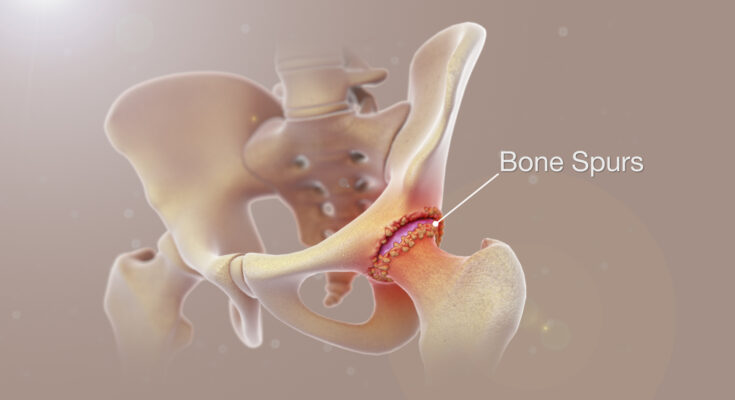
Bone Spurs Treatment: Bone spurs, also known as osteophytes, are bony projections that develop along the edges of bones, often where bones meet each other in the joints.
While they can occur anywhere in the body, they are most commonly found in the spine, shoulders, hands, hips, knees, and feet.
This comprehensive guide aims to delve deep into the diagnosis and treatment of bone spurs, providing readers with essential insights and actionable advice.
What are Bone Spurs?
Bone spurs, also known as osteophytes, are bony projections that develop along the edges of bones. They often form where bones meet each other – in the joints. However, they can also appear on bones anywhere in the body. Bone spurs are a common condition and are often a result of the aging process. They may not always cause symptoms, but when they do, the effects can range from mild discomfort to significant pain and mobility issues.
Causes and Risk Factors of Bone Spurs
Joint Damage from Osteoarthritis: The most common cause of bone spurs is joint damage from osteoarthritis. This condition leads to the breakdown of cartilage, which cushions the ends of the bones. As the cartilage wears away, the body tries to repair the loss by growing extra bone.
Aging: As people age, the likelihood of developing bone spurs increases. The body’s normal aging process can lead to changes in the bones and joints, contributing to bone spur formation.
Disc Degeneration in the Spine: Degenerative disc disease, a common part of aging, can lead to the formation of bone spurs in the spine.
Sports and Activities: Activities that put stress on certain joints or bones, especially repetitive or high-impact activities, can contribute to the formation of bone spurs.
Excess Weight and Obesity: Carrying excess weight can put additional stress on the joints, particularly in the knees, hips, and spine, leading to the development of bone spurs.
Genetics: There may be a genetic component to bone spurs, with some individuals being more predisposed to developing them due to family history.
Common Locations for Bone Spurs
Spine: Bone spurs commonly develop along the spine, where they can press on nerves, causing pain and potentially affecting nerve function.
Shoulders: The shoulder joint is prone to bone spurs, which can limit the range of motion and cause a condition known as “impingement syndrome.”
Knees: Bone spurs in the knee can make bending the knee painful and difficult.
Hips: Spurs in the hip joint can lead to pain and reduced movement in the hips.
Feet: Common areas in the feet include the heel, where they can lead to conditions like plantar fasciitis, and the toes, particularly the big toe.
Hands and Fingers: Bone spurs can develop in the small joints of the hands and fingers, often associated with osteoarthritis.
Understanding the causes and common locations of bone spurs is essential for both prevention and treatment. If you suspect you have bone spurs, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.
Diagnosing Bone Spurs
Diagnosing bone spurs is crucial for effective treatment and management. This section delves into the common diagnostic procedures and the pivotal role of medical imaging in detecting bone spurs.
Common Diagnostic Procedures for Bone Spurs
Medical History and Physical Examination: The initial step in diagnosing bone spurs involves a thorough review of the patient’s medical history and a physical examination. Doctors look for specific symptoms like pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion that might indicate the presence of bone spurs.
X-rays: X-rays are the most common and effective way to confirm the presence of bone spurs. This imaging technique provides clear images of dense structures like bone, making it easier to identify any abnormal growths.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): In cases where more detail is needed, an MRI can be helpful. This imaging method is particularly useful for viewing soft tissues around the bone spur, including muscles and ligaments.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: CT scans combine X-ray images from different angles to create a comprehensive picture of the body’s internal structures. This can be particularly helpful in diagnosing bone spurs in complex areas of the body.
Role of Medical Imaging in Bone Spurs Diagnosis
Medical imaging plays a fundamental role in the diagnosis of bone spurs. It helps in:
Detecting the Presence of Bone Spurs: Imaging tests like X-rays, MRI, and CT scans can confirm the existence of bone spurs and their exact location.
Assessing the Severity: These imaging techniques not only detect bone spurs but also help in assessing their size and impact on surrounding tissues, crucial for treatment planning.
Guiding Treatment Decisions: The detailed information provided by medical imaging allows healthcare providers to decide the most appropriate treatment, be it medication, physical therapy, or surgery.
Monitoring Progress: Post-treatment, imaging is used to monitor the healing process and ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
However, diagnosing bone spurs is a multi-step process that relies heavily on medical imaging. These diagnostic procedures are essential for developing an effective treatment plan and ensuring the best possible outcomes for patients with bone spurs. Remember, early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from this condition.
Bone Spurs Treatment Options
In this article, we explore the various treatment options available for bone spurs, focusing on both non-surgical and surgical methods.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or acetaminophen, are often the first line of treatment. They can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with bone spurs.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapists can design personalized exercise programs to improve flexibility, strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected joint, and reduce the symptoms of bone spurs.
Lifestyle Changes
Modifications in daily activities can significantly alleviate symptoms. These changes may include weight loss to reduce pressure on the joints, wearing appropriate footwear to provide better cushioning and support, and incorporating low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling.
Surgical Treatments
When is Surgery Necessary?
Surgery is considered when non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief, or when the bone spur interferes with joint movement and daily activities significantly.
Types of Surgical Procedures
- Osteotomy: This procedure involves removing a portion of the bone to change its alignment or relieve pressure on the affected area.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive surgery used for spurs in the joints, where small instruments and a camera are inserted through tiny incisions to remove the spurs.
- Laminectomy: Often used for spinal bone spurs, this surgery involves removing a part of the vertebra to create more space and relieve pressure on the nerves.
Bone spurs can be effectively managed with a combination of non-surgical and surgical treatments. Consulting with healthcare professionals is essential to choose the most appropriate treatment plan based on the severity of your symptoms and overall health condition. Early intervention can help maintain joint function and improve quality of life.
Home Remedies and Prevention of Bone Spurs
Managing Symptoms with Home Care Strategies
There are several home remedies that can help manage these symptoms effectively.
Cold and Heat Therapy: Alternating between cold and heat can be beneficial. Cold packs can reduce inflammation and numb the area, providing relief from pain. Heat therapy, on the other hand, can relax muscles and improve blood circulation, which helps in reducing discomfort.
Exercise and Stretching: Regular exercise and stretching can improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness. It’s important to focus on low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling to avoid putting extra stress on the joints.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help in reducing pain and inflammation. However, they should be used cautiously and as per the guidelines provided by healthcare professionals.
Massage Therapy: Gentle massage can increase blood flow and relieve tension around the affected area. It’s beneficial to consult with a professional massage therapist who is experienced in dealing with bone spur-related discomfort.
Proper Footwear (for heel spurs): If the bone spur is in the heel, wearing shoes with good support and cushioning can provide significant relief.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the stress on joints, thereby alleviating symptoms associated with bone spurs.
Preventative Measures to Avoid Bone Spur Development
Preventing the development of bone spurs involves taking care of your joints and bones. Here are some effective strategies:
Maintain a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D supports bone health. Including green leafy vegetables, dairy products, and fish can be beneficial.
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity helps in maintaining joint and bone health. Weight-bearing exercises, in particular, strengthen the bones and joints.
Posture and Ergonomics: Maintaining proper posture and ergonomics, especially while sitting or working for long hours, helps in reducing undue stress on the joints.
Avoid High-Impact Activities: High-impact exercises can put excessive stress on the joints, leading to the development of bone spurs. Opting for low-impact activities is a wiser choice.
Regular Health Check-Ups: Regular visits to a healthcare provider for check-ups can help in early detection and management of conditions that might lead to bone spurs.
Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining the health of the joints and can aid in preventing bone spur formation.
Implementing these home remedies and preventive measures can significantly help in managing and avoiding the development of bone spurs. Remember, it’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment or exercise regimen.
Complications Associated with Bone Spurs
While they may not always cause symptoms, untreated bone spurs can lead to various complications, emphasizing the importance of timely treatment.
Possible Complications if Left Untreated
Joint Damage: Bone spurs can cause wear and tear in the joints, potentially leading to joint damage and osteoarthritis.
Pain and Discomfort: As they grow, bone spurs can irritate surrounding tissues, leading to chronic pain, discomfort, and inflammation.
Nerve Compression: In certain areas, like the spine, bone spurs can compress nearby nerves, resulting in numbness, tingling, or weakness.
Reduced Mobility: Over time, bone spurs can limit the range of motion in the affected joints, hindering daily activities and reducing quality of life.
Tendon and Ligament Damage: Spurs can rub against tendons and ligaments, leading to tears or rupture, which can be both painful and debilitating.
Importance of Timely Treatment
Prevention of Progression: Early intervention can prevent the progression of bone spurs, reducing the risk of severe complications.
Maintaining Joint Health: Timely treatment helps maintain joint function and overall joint health.
Alleviating Symptoms: Treatment can alleviate pain and discomfort, improving the individual’s quality of life.
Avoiding Surgical Interventions: In some cases, early treatment can prevent the need for more invasive procedures like surgery.
Ensuring Overall Well-being: Addressing bone spurs promptly can help maintain overall health and well-being, preventing the disruption of daily activities.
However, while bone spurs may seem innocuous at first, their potential complications should not be underestimated. Seeking medical advice and treatment at the earliest signs can be crucial in preventing long-term damage and maintaining a healthy, active lifestyle.
FAQs: Understanding and Treating Bone Spurs
What are Bone Spurs?
Bone spurs, also known as osteophytes, are bony projections that develop along the edges of bones. They commonly occur in joints, where two bones meet, and are often seen in people with osteoarthritis, as the body attempts to repair bone loss.
How Do I Know if I Have Bone Spurs?
Symptoms of bone spurs can include joint pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. However, many people experience no symptoms at all. A definitive diagnosis usually requires an X-ray, MRI, or CT scan.
What Causes Bone Spurs?
Bone spurs are typically a result of joint damage from osteoarthritis. Other causes can include overuse of a joint, injuries, or conditions that increase bone formation, such as diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH).
Are Bone Spurs Dangerous?
Bone spurs themselves aren’t dangerous, but they can lead to pain and discomfort, depending on their location. For instance, a bone spur on the spine can press on nerves, causing pain and potentially affecting nerve function.
How are Bone Spurs Treated?
Treatment for bone spurs depends on the severity of symptoms. Options include:
- Physical Therapy: To improve joint function and alleviate pain.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can reduce inflammation and pain.
- Steroid Injections: To decrease inflammation in the affected joint.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery might be necessary to remove the bone spur.
Can Bone Spurs Be Prevented?
While you can’t completely prevent bone spurs, you can reduce your risk by:
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce joint stress.
- Staying active to keep joints flexible.
- Protecting joints from injury and overuse.
When Should I See a Doctor?
Consult a doctor if you experience persistent joint pain or stiffness, especially if it limits your range of motion or affects your daily activities.
Conclusion
We strongly encourage anyone experiencing symptoms or discomfort that might be related to bone spurs to consult with healthcare professionals. Each individual’s situation is unique, and a personalized treatment plan is essential for effective management and relief.
Professional medical advice is invaluable in navigating the treatment options and making informed decisions about your health. Remember, early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the quality of life for those suffering from bone spurs.