Atrial Tachycardia Treatment: Atrial tachycardia is a complex cardiac condition characterized by an abnormally fast heartbeat originating from the upper chambers of the heart, known as the atria.
This condition, while often considered less severe than other types of arrhythmias, still requires prompt and accurate diagnosis, followed by effective treatment strategies to manage symptoms and reduce potential complications.
What is Atrial Tachycardia?
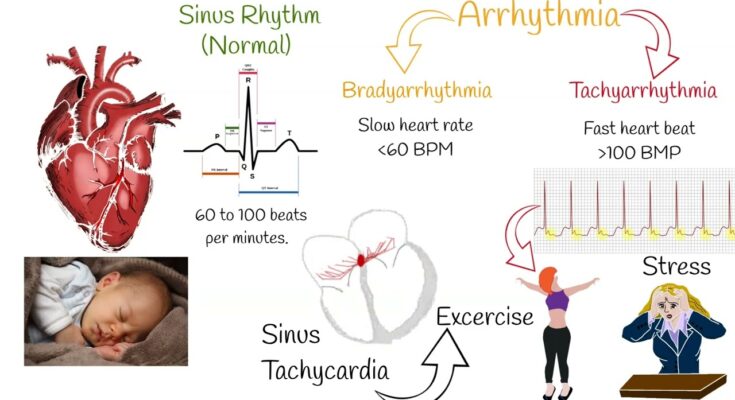
Atrial Tachycardia (AT) is a type of cardiac arrhythmia characterized by a rapid heart rate originating from the atria, the upper chambers of the heart. This condition involves the heart beating at an abnormally high rate, typically over 100 beats per minute, which can disrupt normal heart function. Unlike normal heart rhythms driven by the sinoatrial node, AT arises from abnormal electrical impulses within the atria. These irregular impulses lead to rapid, uncoordinated atrial contractions, impacting the heart’s ability to effectively pump blood.
Causes and Risk Factors
The development of atrial tachycardia can be influenced by several factors. Key causes include:
- Heart Conditions: Existing heart disorders like coronary artery disease, heart valve disease, or congenital heart defects can precipitate AT.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Imbalances in minerals, such as potassium and magnesium, which are critical for heart function, can trigger AT.
- High Blood Pressure: Chronic hypertension can increase the risk.
- Stress and Stimulants: Excessive stress, caffeine, alcohol, or tobacco use can contribute to its onset.
- Age and Genetics: Older individuals and those with a family history of cardiac issues are at higher risk.
Common Symptoms Associated with AT
Recognizing the symptoms of atrial tachycardia is crucial for timely intervention. Common signs include:
- Rapid Heartbeat: A noticeable, unusually fast heartbeat.
- Palpitations: Sensations of a racing, uncomfortable, or irregular heartbeat.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest, which should be promptly evaluated.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Feeling faint or unsteady, which can lead to fainting in severe cases.
- Fatigue: Unexplained tiredness, particularly during or after physical activities.
Understanding atrial tachycardia, its causes, and symptoms can significantly aid in its management and treatment. If you experience any of these symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional is essential for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Diagnosing Atrial Tachycardia
Let’s provides a detailed overview of the various diagnostic methods employed to identify this condition, underscoring their significance and the role of differential diagnosis.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): The Primary Diagnostic Tool
The Electrocardiogram (ECG) is the cornerstone in diagnosing atrial tachycardia. This non-invasive test records the electrical activity of the heart and helps detect abnormalities in heart rhythms. An ECG can provide critical information about the rate and regularity of heartbeats, as well as the size and position of the heart chambers. It’s a quick, painless test that plays a pivotal role in the initial diagnosis of atrial tachycardia.
Holter Monitor: Tracking Heart Rhythms Over Time
A Holter monitor is a portable ECG device worn for a day or more to record the heart’s activity as you go about your daily routine. This extended monitoring is crucial for detecting arrhythmias that might not appear during a standard ECG exam. The Holter monitor provides a detailed picture of the heart’s behavior over an extended period, making it an invaluable tool in diagnosing intermittent episodes of atrial tachycardia.
Stress Tests: Assessing the Heart Under Exertion
Stress tests involve exercising on a treadmill or stationary bike while heart activity is monitored. These tests help determine how the heart responds to physical exertion and can reveal heart rhythm issues that may not be present at rest. Stress tests are particularly useful in assessing the impact of exercise on atrial tachycardia and in guiding treatment planning.
The Importance of Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is crucial in accurately identifying atrial tachycardia, as its symptoms and ECG findings can mimic other cardiac conditions. Proper differential diagnosis involves ruling out other types of arrhythmias and heart diseases, ensuring that the treatment plan is appropriately tailored to atrial tachycardia.
Role of Medical History and Physical Examination
A thorough medical history and physical examination are fundamental in the diagnostic process. They provide context to the test results, helping to identify potential causes and risk factors for atrial tachycardia. Information about symptoms, medical history, family history of heart disease, and a physical examination form the basis for ordering appropriate diagnostic tests.
However, diagnosing atrial tachycardia requires a multifaceted approach. The combination of ECG, Holter monitoring, stress tests, differential diagnosis, and a thorough medical history and physical examination offers the most comprehensive strategy for accurately diagnosing and effectively treating atrial tachycardia.
Treatment Options for Atrial Tachycardia
Understanding the treatment options for Atrial Tachycardia is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
First-Line Treatments and Lifestyle Changes
The initial approach to managing Atrial Tachycardia often involves a combination of lifestyle changes and first-line treatments. These include:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in moderate physical activity can improve cardiovascular health.
- Healthy Diet: Adopting a heart-healthy diet, low in saturated fats and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can help in managing stress, which is often a trigger for AT episodes.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers such as caffeine or alcohol can be beneficial.
Medications Used in AT Treatment
Medications play a pivotal role in the treatment of Atrial Tachycardia. These drugs aim to control the heart rate and prevent recurrence of AT episodes.
Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Antiarrhythmic drugs are commonly prescribed for Atrial Tachycardia treatment. They work by correcting irregular heartbeats and include medications like:
- Flecainide: Effective in controlling heart rhythm.
- Propafenone: Often used in patients without significant heart disease.
- Amiodarone: Used in severe cases due to its broad spectrum of action.
Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers are another class of medication used in AT treatment. They work by slowing down the heart rate, thus alleviating the symptoms of Atrial Tachycardia. Common beta-blockers include:
- Metoprolol: Helps in reducing heart rate and blood pressure.
- Atenolol: Known for its fewer side effects on the respiratory system.
Calcium Channel Blockers
Calcium channel blockers are effective in controlling the heart rate, especially in patients who cannot take beta-blockers. Examples include:
- Diltiazem: Helps in relaxing the heart muscles.
- Verapamil: Effective in reducing the number of electrical signals that contribute to AT.
Discussing “Atrial Tachycardia Treatment” in the Context of Pharmaceutical Approaches
When discussing Atrial Tachycardia Treatment, it’s important to consider the pharmaceutical approaches as a cornerstone of managing this condition. The choice of medication often depends on the individual’s overall health, the severity of the AT, and any underlying heart conditions. Regular consultations with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the effectiveness of these treatments and to make adjustments as necessary.
However, the treatment of Atrial Tachycardia involves a comprehensive approach combining lifestyle modifications and a range of medications. Understanding these options can empower patients to effectively manage their condition and maintain a healthy heart rhythm.
Advanced Treatment Techniques for Atrial Tachycardia
1. Catheter Ablation
Catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure widely recognized as a primary treatment for atrial tachycardia (AT). This method involves inserting a catheter into the heart through the blood vessels. Once positioned, the catheter emits energy (usually radiofrequency) to destroy small areas of heart tissue that cause irregular heartbeats. The precision of catheter ablation allows for targeted treatment, reducing the risk of damaging healthy heart tissue. It’s effective in restoring normal heart rhythm and is generally considered safe, with a low risk of complications.
2. Surgery Options
In rare cases where catheter ablation is not effective or suitable, surgical options may be considered for treating AT. One such procedure is the Maze surgery, where a surgeon creates a series of precise incisions in the heart tissue to form scar tissue. This scar tissue disrupts the abnormal electrical signals causing AT. Although more invasive than catheter ablation, Maze surgery can be highly effective, especially in patients with structural heart problems. It’s typically performed during open-heart surgery for other heart conditions.
3. Latest Advancements in AT Treatment
The field of atrial tachycardia treatment is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and emerging technologies. One of the newest advancements is the development of more sophisticated mapping systems. These systems provide detailed images of the heart’s electrical activity, allowing for more accurate identification of problematic areas. Additionally, there’s a growing interest in cryoablation, a technique using extreme cold to disable heart tissue causing AT. This method shows promise as it may cause less damage to surrounding tissues compared to traditional ablation techniques.
However, the treatment of atrial tachycardia has advanced significantly, with catheter ablation being the most common and effective method. Surgical options remain a secondary approach, used in specific cases. The continuous development of new technologies and techniques promises even more effective treatments in the future, enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life.
Managing Atrial Tachycardia: Essential Strategies for Long-Term Care
We’ll explore the crucial strategies for managing this condition, emphasizing the importance of follow-up care and highlighting key lifestyle and dietary considerations. By adhering to these guidelines, individuals can better manage their Atrial Tachycardia and maintain a healthier life.
Long-Term Management Strategies for Atrial Tachycardia
- Regular Monitoring and Medication Management: Consistent monitoring of heart rhythm and adherence to prescribed medications are pivotal. It’s crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to adjust medications as needed and monitor their effectiveness.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs: Participating in cardiac rehabilitation can significantly improve heart health. These programs offer tailored exercises, education, and support, helping patients to manage their condition more effectively.
- Use of Wearable Technology: Wearable devices that monitor heart rate and rhythm can be valuable tools. They provide real-time data, allowing for prompt response to any irregularities.
The Importance of Follow-Up Care in Atrial Tachycardia
- Routine Check-Ups: Regular visits to a cardiologist are essential. These check-ups help in assessing the progress of the condition and making necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
- Electrocardiograms (ECGs) and Other Tests: Periodic ECGs and possibly other tests like echocardiograms or stress tests are important to monitor the heart’s condition and response to treatment.
- Being Proactive in Health Management: Patients should be proactive in their care, reporting any new symptoms or concerns to their healthcare provider immediately.
Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations for Atrial Tachycardia
- Heart-Healthy Diet: Incorporating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low in saturated fats can have a positive impact on heart health.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular, moderate exercise, as recommended by a healthcare provider, can strengthen the heart and improve overall cardiovascular health.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial in managing stress, which is important for heart health.
- Avoiding Triggers: Understanding and avoiding personal triggers, such as caffeine or alcohol, that may exacerbate Atrial Tachycardia is crucial.
By embracing these long-term management strategies, prioritizing follow-up care, and adopting healthy lifestyle and dietary habits, individuals with Atrial Tachycardia can lead a healthier and more balanced life. It’s always important to work closely with healthcare providers to tailor these strategies to individual needs and conditions.
Patient Education and Support of Atrial Tachycardia
Understanding Atrial Tachycardia: Why It Matters
When patients are well-informed about Atrial Tachycardia, they can recognize symptoms early, understand the risks, and make informed decisions about their treatment options. This understanding also helps in mitigating anxiety and fear, as patients know what to expect and how to respond.
The Role of Support Groups and Resources
Dealing with Atrial Tachycardia can be challenging, but patients don’t have to face it alone. Support groups play a vital role in providing emotional and practical support. These groups offer a platform for sharing experiences, tips, and coping strategies. Moreover, they provide a sense of community and understanding that can be incredibly comforting. Resources such as educational websites, brochures, and patient forums are also invaluable. They offer a wealth of information about the condition, treatment options, lifestyle adjustments, and more, helping patients to stay informed and connected.
Patient Education: A Key to Effective Treatment
Education is a cornerstone of effective treatment for Atrial Tachycardia. It involves more than just understanding the medical aspects; it’s about learning how to live with the condition. This includes knowledge about medication management, lifestyle changes like diet and exercise, and recognizing when to seek medical help. Healthcare providers play a significant role in patient education, offering guidance tailored to each individual’s needs. A well-educated patient is more likely to adhere to treatment plans, attend follow-up appointments, and maintain a healthier lifestyle, all of which contribute to better health outcomes.
However, patient education and support are essential in managing Atrial Tachycardia. Understanding the condition, accessing support resources, and continuous learning are key elements that empower patients to take an active role in their treatment and improve their quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while Ankylosing Spondylitis remains a complex condition, advancements in medical science are continually enhancing diagnosis and treatment options.
With the right approach and professional guidance, individuals with AS can lead fulfilling lives. Remember, an informed and proactive approach is key to managing Ankylosing Spondylitis effectively.