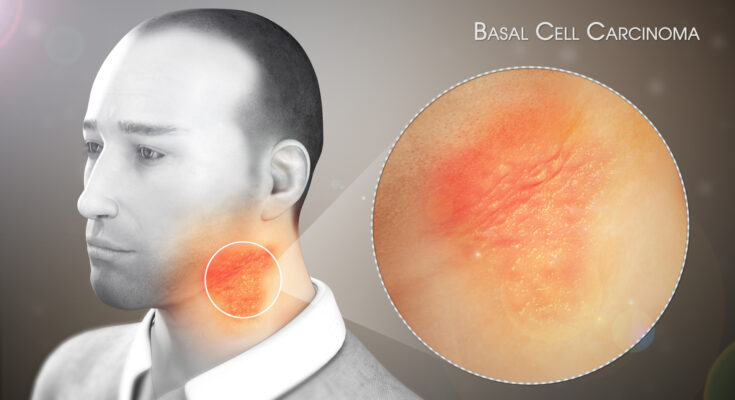
Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment: Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) is the most common form of skin cancer, affecting millions of individuals worldwide.
This non-melanoma skin cancer arises from basal cells, which are located in the lower epidermis. Despite its prevalence, BCC is often treatable, especially when diagnosed early.
What is Basal Cell Carcinoma?
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) is a type of skin cancer that arises from the basal cells, which are located in the lower part of the epidermis. It’s the most common form of skin cancer globally. BCC tumors typically appear as small, shiny bumps on the skin, mainly in areas exposed to the sun, like the head, neck, and arms. They may also resemble a flat, flesh-colored or brown scar and can be mistaken for noncancerous skin conditions. Unlike other skin cancers, BCC rarely spreads to other parts of the body, but it can grow deep into the skin and cause significant local damage if untreated.
Statistics and Prevalence
The prevalence of Basal Cell Carcinoma is remarkable, making it the most frequently occurring form of all cancers. Millions of cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. In countries like the United States, BCC accounts for approximately 80% of nonmelanoma skin cancers. Its incidence has been steadily increasing, likely due to factors such as increased sun exposure and aging populations.
Risk Factors and Causes
Several risk factors contribute to the development of Basal Cell Carcinoma. The primary cause is prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun and tanning beds, leading to DNA damage in skin cells. Other risk factors include:
- Fair Skin: Individuals with lighter skin are more susceptible to UV damage, increasing BCC risk.
- Age and Gender: BCC is more common in older individuals and tends to affect men more than women.
- Genetic Factors: A history of BCC in the family increases one’s risk.
- Radiation Exposure: Past radiation treatments can elevate the risk of developing BCC.
- Immune-Suppressing Medications: These can increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Exposure to Certain Chemicals: Arsenic exposure, for example, can increase BCC risk.
Understanding these factors can help in the prevention and early detection of Basal Cell Carcinoma, which is crucial for effective treatment.
Symptoms of Basal Cell Carcinoma
It’s crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms of BCC to ensure early detection and treatment. This article outlines the common symptoms, different types of BCC, and when to seek medical advice.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Appearance of a Shiny Bump or Nodule: Often pearly or translucent, these bumps are most common on sun-exposed areas like the face, ears, and neck.
- Reddish Patch of Skin: This might be itchy, crusty, or bleed when scraped. These patches can commonly be found on the chest, back, arms, or legs.
- A Sore that Doesn’t Heal: BCC can appear as a sore that bleeds, heals, and then reopens.
- Scar-Like Area: A white, yellow, or waxy area with poorly defined borders can be a sign of an invasive BCC.
Different Types of BCC and Their Appearances
- Nodular BCC: The most common type, appearing as a pearly bump.
- Superficial BCC: Often looks like a red, scaly patch and might be mistaken for eczema or psoriasis.
- Morpheaform (Sclerosing) BCC: This type looks like a white, waxy scar and is more difficult to detect.
- Pigmented BCC: Similar to nodular BCC but with dark areas, often confused with moles or melanoma.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional if you notice any changes in your skin that persist for more than a few weeks. Early detection of BCC is key to effective treatment. Look out for new growths, changes in existing moles or freckles, and any sore that doesn’t heal. Regular skin self-exams and annual check-ups with a dermatologist are recommended, especially if you have a history of sunburns or extensive sun exposure.
However, understanding and recognizing the symptoms of Basal Cell Carcinoma can lead to early diagnosis and effective treatment. If you notice any unusual skin changes, consult a dermatologist promptly. Early action is essential in managing BCC and ensuring the best possible outcome.
Diagnosing Basal Cell Carcinoma
This guide delves into the crucial steps for diagnosing BCC, underscoring the importance of skin examinations and biopsies in the process.
Steps in Diagnosing BCC
- Initial Observation: The diagnosis journey often starts with noticing suspicious skin changes. These can include new growths, changes in existing moles, or unusual skin patches. It’s essential to monitor any changes in skin appearance, especially those that persist over time.
- Professional Skin Examination: Consulting a dermatologist is a pivotal step. These skin experts conduct thorough examinations, assessing any concerning areas. They may use a dermatoscope, a specialized tool that provides a magnified view of the skin, aiding in a more accurate assessment.
- Detailed Medical History: A comprehensive medical history helps the dermatologist understand your risk factors. This includes exposure to sun, previous skin cancers, and family history of skin cancer.
Role of Skin Examinations and Biopsies
- Skin Examination Techniques: Dermatologists often employ various techniques during skin examinations. Besides visual inspections, they might use digital imaging to track changes over time.
- Biopsy Procedure: If a lesion appears suspicious, the next step is a biopsy. This involves taking a small sample of the skin tissue for laboratory analysis. The biopsy is crucial for confirming whether the lesion is cancerous and, if so, determining its type and extent.
Importance of Early Detection
- Better Outcomes: Early detection of BCC significantly enhances treatment success rates. When caught early, BCC is highly treatable, often with minimally invasive procedures.
- Prevention of Complications: Undiagnosed and untreated BCC can lead to more serious health issues, including extensive skin damage and, in rare cases, spread to other body parts. Early diagnosis prevents these complications.
- Awareness and Regular Check-ups: Regular skin examinations, both self-conducted and by a professional, play a critical role in early detection. Being aware of the signs and seeking prompt medical advice if changes occur can make a significant difference.
However, understanding the steps involved in diagnosing Basal Cell Carcinoma, recognizing the role of skin examinations and biopsies, and appreciating the importance of early detection are vital in effectively managing this common skin cancer. Regular check-ups and staying vigilant about changes in your skin are key to early diagnosis and successful treatment.
Treatment Options for Basal Cell Carcinoma
Understanding the various treatment options available for BCC is crucial for effective management and care. Here, we explore both surgical and non-surgical methods to treat Basal Cell Carcinoma, aiming to provide a comprehensive overview for patients and caregivers.
Surgical Treatments
- Mohs Micrographic Surgery: This precise method involves removing the cancerous tissue layer by layer. Each layer is examined under a microscope until no cancer cells remain. This technique minimizes the removal of healthy tissue and is highly effective, especially for BCCs in cosmetically sensitive areas like the face.
- Excisional Surgery: In this procedure, the doctor cuts out the cancerous tissue along with a margin of healthy skin around it. It’s a common treatment for BCC and typically done under local anesthesia.
- Curettage and Electrodesiccation: This approach involves scraping away the cancer cells with a curette (a sharp, spoon-shaped instrument) and then using an electric current to destroy any remaining cancer cells. This method is often used for small or superficial BCCs.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Topical Medications: Creams or ointments containing anti-cancer agents can be applied directly to the skin. These are generally used for superficial BCCs and require several weeks of treatment.
- Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells. It’s an option for patients who can’t undergo surgery or for treating tumors in difficult-to-treat areas.
- Photodynamic Therapy (PDT): PDT involves applying a photosensitizing agent to the skin, which is then activated by a special light. This process destroys cancer cells. PDT is typically used for superficial BCCs and offers the advantage of minimal scarring.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatment can vaporize superficial BCCs, especially in delicate areas. It’s less invasive than traditional surgery and may be an option for some patients.
- Immunotherapy: This involves applying a cream that stimulates the body’s immune system to attack cancer cells. It’s a newer method and is used for superficial BCCs.
- Targeted Therapy: These are drugs that target specific genes or proteins in cancer cells, blocking their growth and spread. They are usually reserved for advanced BCCs that can’t be treated with surgery or radiation.
Choosing the right treatment for Basal Cell Carcinoma depends on various factors, including the size, location, and depth of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences. It’s important for patients to discuss these options with their healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for their specific condition. Early detection and treatment are key to successfully managing BCC and preventing its spread.
Factors Influancing Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment Choice
Understanding these factors can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about the most effective treatment options.
Location, Size, and Depth of the Carcinoma
- Location: The location of BCC on the body significantly influences the treatment choice. Lesions on cosmetically sensitive areas like the face may require more precise surgical techniques to minimize scarring.
- Size: Larger carcinomas often necessitate more extensive treatment compared to smaller lesions. Larger size may limit some treatment options and require more aggressive approaches.
- Depth: The depth of the carcinoma is crucial in deciding the treatment method. Deeper lesions might need more invasive treatments to ensure complete removal and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Patient’s Health and Medical History Considerations
- Overall Health: A patient’s general health and age can affect treatment choices. For example, older patients or those with comorbidities might not be suitable candidates for certain surgical procedures.
- Medical History: Previous skin cancer history, particularly prior BCC, influences the approach to treatment. Patients with a history of multiple BCCs may require a different strategy compared to those with their first lesion.
Cosmetic Outcomes and Recurrence Rates
- Cosmetic Concerns: Since BCCs often occur on the face, cosmetic outcomes are a significant consideration. Techniques like Mohs surgery, which offers precise removal with minimal tissue loss, are preferred for lesions in visible areas.
- Recurrence Rates: The potential for recurrence plays a vital role in treatment decisions. Treatments that offer lower recurrence rates might be preferred, especially in areas where recurrence would be more problematic.
However, the choice of treatment for Basal Cell Carcinoma is multifaceted, depending on lesion characteristics, patient health, and the desire for favorable cosmetic outcomes. These factors, collectively analyzed by medical professionals, guide the selection of the most appropriate and effective treatment plan for each individual case.
Prevention and Management of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Strategies for Preventing Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC), a common form of skin cancer, can largely be prevented through proactive measures. Here’s what you can do:
- Sun Protection: Regularly use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Wear protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses when outdoors.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Tanning beds significantly increase the risk of BCC. Opt for sunless tanning products instead.
- Routine Skin Checks: Regularly inspect your skin for any new growths or changes in existing moles, freckles, or spots.
Regular Skin Checks and Self-Examination Tips
Early detection plays a crucial role in the successful treatment of BCC. Here are tips for self-examination:
- Examine Entire Body: Once a month, check your whole body for any unusual skin changes.
- Use a Mirror: Use a hand-held mirror for hard-to-see areas, like your back.
- Know What to Look For: Be aware of new growths, sores that won’t heal, or changes in existing skin lesions.
Managing the Condition and Follow-Up Care
If you’ve been diagnosed with BCC, management and follow-up care are vital. This includes:
- Follow Doctor’s Recommendations: Stick to the treatment plan prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Regular Dermatologist Visits: Post-treatment, keep regular appointments with your dermatologist for skin checks.
- Self-Care: Maintain a healthy lifestyle, and follow protective measures to prevent recurrence.
Remember, while Basal Cell Carcinoma is highly treatable, prevention and early detection are your best defenses. Regular skin checks and protecting your skin from the sun are key strategies in managing and preventing BCC.
Innovations in Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment
The realm of Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) treatment has witnessed significant advancements, thanks to continuous research and innovation. This section delves into the latest developments and emerging therapies in BCC treatment, highlighting their potential and impact on patient care.
Latest Advancements and Research in BCC Treatment
Recent years have seen remarkable progress in the treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma, a common form of skin cancer. These advancements range from improved surgical techniques to innovative non-invasive options, catering to diverse patient needs and tumor characteristics.
One notable development is the refinement of Mohs surgery. This precise surgical technique, known for its high success rate, now incorporates enhanced methods for tissue preservation and aesthetic outcomes. Additionally, advancements in radiation therapy, such as more targeted and less invasive options, offer alternative treatments for patients where surgery is not viable.
Moreover, the evolution of topical treatments and creams has opened new avenues for early-stage BCC management, minimizing the need for invasive procedures. These topical agents, often incorporating novel mechanisms of action, are designed to target cancer cells selectively, reducing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Emerging Therapies and Their Potential
The landscape of BCC treatment is further enriched by the emergence of new therapies. These include innovative drugs and cutting-edge approaches that promise to revolutionize the management of this cancer type.
A significant breakthrough in this area is the development of targeted therapy drugs. These drugs specifically target molecular pathways involved in the growth and spread of BCC cells. By focusing on these pathways, such therapies offer a more personalized treatment approach, potentially yielding better outcomes with fewer side effects.
Another exciting area is immunotherapy, which leverages the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells. While still in the experimental stages for BCC, early trials have shown promising results, suggesting a potential for long-term control and even cure in some cases.
Furthermore, advancements in genetic research have led to a better understanding of the mutations driving BCC. This knowledge paves the way for the development of gene-based therapies, offering a tailored approach to treatment based on an individual’s genetic makeup.
However, the innovations in Basal Cell Carcinoma treatment reflect a significant stride towards more effective, less invasive, and personalized care. These advancements not only offer new hope for patients but also underscore the importance of ongoing research and development in the field of oncology.
Living with Basal Cell Carcinoma
Understanding how to live with BCC is crucial for maintaining not only physical health but also mental wellbeing.
Embracing Lifestyle Modifications
- Sun Protection: Since BCC is often linked to sun exposure, implementing rigorous sun protection is vital. This includes using broad-spectrum sunscreens, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding peak sun hours.
- Regular Skin Checks: Incorporate routine skin examinations into your lifestyle. Regular check-ups with a dermatologist can catch any new lesions early, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
- Healthy Diet and Exercise: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants and regular physical activity can boost your immune system, aiding in your fight against BCC.
- Avoiding Tanning Beds: Tanning beds are a significant risk factor for BCC. Abstaining from artificial tanning can substantially reduce your risk of developing further skin cancers.
Navigating Patient Support
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have BCC can provide emotional support and practical advice. Consider joining online forums or local support groups.
- Family and Friends: Open communication with loved ones about your BCC experience is important. They can offer support and understanding during your treatment journey.
- Educational Resources: Stay informed about BCC. Understanding your condition empowers you to make informed decisions about your care.
Coping Strategies and Mental Health Considerations
- Mental Health Support: Living with BCC can be emotionally taxing. Seeking support from mental health professionals can help in coping with anxiety, stress, or depression that may arise.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practices like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can be beneficial in managing stress and improving overall mental health.
- Setting Realistic Expectations: Understanding the nature of BCC and setting realistic expectations regarding treatment and recovery can help in mentally preparing for the journey ahead.
- Positive Outlook: Maintaining a positive attitude can influence your overall experience. Celebrate small victories and stay hopeful about the future.
However, living with Basal Cell Carcinoma involves a holistic approach that encompasses lifestyle changes, patient support, and mental health strategies. By adopting these practices, individuals can navigate their BCC journey with greater ease and confidence. Remember, you are not alone in this fight, and there are resources and support systems to help you along the way.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma should never be taken lightly. Awareness and proactive measures are vital. Remember, BCC is not just a skin condition; it’s a health concern that demands attention and care. By prioritizing regular skin check-ups and seeking prompt treatment, you can effectively manage and overcome this condition.
Let this be a reminder of the power of awareness and the importance of timely action in the fight against Basal Cell Carcinoma.