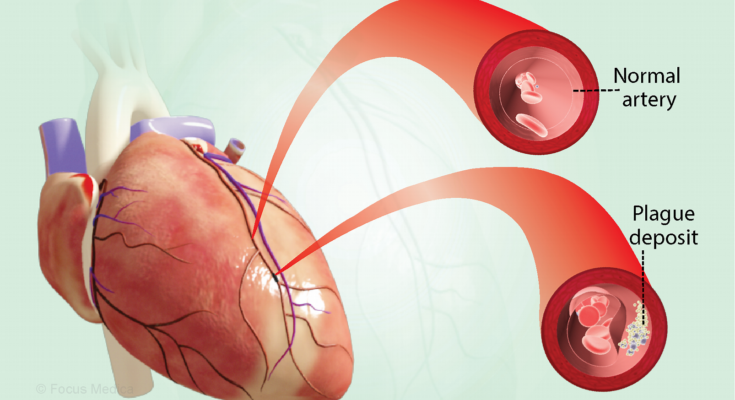
Arteriosclerosis / Atherosclerosis Treatment: Arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis are terms often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. Arteriosclerosis refers to the hardening and loss of elasticity of the arteries.
Atherosclerosis, a type of arteriosclerosis, involves the buildup of fats, cholesterol, and other substances in and on the artery walls.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the diagnosis and treatment of these conditions.
Understanding Arteriosclerosis and Atherosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis are often confused, yet they represent distinct conditions affecting the arteries. Understanding their definitions, differences, causes, risk factors, and impact on overall health is essential for maintaining cardiovascular well-being.
Definitions and Differences
Arteriosclerosis refers to the general hardening and thickening of the arteries. It’s a broad term encompassing various conditions where the arterial walls lose elasticity. Atherosclerosis, on the other hand, is a type of arteriosclerosis. It specifically involves the buildup of fats, cholesterol, and other substances in and on the artery walls (plaque), which can restrict blood flow.
The key difference lies in their nature: arteriosclerosis is the broad category of artery stiffness, while atherosclerosis is a specific manifestation involving plaque buildup.
Causes and Risk Factors
Both conditions share common risk factors:
- Age: As you get older, your arteries naturally harden.
- High blood pressure: This can damage artery walls, making them more susceptible to plaque accumulation.
- High cholesterol: Elevated levels of bad cholesterol contribute to plaque formation.
- Smoking and alcohol use: These habits damage the inner lining of arteries.
- Lifestyle: Lack of exercise and unhealthy eating can escalate the risk.
- Family history: Genetics play a role in your susceptibility to these conditions.
Understanding these risk factors is crucial for prevention and management.
Impact on Overall Health
The impact of arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis on health is significant. They can lead to dangerous conditions such as:
- Heart attack: Caused by blocked coronary arteries.
- Stroke: Occurs when brain arteries are blocked or burst.
- Peripheral artery disease: Affects legs and arms when their arteries are narrowed.
Prevention and management involve lifestyle changes, medications, and in severe cases, surgery. Regular check-ups, maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking are vital steps in mitigating these risks.
By understanding the nuances of arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis, individuals can take proactive steps towards heart health and overall well-being.
Signs and Symptoms of Arteriosclerosis and Atherosclerosis
This guide outlines the common symptoms associated with each stage of these conditions, helping you stay informed about your cardiovascular health.
Common Symptoms
- Chest Pain or Angina: One of the most noticeable symptoms, often caused by the reduced blood flow to the heart.
- Shortness of Breath: This symptom may occur as a result of the heart not getting enough oxygen-rich blood.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Limited blood flow can lead to a lack of energy.
- Pain in Specific Body Parts: This can include pain in the legs while walking, or in other areas, depending on which arteries are affected.
- High Blood Pressure: As arteries narrow, blood pressure can increase.
- Numbness or Weakness: This can occur in parts of the body where blood flow is restricted.
Subtle Signs
Some symptoms of arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis can be subtle, such as mild chest discomfort or breathlessness during physical activity. These early signs should not be ignored.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Prompt medical attention is crucial in managing arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis. It’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Persistent Chest Pain: If chest pain lasts for more than a few minutes or is recurring.
- Sudden Severe Breathlessness: This can be an indication of a heart problem.
- Unexplained Fatigue: Especially if it’s accompanied by other symptoms.
- Irregular Heartbeats: Any change in the rhythm or pattern of your heartbeat.
- Any Sign of a Stroke: Including sudden numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the body, difficulty speaking, or sudden vision problems.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis is crucial for early intervention and effective management. Regular check-ups and consultations with a healthcare provider are key to preventing serious complications associated with these conditions. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, do not hesitate to seek medical advice.
Diagnosis of Arteriosclerosis and Atherosclerosis: A Comprehensive Guide
Recognizing these conditions early is pivotal for effective management and treatment. Here, we delve into the commonly employed methods for diagnosing both arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis.
Key Diagnostic Methods
Physical Examination and Medical History: The first step in diagnosing these conditions involves a thorough physical examination and review of the patient’s medical history. This process helps identify risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and family history of heart disease.
Blood Tests: Blood tests are critical in measuring cholesterol levels, triglycerides, and other substances that may indicate atherosclerosis.
Imaging Tests: Several imaging techniques play a crucial role in diagnosing these conditions:
- Ultrasound: This non-invasive method uses sound waves to create images of the arteries, helping detect plaque buildup and blood flow issues.
- Angiography: Involves injecting a dye into the arteries, visible on X-rays, to locate blockages or narrowing.
- CT Scans and MRI: These advanced imaging methods provide detailed pictures of the arteries and can detect hardening and plaque accumulation.
Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI): This simple test compares blood pressure measurements in the ankle and arm to check for poor blood flow often associated with atherosclerosis.
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): This test records the heart’s electrical activity and can detect irregular heart rhythms, a common consequence of arterial diseases.
Stress Tests: These tests monitor heart function and blood flow during physical exertion, highlighting issues not always evident at rest.
The Importance of Accurate Diagnosis in Treatment Planning
Accurate diagnosis of arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis is critical for several reasons:
- Personalized Treatment: Each patient’s condition varies, and an accurate diagnosis allows for tailored treatment plans addressing specific needs and risk factors.
- Preventing Complications: Early detection and appropriate treatment can prevent severe complications like heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease.
- Monitoring Disease Progression: Regular diagnostic evaluations help monitor the progression of the disease, allowing timely adjustments in treatment.
- Improving Quality of Life: Accurate diagnosis and effective management of these conditions significantly enhance patients’ quality of life and overall health outcomes.
However, the diagnosis of arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis involves a combination of physical assessments, blood tests, and advanced imaging techniques. Accurate diagnosis is essential in devising personalized treatment plans, preventing complications, monitoring disease progression, and ultimately improving patient outcomes. Regular check-ups and adherence to treatment guidelines are crucial in managing these arterial conditions effectively.
Treatment Strategies for Arteriosclerosis / Atherosclerosis
Effective management and treatment of these conditions are crucial for reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other serious complications. This article discusses various treatment strategies, focusing on lifestyle changes, medications, and surgical options.
Lifestyle Changes and Their Impact on Treatment
- Dietary Adjustments: A heart-healthy diet plays a pivotal role in managing arteriosclerosis. This includes consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limiting saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can also significantly reduce arterial plaque buildup.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity helps improve heart health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise per week, as recommended by health professionals.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking is a major risk factor for arteriosclerosis. Quitting smoking can dramatically improve heart health and reduce the progression of artery hardening.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on your heart and can decrease cholesterol levels, thereby slowing the progression of arteriosclerosis.
- Stress Reduction: Chronic stress can contribute to artery damage. Techniques like meditation, yoga, or other stress-management strategies can be beneficial.
Medications Commonly Used in Treatment
- Cholesterol-lowering Drugs: Statins are the most commonly prescribed drugs for lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol, which is a significant contributor to plaque buildup in arteries.
- Blood Pressure Medications: High blood pressure can accelerate arteriosclerosis. Medications such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and diuretics are used to manage hypertension.
- Antiplatelet Drugs: These medications, including aspirin, help prevent blood clots, a common complication of atherosclerosis.
Surgical Options and When They Are Necessary
- Angioplasty and Stent Placement: This procedure involves inflating a small balloon inside a narrowed artery and then placing a stent to keep the artery open.
- Bypass Surgery: In severe cases, a blood vessel from another part of the body is grafted to bypass the blocked artery.
- Endarterectomy: This involves the removal of plaque from the artery wall, commonly performed in arteries of the neck to prevent stroke.
- Thrombolytic Therapy: Used in emergency situations, this involves the injection of drugs to dissolve blood clots.
These treatment strategies for arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis should be tailored to individual patient needs and medical conditions. Early diagnosis and intervention are key to managing these conditions effectively. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized treatment plans.
Advanced Treatments and Therapies for Arteriosclerosis / Atherosclerosis
Fortunately, recent advancements in medical science have led to the development of innovative treatments and therapies, offering new hope to those affected.
Exploring Emerging Therapies and Their Effectiveness
- Gene Therapy: A groundbreaking approach involves using gene therapy to target the underlying genetic factors of arteriosclerosis. By manipulating specific genes, researchers aim to reduce plaque buildup in arteries, thereby mitigating the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Nanotechnology: This cutting-edge technology utilizes nanoparticles to deliver medication directly to the affected artery walls. This targeted delivery system enhances the effectiveness of the drug while minimizing side effects, marking a significant step forward in treatment precision.
- Immunotherapy: Recent studies have explored the role of the immune system in arteriosclerosis. Immunotherapy treatments are being developed to modulate immune responses, reducing inflammation and plaque formation in arteries.
- Regenerative Medicine: Stem cell therapy and tissue engineering are at the forefront of regenerative medicine. These therapies aim to repair and regenerate damaged artery tissues, offering a potentially curative approach to arteriosclerosis.
- Lifestyle Modification Programs: While not a direct medical treatment, comprehensive lifestyle modification programs are gaining recognition for their role in managing arteriosclerosis. These programs focus on diet, exercise, and stress management to improve overall cardiovascular health.
The landscape of arteriosclerosis treatment is evolving rapidly, with new therapies showing promise in effectively managing and possibly reversing the condition. These advancements represent a significant leap forward in cardiovascular medicine, offering hope for improved patient outcomes and quality of life. As research continues, it is expected that these treatments will become more refined and widely accessible, marking a new era in the fight against arteriosclerosis and its complications.
Living with Arteriosclerosis / Atherosclerosis
Managing Arteriosclerosis / Atherosclerosis with Lifestyle Changes
Living with arteriosclerosis, also known as atherosclerosis, can be challenging, but making lifestyle changes can significantly manage the condition and improve your overall health.
- Healthy Diet: Emphasize a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Reduce the intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol to lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, crucial in slowing the progression of arteriosclerosis.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Exercise helps improve blood circulation, lowers cholesterol, and maintains a healthy weight.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for arteriosclerosis. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the progression of the disease and improve cardiovascular health.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the burden on your heart and blood vessels, easing the symptoms of arteriosclerosis.
- Stress Management: High stress can exacerbate arteriosclerosis. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help manage stress levels.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Regular visits to your healthcare provider for blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes screenings are essential. These check-ups help in early detection and management of complications related to arteriosclerosis.
Long-term Outlook and Quality of Life Considerations
The long-term outlook for individuals with arteriosclerosis varies depending on the severity of the condition and how well they manage it with lifestyle changes and medical treatment.
- Proactive Management: Proactive management of arteriosclerosis, including adhering to treatment plans and lifestyle changes, can slow or even halt the progression of the disease.
- Quality of Life: By making the necessary lifestyle adjustments, individuals with arteriosclerosis can lead a fulfilling and active life. It’s essential to stay informed about the condition and work closely with healthcare providers.
- Complications Awareness: Be aware of potential complications, such as heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking prompt medical care is vital.
- Support Systems: Leverage support systems, including family, friends, and support groups, which play a crucial role in managing the emotional aspects of living with a chronic condition.
- Continual Learning: Staying informed about the latest research and advancements in the treatment of arteriosclerosis can empower patients to make informed decisions about their health care.
However, living with arteriosclerosis requires a commitment to lifestyle changes and medical management. With the right approach, it is possible to manage the condition effectively and maintain a high quality of life. Remember, every positive step counts towards a healthier heart and a better life.
Prevention Tips for Arteriosclerosis and Atherosclerosis
Embrace a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Preventing arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis starts with a heart-healthy lifestyle. Key factors include:
- Balanced Diet: Incorporate a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit intake of saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium to maintain healthy blood vessels.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. This enhances blood circulation and helps in maintaining a healthy weight.
- No Smoking: Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke. Smoking is a major risk factor for developing these conditions.
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Limit alcohol intake. Excessive alcohol can raise blood pressure and contribute to heart disease.
Regular Health Check-ups: A Key to Early Detection
Regular health check-ups are crucial in preventing arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis. These check-ups can help in:
- Early Detection: Regular monitoring of blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other risk factors can detect early signs of artery problems.
- Personalized Advice: Healthcare professionals can provide tailored advice based on your health screenings.
- Monitoring Progress: Regular check-ups allow you to track the effectiveness of your lifestyle changes and make adjustments as needed.
Stay Informed and Proactive
- Educate Yourself: Understanding the risk factors and symptoms of arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis empowers you to make informed health decisions.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact heart health. Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Community Support: Joining support groups or community programs focused on heart health can provide motivation and tips for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
By incorporating these tips into your daily life, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis. Remember, a proactive approach and regular health check-ups are key to maintaining good heart health.
FAQs: Understanding Arteriosclerosis/Atherosclerosis Treatment
Understanding their treatment can be crucial for those affected. Here, we address some of the most common questions related to the treatment of these conditions.
1. What is the Difference Between Arteriosclerosis and Atherosclerosis?
Arteriosclerosis is a general term for the thickening and hardening of arteries. Atherosclerosis, a type of arteriosclerosis, specifically involves the buildup of plaques in the artery walls. Recognizing the differences can guide effective treatment approaches.
2. What Are the Treatment Options for Arteriosclerosis/Atherosclerosis?
Treatment typically includes lifestyle changes, medications, and possibly surgical procedures. Lifestyle modifications such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking are foundational. Medications may include cholesterol-lowering drugs, antiplatelet agents, or blood pressure medications. In severe cases, surgical interventions like angioplasty or bypass surgery might be necessary.
3. Can Lifestyle Changes Reverse Arteriosclerosis/Atherosclerosis?
While lifestyle changes cannot completely reverse these conditions, they can significantly slow their progression and reduce the risk of complications. A heart-healthy lifestyle is critical in managing these conditions.
4. Are There Any Natural Remedies for These Conditions?
While natural remedies alone cannot cure arteriosclerosis/atherosclerosis, certain dietary supplements and herbal remedies may support overall heart health. However, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider before starting any natural remedies.
5. How Often Should I Be Screened for Arteriosclerosis/Atherosclerosis?
Screening frequency depends on individual risk factors such as age, family history, and existing health conditions. Your healthcare provider can offer personalized advice on screening intervals.
6. What Are the Risks of Not Treating These Conditions?
Untreated arteriosclerosis/atherosclerosis can lead to serious complications like heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Timely treatment is crucial to prevent these outcomes.
7. Is Medication Always Necessary for Treating Arteriosclerosis/Atherosclerosis?
Medication is often a key component of treatment, especially for individuals at high risk of cardiovascular events. However, the necessity and type of medication will vary based on individual health profiles.
8. Can Diet Alone Manage Arteriosclerosis/Atherosclerosis?
While a healthy diet is a vital part of managing these conditions, it is usually part of a broader treatment plan that may include medications and lifestyle changes.
By addressing these FAQs, individuals can gain a clearer understanding of arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis treatment, paving the way for informed discussions with their healthcare providers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis pose significant health challenges, understanding their diagnosis and treatment paves the way for better management and healthier living. However, it’s essential to remember that each individual’s journey is unique.
We strongly encourage you to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice tailored to your specific health needs. By partnering with medical experts and taking proactive steps towards heart health, you can navigate these conditions with confidence and clarity, ensuring a healthier, more vibrant life.