Astigmatism Symptoms: Astigmatism, a common vision condition, affects millions of people worldwide. It’s characterized by an irregular curvature of the eye’s cornea or lens, leading to blurred or distorted vision.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of astigmatism is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management.
What is Astigmatism?
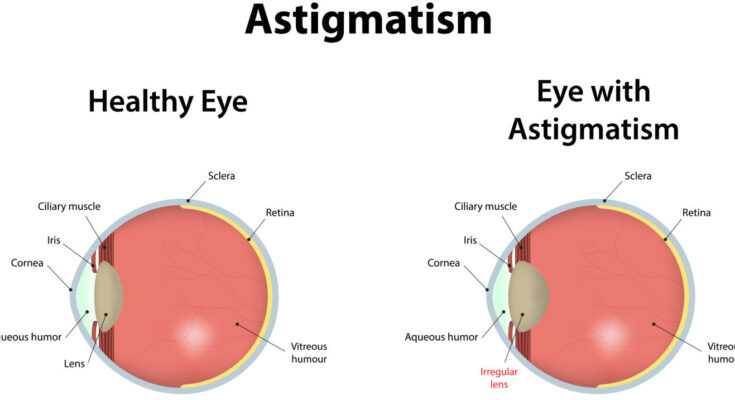
Astigmatism is a common vision condition that can cause blurred vision due to an irregular shape of the cornea or, in some cases, the curvature of the lens inside the eye. This irregularity prevents light from focusing properly on the retina, the light-sensitive surface at the back of the eye. As a result, vision becomes blurred at any distance.
Definition and Explanation of Astigmatism
Astigmatism occurs when the cornea, the clear front cover of the eye, is not perfectly round. Ideally, the cornea should have a symmetrically round shape, like a soccer ball. However, in astigmatism, the cornea often has an elliptical shape, resembling more of a football. This irregular shape distorts the light entering the eye, leading to blurred or distorted vision.
Astigmatism can occur in combination with other vision conditions like nearsightedness (myopia) or farsightedness (hyperopia). It’s a refractive error, meaning it’s related to how the eye bends or refracts light.
How Astigmatism Differs from Other Common Vision Problems
Unlike nearsightedness and farsightedness, which are caused by the eye’s length affecting the focus of light, astigmatism is primarily due to an irregular corneal shape. Here’s how it stands out:
- Nearsightedness (Myopia): This condition occurs when the eyeball is too long or the cornea is too curved, causing light rays to focus in front of the retina. This leads to difficulty seeing distant objects clearly.
- Farsightedness (Hyperopia): In this case, the eyeball is too short or the cornea is not curved enough, causing light to focus behind the retina. This results in poor near vision.
- Astigmatism: Astigmatism uniquely involves an irregular corneal shape, causing light to focus on multiple points either in front of or behind the retina, or both. This leads to overall blurred vision.
Understanding these differences is crucial for proper vision correction. Eyeglasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery like LASIK can effectively correct astigmatism. However, a specific diagnosis from an eye care professional is necessary to determine the best course of treatment.
Astigmatism Symptoms
Recognizing its symptoms is key to seeking timely treatment and maintaining quality of life. This article provides a comprehensive list of astigmatism symptoms and explains how they can impact your everyday activities.
Common Symptoms of Astigmatism
- Blurred Vision: One of the primary symptoms of astigmatism is blurred or distorted vision. This can occur at any distance, making tasks like reading, driving, or using a computer challenging.
- Eye Strain and Discomfort: People with astigmatism often experience eye strain, especially after prolonged periods of focusing, such as reading or working on a computer.
- Headaches: Frequent headaches, especially after visual tasks, can be a sign of astigmatism. This is often due to the extra effort your eyes make to compensate for the blurred vision.
- Difficulty with Night Vision: Astigmatism can make it hard to see clearly in low light conditions, impacting activities like night driving.
- Squinting: To see objects more clearly, individuals with astigmatism might find themselves squinting often, which can lead to headaches and eye strain.
- Fatigue: As your eyes struggle to focus, you may feel more tired than usual, particularly after tasks that require visual concentration.
Impact on Daily Activities
- Reading and Screen Time: Astigmatism can make reading books, using smartphones, or working on computers uncomfortable, leading to reduced productivity and enjoyment.
- Driving: Blurred and distorted vision can make driving, especially at night, dangerous.
- Professional Life: In careers that require sharp visual focus, such as graphic design or piloting, uncorrected astigmatism can severely impact performance.
- Sports and Recreation: Activities that rely on good vision, like sports, can become more challenging, affecting your ability to participate and enjoy them.
- General Fatigue: The overall strain and discomfort caused by astigmatism can lead to a general feeling of tiredness, affecting all areas of life.
Understanding these symptoms and their effects on daily activities is crucial. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult with an eye care professional. Early detection and treatment can greatly improve your quality of life.
Causes of Astigmatism
Let’s delve into how these factors play a role in the development or exacerbation of astigmatism, offering insights that can help in understanding and managing this condition.
Genetic Factors Contributing to Astigmatism
- Hereditary Influence: Astigmatism often runs in families. If one or both parents have astigmatism, the likelihood of their children developing the condition increases. This genetic predisposition is linked to inherited irregularities in the shape of the cornea or lens of the eye.
- Corneal Shape and Structure: The genetic makeup can determine the curvature and structure of the cornea. A perfectly curved cornea refracts light to create a sharply focused image; however, a genetically misshapen cornea leads to astigmatism.
- Eye Development Factors: Genetics also play a role in the overall development of the eye. Any inherited irregularities in eye development can contribute to astigmatism.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors That Can Lead to or Worsen Astigmatism
- Prolonged Visual Stress: Activities that strain the eyes, such as extensive screen time, reading in poor light, or doing intricate work, can lead to the development or worsening of astigmatism.
- Eye Injury or Surgery: Trauma to the eye or certain types of eye surgery can alter the shape of the cornea, leading to astigmatism.
- Poor Posture and Eye Use Habits: Poor posture while reading or using digital devices, and habits like squinting, can modify the shape of the eye over time, contributing to astigmatism.
- Health Conditions and Medications: Certain systemic health conditions and medications can impact the health and shape of the eyes, potentially leading to astigmatism.
However, astigmatism is influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Understanding these can aid in early detection and effective management of the condition. Regular eye examinations are recommended to monitor eye health and detect any changes in vision.
Diagnosing Astigmatism: Methods and Importance
The primary tool for diagnosing astigmatism is a comprehensive eye exam. This exam typically includes:
- Visual Acuity Test: This test measures how well you can see at various distances. It involves reading letters on a chart positioned a specific distance away.
- Keratometry/Topography: These tests measure the curvature of your cornea. In astigmatism, the cornea often has an irregular shape, causing blurred vision.
- Refraction Test: This test determines the exact lens prescription you need. The optometrist uses a device called a phoropter, which places different lenses in front of your eyes to assess which ones correct your vision best.
The Importance of Early Detection and Regular Eye Check-ups
Early detection of astigmatism is crucial. Undiagnosed or untreated astigmatism can lead to headaches, eye strain, and progressively worsening vision. Children, particularly, need regular eye exams to detect astigmatism early. This is vital because undiagnosed vision issues can impact their learning and development.
Regular eye check-ups are recommended for everyone, not just those with vision problems. These check-ups can detect astigmatism before it causes significant issues and ensure that those with the condition receive the correct prescription for glasses or contact lenses. Additionally, regular eye exams can help monitor any changes in your vision, ensuring that your corrective lens prescription remains up-to-date.
However, understanding the diagnostic methods for astigmatism and recognizing the importance of early detection and regular eye check-ups are essential steps in maintaining good eye health and clear vision.
The Impact of Astigmatism on Vision
Understanding how astigmatism affects vision is crucial for those experiencing it or for those who wish to gain insights into this eye condition.
Detailed Explanation of How Astigmatism Affects Vision
Astigmatism occurs when the cornea, the clear front cover of the eye, is irregularly shaped. Unlike the normal spherical shape of the cornea, in astigmatism, the cornea tends to have a more oval shape. This irregularity disrupts the way light passes, or refracts, onto the retina, which is responsible for sending images to the brain. The result is a distortion in the person’s vision.
- Blurred Vision: The most significant impact of astigmatism is blurred vision. This blurring can occur at all distances, both near and far. It’s often described as a general haziness in vision.
- Eye Strain and Discomfort: People with astigmatism may experience additional strain on their eyes. This is because their eyes are constantly working harder to focus, leading to fatigue, headaches, and even discomfort.
- Difficulty with Night Vision: Astigmatism can also lead to challenges with night vision. Glare and halos around lights are common, which can make driving at night particularly difficult.
- Squinting and Eye Irritation: To try and see more clearly, individuals with astigmatism often squint, which can lead to eye irritation and further discomfort.
Comparison with Normal Vision
In contrast, normal vision, also known as emmetropia, occurs when the cornea has a perfectly spherical shape, allowing light to refract properly onto the retina. This results in a clear image being transmitted to the brain. For people with normal vision:
- Clarity at All Distances: They can see clearly at various distances without the need for corrective lenses.
- No Excessive Eye Strain: There is less strain on the eyes, and they don’t experience the same levels of fatigue or discomfort as those with astigmatism.
- Better Night Vision: Without the irregular shape of the cornea, there’s less likelihood of experiencing glare or halos around lights at night.
However, astigmatism can have a considerable impact on an individual’s vision, affecting their daily activities and quality of life. Understanding these effects is essential for managing the condition effectively, whether through corrective lenses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery. Regular eye check-ups are crucial to detect astigmatism early and to maintain good eye health.
Managing Astigmatism Symptoms
It’s essential to understand your options, ranging from non-invasive to surgical, to make an informed decision.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Glasses: A simple and widely used solution, glasses for astigmatism are specially designed with cylindrical lens prescriptions to counteract the irregular shape of the cornea or lens in your eye. They are an affordable and easy-to-adapt option for many.
Contact Lenses: For those seeking a glasses-free approach, contact lenses, including toric lenses specifically made for astigmatism, offer a more natural vision experience. They correct astigmatism by compensating for the uneven curvature of your cornea or lens.
- Soft Toric Lenses: These are comfortable and suit most lifestyles.
- Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) Lenses: They offer clearer vision but might take some getting used to.
- Hybrid Lenses: These combine the clarity of RGP lenses with the comfort of soft lenses.
Surgical Options
LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis): This popular refractive surgery reshapes the cornea using a laser, thereby correcting the astigmatism. It’s quick, with most patients experiencing improved vision almost immediately and minimal recovery time.
Other Refractive Surgeries: Apart from LASIK, there are other surgical options available:
- PRK (Photorefractive Keratectomy): Similar to LASIK, but instead of creating a flap, the outer layer of the cornea is completely removed.
- LASEK (Laser Epithelial Keratomileusis): A variant of PRK, where the outer layer of the cornea is loosened and moved aside before reshaping the underlying tissue.
- Epi-LASIK: This procedure separates a thin layer of the cornea, which is then reshaped with a laser.
Each surgical method has its specific indications, benefits, and risks. Consulting with an eye care professional is crucial to determine the most suitable option for your individual case.
However, managing astigmatism effectively hinges on understanding and choosing the right treatment option for your lifestyle and vision needs. Whether it’s the simplicity of glasses, the convenience of contact lenses, or the permanence of surgical options, there’s a solution to help you see clearly and comfortably.
Prevention and Lifestyle Adjustments for Astigmatism
While it often requires corrective lenses or surgery for treatment, there are also lifestyle adjustments and preventive measures that can help manage or prevent its worsening.
Tips for Reducing Eye Strain
- Regular Eye Exams: Regular check-ups with an optometrist can help in early detection and management of astigmatism.
- Proper Lighting: Ensure adequate lighting while reading or working to reduce strain on your eyes.
- Limit Screen Time: Reduce the time spent on digital devices. When using them, follow the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds.
- Eye Protection: Wear sunglasses to protect your eyes from harmful UV rays, which can exacerbate astigmatism.
- Adjust Workstation Ergonomics: Position your computer screen about an arm’s length away and slightly below eye level to reduce strain.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Astigmatism
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in vitamins A, C, and E, along with omega-3 fatty acids, can support eye health.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get enough sleep to rest and rejuvenate your eyes.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining eye moisture.
- Control Blood Sugar Levels: If you have diabetes, controlling your blood sugar levels can prevent changes in the shape of your lens, which can affect astigmatism.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can worsen astigmatism and other eye conditions.
By incorporating these simple yet effective practices into your daily routine, you can help manage and even prevent the worsening of astigmatism. Remember, regular eye check-ups play a crucial role in maintaining overall eye health.
When to See an Eye Specialist
Recognizing the Signs for Professional Eye Consultation
It’s crucial to be aware of the signs that suggest you should consult an eye specialist. Early detection and treatment can be vital in maintaining good eye health. Here are some key indicators:
- Blurred Vision: This is a common sign that you might need to see an eye specialist. If objects at a distance or close up start to look fuzzy, it’s time to get your eyes checked.
- Frequent Headaches: Regular headaches can sometimes be linked to vision problems. If you’re experiencing headaches more often, it might be due to your eyes straining to see clearly.
- Eye Strain or Fatigue: Spending long hours in front of screens can cause eye strain. If you’re experiencing discomfort, dry eyes, or fatigue, it’s wise to consult an eye specialist.
- Sudden Changes in Vision: Any sudden changes, like flashes of light, increased floaters, or a loss of vision, require immediate attention from an eye specialist.
- Difficulty with Night Vision: Struggling to see in low light conditions or while driving at night is a sign that you should visit an eye specialist.
The Role of Regular Eye Examinations in Managing Astigmatism
Regular eye examinations play a pivotal role in the management of astigmatism, a common vision condition characterized by an irregularly shaped cornea. Here’s why regular check-ups are essential:
- Early Detection: Regular eye exams help in the early detection of astigmatism. Early diagnosis means timely treatment, which can prevent the condition from worsening.
- Prescription Accuracy: For those with astigmatism, vision can change over time. Regular eye exams ensure that any corrective lenses are up-to-date, providing optimal vision correction.
- Monitoring Eye Health: Eye specialists can monitor the overall health of your eyes. This is crucial as astigmatism can sometimes be associated with other eye conditions.
- Customized Treatment Plans: Regular check-ups allow eye specialists to provide personalized treatment plans. These plans are tailored to the unique needs of each individual, ensuring the best care for your eyes.
However, recognizing when to see an eye specialist and understanding the importance of regular eye examinations, especially in managing conditions like astigmatism, are essential steps in ensuring lifelong eye health. Taking proactive steps towards eye care can lead to better vision and overall wellbeing.
FAQs About Astigmatism
What is Astigmatism?
Astigmatism is a common vision condition caused by an irregular shape of the cornea or lens in the eye. This irregularity can lead to blurred vision at various distances.
How is Astigmatism Diagnosed?
Astigmatism is typically diagnosed through a comprehensive eye exam, which includes testing for visual acuity and a keratometry test to measure the curvature of the cornea.
Can Astigmatism Get Worse Over Time?
Astigmatism can change over time, usually due to natural changes in the shape of the eye. Regular eye exams are important to monitor any changes in your vision.
Is Astigmatism Treatable?
Yes, astigmatism can be corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery, depending on the severity and the individual’s needs.
Does Astigmatism Affect Only Adults?
No, astigmatism can occur in both children and adults. It’s important for children to have regular eye exams to detect astigmatism early.
Can Astigmatism Be Prevented?
There are no specific ways to prevent astigmatism as it is often a natural variation in the eye’s structure. However, protecting your eyes and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall eye health.
Will Astigmatism Affect My Lifestyle?
With proper correction, astigmatism generally does not significantly impact daily activities. Many people with astigmatism lead a normal, active lifestyle.
Do I Need Special Lenses for Astigmatism?
If you have astigmatism, your eye doctor may prescribe special lenses called toric lenses for glasses or contacts that are specifically designed to correct the irregular curvature of your eye.
Remember, it’s always best to consult with an eye care professional for any concerns or questions about astigmatism or your vision health.
Conclusion
We encourage readers to take their eye health seriously. If you’re experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned, it’s advisable to consult with an eye care professional. Early detection and treatment of astigmatism can prevent further complications and ensure that your vision remains as clear and comfortable as possible.
Remember, taking care of your eyes is a vital part of your overall health care routine. Don’t overlook the importance of regular eye check-ups and be proactive in seeking professional advice if you notice any changes in your vision.
Your eyes deserve the best care, and addressing astigmatism symptoms promptly can help maintain their health and functionality.