Atrial Septal Defect Symptoms: Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) is a congenital heart anomaly characterized by an abnormal opening in the atrial septum, the wall separating the upper chambers of the heart.
This condition can lead to various complications if left untreated, impacting an individual’s health and quality of life.
What is Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)?
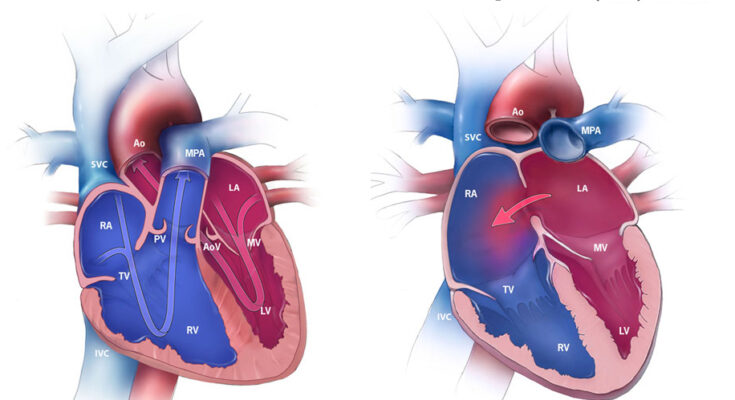
An Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) is a heart condition characterized by a hole in the atrial septum, the wall dividing the upper two chambers of the heart. This defect allows oxygen-rich blood from the left atrium to mix with oxygen-poor blood in the right atrium. Normally, the heart’s left and right sides do not directly communicate, ensuring efficient circulation of oxygenated blood throughout the body. However, ASD disrupts this process, leading to various potential health issues.
The presence of an ASD can lead to increased blood flow to the lungs, causing the right side of the heart to work harder than usual. Over time, this can cause complications like heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, arrhythmias, and increased risk of stroke. Notably, ASDs vary in size and impact; small ASDs might close on their own and cause minimal issues, while larger defects may require medical intervention.
Statistics and Demographics Affected
ASD is a relatively common congenital heart defect, affecting about 1 in 1,500 live births. It is more frequently diagnosed in females compared to males. This condition can remain undiagnosed until adulthood, as smaller ASDs may not cause noticeable symptoms. However, larger ASDs or those identified later in life can lead to significant cardiovascular complications.
In terms of demographics, ASD occurs across all racial and ethnic groups. Early detection and treatment are critical for managing the condition effectively. Advances in medical technology have made the detection and treatment of ASD more efficient, allowing individuals with the condition to lead healthier lives with proper medical care.
This congenital heart defect, while serious, is highly manageable with modern medical interventions, including minimally invasive surgery and regular cardiac monitoring. Understanding ASD’s impact on heart function is crucial for anyone diagnosed with the condition, as well as for their families and caregivers.
Symptoms of Atrial Septal Defect
Recognizing its symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. This article provides an in-depth look at the common symptoms of ASD, along with a comparison of how these symptoms manifest differently in children and adults.
Common Symptoms of Atrial Septal Defect
ASD symptoms can vary widely, but some are more prevalent. They include:
- Shortness of Breath: Especially during physical activities or exercise.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired, a common symptom in many heart conditions.
- Swelling: Often noticed in the legs, feet, or abdomen due to fluid accumulation.
- Heart Palpitations: Irregular heartbeats that are felt as fluttering or pounding in the chest.
- Frequent Respiratory Infections: Especially in children, who may have more colds, bronchitis, or pneumonia.
Symptoms in Children vs. Adults
The manifestation of ASD symptoms can differ significantly between children and adults:
Children:
- May show signs of poor growth or development.
- Are prone to more frequent respiratory infections.
- Might display symptoms like breathlessness or fatigue during play or physical activities.
Adults:
- Often experience shortness of breath and fatigue, especially during exertion.
- May develop heart rhythm abnormalities, like atrial fibrillation.
- Could have symptoms related to heart failure, such as swelling in the legs and abdomen.
Why Understanding Symptoms Matters
Early detection of ASD can prevent complications like pulmonary hypertension, a condition where high blood pressure affects the arteries in the lungs and the right side of the heart. Being aware of these symptoms, especially in the context of age-related differences, is crucial for seeking timely medical advice and intervention.
Whether you’re a parent observing your child or an adult monitoring your health, understanding the symptoms of Atrial Septal Defect is vital. It aids in early diagnosis, allowing for prompt and effective treatment. If you or someone you know exhibits these symptoms, consulting with a healthcare provider is strongly advised.
Causes and Risk Factors of Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
Understanding the causes and risk factors is crucial for early detection and effective management.
In-Depth Look at the Causes of ASD
ASD’s origins can be complex, often involving a combination of genetic and environmental factors. However, in many cases, the exact cause remains unknown. Here’s a closer look:
- Genetic Factors: ASD can be part of genetic syndromes like Down syndrome or Holt-Oram syndrome. In these cases, the defect is a result of chromosomal abnormalities.
- Spontaneous Mutation: Sometimes, ASD occurs due to spontaneous genetic mutations during fetal development, without any family history of the condition.
- Maternal Factors: Certain conditions during pregnancy, such as diabetes, alcoholism, or drug use, can increase the risk of the fetus developing ASD.
Discussion on Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors
Genetic Risk Factors:
- Family History: A family history of heart defects or ASD specifically can increase the risk.
- Chromosomal Abnormalities: As mentioned, syndromes like Down syndrome are linked to ASD.
Environmental Risk Factors:
- Maternal Health: Conditions like obesity, diabetes, and lupus in the mother can contribute to the risk.
- Exposure to Harmful Substances: Use of certain medications, alcohol, or drugs during pregnancy can elevate the risk.
- Infections During Pregnancy: Certain infections, such as rubella, contracted by the mother during pregnancy can impact fetal heart development.
It’s important to note that having one or more risk factors does not guarantee that a child will develop ASD, just as the absence of these factors does not ensure they won’t. Early screening and monitoring during pregnancy can help in identifying potential issues and planning for necessary care.
Diagnosing Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
Detecting this condition early is crucial for effective treatment. The diagnosis process for ASD involves a comprehensive approach that typically includes a mix of physical examinations, symptom review, and advanced diagnostic tests.
Key Diagnostic Tests and Their Roles
- Physical Examination and Medical History: The journey to diagnosing ASD begins with a thorough physical examination and a review of the patient’s medical history. Doctors look for physical signs such as heart murmurs, which are unusual sounds heard during a heartbeat. A detailed medical history helps to identify any symptoms or risk factors associated with ASD.
- Echocardiogram: This is the primary test for diagnosing ASD. An echocardiogram uses sound waves to create a detailed image of the heart. It helps in identifying the size and location of the hole in the septum and assessing the heart’s function.
- Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray can show whether the heart is enlarged – a common sign of ASD. It also helps in evaluating the condition of the lungs.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): An ECG records the electrical activity of the heart. It can reveal patterns that suggest a hole in the heart or damage caused by a long-standing ASD.
- Cardiac Catheterization: In some cases, doctors may recommend cardiac catheterization. This involves inserting a thin tube into a blood vessel and guiding it to the heart to measure pressure and oxygen levels in different parts of the heart.
- MRI and CT Scans: These imaging tests provide detailed images of the heart and are useful in complex cases where more information is needed.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of ASD is vital for preventing complications such as heart failure, atrial fibrillation, and pulmonary hypertension. It’s important for individuals experiencing symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, or heart palpitations, especially if they have a family history of heart defects, to seek medical attention promptly.
Diagnosing Atrial Septal Defect accurately is crucial for effective treatment planning. Through a combination of physical exams, imaging tests, and heart function assessments, healthcare professionals can identify ASD and make informed decisions about the best course of action for each patient. Regular check-ups and being attentive to heart health are key steps in detecting and managing this condition.
Potential Complications of Untreated Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
Let’s delves into the potential risks and long-term impacts of ASD on overall health, emphasizing the importance of timely intervention and management.
Complications Arising from Untreated ASD
- Heart Failure: The most critical complication of an untreated ASD is the risk of heart failure. The abnormal opening in the heart’s septum causes increased blood flow to the lungs and overworks the right side of the heart, potentially leading to heart failure.
- Pulmonary Hypertension: ASD can lead to increased pressure in the pulmonary arteries (pulmonary hypertension). This condition, if severe, can cause irreversible damage to the lung’s blood vessels.
- Arrhythmias: Patients with ASD are at a higher risk of developing arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation. These irregular heart rhythms can lead to additional complications, including stroke.
- Stroke: The presence of ASD increases the likelihood of a stroke. The abnormal heart structure allows blood clots to pass from the right to the left side of the heart and potentially travel to the brain.
- Reduced Exercise Capacity: Individuals with untreated ASD may experience decreased stamina and exercise intolerance due to the heart’s reduced efficiency in circulating oxygen-rich blood.
Long-Term Health Impact of ASD
Untreated ASD can have lasting effects on a person’s health and quality of life. The continuous strain on the heart and lungs can lead to chronic conditions and may severely limit physical activities and lifestyle choices. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial in preventing these long-term consequences.
By understanding the potential complications of untreated ASD, individuals and healthcare providers can make informed decisions about timely and effective treatment options. Addressing ASD early can significantly reduce the risk of severe health complications and improve overall life expectancy and quality.
Treatment Options for Atrial Septal Defect
Fortunately, there are several treatment options available, ranging from non-invasive to surgical methods. The choice of treatment depends on the size of the defect, the patient’s symptoms, and overall health.
Non-Invasive Treatment Options
- Observation and Monitoring: In cases where the ASD is small and asymptomatic, doctors might recommend a watchful waiting approach. Regular check-ups and echocardiograms are used to monitor the defect.
- Medications: While medications cannot close an ASD, they can be used to manage symptoms. Medicines like diuretics help reduce fluid accumulation in the body, and beta-blockers or digoxin are used to control heart rate.
- Device Closure: A less invasive option for some patients is a catheter-based procedure. A device is inserted through a catheter into the heart to close the hole. This method is typically used for secundum ASDs and is less invasive than open-heart surgery.
Surgical Treatment Options
- Open-Heart Surgery: This is the most common method for repairing larger ASDs. The procedure involves making an incision in the chest to access the heart and sewing a patch or suturing the hole closed.
- Minimally Invasive Cardiac Surgery: For suitable candidates, surgeons can perform the procedure through smaller incisions using specialized instruments. This approach may reduce recovery time and scarring.
Deciding on the appropriate treatment for ASD depends on multiple factors including the type and size of the defect, symptoms, and patient’s overall health. In some cases, monitoring and medications may suffice, while in others, surgical intervention is necessary. It’s crucial to have regular consultations with a cardiologist to determine the best course of action. Early detection and treatment of ASD can significantly improve the quality of life and prevent future complications.
Living with Atrial Septal Defect
This defect can cause various health issues and necessitates a unique approach to daily living.
Lifestyle Changes for ASD Management
- Healthy Diet: Emphasize a heart-healthy diet. This includes consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid excessive salt and saturated fats to reduce the risk of hypertension and heart disease.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular, moderate exercise to maintain cardiovascular health. Consult with a healthcare professional to define the best exercise regimen, considering the severity of your ASD.
- Routine Medical Check-ups: Regular check-ups with a cardiologist are crucial. They can monitor heart health, adjust medications, and provide guidance on managing ASD effectively.
- Avoid Certain Activities: Some activities, like heavy weightlifting or extreme sports, might be risky. It’s important to discuss your physical limitations with a doctor.
- Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking: Alcohol can affect heart health, and smoking is a significant risk factor for heart diseases. Limiting or avoiding these can greatly benefit individuals with ASD.
Support Systems and Resources for ASD
- Support Groups: Joining ASD-specific support groups can provide emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of community.
- Educational Resources: Utilize resources from reputable medical organizations for up-to-date information on ASD management.
- Mental Health Support: Living with a chronic condition like ASD can be challenging. Seeking help from a mental health professional can be beneficial in coping with emotional stress.
- Family and Friends: Engage your family and friends in your journey. Educate them about ASD and how they can support you.
- Professional Guidance: Regular consultations with healthcare providers, including cardiologists and nutritionists, are essential for tailored health management.
Living with Atrial Septal Defect requires careful management and lifestyle adjustments. By embracing a heart-healthy lifestyle, engaging with support systems, and staying informed, individuals with ASD can lead fulfilling lives.
Prevention and Early Detection of Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
Understanding the significance of these strategies is essential for minimizing potential health complications associated with ASD.
Key Strategies for Prevention
While the exact cause of ASD is often unknown, embracing certain preventive measures can mitigate risks, especially during pregnancy. These include:
- Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle: Expectant mothers should follow a balanced diet, avoid harmful substances like alcohol and tobacco, and manage chronic conditions such as diabetes or obesity.
- Regular Prenatal Care: Consistent check-ups during pregnancy can help in early detection of fetal heart abnormalities, including ASD.
- Genetic Counseling: For families with a history of congenital heart defects, genetic counseling can provide valuable insights and guidance.
The Importance of Early Detection
Detecting ASD early is crucial in managing its impact effectively. Here’s why early detection matters:
- Reducing Health Risks: Early detection and treatment of ASD can prevent complications like heart failure, arrhythmia, and pulmonary hypertension.
- Improving Quality of Life: Timely intervention often leads to better long-term health outcomes and quality of life for individuals with ASD.
- Informed Health Decisions: Early diagnosis enables individuals and families to make informed decisions regarding treatment options and lifestyle adjustments.
The Role of Regular Medical Check-Ups
Regular medical check-ups play a pivotal role in the early detection of ASD. These check-ups should include:
- Heart Monitoring: Routine heart evaluations, including echocardiograms and electrocardiograms, can identify ASD in its early stages.
- Pediatric Assessments: Children should undergo regular health examinations, where pediatricians can spot signs of heart issues.
- Listening to Your Body: Be attentive to symptoms like shortness of breath, fatigue, or heart palpitations, and seek medical advice promptly.
However, while the prevention of ASD starts with a healthy lifestyle and prenatal care, its early detection hinges on regular medical check-ups and staying attuned to one’s health. Embracing these practices enhances the chances of managing ASD effectively, ensuring a better quality of life.
Conclusion
Encountering any of these symptoms warrants a consultation with a healthcare provider. A thorough evaluation by a medical professional is the only way to accurately diagnose ASD and determine the most appropriate course of action. This may include monitoring, medication, or in some cases, surgical intervention.
Early diagnosis and treatment of ASD can significantly reduce the risk of complications, improve the quality of life, and ensure a better health outcome. Remember, proactive healthcare is a vital step towards wellness, and your healthcare provider is your best ally in this journey.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms related to Atrial Septal Defect, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. Prioritizing your heart health is not just a choice—it’s a necessity.