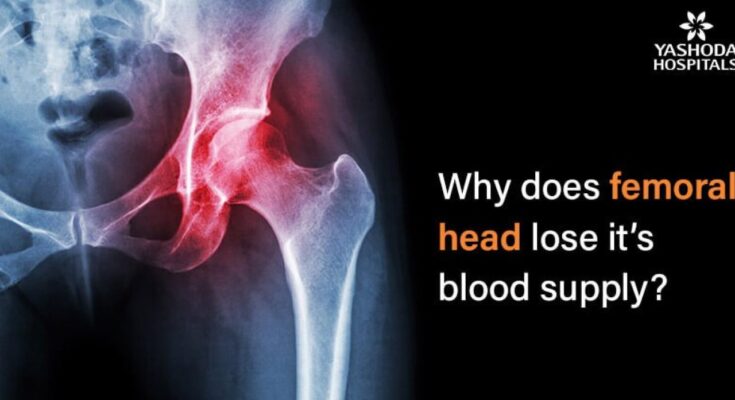
Avascular Necrosis Symptoms: Avascular necrosis, also known as osteonecrosis, is a condition that occurs when bone tissue dies due to a lack of blood supply. This can lead to significant pain and disability, affecting the quality of life of those afflicted.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of avascular necrosis is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
What is Avascular Necrosis?
Avascular Necrosis (AVN), also known as osteonecrosis, is a condition that occurs when there is a loss of blood to the bone. This lack of blood flow can lead to the death of bone tissue, causing the bone to collapse if not treated promptly. AVN most commonly affects the hip but can occur in other bones and joints.
Impact on Bones and Joints
AVN primarily affects the joints, often leading to pain and reduced mobility. In the early stages, you might not notice any symptoms, but as the condition progresses, the affected bone might start to weaken. This weakening can lead to tiny fractures, which can cause the bone to collapse. The most common site for AVN is the hip, but it can also affect other joints such as the shoulder, knee, or ankle. Early detection and treatment are crucial in managing AVN to prevent joint damage and preserve joint function.
Symptoms of Avascular Necrosis
Recognizing its symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. Here’s a detailed look at the common symptoms and their impact on daily life.
Common Symptoms of Avascular Necrosis
- Joint Pain: Initially, the pain may only occur when putting weight on the affected joint. Over time, it becomes more constant, even when resting.
- Limited Range of Motion: As AVN progresses, it becomes harder to move the affected joint. Activities like bending, walking, or lifting objects can become challenging.
- Joint Stiffness: The affected area often feels stiff, making it difficult to perform routine movements.
- Swelling and Tenderness: In some cases, swelling and tenderness around the joint are noticeable.
- Bone Collapse: In advanced stages, the bone may collapse, leading to severe pain and disability.
- Groin Pain: When AVN affects the hip, groin pain is a common symptom, especially when putting pressure on the hip joint.
Impact on Daily Life
The symptoms of Avascular Necrosis significantly affect daily activities and quality of life:
- Mobility Issues: Pain and stiffness in joints can lead to difficulty in walking, climbing stairs, or even standing for long periods, severely limiting mobility.
- Chronic Pain: Persistent pain can be distressing and debilitating, affecting mental health and overall well-being.
- Reduced Activity Levels: Due to pain and limited joint movement, individuals with AVN may find it hard to engage in physical activities they once enjoyed.
- Impact on Employment: The condition can affect the ability to perform certain jobs, especially those requiring physical exertion or long periods of standing.
- Social Isolation: Chronic pain and mobility issues may lead to social withdrawal, as participating in social activities becomes more challenging.
- Sleep Disturbances: Pain and discomfort can interfere with sleep, leading to fatigue and other health issues.
The Importance of Early Detection
Detecting AVN in its early stages is vital for several reasons:
- Preventing Further Damage: Early treatment can help prevent the affected bone from collapsing.
- Better Treatment Outcomes: When diagnosed early, treatment options like medication, physical therapy, or less invasive surgeries can be more effective.
- Maintaining Joint Health: Early intervention can help preserve the joint and its function, reducing the likelihood of needing joint replacement surgery in the future.
Understanding these symptoms and their impact is essential for seeking timely medical intervention and adapting lifestyle choices to manage the condition effectively. Early diagnosis and treatment can help mitigate the effects of Avascular Necrosis on daily life.
Causes of Avascular Necrosis
Understanding the various causes of AVN is crucial for both prevention and treatment. Here’s an in-depth look at the most common causes and how they lead to bone damage:
1. Trauma or Injury
- Impact on Blood Supply: Injuries such as fractures or dislocations can damage nearby blood vessels, curtailing blood flow to the bone.
- Bone Tissue Damage: Without adequate blood, the bone tissue starts to die, leading to the development of AVN.
2. Steroid Use
- Effects of Long-Term Use: Prolonged or high-dose use of corticosteroids is a significant risk factor. These medications can interfere with blood flow to the bone.
- Implications for Bone Health: Steroid-induced AVN particularly affects the hips and shoulders, leading to joint deterioration.
3. Alcoholism
- Blood Vessel Compromise: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to fatty deposits in the blood vessels, impeding blood flow.
- Risk of Bone Damage: Chronic alcohol use significantly increases the risk of AVN, particularly in the hip.
4. Medical Conditions
- Conditions like Sickle Cell Anemia: Diseases causing blood to thicken or clot can reduce blood flow, precipitating AVN.
- Impact on Bone Tissue: These conditions can lead to recurrent and chronic interruptions in blood supply, resulting in bone necrosis.
5. Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy
- Effect on Blood Vessels: These cancer treatments can damage blood vessels and reduce blood supply to bones.
- Potential for Bone Damage: Long-term cancer survivors, especially those treated around the pelvis and hip, are at increased risk for AVN.
6. Decompression Disease
- Caused by Rapid Pressure Changes: Commonly seen in deep-sea divers, this condition occurs when nitrogen bubbles form in the blood, blocking blood vessels.
- Resulting Bone Issues: This can lead to localized areas of bone necrosis, particularly in divers who do not decompress properly.
Avascular necrosis is a complex condition with multifaceted causes. Each cause leads to a reduction in blood flow to the bone, resulting in bone tissue death. Early detection and addressing the underlying causes are essential for effective management and prevention of further bone damage.
Risk Factors for Avascular Necrosis
Understanding these factors is crucial for early detection and effective management of the condition.
Factors Elevating the Risk
- Prolonged Steroid Use: Extended use of corticosteroids has been linked to increased risk of avascular necrosis. These medications, while effective for numerous conditions, can interfere with blood flow to the bones.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Heavy drinking over a prolonged period can cause fatty deposits to form in the blood vessels, impeding blood flow and increasing the risk of avascular necrosis.
- Traumatic Injury: Injuries such as hip dislocations or fractures can damage nearby blood vessels, leading to a compromised blood supply to the bone and the potential development of avascular necrosis.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Diseases like sickle cell anemia and Gaucher’s disease are known to disrupt blood flow to the bone, thereby heightening the risk of avascular necrosis.
- Deep Sea Diving and High Altitude Exposure: Activities that involve significant changes in atmospheric pressure, such as scuba diving or mountain climbing, can lead to decompression sickness, which in turn can block blood vessels and affect bone health.
Implications and Preventive Measures
Understanding these risk factors is pivotal for anyone at potential risk of avascular necrosis. Regular health check-ups, moderation in alcohol consumption, careful use of steroids, and immediate attention to traumatic injuries can significantly reduce the risk. Those with underlying health conditions should consult healthcare providers for personalized preventive strategies.
Diagnosis of Avascular Necrosis
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and to prevent further deterioration of the affected bone. Here is a comprehensive list of diagnostic methods used for detecting avascular necrosis:
1. Medical History and Physical Examination: The first step in diagnosing AVN involves a thorough review of the patient’s medical history and a physical examination. Physicians look for specific symptoms like joint pain and range of motion limitations. Factors like a history of steroid use, alcoholism, or trauma can be significant clues.
2. X-rays: This is often the first imaging test done. Early-stage AVN may not be visible on X-rays, but in later stages, X-rays can show changes in the bone structure or osteoarthritis.
3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI is the most sensitive method for diagnosing AVN in its early stages. It can detect changes in the bone marrow and visualize bone blood flow patterns.
4. Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: While not as sensitive as MRI, a CT scan can show bone changes earlier than X-rays. It provides detailed cross-sectional images of the bone.
5. Bone Scan: In a bone scan, a small amount of radioactive material is injected into the bloodstream and detected by a scanner. This test helps identify new areas of bone growth or breakdown.
6. Biopsy: In rare cases, a biopsy may be performed. A small piece of bone is removed and examined to confirm the diagnosis of AVN.
7. Functional Evaluation: This includes assessing the joint function, range of motion, and strength. It helps in understanding the impact of AVN on mobility and daily activities.
8. Blood Tests: While blood tests cannot diagnose AVN directly, they are useful in ruling out other conditions that may cause joint pain, such as autoimmune diseases.
Each of these diagnostic methods plays a crucial role in the early detection and management of avascular necrosis. The choice of diagnostic method will depend on the stage of the disease, the patient’s symptoms, and their overall health condition. Early detection through these methods can significantly improve the treatment outcomes for patients with avascular necrosis.
Treatment Options for Avascular Necrosis
The management and treatment of AVN are crucial for restoring blood flow, preserving bone tissue, and reducing symptoms. This section delves into the current treatment options available, providing insights into how these treatments correlate with alleviating symptoms.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Medications and Supplements: To manage pain and inflammation, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often prescribed. Additionally, cholesterol-lowering medications, blood thinners, and bisphosphonates may be recommended to improve blood flow and bone health.
- Physical Therapy: A tailored physical therapy regimen can help maintain joint mobility and reduce the stress on affected bones.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management and the avoidance of alcohol and tobacco are crucial. These changes can enhance blood flow and reduce the progression of AVN.
Surgical Treatments
- Core Decompression: This procedure involves removing part of the inner layer of the bone to relieve pressure and create a channel for new blood vessels to nourish bone tissues.
- Bone Grafts: Bone grafting can help regenerate healthy bone tissue and support damaged areas.
- Joint Replacement: In advanced cases, replacing the affected joint with an artificial one may be the best option to restore function and relieve pain.
Treatment Relation to Symptoms
The choice of treatment is largely influenced by the stage of AVN and the severity of symptoms. Early-stage AVN may respond well to non-surgical methods, focusing on pain management and preserving bone health. In contrast, advanced AVN often requires surgical intervention to effectively address joint destruction and severe pain.
- Pain Management: Both non-surgical and surgical treatments aim to alleviate pain, a primary symptom of AVN.
- Mobility Improvement: Physical therapy and certain surgical procedures help in improving joint function and mobility.
- Disease Progression: Timely intervention can slow or halt the progression of AVN, preserving the affected bone and joint.
Understanding the relationship between treatments and symptoms allows patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions, optimizing outcomes in the management of avascular necrosis.
Prevention and Management of Avascular Necrosis
Preventing AVN primarily involves addressing the risk factors and maintaining overall bone health. Here are some key strategies:
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol use is a known risk factor for AVN. Limiting alcohol intake can significantly reduce the risk.
- Manage Steroid Use: If you’re on long-term steroid medication, work with your doctor to monitor and potentially minimize their use, as steroids can increase the risk of AVN.
- Control Cholesterol Levels: High lipid levels can lead to fat deposits in blood vessels, impacting blood flow. Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels is crucial.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular, low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling can improve blood flow and bone strength, reducing the risk of AVN.
- Avoid Trauma: Protecting yourself from injuries, especially around joints, can prevent the conditions that lead to AVN.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D supports bone health. Incorporate foods like leafy greens, dairy, and fish into your diet.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Regular visits to your doctor can help in early detection of any conditions that might lead to AVN.
Managing Symptoms of Avascular Necrosis
If you’re diagnosed with AVN, managing symptoms effectively is crucial for maintaining quality of life. Here’s how you can manage the symptoms:
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers can help, but for more severe pain, consult your doctor for appropriate medication.
- Physiotherapy: Engaging in physiotherapy can help maintain joint function and relieve pain.
- Rest and Joint Care: Avoid activities that put stress on the affected joints. Using supportive devices like braces can help.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold to the affected area can reduce pain and swelling.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can increase stress on affected joints. Keeping a healthy weight can alleviate symptoms.
- Surgical Options: In advanced cases, surgical options like core decompression or joint replacement may be considered.
- Mental Health Support: Living with a chronic condition like AVN can be challenging. Seeking support from mental health professionals can be beneficial.
However, prevention of Avascular Necrosis involves a proactive approach to risk factors and maintaining bone health. If you’re already diagnosed, effective symptom management can greatly improve your quality of life. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment plans.
FAQs About Avascular Necrosis: Symptoms and Causes
1. What is Avascular Necrosis (AVN)?
Avascular Necrosis, also known as osteonecrosis, is a condition where bone tissue dies due to a lack of blood supply. This can lead to small breaks in the bone and the bone’s eventual collapse.
2. What are the primary symptoms of Avascular Necrosis?
The most common symptom of AVN is pain. At first, you may only feel pain when putting pressure on the affected bone. Eventually, the pain becomes constant. Other symptoms can include joint stiffness and a limited range of motion.
3. What causes Avascular Necrosis?
The main cause of AVN is the interruption of the blood supply to the bone. This can be due to joint or bone trauma, alcoholism, long-term use of high-dose steroids, and certain medical conditions like blood disorders and autoimmune diseases.
4. Can Avascular Necrosis occur in any bone?
While AVN can occur in any bone, it most commonly affects the ends of long bones such as the femur (the bone in the thigh). The hips, shoulders, and knees are also commonly affected.
5. Is Avascular Necrosis a progressive condition?
Yes, AVN typically progresses over time if not treated. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing symptoms and preventing bone and joint damage.
6. How is Avascular Necrosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis usually involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans.
7. Can Avascular Necrosis be treated non-surgically?
Yes, in its early stages, non-surgical treatments like medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes can be effective. However, in more advanced cases, surgery might be necessary.
8. Does Avascular Necrosis affect a specific age group or gender more?
AVN can affect anyone but is more common in people between the ages of 30 and 60. It also appears to be more prevalent in men than in women.
9. Can lifestyle changes reduce the risk of Avascular Necrosis?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as reducing alcohol intake, quitting smoking, and managing underlying health conditions can help lower the risk of AVN.
10. Is Avascular Necrosis linked to any specific lifestyle or health conditions?
Yes, lifestyle factors like heavy alcohol use and prolonged corticosteroid use, as well as health conditions like lupus, sickle cell disease, and decompression disease (the bends), are linked to a higher risk of AVN.
Conclusion
It’s essential to be aware of the potential causes of Avascular Necrosis, which range from injury and excessive alcohol use to specific medical treatments and conditions. Knowledge of these causes can help in identifying risks and taking preventive measures.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms that could be indicative of Avascular Necrosis, it’s imperative to seek medical advice immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing this condition effectively and preventing further damage to the bones.
Remember, your health and well-being are paramount. Paying attention to your body’s signals and consulting with healthcare professionals can make a significant difference in managing Avascular Necrosis and maintaining a healthy, active life.