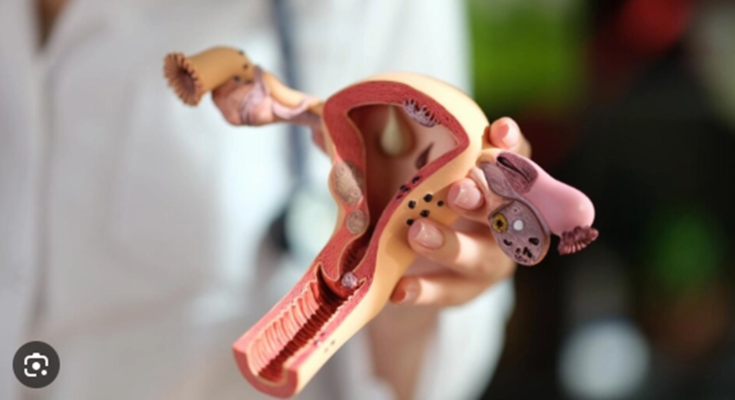
Ovarian Cysts Symptoms: Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs or pockets that develop within or on the surface of an ovary.
While many women will experience at least one ovarian cyst during their lifetime, often they remain symptom-free and are harmless.
However, when symptoms do occur, they can cause significant discomfort and require professional medical attention.
What are Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs or pockets that develop within or on the surface of an ovary. These cysts are usually benign (non-cancerous) and can form during the menstrual cycle, known as functional cysts. While most ovarian cysts are harmless and often resolve on their own without treatment, some can cause symptoms such as pelvic pain, bloating, and changes in menstrual cycles. It’s important to diagnose and monitor ovarian cysts because, on rare occasions, they can become problematic.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
There are several types of ovarian cysts, each with distinct characteristics:
- Functional Cysts: These are the most common type and are related to the menstrual cycle. They include follicular cysts, which form when the follicle doesn’t release its egg, and corpus luteum cysts, which occur when the follicle doesn’t dissolve after releasing the egg.
- Dermoid Cysts: Also known as teratomas, these cysts can contain hair, skin, or even teeth. They are rarely cancerous.
- Cystadenomas: These cysts develop from ovarian tissue and can be filled with a watery or a mucous material.
- Endometriomas: Often associated with endometriosis, these cysts are formed when endometrial tissue grows on the ovaries and can be painful during menstruation.
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): This condition is characterized by the presence of multiple small cysts within the ovaries and is associated with a range of symptoms, including irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, and hormonal imbalances.
How Common are Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts are quite common and can occur in women of all ages. They are most frequently diagnosed in women during their reproductive years. It is estimated that most premenopausal women and up to 14.8% of postmenopausal women will develop ovarian cysts at some point in their lives.
Who Typically Gets Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts can affect any woman who has menstrual cycles. However, they are most prevalent among:
- Pre-menopausal women: Women in their reproductive years are more likely to develop functional cysts due to their active menstrual cycles.
- Post-menopausal women: While less common, post-menopausal women can still develop cysts, and these cases are monitored more closely due to a higher risk of cancer.
- Women with hormonal imbalances: Conditions like PCOS, which is linked to hormonal imbalances, can increase the likelihood of developing cysts.
- Women with a history of ovarian cysts: Those who have had cysts previously are at a higher risk of developing new cysts.
However, understanding the nature of ovarian cysts and recognizing the signs can lead to early detection and management, ensuring better outcomes and health for women experiencing this condition.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs or pockets within or on the surface of an ovary. While many women may not experience noticeable symptoms, others may encounter a range of signs indicating the presence of cysts. Understanding these symptoms can aid in early detection and management.
Detailed Explanation of Common Symptoms
- Pelvic Pain: A persistent or intermittent pain that may radiate to the lower back and thighs. This pain often occurs just before the menstrual period begins or ends.
- Bloating or Swelling: An uncomfortable sensation of fullness or tightness in the abdomen, which can sometimes be mistaken for digestive issues.
- Menstrual Irregularities: Unusually heavy or light periods, or irregular menstrual cycles, can be a sign of ovarian cysts.
- Pain During Intercourse: Often described as a sharp or deep pain during or after sexual activity.
- Pressure Symptoms: Increased urgency to urinate or difficulties emptying the bladder fully, as well as constipation, can occur if a cyst is pressing on nearby organs.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Similar to pregnancy symptoms, nausea paired with other symptoms on this list can suggest the presence of a cyst.
How to Identify Early Signs of Ovarian Cysts
Recognizing early signs of ovarian cysts often involves paying close attention to your body’s signals. Here’s what to look out for:
- Subtle Pain Changes: Note any new, unusual, or worsening pain around the pelvic area, especially around your menstrual cycle.
- Changes in Menstrual Patterns: Be aware of any significant changes in your menstrual cycle, including timing, flow, and associated pain.
- Unexplained Bloating: Persistent bloating that doesn’t go away with usual dietary changes or digestive aids can be an early warning sign.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It is crucial to consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Severe, Sudden Abdominal Pain: This can be a sign of a ruptured cyst or ovarian torsion, both of which require immediate medical attention.
- Persistent or Worsening Symptoms: If the common symptoms listed earlier persist or worsen, it’s important to get evaluated.
- Unusual Menstrual Changes: Any marked changes in your menstrual cycle that deviate from your norm should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
If you’re unsure about your symptoms or their severity, it’s always better to err on the side of caution and consult a healthcare provider.
Causes and Risk Factors of Ovarian Cysts
Below, we detail the common causes and enumerate the risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing these cysts.
Causes of Ovarian Cysts
- Hormonal Fluctuations: The most common type of ovarian cysts, functional cysts, form during the menstrual cycle. They are typically harmless and often resolve without treatment.
- Endometriosis: Women with endometriosis can develop a type of ovarian cyst called an endometrioma. Tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus grows outside it and can attach to the ovaries, forming a cyst.
- Pregnancy: During early pregnancy, cysts may develop to support the pregnancy until the placenta forms. Sometimes, these cysts can remain on the ovary throughout pregnancy and occasionally even after the birth.
- Severe Pelvic Infections: Infections that spread to the ovaries and fallopian tubes can lead to the formation of cysts.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): This condition is characterized by many small cysts on the ovaries and hormonal imbalances that can affect menstrual periods and fertility.
List of Risk Factors for Ovarian Cysts
- Reproductive Age: Women of reproductive age are at higher risk since cysts often relate to the menstrual cycle.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions like PCOS, which is associated with an imbalance of reproductive hormones, increase the likelihood of cyst development.
- Past Ovarian Cyst History: Women who have previously had one or more ovarian cysts are more prone to developing new cysts in future menstrual cycles.
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Irregular cycles can indicate hormonal imbalances, which may increase the risk of cyst formation.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can influence hormone levels and increase the risk of developing ovarian cysts and other health issues.
- Tamoxifen Therapy: Use of the drug Tamoxifen for breast cancer treatment has been linked to an increased risk of ovarian cysts in premenopausal women.
- Fertility Drugs: The use of fertility drugs can stimulate the ovaries, sometimes leading to the formation of cysts.
If you experience symptoms like pain, bloating, or changes in your menstrual cycle, consulting a healthcare provider is advisable.
Diagnosing Ovarian Cysts
Below, we explore the common diagnostic methods, the importance of medical history and physical exams, and what to expect during a diagnostic appointment.
Common Diagnostic Methods for Ovarian Cysts
- Ultrasound: This is the most commonly used method to confirm the presence of ovarian cysts. An ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the ovaries, allowing healthcare providers to see and evaluate the cyst’s shape, size, and location.
- CT Scan: For further detailed imaging, a CT scan may be utilized. This method provides cross-sectional images of the pelvic region and can help identify more complex cysts or rule out other causes of symptoms.
- MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) offers high-resolution images of the ovaries and is particularly useful in differentiating between benign and malignant cysts.
- Blood Tests: Certain blood tests can be performed to check for cancer markers. CA-125, a protein found at higher levels in some women with ovarian cancer, is often measured if a cyst appears potentially cancerous.
- Laparoscopy: In some cases, a diagnostic laparoscopy may be done. This minimally invasive surgery involves inserting a small camera through a tiny incision to take a direct look at the ovaries, and possibly removing the cyst.
The Role of Medical History and Physical Exams in Diagnosis
- Medical History: Discussing your medical history with your healthcare provider is vital. It includes any previous diagnoses of cysts, menstrual cycle regularity, symptoms experienced, and family history of ovarian or breast cancer.
- Physical Exam: During the physical exam, the doctor will palpate the abdomen to check for masses or swelling. They may also perform a pelvic exam to manually feel for abnormalities in the uterus, ovaries, and other pelvic organs.
What to Expect During a Diagnostic Appointment
- Review of Symptoms: Be prepared to discuss the specific symptoms you’ve been experiencing, such as pelvic pain, bloating, or changes in menstruation.
- Personal and Family Medical History: You will need to provide detailed information about your own and your family’s medical history, especially related to any reproductive health issues.
- Physical Examinations: Expect a thorough physical and pelvic examination. The doctor will check for any noticeable abnormalities that might suggest the presence of cysts.
- Diagnostic Tests: Based on the initial examination, your doctor might schedule one or more diagnostic tests like an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to confirm the diagnosis and assess the cysts’ characteristics.
- Discussion of Next Steps: After the diagnosis, your doctor will discuss the next steps with you, including possible treatment options or follow-up tests if necessary.
However, understanding the diagnostic process for ovarian cysts can help ease any anxieties about medical appointments and allows patients to prepare for discussions with their healthcare provider.
Complications Associated with Ovarian Cysts
Understanding these potential complications is crucial for timely intervention and management.
List of Potential Complications
- Rupture: A ruptured ovarian cyst can cause severe pain and internal bleeding. This is often a sudden and intense situation requiring immediate medical attention.
- Torsion: Ovarian torsion occurs when a cyst becomes so large that it causes the ovary to move from its original position, potentially cutting off its blood supply. This can lead to ovarian damage and is considered a medical emergency.
- Infection: Though rare, if a cyst becomes infected, it can lead to serious complications and may necessitate surgical removal.
- Cancer: In some cases, what appears to be a benign cyst may actually be an early form of ovarian cancer. Regular monitoring of cysts is essential to rule out malignancy.
Symptoms of Emergencies Related to Ovarian Cysts
It is important to recognize the symptoms that may indicate a cyst-related emergency:
- Sudden, severe abdominal pain
- Pain accompanied by fever or vomiting
- Rapid breathing or shortness of breath
- Dizziness, weakness, or feeling faint
- Rapid heart rate
Immediate medical evaluation is required if any of these symptoms occur, as they can signify a ruptured cyst or ovarian torsion.
Importance of Monitoring and Managing Ovarian Cysts
Regular monitoring of ovarian cysts is vital for several reasons:
- Preventing complications: Early detection of changes in cyst size or appearance can help prevent serious complications.
- Differentiating between benign and malignant cysts: Regular ultrasounds and follow-up visits help ensure that cysts are benign and monitor any changes that might suggest malignancy.
- Guiding treatment decisions: Monitoring provides critical information that can help decide whether a wait-and-see approach, medication, or surgery is the best course of action.
However, managing ovarian cysts effectively involves regular medical check-ups, understanding the symptoms of potential emergencies, and maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider.
Treatment Options for Ovarian Cysts
Understanding the treatment options available is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing complications. Below, we outline common treatment approaches, factors influencing treatment decisions, and what to expect from different treatment options.
Common Treatment Approaches
1. Watchful Waiting: Many ovarian cysts are benign and may resolve without treatment. Doctors often recommend regular monitoring with ultrasounds to ensure the cysts do not grow or cause complications.
2. Medication: Hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills, may be prescribed to prevent the formation of new cysts in premenopausal women, though they do not shrink existing cysts.
3. Surgery: Surgical intervention may be required if cysts are large, cause symptoms, or persist. The type of surgery depends on the size and type of the cyst. Options include:
- Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive surgery used for smaller cysts. It involves small incisions and a camera to guide the surgery.
- Laparotomy: Used for larger cysts or cysts that may be cancerous. This procedure involves a larger incision in the abdomen to remove the cyst.
Factors Influencing Treatment Decisions
- Size and Appearance of the Cyst: Larger cysts that appear unusual may require aggressive treatment like surgery to rule out cancer.
- Symptoms: Painful or symptomatic cysts often necessitate more immediate treatment to relieve discomfort and prevent further complications.
- Age and Menopausal Status: Postmenopausal women have a higher risk of ovarian cancer, and doctors may recommend surgery to eliminate this risk.
- Cyst Type: Functional cysts often resolve on their own, while dermoid cysts, cystadenomas, and endometriomas may require surgical removal.
What to Expect from Different Treatment Options
- Watchful Waiting: Patients can expect regular check-ups and ultrasounds. It’s essential to monitor any changes in symptoms and report them to a healthcare provider.
- Medication: While medications do not eliminate existing cysts, they can help prevent new ones. Side effects can include nausea, breast tenderness, and changes in mood or bleeding patterns.
- Surgery: Recovery time varies by type of surgery. Laparoscopy offers a faster recovery with minimal scarring, while laparotomy may require a longer recovery period. Both procedures carry risks such as infection, bleeding, or damage to nearby organs.
By understanding these treatment options and what to expect, patients can make informed decisions with their healthcare providers, leading to better management of ovarian cysts and improved outcomes.
Prevention and Management of Ovarian Cysts
Here’s a comprehensive guide to the prevention and management of ovarian cysts, focusing on at-home symptom management, lifestyle adjustments, and the importance of regular gynecological check-ups.
Tips for Managing Symptoms at Home
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate the pain associated with ovarian cysts. Always consult with your doctor before starting any medication.
- Heat Therapy: Applying a heat pad or a hot water bottle to your lower abdomen can help soothe the pain caused by ovarian cysts.
- Relaxation Techniques: Stress can exacerbate symptoms, so practices like yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can be beneficial.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids throughout the day helps maintain overall health and can reduce bloating and discomfort.
- Dietary Adjustments: Some women find relief by adjusting their diets. Reducing salt intake can decrease bloating, and incorporating more fiber can help reduce constipation, which may aggravate cyst pain.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent or Reduce the Risk of Ovarian Cysts
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity can increase the risk of developing cysts. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce your risk.
- Regular Physical Activity: Exercise helps to regulate the menstrual cycle and hormonal levels, which may reduce the risk of forming cysts.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help maintain a healthy hormonal balance.
- Limiting Caffeine and Alcohol: Some studies suggest that reducing the intake of caffeine and alcohol may help in preventing cysts, though more research is needed in this area.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can affect hormonal balance. Finding effective ways to manage stress in your daily life can support overall reproductive health.
Importance of Regular Gynecological Check-Ups
- Early Detection: Regular visits to a gynecologist can help detect cysts early before they grow large enough to cause serious issues.
- Monitoring Cyst Development: Not all cysts require treatment, but monitoring their development can help manage potential complications. A gynecologist can track changes in cyst size and structure over time through ultrasounds.
- Expert Guidance: Gynecologists can provide tailored advice on managing symptoms and reducing the risk of future cysts based on your health history and lifestyle.
- Screening for Ovarian Cancer: Although most ovarian cysts are benign, regular check-ups are important as they also serve to rule out ovarian cancer, which can exhibit similar symptoms.
By implementing these management strategies and lifestyle changes, women can significantly improve their comfort and reduce the risk of developing ovarian cysts. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options.
FAQs about Ovarian Cyst Symptoms
What are the common symptoms of ovarian cysts?
Most ovarian cysts are small and often cause no symptoms. However, larger cysts or those that rupture may cause noticeable symptoms. Common signs include pelvic pain, bloating, swelling, and pressure in the lower abdomen. These symptoms can vary depending on the size and type of the cyst.
Can ovarian cysts cause pain during activities?
Yes, ovarian cysts can cause pain or discomfort during physical activities, especially those that involve significant movement of the lower body, such as running or jumping. Some women also report increased pain during sexual intercourse.
Do ovarian cysts affect menstruation?
Ovarian cysts can impact menstrual cycles, leading to irregularities such as delayed, missed, or unusually heavy periods. Some women with ovarian cysts may experience more painful menstrual cramps than usual.
What are the symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst?
A ruptured ovarian cyst can cause severe, sudden pain in the lower abdomen. This pain can be accompanied by symptoms like nausea, vomiting, fever, and rapid breathing. If you experience these symptoms, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial as complications can be serious.
Can ovarian cysts cause symptoms similar to pregnancy?
While ovarian cysts can cause bloating, nausea, and breast tenderness, similar to early pregnancy symptoms, they do not lead to other pregnancy signs like missed periods or positive pregnancy tests. If you suspect pregnancy, it is advisable to take a pregnancy test and consult with your healthcare provider.
When should I see a doctor for ovarian cyst symptoms?
You should consult a healthcare provider if you experience symptoms like sudden or severe pelvic pain, changes in menstrual patterns, or signs of a ruptured cyst. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and help manage symptoms effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or within an ovary. The symptoms of these cysts can vary widely, from pelvic pain and bloating to irregular menstrual cycles and pain during intercourse. Causes of ovarian cysts include hormonal imbalances, endometriosis, pregnancy, and pelvic infections. It’s important to recognize that while many ovarian cysts are harmless and resolve on their own, some can pose serious health risks.
If you’re experiencing any symptoms associated with ovarian cysts, or if there’s any concern about your reproductive health, it’s crucial to seek guidance from a healthcare provider. Only a medical professional can provide personalized advice and appropriate treatment options based on your specific condition. Early consultation can lead to better management of symptoms and prevention of potential complications. Remember, prioritizing your health is essential.
References
For those seeking further information or verification of the details discussed regarding ovarian cyst symptoms, the following reputable sources are highly recommended:
- Mayo Clinic – This trusted medical resource provides comprehensive insights into the symptoms, causes, and treatments of ovarian cysts. Visit their detailed page on ovarian cysts here.
- WebMD – Known for its accessible medical content, WebMD offers an in-depth look at ovarian cysts, including symptom descriptions and potential health implications. Learn more by clicking this link.
- MedlinePlus – A service of the U.S. National Library of Medicine, MedlinePlus provides reliable health information on ovarian cysts, supported by medical literature and experts. Access their resource here.
- Healthline – Healthline breaks down complex medical information into easy-to-understand articles. Their overview of ovarian cysts is helpful for understanding symptoms and when to seek medical advice. View the article here.
- Cleveland Clinic – As one of the leading medical centers, the Cleveland Clinic offers a detailed guide on ovarian cysts, covering everything from symptoms to diagnosis and management. Check out their information here.
These resources are intended to provide additional information and should not replace professional medical advice. If you are experiencing symptoms or have concerns about ovarian cysts, it is best to consult with a healthcare provider.