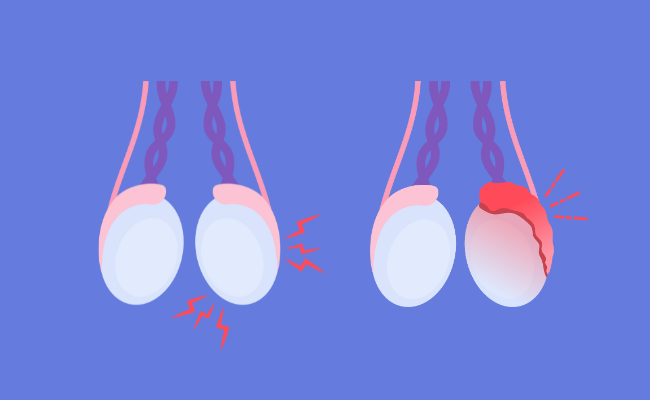
Orchitis Treatment: Orchitis is a medical condition characterized by the inflammation of one or both testicles, often associated with infections or other health conditions.
This inflammation can cause significant discomfort, swelling, and in some cases, long-term consequences if not adequately addressed.
Understanding the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for orchitis is crucial for effective management and recovery.
Understanding Orchitis
Orchitis is a medical condition characterized by the inflammation of one or both testicles in males, often associated with pain, swelling, and discomfort. It can arise from various causes and manifests through several recognizable symptoms. Understanding the types, causes, and symptoms of orchitis is crucial for early detection and effective management.
Types of Orchitis
Orchitis can be classified into two main types:
- Viral Orchitis: This type is most commonly caused by the mumps virus, typically occurring in conjunction with mumps infection. It usually affects one testicle and can develop about 4 to 6 days after the onset of mumps.
- Bacterial Orchitis: Often a complication of epididymitis (inflammation of the tube at the back of the testicle that stores and carries sperm), this type is caused by bacterial infections, including sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like gonorrhea or chlamydia.
Causes of Orchitis
Several factors can lead to the development of orchitis, including:
- Infections: As noted, mumps and other viral infections can lead to viral orchitis. Bacterial infections related to STIs or urinary tract infections can cause bacterial orchitis.
- Injury: Trauma or injury to the groin area might precipitate orchitis.
- Surgery: Surgical procedures involving the groin or genital area can sometimes lead to complications resulting in orchitis.
- Autoimmune response: In rare cases, the body’s immune system may mistakenly attack healthy cells in the testicles, leading to inflammation.
Common Symptoms to Recognize
Recognizing the symptoms of orchitis early can lead to quicker treatment and better outcomes. Some common symptoms include:
- Swelling and tenderness: One or both testicles may become swollen or tender.
- Pain: The pain may vary in intensity and could be exacerbated by physical activity.
- Fever: A high temperature or fever can accompany the inflammation.
- Nausea and vomiting: These are less common but can occur, particularly if the orchitis is associated with a viral infection like mumps.
- Discharge from penis: In cases of bacterial orchitis, there may be a discharge from the penis.
- Erythema: Redness of the skin around the affected testicle is often observed.
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned, consulting a healthcare provider promptly is advisable. Understanding these aspects of orchitis enhances awareness and promotes proactive health management.
Diagnosis of Orchitis
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Below are the primary diagnostic tests and procedures used to identify orchitis, alongside the significance of medical history in its diagnosis.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
- Physical Examination: A doctor will start with a thorough examination of the scrotum, testicles, and groin area to check for pain, swelling, and tenderness.
- Ultrasound: This imaging test uses high-frequency sound waves to create an image of the testicles and the scrotum. It helps in assessing the presence of inflammation, blood flow to the area, and any potential abnormalities like masses or cysts.
- Urine Tests: A urinalysis can help detect infections and other conditions that might cause symptoms similar to those of orchitis.
- Blood Tests: Blood samples might be taken to check for infections and inflammation markers that indicate orchitis.
- Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) Tests: Since STIs often cause orchitis, tests may be conducted to rule out gonorrhea, chlamydia, and other infections.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): In rare cases, an MRI might be used to get a detailed view of the testicles and surrounding areas, especially if the diagnosis remains uncertain after other tests.
The Role of Medical History in Diagnosing Orchitis
Medical history plays a pivotal role in diagnosing orchitis. During the consultation, the healthcare provider will ask about:
- Symptom Onset: Understanding when and how symptoms began can help differentiate orchitis from other conditions.
- Medical Background: Information on previous infections, surgeries, injuries, or medical treatments provides insights into potential causes of orchitis.
- Sexual History: Since some forms of orchitis are related to STIs, a patient’s sexual history can guide diagnostic testing and treatment.
- Immunization Records: For younger patients, vaccination history, especially regarding mumps, is crucial since mumps can lead to orchitis.
However, gathering detailed medical history assists doctors in forming a comprehensive view of the patient’s health, leading to a more accurate diagnosis and an effective treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Orchitis
Here’s a comprehensive guide to the treatment options, supportive home remedies, and the importance of following the prescribed treatment regimen.
Medical Treatment Options for Orchitis
- Antibiotics: If the orchitis is bacterial, doctors will prescribe antibiotics. It’s important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve earlier.
- Antiviral Medications: In cases where a virus, such as the mumps, causes orchitis, antiviral medications may be used, although they are less common.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB) or acetaminophen (Tylenol), can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Epididymitis-Orchitis Treatment: If the condition extends to the epididymis, treatment may include a longer course of antibiotics and possibly hospitalization in severe cases.
Home Remedies and Supportive Care
- Rest: Getting ample rest is essential to help the body fight off the infection.
- Elevation: Elevating the scrotum using a folded towel can help reduce swelling and alleviate discomfort.
- Cold Packs: Applying cold packs to the groin area for 20-minute intervals can help relieve pain and swelling.
- Wear Supportive Underwear: Tight-fitting underwear or an athletic supporter can support the scrotum and reduce discomfort.
- Avoidance of Lifting: Refrain from heavy lifting or straining, which can worsen the symptoms.
Importance of Following the Treatment Regimen
Adhering to the treatment regimen prescribed by a healthcare provider is crucial for several reasons:
- Prevents Complications: Proper treatment helps prevent potential complications such as reduced fertility or chronic pain.
- Speeds Up Recovery: Completing the full course of medication ensures the infection is fully eradicated, which can prevent recurrence and speed up recovery.
- Limits Spread of Infection: Particularly with infectious causes, following the treatment plan helps limit the spread of infection to others, in cases where the infection is contagious.
If symptoms persist or worsen, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and possibly adjust the treatment plan. Always follow your healthcare provider’s advice and complete all prescribed treatments to ensure the best outcome.
Complications and Management of Untreated Orchitis
Understanding the potential risks and effective management strategies is crucial for safeguarding reproductive and overall health.
Potential Complications of Untreated Orchitis
- Testicular Atrophy: The affected testicle may shrink in size, leading to potential loss of function.
- Chronic Pain: Persistent pain in the groin area can occur, which may be intermittent or constant.
- Abscess Formation: In severe cases, an abscess might develop in the testicle, necessitating surgical intervention.
- Epididymo-orchitis: The infection can spread to the epididymis, causing additional swelling and pain.
- Infertility: Prolonged inflammation can impair the production of sperm and significantly affect fertility.
Long-term Effects on Fertility and Sexual Health
Untreated orchitis has notable long-term consequences, particularly concerning fertility and sexual health:
- Decreased Sperm Count and Motility: Orchitis can reduce both the number and mobility of sperm, complicating efforts to conceive.
- Impaired Testosterone Production: Testicular damage might lead to decreased testosterone levels, affecting libido, mood, and muscle mass.
- Psychological Impact: Chronic testicular pain and fertility concerns can lead to stress, anxiety, and depression, impacting overall quality of life.
Strategies for Managing and Preventing Complications
Managing and preventing complications associated with orchitis involves a proactive approach to treatment and lifestyle adjustments:
- Prompt Medical Treatment: Early intervention with appropriate antibiotics or antiviral medications can prevent the progression of symptoms and complications.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Follow-up appointments are crucial for monitoring the condition and adjusting treatment plans as necessary.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers and supportive underwear can alleviate discomfort.
- Cold Compresses: Applying cold packs to the groin area may reduce swelling and pain.
- Sexual Rest: Avoiding sexual activity during acute phases of the condition can prevent exacerbation of symptoms.
- Vaccination: In cases where mumps is the cause, ensuring vaccination against mumps can prevent the onset of orchitis.
However, by engaging with healthcare providers to tailor a prevention and management strategy is essential for optimal outcomes.
Prevention of Orchitis
Preventing orchitis involves a combination of personal hygiene practices, safe sexual behavior, and preventive healthcare measures. Below, we outline key strategies to reduce the risk of developing orchitis.
Implement Strict Personal Hygiene
- Regular Washing: Cleanse the genital area at least once a day with mild soap and warm water. This helps remove bacteria and other pathogens that could cause infections.
- Proper Drying: After washing, dry the genital area thoroughly to prevent moisture accumulation, which is conducive to the growth of bacteria.
Practice Safe Sexual Behavior
- Use Protection: Consistently use condoms during sexual activity. Condoms are effective in reducing the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) that can lead to orchitis.
- Limit Number of Sexual Partners: Reducing the number of sexual partners decreases the likelihood of contracting STIs.
- Regular STI Screenings: Regular screenings for STIs can detect and treat infections early, preventing the progression to orchitis.
Stay Up-to-Date with Vaccinations
- MMR Vaccine: The MMR vaccine protects against mumps, measles, and rubella—viruses that can lead to orchitis. Ensure that vaccinations are up to date according to local health guidelines.
- Hepatitis B Vaccine: Although not directly linked to orchitis, hepatitis B can affect overall genital health and immunity. Vaccination against hepatitis B is recommended.
Adopt Other Preventive Health Measures
- Prompt Treatment of Infections: Seek immediate medical attention for any signs of urinary or sexually transmitted infections. Early treatment can prevent complications such as orchitis.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Routine health examinations help monitor overall health and catch potential issues early, including conditions that might predispose one to orchitis.
By adhering to these preventative measures, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing orchitis, ensuring better reproductive health and overall well-being.
FAQs about Orchitis Treatment
What is orchitis?
Orchitis is an inflammation of one or both testicles, often caused by bacterial or viral infections such as mumps. It can cause pain, swelling, and sometimes fever.
How is orchitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of orchitis usually involves a physical examination, medical history review, and potentially an ultrasound to assess the inflammation. Blood tests and urine tests may also be conducted to identify the underlying cause.
What are the common treatments for orchitis?
Treatment for orchitis depends on the cause. For bacterial infections, antibiotics are typically prescribed. For viral infections, treatment focuses on relieving symptoms, such as using over-the-counter pain relievers, applying ice packs, and resting.
Can orchitis be prevented?
Preventing orchitis involves general health measures such as practicing safe sex, maintaining good personal hygiene, and ensuring complete vaccination against mumps and other related infections.
What are the potential complications of untreated orchitis?
If left untreated, orchitis can lead to more severe complications like reduced fertility, testicular atrophy, or the formation of an abscess. Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent these outcomes.
How long does it take to recover from orchitis?
Recovery time can vary depending on the cause and severity of the infection. With proper treatment, symptoms usually improve within a few days, but complete recovery might take weeks.
Conclusion
In summary, diagnosing and treating orchitis effectively requires recognizing its common symptoms, such as swelling, pain in the testicles, fever, and nausea. Key diagnostic tools include physical exams, ultrasounds, and urinalysis, which help differentiate orchitis from other conditions like testicular torsion. Treatment typically involves antibiotics for bacterial infections, pain relievers, and supportive measures like rest and scrotal elevation.
It is crucial for individuals experiencing symptoms of orchitis to seek prompt medical attention. Early intervention not only alleviates discomfort but also prevents potential complications such as reduced fertility or chronic pain. If you notice any signs of orchitis, consulting with a healthcare provider immediately ensures the best possible outcome. Remember, your health is paramount, and addressing issues early with professional guidance is the best approach to maintaining it.
References
For those seeking further information on orchitis treatment, the following resources offer reliable and detailed guidance. These sources are recognized for their medical accuracy and are helpful for both patients and healthcare professionals looking to deepen their understanding of orchitis management.
- Mayo Clinic – Orchitis Overview: Explore a comprehensive guide to the symptoms, causes, and treatments of orchitis, provided by one of the leading healthcare institutions. Read more about orchitis at Mayo Clinic.
- WebMD – Understanding Orchitis: This resource offers an easy-to-understand overview of orchitis, including potential complications and typical treatments. Visit WebMD to learn more about orchitis.
- Healthline – How to Manage Orchitis: Healthline provides practical advice on managing orchitis, including medicinal treatments and home remedies. Check out Healthline’s management tips for orchitis.
- CDC – Epididymitis and Orchitis Information: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention give an in-depth look at the infections that can lead to orchitis, emphasizing prevention and public health. Learn more from the CDC about epididymitis and orchitis.
These sources are excellent starting points for understanding and managing orchitis. They are updated regularly to reflect the latest research and healthcare guidelines, ensuring that readers have access to the most current information available.