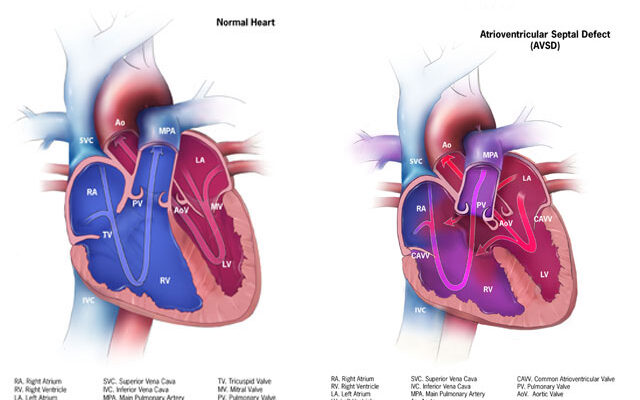
Atrioventricular Canal Defect Symptoms: Atrioventricular Canal Defect (AVCD) is a significant congenital heart defect that affects the structure of a baby’s heart during fetal development.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of AVCD is essential for early diagnosis and treatment, which can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected.
What is Atrioventricular Canal Defect (AVCD)?
Atrioventricular Canal Defect (AVCD), also known as Atrioventricular Septal Defect, is a congenital heart condition. This defect is characterized by a combination of abnormalities in the heart’s structure, affecting the atrial and ventricular septa (the walls separating the heart’s chambers) and the valves that control the flow of blood between these chambers.
Prevalence and Significance of AVCD
AVCD is a relatively rare condition, yet it holds significant importance due to its impact on an individual’s health. The prevalence rate of AVCD varies, but it is a notable form of congenital heart disease. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial. Without proper treatment, individuals with AVCD may experience complications such as heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, and other serious conditions. The condition underscores the importance of prenatal and postnatal screening for congenital heart defects.
Symptoms of Atrioventricular Canal Defect
Understanding the early signs is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Initially, symptoms may be subtle and can include:
- Difficulty Feeding: Infants with AVCD often struggle with feeding, showing signs like fatigue during feeding or poor weight gain.
- Rapid Breathing or Breathlessness: Watch for signs of labored breathing, especially during feeding or activity.
- Unusual Heart Rhythms: Irregular heartbeats or palpitations can be a sign of AVCD.
- Excessive Sweating: Infants might sweat more than usual, particularly during feeding.
- Blue Tint to Skin or Lips (Cyanosis): This occurs when oxygen levels in the blood are low.
Progression: How Symptoms May Develop or Worsen Over Time
As the child grows, the symptoms of AVCD can become more pronounced and may include:
- Increased Fatigue: Children may show reduced energy levels and get tired easily during play.
- Breathing Difficulties: Shortness of breath and rapid breathing can become more apparent, especially during physical activities.
- Swelling in Legs, Ankles, or Feet: This is a sign of fluid retention, indicating worsening heart function.
- Frequent Respiratory Infections: Children with AVCD might experience more colds, pneumonia, or other respiratory issues.
Comparison with Normal Heart Function Symptoms
In a healthy heart, blood flows smoothly and oxygenates the body efficiently. In contrast, AVCD disrupts normal heart function, leading to symptoms like:
- Oxygenation Issues: A healthy heart ensures adequate oxygen levels in the blood. In AVCD, oxygen levels can be lower, leading to symptoms like cyanosis.
- Heart Rhythms: Unlike the regular rhythm of a normal heart, AVCD can cause irregular or rapid heartbeats.
- Efficient Breathing: Normal heart function supports effortless breathing, while AVCD can cause labored breathing and fatigue.
However, these symptoms is key in seeking timely medical advice and care for AVCD. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes for children with this condition.
Causes of Atrioventricular Canal Defect
Understanding the causes is crucial for both prevention and treatment. This article delves into the main factors contributing to AVCD, encompassing genetic elements, environmental influences, and their interplay.
Genetic Factors: The Role of Genetics in AVCD
Genetics play a significant role in the development of Atrioventricular Canal Defect. Research has shown that certain genetic mutations and chromosomal abnormalities are strongly associated with AVCD. These genetic factors can be inherited, meaning that a family history of AVCD or related heart defects increases the risk. This section will explore the specific genetic markers identified in AVCD, their inheritance patterns, and the implications for genetic counseling and testing.
Environmental Influences: External Factors Contributing to AVCD
While genetics are a key component, environmental factors also contribute significantly to the development of AVCD. This includes maternal health and behavior during pregnancy, such as the use of certain medications, exposure to harmful substances, and overall nutritional status. We will examine how these external elements can increase the risk of AVCD in the fetus and the preventative measures that can be taken to mitigate these risks.
Combination of Causes: Understanding the Interaction between Genetic and Environmental Factors
Often, the causes of AVCD involve a complex interplay between genetic predispositions and environmental exposures. This section will delve into how these factors interact, potentially exacerbating the risk of developing AVCD. By understanding this interaction, healthcare providers can better identify individuals at high risk and develop more effective prevention and management strategies.
Diagnosing Atrioventricular Canal Defect (AVCD)
When it comes to identifying Atrioventricular Canal Defect (AVCD), a range of medical tests and procedures are crucial. Here’s an overview:
- Echocardiogram: This is the primary tool for diagnosing AVCD. It uses sound waves to create detailed images of the heart, allowing doctors to see the structure of the heart and blood flow through its chambers.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test records the electrical activity of the heart and can identify rhythm problems associated with AVCD.
- Chest X-ray: Doctors may use a chest X-ray to see the condition of the heart and lungs. This helps in identifying complications like heart enlargement or lung congestion.
- Cardiac MRI: A Cardiac MRI provides detailed images of the heart and is useful in complex cases of AVCD.
- Cardiac Catheterization: In some cases, this procedure is done to measure the pressure in the heart chambers and to provide additional information about the heart’s function.
These tests are typically non-invasive and provide critical information for diagnosing AVCD.
Importance of Early Diagnosis of Atrioventricular Canal Defect
Early diagnosis of AVCD is vital for several reasons:
- Better Treatment Outcomes: Early detection allows for timely intervention, which can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
- Prevention of Complications: It helps in preventing or managing potential complications, such as heart failure or pulmonary hypertension.
- Guided Treatment Planning: Early diagnosis aids in planning appropriate treatments, which may include medications, surgical interventions, or a combination of both.
- Improved Prognosis: Children diagnosed early with AVCD often have a better prognosis and a higher quality of life post-treatment.
However, using a combination of specialized tests for diagnosing AVCD is crucial. Early detection plays a significant role in managing the condition effectively, preventing complications, and ensuring better overall outcomes for patients. Regular check-ups and attention to symptoms are key in early identification of AVCD.
Treatment Options for Atrioventricular Canal Defect (AVCD)
Atrioventricular Canal Defect (AVCD), a congenital heart defect, requires specialized treatment and care. Understanding the available options is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Non-Surgical Interventions
Non-surgical approaches play a pivotal role in managing AVCD, particularly in stabilizing patients before surgery or in cases where surgery is not immediately required. These include:
- Medication: Medications are often the first line of treatment. They aim to manage symptoms and improve heart function. Common medications include diuretics, which reduce fluid buildup, and inotropes, which strengthen heart contractions.
- Monitoring and Regular Check-ups: Close monitoring of heart function and regular medical check-ups are essential. This helps in early detection of any changes in the condition and in making timely decisions regarding the need for surgery.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: For some patients, especially children, slight modifications in lifestyle can be beneficial. These include nutritional management and activity adjustments to reduce the strain on the heart.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery is often necessary for AVCD to repair the structural defects of the heart. The types of surgeries include:
- Complete Repair Surgery: This involves repairing the holes in the heart and reconstructing the valves. It’s usually done in infancy or early childhood.
- Partial Repair Surgery: In some cases, partial repair is an option, where only certain defects are corrected.
- Outcomes and Recovery: Post-surgery, patients generally have a good prognosis. Recovery involves close monitoring, medications, and gradual return to normal activities.
Ongoing Care and Management
Long-term management of AVCD is crucial for maintaining heart health and preventing complications. This includes:
- Regular Cardiac Assessments: Lifelong follow-up with a cardiologist is essential. This includes regular echocardiograms and possibly other heart tests.
- Management of Associated Conditions: Some patients may develop other heart-related issues, which need to be managed alongside AVCD.
- Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations: Healthy lifestyle choices, including a heart-healthy diet and regular exercise, are recommended.
- Emotional and Psychological Support: Dealing with a chronic condition like AVCD can be challenging. Support from family, friends, and possibly professional counselors is important.
However, managing Atrioventricular Canal Defect involves a combination of non-surgical interventions, potential surgical treatments, and ongoing care. With the right approach, individuals with AVCD can lead a healthy and active life.
Living with Atrioventricular Canal Defect (AVCD)
Living with Atrioventricular Canal Defect (AVCD) requires careful daily life adjustments to manage the condition effectively. AVCD, a congenital heart defect, can significantly impact a person’s lifestyle, necessitating adaptations for both physical well-being and emotional health.
- Dietary Changes: Emphasizing heart-healthy foods is crucial. Patients are advised to adopt a diet low in sodium, saturated fats, and cholesterol. Incorporating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can positively affect heart health.
- Regular Exercise: Depending on the severity of AVCD, patients may need to modify their exercise routines. Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or yoga can be beneficial, but it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise program.
- Medication Adherence: Many with AVCD require regular medication. Adhering to prescribed medication schedules is vital for managing the condition.
- Monitoring Symptoms: Regular monitoring for any changes in symptoms like fatigue, breathing difficulties, or chest pain is essential. Immediate medical attention should be sought if any significant changes occur.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding tobacco and limiting alcohol consumption are crucial steps. Stress management techniques like meditation or counseling can also be beneficial.
Support Systems: A Pillar in Managing AVCD
The role of support systems in managing Atrioventricular Canal Defect cannot be overstated. A strong network of family, medical professionals, and community resources is vital for patients.
- Family Support: Emotional and practical support from family members can significantly improve the quality of life for AVCD patients. Families can assist in daily routines, medication management, and provide emotional comfort.
- Medical Team Collaboration: Regular check-ups with cardiologists and primary care physicians are critical. These professionals can monitor the patient’s condition, adjust treatments, and provide valuable advice on lifestyle modifications.
- Community Resources: Joining support groups and connecting with others who have similar conditions can offer emotional support and practical advice. Educational resources and community programs tailored to those with heart conditions can also be beneficial.
- Educational Resources: Understanding the condition is key. Patients and families should be encouraged to educate themselves about AVCD, its implications, and ways to manage it effectively.
- Mental Health Support: The psychological impact of living with a chronic condition like AVCD is significant. Access to mental health professionals, counseling, and therapy can be crucial for maintaining emotional well-being.
However, living with Atrioventricular Canal Defect involves a multi-faceted approach encompassing lifestyle changes, adherence to medical advice, and a robust support system. By embracing these adjustments and resources, individuals with AVCD can lead fulfilling lives while effectively managing their condition.
Prevention and Awareness of Atrioventricular Canal Defect (AVCD)
Understanding the preventative measures for Atrioventricular Canal Defect (AVCD) is crucial. While AVCD is often a congenital condition, implying limited prevention options, certain steps can still be beneficial:
- Prenatal Care: Regular prenatal check-ups are essential. Expectant mothers should follow a balanced diet, avoid harmful substances like alcohol and tobacco, and maintain a healthy lifestyle to reduce risks associated with AVCD.
- Genetic Counseling: For families with a history of congenital heart defects, genetic counseling is recommended. It can provide valuable insights into potential risks and preventive measures for AVCD.
- Medication Review: Women planning to conceive should consult healthcare providers to review any medications that might affect fetal heart development.
- Managing Chronic Conditions: Controlling chronic health issues like diabetes is vital, as they can increase the risk of congenital heart defects.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can contribute positively to fetal heart health.
Raising Awareness about AVCD
The importance of public knowledge about Atrioventricular Canal Defect cannot be overstated:
- Early Detection: Awareness leads to early detection, which is critical for effective management of AVCD.
- Support and Resources: Educating the public about AVCD fosters a supportive environment for affected families and helps in accessing resources and care.
- Research and Funding: Greater awareness can lead to increased funding and research, improving treatment options and outcomes for AVCD patients.
- Reducing Stigma: Knowledge dispels myths and reduces the stigma associated with congenital conditions, promoting a more inclusive society.
However, while preventive measures for AVCD are limited due to its congenital nature, certain steps can mitigate risks. Moreover, raising awareness about AVCD is vital for early detection, support, and advancing research.
Conclusion
Awareness and early detection are paramount in addressing AVCD effectively. Understanding the symptoms and acknowledging their impact is the first step towards seeking appropriate help. Early detection can significantly improve the management of AVCD, allowing individuals to adopt coping strategies or receive suitable medical intervention. As such, spreading awareness about AVCD is crucial, not only for those who might be directly affected but also for caregivers, educators, and the broader community.
In conclusion, a thorough grasp of AVCD symptoms and causes, coupled with heightened awareness and prompt action, can greatly enhance the quality of life for those experiencing this condition. It is our collective responsibility to foster an environment where understanding and support for AVCD are readily available.