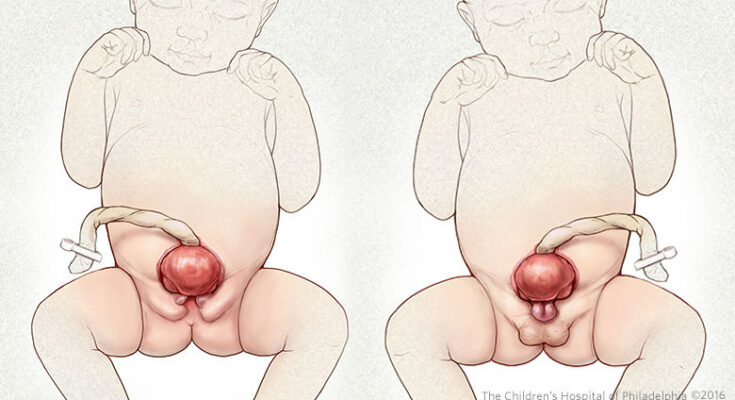
Bladder Exstrophy Symptoms: Bladder exstrophy is a rare and complex congenital condition in which the bladder and surrounding structures are improperly formed.
This medical condition is not just a physical health issue but also impacts the emotional and psychological well-being of those affected.
Understanding its symptoms and causes is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
What is Bladder Exstrophy?
Bladder exstrophy is a rare congenital condition characterized by the abnormal development of the urinary bladder. It’s a part of a spectrum of anomalies that affect the lower abdominal wall, bladder, and genitals. In this condition, the bladder is turned inside out and is exposed outside the body. This occurs early in fetal development when the muscles and skin that should cover the lower abdomen do not form properly.
Epidemiology and Demographics: Insights into Bladder Exstrophy Prevalence
The occurrence of bladder exstrophy is relatively rare, with estimates suggesting that it affects about 1 in every 30,000 to 50,000 live births. The condition appears to have a slightly higher prevalence in males compared to females. Understanding the demographics and epidemiology of bladder exstrophy is crucial for medical professionals to provide targeted care and for researchers to develop better treatment strategies.
Tracing the History: Evolution of Bladder Exstrophy Understanding and Treatment
The history of understanding and treating bladder exstrophy has evolved significantly over the years. Initially, this condition was poorly understood, and treatment options were limited. However, advancements in medical science have led to better diagnostic techniques and more effective surgical interventions. Today, individuals with bladder exstrophy have a much better prognosis, thanks to early detection and the evolution of surgical techniques that focus on reconstructing the bladder and the abdominal wall.
However, bladder exstrophy, though rare, presents significant challenges in terms of diagnosis and treatment. Continued research and advancements in medical science are essential to improve the quality of life for individuals affected by this condition.
Symptoms of Bladder Exstrophy
It’s crucial to recognize the symptoms early for effective management. Here’s a detailed guide on the symptoms, their variations, and the impact on quality of life.
Detailed List of Common Symptoms
Bladder exstrophy presents a range of symptoms that are typically noticeable from birth. The most common signs include:
- Visible bladder: The bladder is turned inside out and exposed outside the abdomen.
- Epispadias: In males, the urethra is not fully formed, leading to an abnormal opening. In females, the urethra and vagina may be affected.
- Inguinal hernia: A bulge in the groin area due to a weakened abdominal wall.
- Abnormal genitalia: Often, the external genitalia are not fully formed or are displaced.
- Urinary incontinence: Difficulty in controlling urine flow is a common challenge.
Physical Symptoms
The physical symptoms of bladder exstrophy can be quite evident and include:
- Abdominal wall defects: A gap in the abdominal muscles where the bladder is exposed.
- Pelvic bone abnormalities: The pelvic bones might be separated more than usual.
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs): Frequent UTIs are common due to the bladder’s exposure.
Potential Complications
Living with bladder exstrophy can lead to several complications, such as:
- Kidney problems: Due to frequent UTIs and abnormal urinary function.
- Psychological impact: Emotional and psychological challenges due to the physical appearance and incontinence.
- Fertility issues: Reproductive challenges can occur in both males and females.
Variation in Severity and Presentation
The severity and presentation of symptoms can vary significantly among individuals. Some may experience mild incontinence and minimal physical abnormalities, while others might face severe urinary issues and noticeable physical deformities. The treatment and management strategies depend on the severity and individual circumstances.
Impact on Quality of Life
Bladder exstrophy can significantly impact one’s quality of life. The physical symptoms and potential for social embarrassment due to incontinence can lead to:
- Social isolation: Difficulty in forming social connections due to embarrassment or fear of stigma.
- Emotional distress: Increased risk of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
- Challenges in daily activities: Limitations in physical activities and frequent medical interventions.
Recognizing and understanding these symptoms is vital for early intervention and improved quality of life. If you suspect bladder exstrophy, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Causes and Risk Factors of Bladder Exstrophy
Understanding its causes and risk factors is pivotal, not only for medical advancements but also for providing better care to those affected.
Genetic Contributions: The Inherited Puzzle
The role of genetics in bladder exstrophy is a field of continuous exploration. Studies suggest a possible genetic component, though no specific gene has been conclusively identified. This section of the article delves into:
- Familial Patterns: While not common, instances of bladder exstrophy appearing in families suggest a potential hereditary link. We explore these patterns and what they mean for future genetic research.
- Chromosomal Insights: Discussions on any identified chromosomal anomalies associated with the condition, providing a window into the genetic complexities of bladder exstrophy.
Environmental Factors: External Influences
Environmental factors, though less understood, are thought to play a role in the development of bladder exstrophy. This section examines:
- Prenatal Exposures: Analysis of maternal factors such as medication, nutrition, and lifestyle during pregnancy that could influence the condition’s onset.
- Epidemiological Studies: A look at the prevalence and distribution of bladder exstrophy across different geographical and demographic groups, offering clues about environmental influences.
Integrating Research and Theories
The development of bladder exstrophy is not attributed to a single cause but rather a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. This section offers:
- Current Research Highlights: Summarizing the latest studies and findings in the field, giving readers an up-to-date understanding of where research stands.
- Emerging Theories: Discussing new hypotheses and theories in the scientific community about how bladder exstrophy develops, opening doors to future research avenues.
Understanding the causes and risk factors of bladder exstrophy is crucial for developing effective treatments and preventive strategies. This comprehensive analysis not only enlightens readers about the current state of knowledge but also underscores the importance of ongoing research in unraveling the mysteries of this complex condition.
Diagnosis of Bladder Exstrophy
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and improved outcomes.
Methods Used in Diagnosing Bladder Exstrophy
- Prenatal Ultrasound: This is often the first method used to detect bladder exstrophy. It can identify abnormalities in the bladder’s development during pregnancy.
- Physical Examination: After birth, a thorough physical examination can reveal visible signs of bladder exstrophy, such as the bladder being outside the body.
- Blood Tests: These tests help in assessing kidney function and overall health, which can be affected by bladder exstrophy.
- Urinalysis: This test checks for infection and other abnormalities in urine, which are common in patients with bladder exstrophy.
Role of Medical Imaging and Diagnostic Tools
Medical imaging plays a pivotal role in diagnosing bladder exstrophy. Advanced imaging techniques such as MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) scans provide detailed images of the urinary tract, helping in confirming the diagnosis and planning treatment.
Challenges in Diagnosing Bladder Exstrophy
- Subtle Symptoms in Mild Cases: In some cases, the symptoms of bladder exstrophy can be subtle, making early diagnosis challenging.
- Differential Diagnosis: Bladder exstrophy can be confused with other pelvic abnormalities, necessitating careful examination and imaging.
- Limited Awareness: Due to its rarity, there might be limited awareness of the condition among healthcare providers, leading to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis.
The diagnosis of bladder exstrophy involves a combination of prenatal screening, physical examination, blood and urine tests, and advanced imaging techniques. Despite the challenges, early diagnosis is achievable and critical for effective management of the condition. Regular consultations with healthcare providers and awareness of the condition are key to ensuring prompt and accurate diagnosis.
Treatment and Management of Bladder Exstrophy Symptoms
Effective management and treatment are crucial for improving the quality of life of those affected. This section provides an insight into the current treatment options, both surgical and non-surgical, and discusses the ongoing advancements in this field.
Overview of Current Treatment Options
Surgical Interventions: Surgical procedures remain the cornerstone of bladder exstrophy treatment. The primary goal is to reconstruct the bladder and urinary tract to ensure proper functioning. These surgeries are often performed in stages, beginning in infancy. The initial surgery typically involves closing the bladder and reconstructing the abdominal wall. Subsequent procedures may include bladder neck reconstruction and, in some cases, urinary diversion techniques.
Non-Surgical Treatments: Alongside surgery, non-surgical approaches play a vital role in managing bladder exstrophy. These include:
- Bladder Management: To ensure bladder function and capacity, various methods like clean intermittent catheterization (CIC) and medication to improve bladder storage are used.
- Infection Prevention: Regular monitoring and proactive treatment of urinary tract infections are essential.
- Nutritional Support: Proper nutrition aids in recovery and overall health, particularly important for children undergoing multiple surgeries.
- Psychological Support: Living with a chronic condition can be challenging, hence psychological support for patients and families is integral to treatment.
Managing Symptoms and Improving Quality of Life
Effective symptom management is key to enhancing the quality of life for patients with bladder exstrophy. This includes:
- Regular Medical Follow-Up: Ongoing assessment by a healthcare team ensures timely intervention and management of complications.
- Physical Therapy: To strengthen pelvic muscles and improve continence.
- Social and Emotional Support: Support groups and counseling services help patients and families cope with the condition’s emotional and social aspects.
Future Prospects in Treatment and Symptom Management
The future of bladder exstrophy treatment is promising, with ongoing research focusing on:
- Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques: Advancements in surgical methods aim to reduce recovery time and improve outcomes.
- Regenerative Medicine: Research in tissue engineering and stem cell therapy holds the potential to revolutionize treatment options.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatment plans based on individual genetic makeup could enhance treatment efficacy.
However, while bladder exstrophy remains a challenging condition, advancements in medical science offer hope for better treatment and improved quality of life for patients. A multidisciplinary approach, encompassing both surgical and non-surgical methods, is vital for effective management.
Living with Bladder Exstrophy: Navigating Challenges and Finding Support
Personal Stories and Case Studies
Living with bladder exstrophy can be a unique and challenging journey. Through personal stories and case studies, individuals affected by this condition share their experiences, offering a window into their daily lives. These narratives provide insight into the emotional and physical complexities of bladder exstrophy, serving as a source of inspiration and understanding for others facing similar challenges.
Coping Strategies for Patients and Families
Adapting to life with bladder exstrophy requires effective coping strategies for both patients and their families. This section delves into various approaches to manage the condition, from practical tips on healthcare and daily routines to emotional support mechanisms. It highlights how patients and their loved ones can work together to overcome obstacles, maintain a positive outlook, and lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by bladder exstrophy.
Support Resources and Communities
Navigating the journey of bladder exstrophy is not something one has to do alone. This segment focuses on the importance of support resources and communities. It guides readers to networks, support groups, and organizations dedicated to helping individuals with bladder exstrophy. These resources offer valuable information, emotional support, and a sense of community, empowering patients and families to connect with others who truly understand their experiences.
Prevention and Research
Exploring Current Research on Prevention and Cure
The journey towards preventing and curing bladder exstrophy is a constantly evolving field. Recent studies have delved deeply into genetic and environmental factors, aiming to unravel the complexities of this condition. This research is pivotal in developing preventive strategies and effective treatments. Understanding the genetic predisposition and environmental triggers can significantly advance our approach to prevention. Additionally, ongoing clinical trials and research studies are actively seeking safer and more effective cures, promising a future where bladder exstrophy can be managed more efficiently or even cured.
Advances in Medical Science Related to Bladder Exstrophy
Medical science has made significant strides in understanding and treating bladder exstrophy. Innovations in surgical techniques have improved the quality of life for patients, reducing complications and enhancing outcomes. Research in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering presents new horizons, potentially leading to breakthrough treatments. These advances not only improve the immediate management of bladder exstrophy but also offer insights into long-term care and rehabilitation, ensuring a better quality of life for patients.
Contributing to Ongoing Research: How Readers Can Help
Readers can play a crucial role in advancing research on bladder exstrophy. Participation in clinical trials, when eligible, contributes valuable data that can shape future treatments. Donating to research foundations or institutions dedicated to studying bladder exstrophy is another impactful way to support. Volunteering for patient advocacy groups or participating in awareness campaigns helps in spreading knowledge and understanding of the condition. Furthermore, sharing personal experiences or joining support groups can provide researchers with essential insights into the daily challenges faced by those living with bladder exstrophy, thereby guiding more patient-centric research.
Conclusion:
Awareness is the cornerstone of coping with any health challenge. Bladder exstrophy, while rare, requires the spotlight of awareness for better community understanding and support. Sharing information, experiences, and support networks can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected.
In closing, let’s emphasize the importance of both awareness and support. These elements are vital in managing bladder exstrophy effectively. As we continue to shed light on this condition, we foster a more informed and compassionate society, ready to support those in need.