Atrial Tachycardia Symptoms: Atrial tachycardia is a type of heart rhythm disorder that is characterized by a rapid heartbeat originating from the atria, the upper chambers of the heart.
This condition can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications, making it crucial to understand its causes, symptoms, and potential treatment options.
What is Atrial Tachycardia?
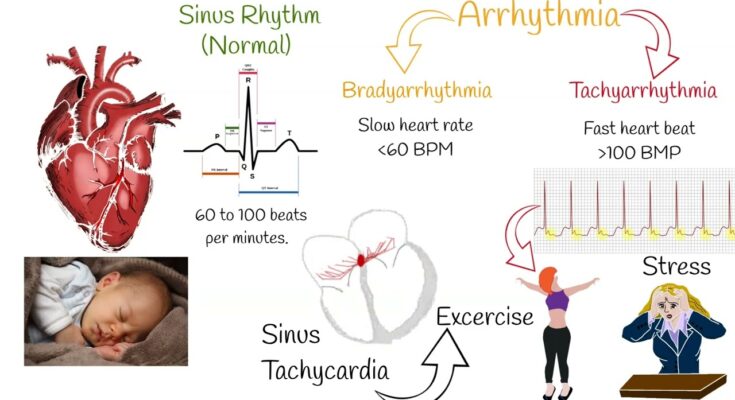
Atrial tachycardia is a type of heart rhythm disorder characterized by a faster than normal heartbeat. It originates from the upper chambers of the heart, known as the atria, where rapid electrical impulses cause the heart to beat more quickly than usual. This condition is a subset of tachycardia, a general term for any rapid heart rate.
Understanding Atrial Tachycardia
The human heart typically beats between 60 to 100 times per minute at rest. In atrial tachycardia, the heart rate can exceed 100 beats per minute due to abnormal electrical signals in the atria. These irregular signals disrupt the normal heart rhythm, leading to a rapid and sometimes irregular heartbeat. This can cause symptoms like palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
Distinction from Other Tachycardias
Atrial tachycardia is distinct from other forms of tachycardia, such as ventricular tachycardia, which originates in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). Another common type is atrial fibrillation, which also begins in the atria but is characterized by a very rapid and irregular heartbeat. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
This condition requires medical attention and may be managed with medication, lifestyle changes, or, in some cases, surgical procedures. If you experience symptoms of a rapid heartbeat, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Common Symptoms of Atrial Tachycardia
Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management. Here’s a detailed list of common symptoms associated with atrial tachycardia:
1. Rapid Heartbeat: The most noticeable symptom is a heart beating unusually fast, which can feel like fluttering or pounding in the chest.
2. Shortness of Breath: This condition can make you feel out of breath, even with minimal exertion or at rest, affecting your ability to perform everyday tasks.
3. Fatigue: Persistent tiredness or weakness, unrelated to physical activity or lack of sleep, is a common sign, impacting your energy levels and productivity.
4. Dizziness or Lightheadedness: You might experience feelings of unsteadiness or faintness, which can be disconcerting and affect your ability to concentrate or stay active.
5. Chest Pain or Discomfort: While not always present, chest pain or discomfort can occur, necessitating immediate medical attention.
6. Palpitations: A sensation of skipped heartbeats or irregular heart rhythm is often reported, causing discomfort and anxiety.
7. Reduced Exercise Tolerance: You may notice a decrease in your ability to engage in physical activities that were previously manageable.
7. Anxiety: The physical symptoms of atrial tachycardia can lead to increased feelings of anxiety, impacting mental health.
These symptoms can vary in intensity and frequency, and not everyone with atrial tachycardia will experience all of them. Their impact on daily life can range from mild inconvenience to severe disruption, affecting physical activities, work productivity, and overall quality of life. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Early intervention can help manage symptoms effectively and reduce the risk of complications, such as stroke or heart failure, associated with atrial tachycardia.
Causes of Atrial Tachycardia
It is crucial to understand the causes, risk factors, and prevention strategies to effectively manage this condition. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of these aspects to enhance awareness and promote heart health.
Diverse Causes of Atrial Tachycardia
Atrial Tachycardia can stem from various factors, each contributing to the abnormal rhythm in distinct ways:
- Structural Heart Changes: Conditions like heart disease, hypertension, or previous heart surgeries can alter the heart’s structure, leading to AT.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Imbalances in essential minerals such as potassium, magnesium, and calcium can disrupt the heart’s electrical system.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can impact heart rhythm, potentially causing AT.
- Excessive Alcohol or Caffeine Consumption: These substances can trigger episodes of AT in some individuals.
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress can accelerate the heart rate, possibly leading to AT episodes.
- Infections: Certain infections, particularly those affecting the lungs or heart, can be a contributing factor.
Risk Factors: Who is at Risk?
Understanding who is at risk for developing Atrial Tachycardia is vital in prevention and early detection:
- Age: Older adults are more likely to develop AT due to the natural aging of the heart and arteries.
- Heart Disease History: Individuals with a history of heart diseases or conditions are at a higher risk.
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and lack of physical activity can increase the risk.
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of AT or other heart rhythm disorders might elevate the risk.
Prevention Strategies
While some causes and risk factors of AT cannot be changed, adopting healthy lifestyle choices can significantly reduce the risk:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity strengthens the heart and improves overall cardiovascular health.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and low in saturated fats, can prevent heart disease and related conditions.
- Limiting Stimulants: Reducing the intake of caffeine and alcohol can help in managing AT.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, or therapy can be effective in reducing stress levels.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Regular monitoring of heart health, especially for those with risk factors, is crucial in early detection and management of AT.
However, understanding the causes and risk factors of Atrial Tachycardia is imperative for prevention and effective management. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and being aware of the symptoms, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing this heart rhythm disorder.
Diagnosing Atrial Tachycardia: A Comprehensive Guide
Diagnosing this condition involves a meticulous process, essential for ensuring accurate treatment and management. The diagnostic journey typically begins with a detailed patient history and physical examination, followed by a series of specialized tests.
- Patient History and Physical Examination: This initial step is crucial. Healthcare professionals gather information about the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and any potential risk factors. A physical examination helps in identifying any visible signs that might be related to Atrial Tachycardia.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG is the cornerstone of diagnosing heart rhythm problems. It records the electrical activity of the heart and helps in identifying the specific type of tachycardia.
- Holter Monitor: For continuous monitoring of the heart’s rhythm, a Holter monitor, a portable ECG device, is used. It’s worn by the patient for 24-48 hours to capture any irregularities that might not show up during a standard ECG.
- Event Monitor: Similar to a Holter monitor, an event monitor is used for a more extended period. It’s particularly useful if the symptoms are sporadic.
- Echocardiogram: This ultrasound test provides a detailed image of the heart’s structure and function, assisting in identifying underlying conditions that might contribute to Atrial Tachycardia.
- Stress Test: Some cases require a stress test to see how the heart functions under physical stress.
- Electrophysiological Study (EPS): In complex cases, an EPS can provide detailed information about the electrical pathways within the heart.
Importance of Early Detection and the Role of Healthcare Professionals
Early detection of Atrial Tachycardia is vital. It not only helps in preventing complications such as stroke and heart failure but also aids in managing symptoms effectively. Healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in this. They are responsible for:
- Identifying Symptoms Early: Recognizing early signs and symptoms of Atrial Tachycardia allows for timely intervention.
- Guiding Patients Through the Diagnostic Process: Healthcare providers guide patients through the necessary tests and procedures, ensuring they understand each step.
- Interpreting Test Results: Their expertise is crucial in accurately interpreting test results, which is fundamental in devising an effective treatment plan.
- Patient Education and Support: Educating patients about their condition, treatment options, and lifestyle modifications forms a significant part of managing Atrial Tachycardia.
However, diagnosing Atrial Tachycardia is a detailed process involving various diagnostic tools and the expertise of healthcare professionals. Early detection and proper management can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with this condition.
Treatment Options for Atrial Tachycardia
Managing this condition effectively is crucial for maintaining heart health and preventing complications.
Current Treatment Methods for Atrial Tachycardia
- Medications: The first line of defense often includes medications such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and antiarrhythmic drugs. These medications help control the heart rate and maintain a regular rhythm.
- Catheter Ablation: For cases where medication is ineffective, catheter ablation is considered. This procedure involves threading a thin tube through the blood vessels to the heart to destroy small areas of tissue causing the abnormal rhythm.
- Pacemakers and Defibrillators: In some instances, especially in patients with severe symptoms, implantable devices like pacemakers or defibrillators might be necessary. These devices help regulate the heart rate and prevent sudden cardiac events.
- Lifestyle Changes: Alongside medical treatments, lifestyle modifications such as reducing caffeine intake, managing stress, and quitting smoking are also recommended to improve symptoms and overall heart health.
Personalized Treatment Plans: The Key to Effective Management
The importance of personalized treatment plans in managing Atrial Tachycardia cannot be overstated. Each patient’s condition is unique, influenced by factors like underlying heart conditions, age, and overall health. Therefore, treatments must be tailored to meet individual needs. Personalized treatment plans often involve:
- Thorough Evaluation: A detailed assessment of the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and lifestyle.
- Regular Monitoring: Ongoing monitoring to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and make adjustments as necessary.
- Collaborative Approach: Involvement of cardiologists, electrophysiologists, and primary care providers to ensure a comprehensive treatment strategy.
- Patient Education: Educating patients about their condition, treatment options, and ways to manage symptoms effectively.
Atrial Tachycardia requires a nuanced approach to treatment, blending medication, potential procedural interventions, lifestyle changes, and continuous monitoring. Emphasizing personalized treatment plans ensures each patient receives the most effective and appropriate care for their specific condition. With the right treatment approach, individuals with Atrial Tachycardia can lead healthy, active lives.
Living with Atrial Tachycardia
Living with atrial tachycardia, a type of heart condition characterized by a rapid heartbeat, can be challenging. However, with the right approach, individuals can effectively manage symptoms and maintain a healthy lifestyle. Here are essential tips to help navigate this journey:
Tips for Symptom Management
- Regular Monitoring: Keep track of your heart rate and symptoms. Regular check-ups with your cardiologist are crucial.
- Medication Adherence: Follow your doctor’s advice regarding medications. These can help regulate your heart rate and prevent complications.
- Dietary Adjustments: A heart-healthy diet can make a significant difference. Focus on low-sodium, low-fat foods and incorporate plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- Stress Management: Stress can aggravate atrial tachycardia. Practices like yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can help keep stress levels in check.
- Physical Activity: Engage in regular, moderate exercise as recommended by your healthcare provider. This improves overall heart health.
Embracing a Healthy Lifestyle
Beyond managing symptoms, it’s vital to adopt a holistic approach towards health:
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for heart conditions. Quitting smoking can drastically improve heart health.
- Limiting Alcohol and Caffeine: Both can trigger episodes of atrial tachycardia. Moderation is key.
- Regular Sleep Patterns: Adequate sleep is essential for heart health. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
Emotional and Psychological Aspects
Living with a heart condition like atrial tachycardia can also have emotional and psychological impacts:
- Seek Support: It’s important to talk about your feelings. Support groups or counseling can be beneficial.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Understanding your condition empowers you and helps those around you to provide better support.
- Positive Outlook: Maintaining a positive mindset can improve your overall well-being and help in managing the condition more effectively.
Remember, every individual’s experience with atrial tachycardia is unique. Working closely with healthcare professionals and following these tips can help in leading a fulfilling and healthy life despite the challenges of the condition.
Prevention and Management of Atrial Tachycardia
Strategies for Preventing Atrial Tachycardia
Proactive measures play a crucial role in maintaining heart health and preventing atrial tachycardia.
- Healthy Diet: Incorporating a heart-healthy diet is fundamental. This means eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Reducing the intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can also help.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy heart rate and weight. It’s recommended to aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week.
- Managing Risk Factors: Keep conditions like high blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes under control. Regular check-ups and adherence to prescribed medications are key.
- Limiting Alcohol and Caffeine: Excessive consumption of alcohol and caffeine can trigger atrial tachycardia. Moderation is essential.
- Stress Management: Stress can adversely affect heart health. Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can be beneficial in managing stress.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disorders. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of developing atrial tachycardia.
Long-term Management and Lifestyle Modifications
Managing atrial tachycardia involves not just treating the condition but also adopting lifestyle changes that promote overall heart health.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring heart health and adjusting treatments as necessary.
- Medication Adherence: If medications are prescribed, it’s important to take them as directed to manage the condition effectively.
- Heart-Healthy Lifestyle: Continuing to follow a heart-healthy lifestyle is key. This includes eating a balanced diet, staying active, managing weight, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol.
- Stress Reduction: Continued focus on stress reduction can have a positive impact on heart health.
- Education and Support: Educating oneself about atrial tachycardia and seeking support from healthcare providers, support groups, or educational resources can be empowering.
By implementing these prevention and management strategies, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of atrial tachycardia and manage the condition effectively, leading to a healthier, more active life.
FAQs about Atrial Tachycardia
What is Atrial Tachycardia?
Atrial tachycardia is a type of heart rhythm disorder characterized by a faster-than-normal heartbeat originating from the upper chambers of the heart, known as the atria. This can lead to a heart rate often exceeding 100 beats per minute.
What Causes Atrial Tachycardia?
This condition can be caused by various factors, including heart disease, hypertension, stress, excessive alcohol or caffeine consumption, and certain medications. Sometimes, the exact cause remains unknown.
How is Atrial Tachycardia Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, a review of your medical history, and tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG), Holter monitor, or an event monitor to track your heart’s rhythm and rate.
What are the Symptoms of Atrial Tachycardia?
Symptoms may include palpitations, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, fatigue, and chest pain. However, some individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms.
Is Atrial Tachycardia Dangerous?
While atrial tachycardia is often not life-threatening, it can lead to complications like heart failure or stroke if left untreated. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Can Atrial Tachycardia be Treated?
Yes, treatments are available and may include lifestyle changes, medication, or procedures like catheter ablation. The treatment approach depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition.
Can Lifestyle Changes Help Manage Atrial Tachycardia?
Absolutely. Lifestyle changes such as reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, quitting smoking, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight can help manage the symptoms and potentially reduce the frequency of episodes.
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you experience symptoms of atrial tachycardia, especially if they’re new or worsening, it’s crucial to see a healthcare provider for an evaluation. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes and prevent complications.
Conclusion
Atrial tachycardia is a condition that requires careful attention and management. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is essential for those affected by this condition.
If you experience symptoms of atrial tachycardia, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.