Joint Stiffness: Lack of movement due to pain or muscle weakness can lead to stiffness in joints, further limiting mobility.
5. Psychological Impact: Dealing with chronic pain and disability can also have significant psychological effects, including depression and anxiety.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Managing a brachial plexus injury is a long-term commitment. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Physical Therapy: Engaging in regular physical therapy can help improve muscle strength and joint mobility. Tailored exercises can prevent muscle atrophy and joint stiffness.
2. Pain Management: Consult with healthcare providers for pain management strategies. This may include medications, nerve blocks, or alternative therapies.
3. Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapists can provide strategies to cope with the loss of sensation and fine motor skills, helping patients adapt to their daily activities.
4. Regular Check-Ups: Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the progress and adjust treatments as necessary.
5. Supportive Devices: Using braces, splints, or other assistive devices can help improve function and reduce pain.
Tips for Coping with Chronic Symptoms or Disability
Living with a brachial plexus injury can be challenging. Here are some tips to cope:
1. Stay Active: Engage in regular exercise within your limits to maintain muscle strength and joint flexibility.
2. Join Support Groups: Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide emotional support and practical advice.
3. Mental Health Support: Seek professional help if you are struggling with the psychological impact of your injury.
4. Home Modifications: Consider making modifications to your home to make daily activities easier and safer.
5. Educate Yourself: Understanding your condition can empower you to make informed decisions about your care.
However, while brachial plexus injuries can lead to significant complications, effective management and coping strategies can help improve quality of life. Regular consultation with healthcare professionals, physical and occupational therapy, and support systems are crucial in navigating the challenges posed by these injuries.
Prevention and Awareness of Brachial Plexus Injury
With proper knowledge and strategies, their occurrence can be significantly reduced. Here are key prevention tips:
Proper Sports Training: Athletes, especially in contact sports, should receive proper training on techniques and use the correct protective gear. Coaches and trainers must emphasize the importance of avoiding risky maneuvers that strain the shoulder area.
Safe Birthing Techniques: During childbirth, careful handling and proper techniques can prevent brachial plexus injuries in newborns. Health professionals should be trained to identify risky situations during delivery and take necessary precautions.
Ergonomic Practices in Daily Activities: Adopting ergonomic principles in daily activities, especially those involving repetitive arm movements or heavy lifting, can reduce the risk. It’s crucial to take regular breaks and use ergonomic tools and furniture.
Awareness in Motor Vehicle Safety: Using seat belts properly and ensuring airbags are functioning can mitigate the risk of brachial plexus injuries during car accidents. Motorcyclists should wear appropriate protective gear.
Regular Physical Therapy: For individuals with a history of shoulder or neck problems, regular physical therapy exercises can strengthen the area and reduce the risk of injury.
Raising Awareness About the Importance of Early Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment of brachial plexus injuries are crucial for recovery. Increased awareness can lead to prompt action, reducing long-term complications. Here’s how awareness can be raised:
Educational Campaigns: Health organizations can conduct educational campaigns targeting athletes, expecting parents, and the general public to inform them about the signs and risks of brachial plexus injuries.
Training for Healthcare Professionals: Regular training for healthcare professionals, including midwives, pediatricians, and emergency medical staff, can ensure early detection and treatment.
Community Engagement: Local community centers and schools can host workshops and seminars on the topic, engaging people directly and providing valuable information.
Online Resources: Creating accessible online resources, such as informative websites, videos, and social media content, can spread awareness broadly.
Support Groups: Encouraging the formation of support groups for those affected by brachial plexus injuries can provide a platform for sharing experiences and advice on early treatment and management.
By combining prevention strategies with efforts to raise awareness about early treatment, we can significantly reduce the impact of brachial plexus injuries on individuals and communities.
FAQs: Understanding Brachial Plexus Injury and Treatment
What is a Brachial Plexus Injury?
A brachial plexus injury involves damage to the network of nerves that send signals from your spine to your shoulder, arm, and hand. These injuries can result from various causes, including traumatic accidents, sports injuries, or during childbirth.
How is a Brachial Plexus Injury Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, understanding the patient’s medical history, and may include imaging tests like MRI or CT scans. Electromyography (EMG) tests can also be used to assess nerve function.
What are the Symptoms of Brachial Plexus Injury?
Symptoms can vary but often include weakness, loss of feeling, or paralysis in the arm. Pain, particularly a severe burning sensation, is also a common symptom.
Can Brachial Plexus Injuries Heal on Their Own?
Some brachial plexus injuries, particularly milder ones, may heal over time. However, severe injuries often require intervention, such as physical therapy or surgery.
What Treatments are Available for Brachial Plexus Injury?
Treatment options depend on the severity and type of injury. They range from physical therapy and medications to manage symptoms, to surgical options like nerve grafts or transfers.
How Long is the Recovery Period for Brachial Plexus Injury?
The recovery time can vary widely depending on the severity of the injury and the treatment method. While some patients may recover in a few months, others might take years or have lingering effects.
Can Physical Therapy Help with Brachial Plexus Injury?
Physical therapy is a crucial part of the recovery process. It helps maintain joint flexibility, improve muscle strength, and can reduce pain.
Is Surgery Always Necessary for Brachial Plexus Injury?
Not all brachial plexus injuries require surgery. Non-surgical treatments can be effective, especially for less severe injuries. However, surgery might be recommended for more serious cases or if there’s no improvement with conservative treatments.
What are the Risks of Brachial Plexus Injury Surgery?
As with any surgery, there are risks such as infection, bleeding, or adverse reactions to anesthesia. Specific risks related to brachial plexus surgery include incomplete recovery of function or sensation, and in rare cases, worsening of symptoms.
Can a Brachial Plexus Injury Reoccur?
Once healed, it’s uncommon for the same injury to reoccur unless there’s a new trauma. However, it’s important to follow preventive measures and rehabilitation guidelines to minimize the risk of further injury.
Conclusion
We strongly encourage anyone suspecting a brachial plexus injury not to delay seeking professional medical advice. These conditions, often resulting from trauma, accidents, or even during birth, require the expertise of specialists who can offer a range of treatments from physical therapy to surgery, depending on the severity of the injury. Remember, timely intervention can be the difference between complete recovery and long-term disability.
As we conclude, remember that knowledge and action are your greatest allies. If you or someone you know might be suffering from symptoms indicative of a brachial plexus injury, such as weakness, loss of feeling, or lack of muscle control in the shoulder, arm, or hand, it’s crucial to act promptly. Contact a healthcare specialist to get a comprehensive evaluation.
Additionally, educating yourself further about brachial plexus injuries, their symptoms, and treatment options is a proactive step towards managing this condition effectively. Your health and well-being are invaluable; never hesitate to take the necessary steps to protect them.