Asbestosis Treatment: Asbestosis is a chronic lung condition caused by prolonged exposure to asbestos fibers. These tiny, sharp fibers can become lodged in the lung tissues, causing inflammation and scarring (fibrosis).
Over time, this scarring impairs the lungs’ ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide, leading to symptoms like shortness of breath and a persistent cough.
What is Asbestosis?
Asbestosis is a chronic lung disease caused by inhaling asbestos fibers. Over time, these fibers can cause scarring and inflammation in the lungs, leading to difficulty breathing and decreased lung function. It’s considered a type of pneumoconiosis, which refers to lung diseases caused by dust inhalation.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Exposure to Asbestos: The primary cause of asbestosis is prolonged exposure to asbestos, a group of minerals found in natural environments and used in various industries due to their resistance to heat, electricity, and chemical damage.
- Occupational Exposure: People working in mining, construction, shipbuilding, and manufacturing industries are at a higher risk due to higher chances of asbestos exposure.
- Environmental Exposure: Living near asbestos mines or processing plants can also increase the risk of developing asbestosis.
- Secondary Exposure: Family members of workers exposed to asbestos can also be at risk due to asbestos fibers brought home on clothing.
- Smoking: Although not a direct cause, smoking can exacerbate the condition and increase the severity of the symptoms.
Prevalence and Impact
Asbestosis cases are more prevalent in regions and industries where asbestos use was or still is widespread. Statistics show that:
- The incidence of asbestosis has decreased in countries where asbestos use is banned or regulated.
- However, in regions where asbestos is still used, cases continue to be reported.
- The latency period of asbestosis can be lengthy, with symptoms appearing years after initial exposure, making early diagnosis challenging.
- Asbestosis contributes significantly to occupational lung diseases, underscoring the importance of workplace safety measures and regulations.
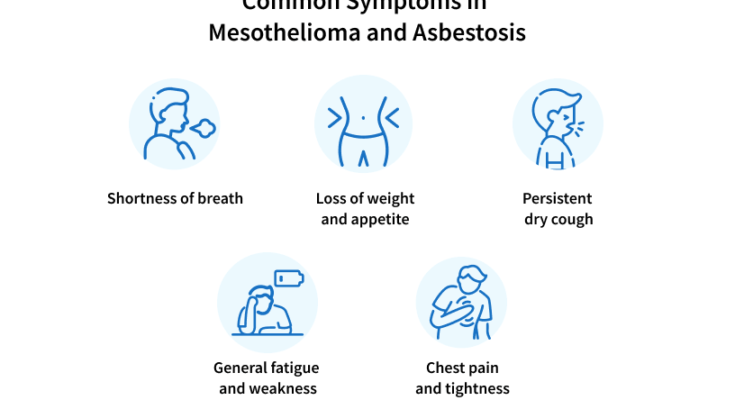
Symptoms of Asbestosis
Understanding the symptoms of asbestosis is crucial for early detection and effective management.
Early Symptoms of Asbestosis
Early symptoms of asbestosis can be subtle and often mistaken for signs of less serious conditions. They include:
- Shortness of Breath: Initially only during physical exertion, but gradually becoming more noticeable.
- Persistent Dry Cough: A non-productive cough that doesn’t seem to go away.
- Chest Tightness or Pain: Discomfort in the chest area, especially when breathing deeply.
- Fatigue: General feeling of tiredness or lack of energy.
Advanced Symptoms of Asbestosis
As the disease progresses, symptoms become more severe and debilitating. Advanced symptoms include:
- Increased Shortness of Breath: Difficulty in breathing even during rest.
- Clubbing of Fingers and Toes: Bulging of the fingertips or toes due to lack of oxygen.
- Crackling Sound When Breathing: A distinctive dry crackling sound heard with a stethoscope.
- Loss of Appetite and Weight Loss: Decrease in body weight and reduced interest in eating.
Differentiating Asbestosis from Other Respiratory Diseases
While asbestosis shares common symptoms with other respiratory conditions, certain factors help differentiate it:
- History of Asbestos Exposure: Asbestosis is primarily linked to a history of prolonged asbestos exposure, unlike other respiratory diseases.
- Progression Rate: The progression of symptoms in asbestosis is typically slower compared to other lung diseases like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Clubbing of Fingers and Toes: This is more specific to asbestosis and some other types of interstitial lung disease.
- Distinctive Lung Scarring: Imaging tests like X-rays and CT scans reveal a unique pattern of scarring in the lungs characteristic of asbestosis.
Recognizing the symptoms of asbestosis early can lead to more effective management and improved quality of life. If you have a history of asbestos exposure and experience any of these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional immediately.
Diagnosing Asbestosis: Key Steps and Methods
Emphasizing Early Diagnosis in Asbestosis Treatment
The timely identification of asbestosis, a lung disease caused by asbestos exposure, is crucial. Early diagnosis significantly enhances the effectiveness of treatments and improves patient outcomes. Detecting asbestosis at an initial stage can prevent the progression of the disease and manage symptoms more effectively. Therefore, understanding the importance of early diagnosis is pivotal for both patients and healthcare providers.
Diagnostic Methods: Comprehensive Approaches
Imaging Tests: These are fundamental in diagnosing asbestosis. High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scans are particularly effective. They provide detailed images of the lungs, helping identify any abnormalities or changes caused by asbestos exposure. Chest X-rays are also used, though they are less detailed compared to HRCT scans.
Lung Function Tests: These tests measure how well your lungs are working. They include spirometry, which assesses how much air you can inhale and exhale, and how quickly you can do it. These tests help in determining the impact of asbestosis on lung function.
Biopsies: In some cases, a lung tissue biopsy may be necessary. This involves taking a small sample of lung tissue for analysis. It’s typically recommended when the imaging tests and lung function tests do not conclusively diagnose asbestosis.
The Role of Medical History and Occupational Exposure Assessment
A comprehensive review of a patient’s medical history and an assessment of their occupational exposure to asbestos are critical. This involves discussing past jobs, the duration of exposure, and any known instances of asbestos contact. This information, combined with the results of imaging and lung function tests, aids physicians in making a precise diagnosis of asbestosis.
Treatment Options for Asbestosis
Although there is no cure, effective treatments can alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Understanding the available options is crucial for those affected.
Medications: Managing Symptoms Effectively
A cornerstone in treating asbestosis involves medications. These drugs aim to manage symptoms, reducing discomfort and improving respiratory function. Commonly prescribed medications include:
- Inhalers: Bronchodilators help open airways, making breathing easier.
- Corticosteroids: Used to reduce inflammation in the lungs.
- Mucolytics: These help thin mucus, making it easier to cough up.
It’s important to note that while these medications can be effective in symptom management, they do not cure asbestosis.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Enhancing Respiratory Health
Pulmonary rehabilitation is a comprehensive program that includes exercise training, health education, and breathing techniques. This therapy aims to enhance the physical and emotional health of individuals with lung diseases like asbestosis. Benefits include:
- Improved lung function.
- Increased stamina and strength.
- Better quality of life.
Oxygen Therapy: A Lifeline in Advanced Cases
For advanced cases of asbestosis, where lung function is significantly impaired, oxygen therapy can be a lifeline. This treatment involves breathing in oxygen-rich air through a mask or nasal prongs. Oxygen therapy can greatly improve daily activities and sleep quality for those with severe respiratory difficulties.
Treating asbestosis requires a tailored approach, considering the individual’s symptoms and disease severity. While current treatments focus on managing symptoms, ongoing research continues to explore new avenues for better outcomes. Consulting with healthcare professionals is crucial for an effective treatment plan.
Advanced Treatments and Research for Asbestosis
Advancements in medical research and treatments offer new hope for patients. This article delves into the cutting-edge therapies and the latest research in the field.
Lung Transplants: A Lifeline for Severe Cases
For individuals with severe asbestosis, lung transplants have emerged as a vital treatment option. This procedure involves replacing the damaged lung(s) with healthy ones from a donor. It’s crucial for patients to understand the criteria for eligibility, the risks involved, and the lengthy recovery process. Lung transplants can dramatically improve the quality of life and extend survival for patients with advanced asbestosis.
Experimental Therapies: The Frontier of Asbestosis Treatment
Researchers are continuously exploring new therapeutic avenues. These experimental treatments, still in the testing phase, promise to revolutionize asbestosis care. They include:
- Gene Therapy: Targeting the genetic factors that contribute to asbestosis.
- Stem Cell Treatment: Utilizing stem cells to repair or replace damaged lung tissue.
- Novel Medications: Developing drugs that can more effectively manage symptoms or halt disease progression.
The Horizon of Asbestosis Research
Recent studies have shed light on various aspects of asbestosis, paving the way for potential future treatments. Key areas of focus include:
- Understanding the Disease Mechanism: Researching how asbestosis develops at the molecular level.
- Early Detection Techniques: Developing methods for earlier diagnosis, leading to more effective treatment.
- Preventive Strategies: Investigating ways to prevent the onset of asbestosis in individuals exposed to asbestos.
However, while asbestosis remains a challenging condition, ongoing research and advanced treatments offer a beacon of hope. Staying informed about these developments is crucial for patients, healthcare providers, and caregivers alike.
Living with Asbestosis: Managing Symptoms and Seeking Support
Embracing Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Adopting certain home remedies can significantly ease discomfort. Here are key strategies:
- Breathing Exercises: Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing can help improve lung efficiency.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking exacerbates asbestosis symptoms; quitting is crucial.
- Maintaining a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet supports overall health and can improve lung function.
- Regular Exercise: Gentle exercises, under medical guidance, can enhance lung capacity.
- Avoiding Lung Irritants: Minimizing exposure to dust, chemicals, and extreme cold can reduce symptom flare-ups.
The Vital Role of Regular Medical Checkups
Regular medical appointments are vital for asbestosis patients. These checkups allow for:
- Monitoring Disease Progression: Regular testing assesses lung function and checks for complications.
- Adjusting Treatments: As the condition evolves, medication and therapy might need modification.
- Addressing New Symptoms: Early detection of new symptoms leads to prompt treatment, preventing further complications.
Seeking Support: Counseling, Groups, and Education
Living with asbestosis can be challenging, making support systems crucial:
- Counseling: Professional counseling can assist in coping with the emotional burden of a chronic illness.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges offers comfort and practical advice.
- Patient Education: Understanding the disease empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care.
However, living with asbestosis requires a combination of lifestyle changes, regular medical monitoring, and robust support systems. These elements together contribute to better disease management and improved quality of life.
Prevention and Awareness of Asbestosis
Strategies for Preventing Asbestosis in High-Risk Occupations
To mitigate this risk, it’s essential to implement robust prevention strategies. Here’s how:
- Strict Adherence to Safety Regulations: Workplaces must rigorously follow safety standards set by occupational health and safety authorities. This includes using protective equipment and ensuring proper ventilation.
- Regular Risk Assessments: Conducting frequent assessments to identify areas of potential asbestos exposure is crucial. This helps in taking timely measures to reduce the risk.
- Training and Education: Employees in high-risk occupations should receive thorough training on the dangers of asbestos, safe work practices, and the correct use of protective gear.
- Health Monitoring: Regular health check-ups for workers in these environments can lead to early detection and better management of any asbestos-related diseases.
- Substituting Materials: Where possible, replacing asbestos with safer alternatives can significantly reduce the risk of asbestosis.
The Importance of Public Awareness and Education About Asbestosis
Educating the public about asbestosis is equally important. Awareness campaigns can play a pivotal role in prevention. Key points include:
- Understanding Asbestosis: Educating about what asbestosis is, its causes, symptoms, and long-term effects can help individuals identify potential risks in their environments.
- Recognizing Asbestos in Buildings: Many older buildings contain asbestos. Public knowledge about recognizing these materials can lead to safer handling and removal.
- Health Implications: Informing about the health risks associated with asbestos exposure encourages people to take necessary precautions in their homes and workplaces.
- Resource Availability: Providing information on where to find professional help for asbestos removal and health check-ups is vital.
However, a combination of stringent safety measures in high-risk occupations and widespread public education can effectively reduce the incidence of asbestosis. By understanding and respecting the dangers of asbestos, we can create a safer environment for everyone.
Conclusion
We strongly encourage our readers to consult healthcare professionals if they suspect they might be suffering from asbestosis. Remember, symptoms like persistent cough and shortness of breath should never be ignored, especially if you have a history of asbestos exposure.
In conclusion, awareness and proactive healthcare engagement are key in combating asbestosis. Stay informed, stay safe, and never hesitate to seek professional medical advice.