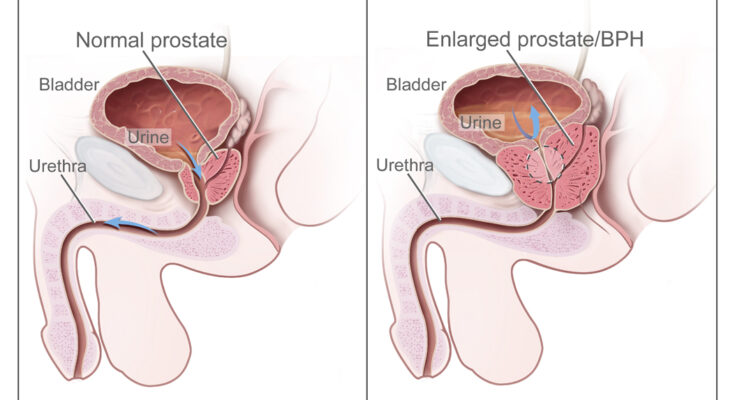
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Treatment: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), commonly known as prostate gland enlargement, is a frequent condition as men get older.
An enlarged prostate gland can cause uncomfortable urinary symptoms, such as blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder. It can also cause bladder, urinary tract, or kidney problems.
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, commonly known as BPH, is a medical condition that involves the enlargement of the prostate gland in men. This enlargement is non-cancerous (benign) but can significantly affect a man’s quality of life. The prostate is a small gland that sits below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine passes out of the body. BPH is a common condition, especially in older men, and understanding its causes, risk factors, and symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors of BPH
The exact cause of BPH is not entirely understood, but it primarily occurs due to changes in hormone levels as men age. Several factors increase the risk of developing BPH:
Age: The risk of BPH increases significantly as men get older. It is most common in men over the age of 50.
Family History: Men with a family history of BPH are more likely to develop the condition.
Lifestyle Factors: Factors such as obesity, lack of physical activity, and an unhealthy diet may contribute to the development of BPH.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, like diabetes and heart disease, have been linked to an increased risk of BPH.
Symptoms of BPH Indicating the Need for Treatment
BPH can lead to a range of urinary symptoms that vary in severity, and recognizing these symptoms is key to seeking timely medical intervention. Some of the symptoms that might indicate the need for treatment include:
Frequent Urination: Especially at night, leading to sleep disturbances.
Difficulty Starting Urination: A weak or hesitant urinary stream.
Urgency to Urinate: A sudden, uncontrollable urge to urinate.
Incomplete Emptying of Bladder: Feeling like the bladder is not fully empty after urination.
Urinary Tract Infections: Frequent UTIs can be a sign of BPH.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and to discuss treatment options. Early diagnosis and management of BPH can significantly improve quality of life and prevent complications.
Remember, BPH is a common condition, and effective treatments are available. Don’t hesitate to seek medical advice if you’re experiencing any symptoms.
Diagnosing Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), commonly known as prostate gland enlargement, is a frequent condition as men age. It involves prostate gland enlargement which can lead to uncomfortable urinary symptoms, such as blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder. It can also cause bladder, urinary tract, or kidney problems.
Initial Consultation and Medical History
The first step in diagnosing BPH is typically a detailed conversation with your healthcare provider. During this initial consultation, you’ll be asked about your symptoms, personal medical history, and family medical history. This discussion is crucial as it guides subsequent diagnostic steps.
Physical Examination
A physical examination, especially a digital rectal examination (DRE), is usually the next step. During a DRE, your doctor will manually check for prostate enlargement.
Urine Test
A urine test helps identify any infection or other conditions that could be causing your symptoms.
Blood Test
A blood test might be conducted to check kidney function and to test for prostate-specific antigen (PSA), which can indicate prostate problems, including BPH.
Prostate Biopsy
In some cases, a prostate biopsy is recommended if the PSA levels are high, to rule out prostate cancer.
Additional Tests
Depending on the situation, additional tests might include:
- A uroflow test to measure the strength and amount of your urine flow.
- Postvoid residual volume test to determine if you can empty your bladder completely.
- Cystoscopy to look inside your urethra and bladder.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis and treatment of BPH are crucial. They can help manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and prevent complications. If you experience any symptoms suggestive of BPH, such as difficulty urinating, frequent urination, or weak urine stream, consult your healthcare provider promptly.
However, diagnosing BPH involves a combination of personal medical history, physical exams, and specific tests. Understanding the diagnosis process can help you prepare for your healthcare visits and make informed decisions about your health.
Treatment Options for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
The approach to treating BPH is largely dictated by the severity of symptoms. Milder cases might respond well to lifestyle changes and medication, while more severe cases may require surgical intervention. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to assess the severity of your condition and to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Medications
- Alpha-Blockers: These medications help relax the muscles of the prostate and bladder neck, easing urinary symptoms.
- 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors: These drugs can shrink the prostate over time and are effective in reducing the symptoms associated with BPH.
Lifestyle Modifications and Home Remedies
- Dietary Changes: Reducing caffeine and alcohol intake can alleviate symptoms.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help improve overall prostate health.
- Scheduled Voiding: Training the bladder to void at regular intervals can reduce symptoms.
Minimally Invasive Therapies
These treatments are less invasive than traditional surgery and include procedures like transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT) and transurethral needle ablation (TUNA), which use heat to reduce prostate size.
Surgical Treatments
Types of Surgeries
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): This is the most common surgery for BPH and involves removing prostate tissue.
- Laser Therapy: Various forms of laser therapy can be used to vaporize or remove excess prostate tissue.
Risks and Benefits of Surgical Options
While surgery can offer significant relief, it’s not without risks. Possible complications include infection, bleeding, and urinary incontinence. However, for many men, the benefits of improved urinary function and quality of life outweigh these risks.
Emerging Trends in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Treatment
Advances in BPH treatment have been significant in recent years, offering new hope and improved outcomes for patients. This article delves into the latest advancements and research in BPH treatment, as well as potential future treatment methods being explored.
Recent Advancements in BPH Treatment
Minimally Invasive Therapies: Recent years have seen a shift towards minimally invasive treatments for BPH. Procedures like UroLift and Rezūm provide alternatives to traditional surgery, reducing recovery time and potential complications.
Laser Therapy Innovations: The evolution of laser therapies, such as Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP) and GreenLight Laser, has enhanced precision in treating BPH. These methods offer fewer side effects and quicker recovery compared to older techniques.
Medication Developments: New medications have emerged, offering better control of BPH symptoms with fewer side effects. Drugs like tadalafil, traditionally used for erectile dysfunction, have shown efficacy in BPH treatment as well.
Personalized Medicine: Advances in genetic and molecular profiling are leading to more personalized BPH treatments. This approach tailors treatment based on individual patient profiles, improving efficacy and minimizing unnecessary interventions.
Potential Future Treatment Methods
Stem Cell Therapy: Research is exploring the potential of stem cells in regenerating prostate tissue and restoring normal function. This approach could revolutionize BPH treatment by offering a more natural and long-lasting solution.
Nanotechnology: The use of nanotechnology in drug delivery could enhance the effectiveness of existing medications, reducing side effects and improving outcomes.
Robotics in Surgery: The future may see an increased role of robotics in BPH surgery, offering more precision and reducing human error.
Gene Therapy: Understanding the genetic factors in BPH progression opens the door for gene therapy approaches, potentially offering targeted and more effective treatments.
However, the landscape of BPH treatment is rapidly evolving, with innovative technologies and methods enhancing patient care. While current advancements offer improved outcomes, future therapies hold the promise of even more effective and personalized solutions for those suffering from BPH.
Living with BPH: Management and Quality of Life
Living with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) can be challenging, but with the right strategies and lifestyle changes, it’s possible to manage symptoms effectively and maintain a good quality of life. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to navigate life with BPH.
Strategies for Managing Symptoms in Daily Life
Stay Active: Regular physical activity can help manage BPH symptoms. Simple exercises, like walking or swimming, can significantly improve urinary symptoms.
Balanced Diet: Incorporate a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Reducing caffeine and alcohol can also alleviate urinary symptoms.
Bladder Training: Practice holding urine for longer periods to train your bladder. This can help in reducing the frequency of urination.
Timed Voiding: Try to urinate at regular intervals, even if you don’t feel the urge, to prevent the bladder from becoming too full.
Stay Hydrated: Drink fluids throughout the day to avoid dehydration, but limit fluid intake in the evening to reduce nighttime urination.
Importance of Regular Medical Check-Ups and Monitoring
Routine Exams: Regular visits to your healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring the progression of BPH and adjusting treatments as needed.
Medication Review: Regularly review your medications with your doctor, as some can exacerbate BPH symptoms.
Symptom Tracking: Keep a symptom diary to track changes and discuss them during your medical appointments.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle with BPH
Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight, as obesity can worsen BPH symptoms.
Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation or yoga, as stress can impact urinary symptoms.
Quit Smoking: Smoking can aggravate urinary symptoms and lead to bladder irritations.
Stay Informed: Educate yourself about BPH and stay updated on new research and treatments.
However, living with BPH requires a combination of medical management and lifestyle adjustments. Regular medical check-ups, symptom management, and a healthy lifestyle are key to improving quality of life with BPH. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options.
FAQs About Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Treatment
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia is the enlargement of the prostate gland, common in older men. This enlargement can cause urinary problems, such as difficulty in starting urination, a weak urine stream, or the need to urinate more often, especially at night.
What Causes BPH?
The exact cause of BPH is not well understood, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes that occur with age. Factors like genetics, lifestyle, and overall health also play a role.
How is BPH Diagnosed?
BPH is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. These tests may include a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test, urinalysis, and a digital rectal exam.
What are the Common Treatments for BPH?
Treatment options for BPH vary depending on the severity of symptoms. They can range from lifestyle changes and medications to minimally invasive therapies and surgery. Common medications include alpha-blockers, which relax bladder neck muscles, and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, which shrink the prostate.
Are There Any Side Effects of BPH Treatments?
Like all medical treatments, BPH therapies can have side effects. These can vary based on the type of treatment but may include sexual dysfunction, dizziness, and other urinary issues. It’s important to discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider.
Can Lifestyle Changes Help Manage BPH Symptoms?
Yes, certain lifestyle changes can help manage BPH symptoms. These include reducing fluid intake before bedtime, limiting caffeine and alcohol, practicing bladder training, and maintaining a healthy weight.
When Should Surgery be Considered for BPH?
Surgery is typically considered when symptoms are severe, or if there are complications such as urinary retention, bladder stones, or kidney problems. The most common surgeries for BPH are transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) and laser therapy.
Are There Any Natural Remedies for BPH?
Some men find relief from BPH symptoms using natural remedies like saw palmetto or beta-sitosterol supplements. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any natural remedy, as they can interact with other medications and may not be effective for everyone.
Conclusion
Treatment options for BPH vary based on the severity of symptoms and individual patient needs. They range from lifestyle changes and medication to minimally invasive therapies and surgery. Medications like alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors are often prescribed to alleviate symptoms. For more advanced cases, surgical options like transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or laser therapy may be recommended.
It’s essential to emphasize the importance of professional healthcare advice in managing BPH. Each individual’s experience with BPH is unique, and thus, a personalized treatment plan is vital. Regular consultations with healthcare professionals ensure that the treatment remains effective and adapts to any changes in the condition.
In conclusion, while BPH is a prevalent condition, effective management is achievable through proper diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan. Consulting with healthcare professionals is the best way to navigate this condition, ensuring both effective treatment and improved quality of life. Remember, proactive and informed healthcare decisions are key to managing BPH effectively.