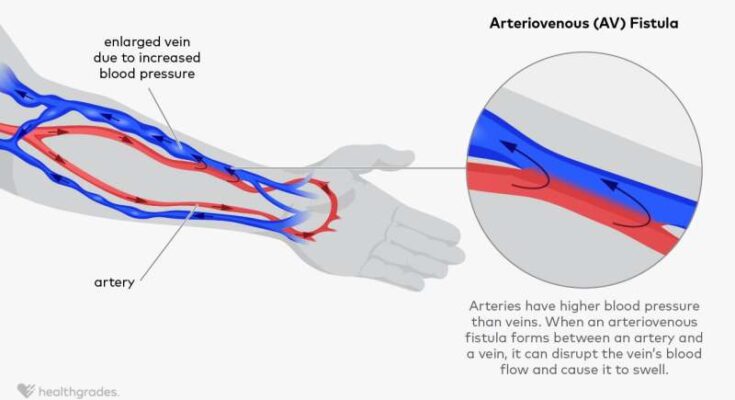
Arteriovenous Fistula Symptoms: An Arteriovenous Fistula (AVF) is an abnormal connection between an artery and a vein, bypassing the capillary system. This condition can occur anywhere in the body but is most commonly seen in the limbs and kidneys.
Understanding its symptoms and causes is crucial for early detection and treatment.
What is an Arteriovenous Fistula?
Arteriovenous fistula (AVF) is a medical condition where there is an abnormal connection between an artery and a vein. Unlike the normal flow of blood from arteries to veins through capillaries, in an arteriovenous fistula, blood flows directly from an artery into a vein, bypassing the capillaries. This condition can occur anywhere in the body but is most commonly found in the limbs.
Types of Arteriovenous Fistulas
There are two primary types of arteriovenous fistulas:
- Congenital Arteriovenous Fistula: This type is present at birth and is the result of a developmental abnormality in the vessels.
- Acquired Arteriovenous Fistula: These occur as a result of injury, surgery, or diseases that damage the blood vessels. They can also be deliberately created for medical treatments such as dialysis in patients with severe kidney disease.
Overview of Development
The development of an arteriovenous fistula can vary based on its type:
- Congenital Arteriovenous Fistula: This form develops during fetal growth. The exact cause is unknown, but it is thought to be related to genetic factors or issues during vessel formation.
- Acquired Arteriovenous Fistula: These often develop following an injury that pierces both an artery and a vein, such as a gunshot or stab wound. They can also arise after surgeries involving blood vessels or as a complication of diseases like atherosclerosis.
In some cases, arteriovenous fistulas are created intentionally for medical treatments. For example, in hemodialysis for kidney failure, an arteriovenous fistula is created to provide easy, reliable access to the blood.
Understanding arteriovenous fistulas is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. While they can be asymptomatic, they may also lead to serious complications like heart failure if left untreated. Therefore, awareness and early detection play a key role in managing this condition.
Symptoms of Arteriovenous Fistula
Here we provides a detailed list of common symptoms and explains how these symptoms can manifest and vary among individuals.
Common Symptoms of Arteriovenous Fistula
- Swelling and Pain: One of the most noticeable symptoms of an AVF is swelling in the area of the fistula. This swelling can be accompanied by pain or discomfort, which may worsen with physical activity.
- Abnormal Pulsation: Due to the abnormal connection between the artery and vein, individuals may feel a throbbing or pulsating sensation in the area of the fistula.
- Altered Skin Coloration: The skin over the fistula may change color, becoming redder or bluer than the surrounding areas. This is due to the increased blood flow and pressure in the region.
- Increased Vein Visibility: Veins near the fistula site may become more prominent or enlarged, often visible on the skin surface.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Some people with AVF may experience general fatigue and weakness, which can be a result of reduced blood flow to certain parts of the body.
- Heart-related Issues: In severe cases, an AVF can lead to heart problems, such as heart failure, due to the increased workload on the heart.
Variability in Symptoms
The manifestation of AVF symptoms can vary significantly from one person to another, influenced by factors such as the size and location of the fistula, as well as the individual’s overall health. For example:
- Location of the Fistula: Symptoms can be more pronounced if the fistula is in a location with a high concentration of nerves or near the skin’s surface.
- Size of the Fistula: Larger fistulas may cause more noticeable symptoms like pronounced swelling or pulsation.
- Individual Health Factors: People with other underlying health conditions may experience more severe or additional symptoms.
Understanding these symptoms and their potential variability is key for individuals to seek timely medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment of AVF can prevent complications and improve the quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Causes and Risk Factors of Arteriovenous Fistula
This atypical connection can develop due to various causes, necessitating a comprehensive exploration to understand its origins.
- Congenital Factors: Some individuals are born with arteriovenous fistulas. These congenital cases result from developmental anomalies in the vascular system during fetal growth.
- Trauma or Injury: Physical injuries, such as those sustained in accidents or during surgeries, can inadvertently create connections between arteries and veins, leading to arteriovenous fistulas.
- Medical Procedures: Certain medical interventions, like catheterization or surgery, particularly in areas dense with blood vessels, can inadvertently result in the formation of these fistulas.
- Disease-Induced: Diseases that weaken blood vessel walls, such as atherosclerosis or high blood pressure, may contribute to the development of arteriovenous fistulas.
Risk Factors and Predispositions
Understanding the risk factors associated with arteriovenous fistulas is crucial for both prevention and early detection.
- Genetic Predisposition: Individuals with a family history of vascular anomalies might have an increased risk of developing arteriovenous fistulas.
- Age and Gender: While arteriovenous fistulas can occur at any age, certain types may be more prevalent in specific age groups or genders.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Those with diseases that affect blood vessels, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, are at an elevated risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle choices, including smoking or a sedentary lifestyle, can exacerbate the risk of vascular diseases, potentially leading to arteriovenous fistulas.
- Previous Surgical Procedures: Individuals who have undergone surgeries involving blood vessels may have an increased risk of developing these fistulas.
However, arteriovenous fistulas stem from a variety of causes, ranging from congenital factors to lifestyle influences. Recognizing these causes and risk factors is paramount in the effective management and prevention of this vascular condition. Regular check-ups and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are vital in reducing the risk of arteriovenous fistulas, particularly for those predisposed to vascular diseases.
Diagnosis of Arteriovenous Fistula
Understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Recognizing Symptoms: The First Step in Diagnosis
The journey to diagnose an arteriovenous fistula often begins with recognizing its symptoms. Symptoms play a pivotal role in alerting individuals and healthcare professionals to the potential presence of an AVF. These symptoms can vary depending on the location and size of the fistula but commonly include swelling, a noticeable throbbing or pulsating sensation, and a change in skin color over the affected area.
Comprehensive Medical Evaluation
After noting these symptoms, a comprehensive medical evaluation is essential. This evaluation typically involves a detailed medical history and a physical examination. During the physical exam, doctors will look for signs like a distinctive whooshing sound, known as a bruit, heard through a stethoscope placed over the fistula.
Advanced Diagnostic Tests
Following the initial examination, further diagnostic tests are often required. These may include:
- Doppler Ultrasound: A non-invasive test that uses sound waves to produce images of blood flow through the vessels.
- CT Angiography: Provides detailed images of blood vessels and helps in assessing the structure and flow of blood through the arteries and veins.
- MRI: Offers detailed images of organs and structures within the body, including blood vessels.
However, diagnosing an arteriovenous fistula is a collaborative effort that starts with recognizing symptoms and leads to a series of diagnostic tests. Timely diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and preventing complications. Patients experiencing any symptoms indicative of an AVF should consult with their healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation.
Impact and Complications of Arteriovenous Fistula
Understanding the Impact of Arteriovenous Fistulas on Overall Health
Arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs) are abnormal connections between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. Their presence in the body can significantly influence overall health in various ways. Firstly, AVFs can alter normal blood flow and pressure dynamics, leading to changes in organ function. Over time, this may result in the affected organs receiving less oxygen and nutrients, impairing their performance and health.
The heart is particularly susceptible to the effects of AVFs. Since these fistulas create a path of lesser resistance for blood flow, the heart pumps harder to maintain adequate circulation. This increased workload can lead to cardiac complications, including heart failure. Moreover, the altered blood flow can affect the efficiency of dialysis treatments in patients with kidney failure, which is a common reason for the intentional creation of AVFs.
Potential Complications If Left Untreated
If arteriovenous fistulas are not appropriately managed, they can lead to a range of complications. Among the most serious are:
- Heart Failure: The heart’s increased workload to compensate for the abnormal blood flow can lead to its enlargement and eventual failure.
- Bleeding: AVFs, especially those near the skin surface, can rupture, causing significant bleeding.
- Blood Clots: The turbulent blood flow within an AVF can promote clot formation, which could lead to serious conditions like stroke or pulmonary embolism if these clots travel to the brain or lungs.
- Leg Swelling and Pain: If an AVF is present in the legs, it can cause swelling, pain, and varicose veins due to increased venous pressure.
- Ischemia: The diversion of blood flow away from certain body parts can lead to ischemia, a condition characterized by inadequate blood supply to an organ or part of the body.
However, arteriovenous fistulas can have a profound impact on overall health, especially if left untreated. They can cause significant cardiovascular strain, bleeding, clotting issues, and other local complications. Therefore, timely diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial to mitigate these risks and maintain overall health and well-being.
Treatment Options for Arteriovenous Fistula
These treatments are designed to address the unique challenges posed by this condition and to restore normal blood flow. Understanding the various treatment methods is crucial for patients and healthcare providers.
- Surgical Repair: The primary treatment for arteriovenous fistulas is surgical intervention. This involves repairing the abnormal connection between the artery and vein. The surgical process can be intricate, requiring the expertise of vascular surgeons.
- Endovascular Therapy: This minimally invasive option uses catheters and other devices to correct the fistula from within the blood vessels. It’s often preferred for its reduced recovery time and lower risk of complications compared to open surgery.
- Embolization: A specialized procedure where materials are used to block the abnormal blood vessels, effectively reducing the blood flow to the fistula. This method is often used when surgery is not feasible or as a supplementary treatment to surgery.
- Medication: While not a direct treatment for the fistula itself, medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms or related conditions. These can include blood pressure medications or anticoagulants to prevent blood clots.
Influence of Symptoms and Severity on Treatments
The choice of treatment for arteriovenous fistula heavily depends on the symptoms and severity of the condition:
- Mild Cases: In less severe cases, where symptoms are minimal, monitoring and conservative management might be recommended. This approach involves regular check-ups to assess the progression of the fistula.
- Moderate to Severe Cases: In cases where the fistula causes significant symptoms or health risks, more aggressive treatments like surgery or endovascular therapy are considered. The severity of symptoms, such as pain, swelling, or the impact on heart function, guides the treatment decision.
- Emergency Situations: In rare instances where an arteriovenous fistula leads to life-threatening complications, emergency treatment is necessary. This could involve immediate surgery or interventions to stabilize the patient’s condition.
However, treating an arteriovenous fistula requires a personalized approach, taking into account the specific characteristics of the fistula, the patient’s overall health, and the severity of symptoms. Collaboration between the patient and healthcare team is essential to choose the most effective and appropriate treatment plan.
Prevention and Management of Arteriovenous Fistula
Managing and preventing this condition is crucial for maintaining vascular health. In this section, we will explore effective strategies for prevention and management, and highlight the importance of early detection through symptom awareness.
Early Detection: The Key to Effective Management
Early detection of arteriovenous fistula is vital. Recognizing the signs and symptoms early can significantly improve the outcome. Common symptoms include swelling, a noticeable mass over the affected area, and a pulsating sensation. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical advice promptly.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing an arteriovenous fistula primarily involves reducing risk factors associated with its development. Here are some practical tips:
- Maintain Cardiovascular Health: A healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise and a balanced diet can help prevent conditions leading to AVF.
- Monitor Blood Pressure: High blood pressure can increase the risk of AVF. Regular monitoring and management are important.
- Avoid Injury to Limbs: Trauma to limbs can lead to AVF. Be cautious during activities that might cause injury.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Routine medical check-ups can help detect any vascular irregularities early.
Management Techniques
If an arteriovenous fistula develops, proper management is crucial. Here’s what you can do:
- Medical Consultation: Always consult with healthcare professionals for appropriate treatments which may include surgery or other procedures.
- Medication: Depending on the severity, medications might be prescribed to manage symptoms or underlying conditions.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can aid in managing AVF, including regular exercise and a nutritious diet.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are necessary to monitor the condition and adjust treatments as needed.
Preventing and managing an arteriovenous fistula effectively involves a combination of lifestyle changes, awareness of symptoms, and seeking timely medical advice. Early detection is crucial for a positive outcome. By following these tips and strategies, individuals can significantly reduce their risk and manage the condition effectively if it arises. Remember, your vascular health is an integral part of your overall well-being. Stay informed and proactive in maintaining it.
Patient Stories and Case Studies: Understanding the Impact of Arteriovenous Fistula
Real-Life Examples to Illustrate the Impact
Arteriovenous fistula (AVF) is a unique medical condition where an abnormal connection forms between an artery and a vein. Understanding the real-world impact of AVF can be best achieved through patient stories and case studies. These real-life examples not only provide insights into the medical aspects of AVF but also into the personal journeys of those affected.
How Symptoms Play a Role
Each case of AVF is unique, and the symptoms can vary widely from patient to patient. In our patient stories and case studies section, we delve into how these symptoms have played a critical role in diagnosis, treatment, and the overall quality of life of the patients. These stories highlight the diversity of AVF symptoms, ranging from mild discomfort to severe complications, and how they guide medical professionals in providing the best care.
Here we designed to be both informative and empathetic, shedding light on the challenges faced by individuals with arteriovenous fistula and how they navigate their health journey. Whether you are a medical professional, a patient, or simply someone interested in learning more about AVF, these stories offer valuable perspectives and insights.
FAQ Section on Arteriovenous Fistula Symptoms and Causes
What is an Arteriovenous Fistula?
An arteriovenous fistula (AVF) is an abnormal connection between an artery and a vein. Normally, blood flows from your arteries to your capillaries and then to your veins. An AVF disrupts this path, allowing blood to flow directly from an artery into a vein.
What Causes an Arteriovenous Fistula?
AVFs can occur naturally or be surgically created for medical treatments like dialysis. Natural causes include genetic conditions, trauma, and certain diseases that weaken blood vessel walls.
What are the Common Symptoms of an Arteriovenous Fistula?
Symptoms of an AVF may include:
- Swelling in the arms or legs
- A throbbing sensation near the site of the fistula
- Decreased blood pressure
- Fatigue and weakness
Can an Arteriovenous Fistula Lead to Complications?
Yes, if left untreated, AVFs can lead to serious complications like heart failure, blood clots, and bleeding.
How is an Arteriovenous Fistula Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves physical examination, ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI to assess the blood flow and structure of the fistula.
What are the Treatment Options for an Arteriovenous Fistula?
Treatment depends on the size and location of the fistula. Options include monitoring, compression therapy, embolization, surgery, or in some cases, no treatment if it’s not causing problems.
Can Lifestyle Changes Help Manage an Arteriovenous Fistula?
While lifestyle changes alone can’t cure an AVF, they can help manage symptoms. This includes regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding activities that put pressure on the fistula area.
When Should I See a Doctor for an Arteriovenous Fistula?
If you experience symptoms like swelling, pain, or changes in your skin color near a vein or artery, you should consult a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing complications.
Conclusion
In summary, an arteriovenous fistula (AVF) is a critical medical condition characterized by an abnormal connection between an artery and a vein. This condition, often associated with chronic kidney disease, demands immediate attention and management due to its complex nature and potential complications.
The importance of awareness about AVF cannot be overstated. Early detection and intervention are crucial in managing this condition effectively. Educating the public and healthcare providers about the signs and symptoms of AVF leads to timely diagnosis and treatment, thereby reducing the risk of serious health issues such as heart failure or stroke.
Furthermore, understanding AVF is essential for patients undergoing hemodialysis, as it is commonly used for vascular access in these treatments. Proper management and care of an AVF can significantly improve the quality of life for these patients.
In conclusion, spreading awareness and promoting early intervention for arteriovenous fistulas is vital for better health outcomes. It not only aids in effective disease management but also highlights the importance of regular medical check-ups and proactive healthcare approaches.