Autoimmune Hepatitis Symptoms: Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic condition in which the body’s immune system attacks liver cells, leading to inflammation and potentially serious liver damage.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of AIH is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
What is Autoimmune Hepatitis?
Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic liver condition characterized by the body’s immune system attacking its own liver cells. This abnormal immune response leads to inflammation and, over time, can cause liver damage. Unlike viral hepatitis, such as hepatitis A, B, or C, autoimmune hepatitis is not caused by a virus but by an immune system malfunction.
Distinguishing Autoimmune Hepatitis from Other Hepatitis Forms
It’s crucial to differentiate autoimmune hepatitis from other hepatitis types, primarily viral hepatitis. While viral hepatitis is caused by specific viruses, autoimmune hepatitis originates from within the body’s immune system. This distinction is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Other forms of hepatitis, like alcoholic hepatitis, are due to external factors such as excessive alcohol consumption, further differentiating them from autoimmune hepatitis.
Prevalence and Demographics: Who is Affected?
Autoimmune hepatitis is relatively rare, affecting between 10-20 people per 100,000 in the population. It can occur at any age, but is most commonly diagnosed in individuals aged 40-50 years. There’s a notable gender bias, with women being more affected than men, accounting for approximately 70% of cases. While it can affect individuals of any race or ethnicity, certain genetic predispositions are noted, making some groups more susceptible than others.
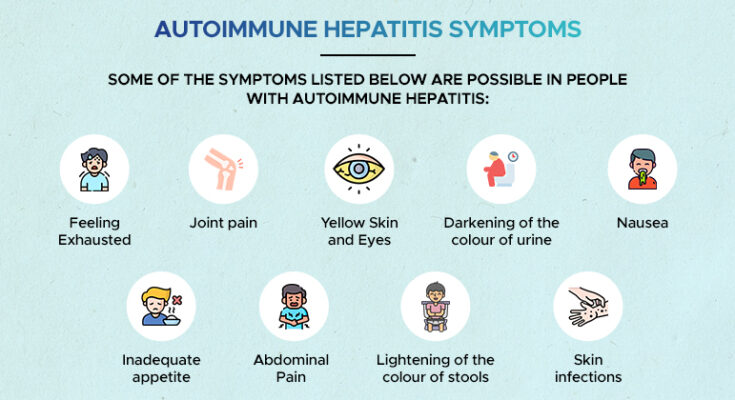
Symptoms of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Recognizing the symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. This article provides a comprehensive list of common symptoms associated with autoimmune hepatitis, differentiates these symptoms from those of other liver diseases, and underscores the importance of early detection and diagnosis.
Common Symptoms of Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Fatigue: This is one of the most common symptoms, often described as feeling unusually tired or exhausted.
- Abdominal Discomfort: Patients may experience pain or discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen.
- Jaundice: Characterized by a yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes.
- Skin Rashes: Various types of skin rashes can occur.
- Joint Pain: Some individuals may experience pain in their joints.
- Dark Urine: The urine may become unusually dark.
- Pale Stools: Stools may lose their normal color, becoming pale or clay-colored.
- Loss of Appetite and Weight Loss: Decreased appetite and unexplained weight loss are common.
- Enlarged Liver: The liver may become enlarged, detectable by a physician during a physical exam.
- Itching: Persistent itching of the skin can occur.
Differentiating Symptoms from Other Liver Diseases
While many of the symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis are similar to other liver diseases, certain aspects can help differentiate them:
- Pattern and Onset: Autoimmune hepatitis often develops gradually but can sometimes present suddenly. The pattern may help distinguish it from other liver conditions.
- Presence of Other Autoimmune Disorders: Patients with autoimmune hepatitis may have other autoimmune diseases, which is less common in other liver diseases.
- Elevated Immunoglobulin Levels: Blood tests showing elevated levels of certain immunoglobulins are more indicative of autoimmune hepatitis.
Importance of Early Detection and Diagnosis
Detecting autoimmune hepatitis early is vital for several reasons:
- Preventing Progression: Early treatment can help prevent the disease from progressing to liver cirrhosis or liver failure.
- Better Treatment Response: Patients who receive an early diagnosis and start treatment sooner often have a better response to therapy.
- Reducing Complications: Early intervention can reduce the risk of complications such as liver scarring and liver cancer.
However, understanding and recognizing the symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis is essential for early detection and effective treatment. If you experience any of these symptoms, especially if they persist, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Remember, early intervention can significantly improve outcomes in autoimmune hepatitis.
Causes and Risk Factors of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH) is a complex and multifactorial condition, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its liver cells, leading to inflammation and, in severe cases, liver failure. Understanding its causes and risk factors is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
1. Genetic Predisposition
Research indicates a significant genetic component in the development of AIH. Individuals with certain genetic markers are more likely to develop this condition. These markers are often associated with the immune system, suggesting a hereditary predisposition. However, having these genetic markers does not guarantee the development of AIH, implying that other factors also play a role.
2. Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors are believed to trigger AIH in genetically susceptible individuals. These can include:
- Infections: Certain viral infections have been linked to the onset of AIH, possibly due to a phenomenon known as molecular mimicry, where the immune system confuses liver cells for virus particles.
- Medications: Some drugs can induce AIH-like symptoms, although the exact mechanism is not fully understood.
- Toxins: Exposure to certain toxins may contribute to the development of AIH, though the evidence is not conclusive.
3. Risk Factors
Apart from genetic predisposition and environmental triggers, several risk factors have been identified:
- Age: AIH can occur at any age, but two peaks are observed – one in adolescence and another in late middle age.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop AIH than men, with some studies suggesting that up to 80% of AIH patients are female.
- Ethnicity and Geographical Location: The prevalence and severity of AIH can vary with ethnicity and geographical location, indicating a possible role of both genetic and environmental factors.
- Other Autoimmune Diseases: Individuals with other autoimmune disorders, such as thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, or celiac disease, have a higher risk of developing AIH.
However, Autoimmune Hepatitis is a condition influenced by a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. While certain groups of people, such as women and those with a family history of AIH, are at a higher risk, the disease can potentially affect anyone. Early recognition of these factors is key to managing AIH effectively.
Diagnosing Autoimmune Hepatitis: Understanding the Process
Diagnosing Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH) is a critical process that requires a detailed and methodical approach. AIH is a chronic condition where the body’s immune system attacks the liver, leading to inflammation and potential liver damage. Proper diagnosis is vital to differentiate AIH from other liver diseases and initiate appropriate treatment.
Steps in Diagnosing Autoimmune Hepatitis
1. Initial Assessment and Medical History: The diagnosis begins with a thorough medical assessment, including a review of the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and any previous liver-related issues.
2. Physical Examination: A physical exam is conducted to check for signs indicative of liver disease, such as jaundice, enlarged liver, or tenderness in the liver area.
3. Laboratory Tests: Blood tests play a crucial role in diagnosing AIH. These include:
- Liver Function Tests (LFTs): To assess the health of the liver by measuring levels of liver enzymes, bilirubin, and proteins.
- Autoantibody Tests: Certain autoantibodies are typically present in AIH, like ANA, SMA, and anti-LKM1.
4. Imaging Studies: Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs may be used to visualize the liver’s structure and check for abnormalities.
5. Liver Biopsy: A liver biopsy is often the definitive test for diagnosing AIH. It involves taking a small liver tissue sample to examine for signs of inflammation and damage.
Differentiating AIH from Other Liver Conditions
Differentiating AIH from other liver conditions, such as viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment. This differentiation is typically achieved through a combination of blood tests, imaging studies, and liver biopsy results.
Role of Diagnostic Tools in AIH
- Blood Tests: Help in detecting abnormal liver function and the presence of specific autoantibodies associated with AIH.
- Liver Biopsy: Essential for confirming the diagnosis, assessing the degree of liver damage, and guiding treatment decisions.
- Imaging Studies: Assist in ruling out other liver diseases and evaluating the overall health of the liver.
Diagnosing AIH is a comprehensive process that involves various diagnostic tools and techniques. Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management and treatment of this autoimmune liver disease. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
The Impact of Autoimmune Hepatitis on Patients’ Lives
Living with Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH) can significantly alter an individual’s day-to-day life, presenting unique challenges and concerns. Understanding how AIH affects daily routines, along with insights into the long-term outlook and real-life stories, can provide valuable perspective for patients and their loved ones.
How AIH Affects Daily Life
- Symptom Management: AIH can manifest with symptoms like fatigue, joint pain, and abdominal discomfort. Managing these symptoms often requires lifestyle adjustments, including diet changes and scheduling rest periods throughout the day.
- Medication Regimen: Patients typically need to adhere to a strict medication schedule to manage their condition, which can impact daily routines.
- Regular Medical Appointments: Frequent visits to healthcare providers for monitoring and treatment adjustments are common, potentially affecting work and personal schedules.
- Psychological Impact: Dealing with a chronic illness can lead to stress, anxiety, and depression, necessitating additional support and coping strategies.
Long-Term Outlook for Patients with AIH
The prognosis for AIH patients varies, depending largely on early diagnosis and effective management. While some individuals may achieve remission, others might experience progressive liver damage, leading to complications like cirrhosis. Lifelong medication and regular medical supervision are often necessary. Advances in medical treatments continue to improve the long-term outlook for many patients.
Personal Stories and Case Studies
Hearing from others who have walked the same path can be incredibly reassuring for AIH patients. Personal stories often highlight:
- Challenges and Triumphs: Learning how others have navigated the complexities of AIH can provide practical tips and emotional support.
- Diverse Experiences: AIH affects individuals differently, and case studies can offer insights into a range of experiences, from mild to severe cases.
- Hope and Resilience: Stories of resilience and success in managing the disease can be a powerful source of motivation and hope.
By comprehensively understanding the impact of AIH, patients and their families can better navigate the challenges and uncertainties associated with this autoimmune liver disease.
Treatment Options for Autoimmune Hepatitis
Treatment for autoimmune hepatitis primarily focuses on slowing the progression of the disease and minimizing liver damage. The most common approach involves medication, typically immunosuppressants, to reduce immune system activity. These treatments aim to achieve remission, where liver inflammation is significantly reduced or eliminated.
Medications and Their Side Effects
- Corticosteroids: Prednisone or prednisolone are often the first line of treatment. They are effective but can have side effects like weight gain, high blood pressure, diabetes, and osteoporosis.
- Azathioprine: This immunosuppressant is frequently used alongside corticosteroids to enhance effectiveness and potentially reduce steroid dosage. Side effects may include nausea, vomiting, and liver toxicity.
- Other Immunosuppressants: Medications like mycophenolate mofetil and cyclosporine are alternatives for those who cannot tolerate standard treatments. They come with their risks, including increased susceptibility to infections and kidney problems.
Lifestyle Changes and Holistic Approaches
Alongside medication, lifestyle adjustments can play a vital role in managing autoimmune hepatitis:
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet supports liver health. Avoiding alcohol and reducing sodium intake can lessen liver strain.
- Regular Exercise: Helps in maintaining a healthy weight, reducing liver fat, and improving overall well-being.
- Avoiding Toxins: Minimizing exposure to substances harmful to the liver, like certain medications and environmental toxins, is crucial.
- Holistic Therapies: Practices like yoga, meditation, and acupuncture may complement traditional treatments by reducing stress and improving quality of life.
However, treating autoimmune hepatitis involves a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, and possibly holistic approaches. Regular monitoring and communication with healthcare providers are key to managing this condition effectively. As research advances, treatment strategies may continue to evolve, offering new hope for those affected by this autoimmune disorder.
Prevention and Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Tips for Managing Symptoms
Living with autoimmune hepatitis can be challenging, but managing symptoms effectively can greatly improve quality of life. Here are some practical tips:
- Medication Adherence: Consistently taking prescribed medications is crucial. These medications help control the immune system’s attack on liver cells.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains supports liver health and overall well-being.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight, reduce liver fat, and boost energy levels.
- Avoid Alcohol: Alcohol can exacerbate liver damage, so it’s important to limit or avoid it.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, or counseling can help manage stress, which is beneficial for overall health.
Strategies for Preventing Flare-Ups
To reduce the risk of autoimmune hepatitis flare-ups, consider the following strategies:
- Avoiding Certain Medications: Some over-the-counter and prescription medications can trigger flare-ups. Consult your doctor before taking any new medication.
- Monitoring for Infections: Infections can provoke a flare-up. Practice good hygiene and stay up to date with vaccinations.
- Regular Blood Tests: Monitoring liver function through blood tests can help detect problems early and adjust treatments accordingly.
- Avoiding Toxins: Exposure to environmental toxins can stress the liver. Avoiding harmful chemicals and pollutants is advisable.
Importance of Regular Medical Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are vital for managing autoimmune hepatitis. These appointments allow for:
- Monitoring Disease Progression: Regular check-ups help track the progression of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment.
- Adjusting Treatment Plans: Based on your current health status, your doctor can adjust medications and treatment strategies.
- Early Detection of Complications: Regular monitoring can catch complications like liver scarring early, when they’re more treatable.
- Personalized Care: Each patient’s experience with autoimmune hepatitis is unique. Regular visits allow for tailored care based on individual needs.
Incorporating these tips and strategies into your daily routine can help in managing autoimmune hepatitis more effectively. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment plans.
Challenges and Future Directions in Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH) Research
While significant advancements have been made in its treatment, the complexity of AIH presents numerous challenges and opens avenues for future research. This section explores these challenges and potential directions for future investigations.
Current Challenges in Treating Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Diagnosis Difficulties: AIH often presents symptoms similar to other liver diseases, making accurate diagnosis challenging. Research into more precise diagnostic tools is essential.
- Understanding Disease Mechanisms: The exact cause of AIH remains unknown. A deeper understanding of the disease’s pathophysiology could lead to more effective treatments.
- Treatment Side Effects: Current treatments, mainly steroids and immunosuppressants, can have significant side effects. Research into safer, more tolerable treatments is needed.
- Disease Management: Managing AIH long-term can be complex, involving regular monitoring and medication adjustments. Improving disease management strategies is crucial for patient quality of life.
- Personalized Medicine: AIH can vary greatly between individuals. There’s a need for personalized treatment approaches based on a patient’s specific disease characteristics.
Future Research Areas in AIH
- New Treatment Development: Exploring new therapies, including biological agents, to treat AIH more effectively with fewer side effects.
- Genetic Research: Investigating the genetic factors contributing to AIH could lead to more targeted and effective treatments.
- Understanding Environmental Triggers: Research into how environmental factors, like viruses or toxins, may trigger AIH could offer insights into prevention and treatment.
- AI and Machine Learning: Utilizing AI and machine learning to analyze large datasets could uncover new patterns and treatment possibilities in AIH.
- Patient-Centered Research: Focusing on the patient experience to improve quality of life, including mental health support and lifestyle modifications.
The field of AIH research is ripe with challenges that, if addressed, could significantly advance treatment and patient care. By focusing on these key areas, researchers can open new paths to understanding and managing this complex disease, ultimately improving outcomes for those affected.
Conclusion
If you or someone you know exhibits symptoms of AIH, it’s imperative to seek medical advice promptly. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatments. Remember, early intervention can make a significant difference in managing AIH effectively.
We encourage everyone to spread awareness about AIH. Understanding and recognizing the condition can lead to early diagnosis and better management. Share this information with your loved ones, and let’s collectively work towards a healthier, more informed society. Your health is paramount—never hesitate to take action for its preservation.