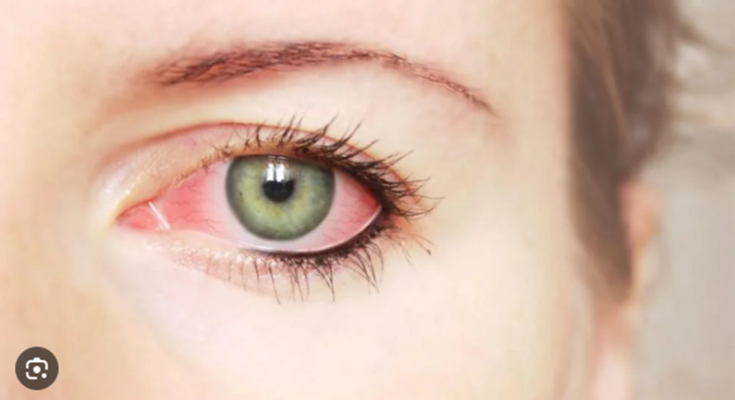
Ocular Rosacea Treatment: Ocular Rosacea is a chronic condition that affects the eyes, commonly associated with the skin disorder rosacea which causes redness and pimples on the face.
The ocular version manifests symptoms primarily around the eyes, including redness, irritation, and swollen eyelids, which can significantly impair daily functioning if left untreated.
What is Ocular Rosacea?
Ocular rosacea is a subtype of rosacea, a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face. This specific form targets the eyes, leading to symptoms such as redness, irritation, and swollen eyelids. Ocular rosacea can cause discomfort and, in more severe cases, blurred vision. The exact cause of ocular rosacea is not well understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of hereditary and environmental factors. Managing the condition often involves a combination of eye care practices and medical treatment to alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications.
Differences Between Ocular Rosacea and Other Forms of Rosacea
Ocular rosacea is distinct from other types of rosacea in several key ways:
- Location of Symptoms: While other forms of rosacea primarily affect the skin of the face (causing redness, pimples, and sometimes thickening of the skin), ocular rosacea specifically affects the eyes.
- Types of Symptoms: Symptoms of ocular rosacea include watery or bloodshot eyes, irritation, burning or stinging sensations in the eyes, and swollen eyelids. These symptoms are less common in other forms of rosacea.
- Complications: Ocular rosacea can lead to more severe eye conditions such as keratitis, which can threaten vision if left untreated, unlike other rosacea forms that typically do not affect vision.
- Treatment Focus: Treatment for ocular rosacea often requires specialized eye care, including lubricating eye drops and eyelid hygiene, whereas other types of rosacea are treated with skin creams, oral medications, and lifestyle changes.
Statistics on Prevalence and Demographics Affected
- Prevalence: Ocular rosacea is a common condition, estimated to affect up to 20% of those with rosacea. It is more likely to occur in people who have rosacea, suggesting a strong link between the two conditions.
- Age Group: While rosacea generally begins after age 30, ocular rosacea can develop at any time once rosacea is present.
- Gender: Similar to rosacea, ocular rosacea is more frequently reported in women, but the condition tends to be more severe in men.
- Ethnicity: Rosacea, including its ocular form, is most commonly observed in individuals of Caucasian descent, particularly those with fair skin.
However, understanding the specifics of ocular rosacea, including its differences from other forms of rosacea and its demographic impacts, helps in better managing the condition and improving the quality of life for those affected.
Symptoms of Ocular Rosacea
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the symptoms, ranging from common to less common, and how they differ from similar eye conditions.
Common Symptoms of Ocular Rosacea
Individuals with ocular rosacea often experience a variety of symptoms that can affect their daily lives. The most frequently observed symptoms include:
- Redness of the Eyes: The eyes may appear persistently red, similar to a bloodshot appearance.
- Burning or Stinging Sensation: There may be a continuous feeling of burning or irritation in the eyes.
- Watery Eyes: Excessive tearing is common, which can be mistaken for allergies.
- Itchy Eyes: The sensation of itchiness can lead many to rub their eyes, potentially exacerbating the condition.
- Sensitivity to Light: Those with ocular rosacea often find bright light uncomfortable or even painful.
Less Common Symptoms
While the above symptoms are frequently reported, there are several less common signs that can also suggest ocular rosacea:
- Blurred Vision: In some cases, vision may become blurry due to irritation or damage to the cornea.
- Swollen Eyelids: The eyelids might swell, making the eyes appear puffy.
- Visible Blood Vessels: Small, visible blood vessels may appear on the whites and margins of the eyelids.
- Dry Eyes: Despite the common symptom of watery eyes, some individuals may experience a sensation of dryness.
Differentiating Ocular Rosacea from Similar Conditions
Ocular rosacea can often be confused with other eye conditions like conjunctivitis or blepharitis, due to overlapping symptoms. Here’s how ocular rosacea differs from these conditions:
- Persistent Symptoms: Unlike temporary ailments like conjunctivitis, ocular rosacea symptoms are persistent and may worsen with triggers such as stress or spicy foods.
- Skin Symptoms: Ocular rosacea is often accompanied by skin symptoms of rosacea, which include redness and visible blood vessels on the face, which are not seen in most other eye conditions.
- Response to Treatment: Treatments that help relieve rosacea symptoms may also alleviate ocular symptoms, whereas treatments for conditions like allergic conjunctivitis will not typically help ocular rosacea.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Causes and Risk Factors of Ocular Rosacea
Understanding the causes and risk factors is essential for managing and possibly preventing this condition.
Causes of Ocular Rosacea
The exact cause of ocular rosacea remains unclear, but it is closely linked to the factors that trigger rosacea itself. Here are some of the commonly associated causes:
- Bacterial Involvement: Bacteria on the skin, particularly around the eyes, can exacerbate inflammation that leads to symptoms of ocular rosacea.
- Blocked Glands: Dysfunction or blockage of the meibomian glands in the eyelids, which are responsible for secreting oils that maintain tear film, can contribute to dry eyes and inflammation, typical of ocular rosacea.
- Demodex Mites: These microscopic mites naturally live on human skin but are found in greater numbers on the skin of people with rosacea. They can cause irritation and inflammation when their populations increase.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to sunlight, wind, and extreme temperatures can trigger or worsen ocular rosacea.
Risk Factors of Ocular Rosacea
Certain factors may increase the likelihood of developing ocular rosacea:
- Genetic Predisposition: Individuals with a family history of rosacea or ocular rosacea are more likely to develop these conditions.
- Age and Gender: Ocular rosacea is more commonly diagnosed in individuals between the ages of 30 and 50, and while it affects both men and women, women are generally more prone to rosacea, though men may experience more severe forms.
- Skin Type: People with fair skin, particularly those who blush easily, are at a higher risk of developing rosacea and ocular rosacea.
- Environmental Exposures: Frequent exposure to sunlight, wind, and extreme temperatures can increase the risk of ocular rosacea.
- Lifestyle Factors: Consumption of hot beverages, spicy foods, and alcohol, as well as experiencing high stress or engaging in activities that cause flushing or overheating of the body, can elevate the risk.
How Ocular Rosacea Develops: A Look at the Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of ocular rosacea involves a complex interplay of inflammatory responses, vascular instability, and possibly microbial action. Here’s a closer look at how these elements come together:
- Vascular Instability: Ocular rosacea can lead to increased blood flow and the instability of blood vessels in and around the eyes, causing redness and visible blood vessels.
- Inflammatory Processes: The body’s immune response is heightened in areas affected by rosacea, leading to inflammation that can affect the eyelids and surface of the eyes.
- Gland Dysfunction: Dysfunction of the meibomian glands contributes to changes in tear film consistency and quality, leading to symptoms such as dryness, irritation, and blurred vision.
- Microbial Flora Changes: Changes in the normal bacteria or mites on the skin can aggravate the immune system, leading to the inflammation characteristic of ocular rosacea.
By understanding these underlying mechanisms, individuals and healthcare providers can better manage ocular rosacea through targeted treatments and lifestyle adjustments, ultimately improving quality of life for those affected.
Impact of Ocular Rosacea on Daily Life
Ocular rosacea, a subtype of the chronic skin condition rosacea, primarily affects the eyes and eyelids. This condition can significantly influence daily activities and overall quality of life. Below, we explore how ocular rosacea impacts vision and eye health, as well as its psychological and social implications.
Effects on Vision and Eye Health
- Recurrent Eye Inflammation: Ocular rosacea often causes inflammation of the eyelids (blepharitis) and the white part of the eye (conjunctivitis), leading to redness, itching, and a burning sensation.
- Dry Eye Syndrome: This condition is characterized by insufficient tear production, which can result in a gritty feeling in the eyes, blurred vision, and increased sensitivity to light.
- Corneal Complications: In severe cases, ocular rosacea can lead to complications involving the cornea, the clear outer layer of the eye. This includes corneal thinning (keratitis) which can impair vision and, if untreated, might lead to corneal damage and scarring.
- Vision Fluctuation: The irregularity in tear film caused by ocular rosacea can lead to periods of blurred vision, complicating tasks that require sharp eyesight, such as reading or driving.
- Frequent Infections: People with ocular rosacea may experience more frequent eye infections due to inflammation and compromised eye surface.
Psychological and Social Implications
- Self-Esteem Issues: The visible symptoms of ocular rosacea, such as red, irritated eyes and swollen eyelids, can affect individuals’ perception of their appearance, leading to decreased self-confidence and self-esteem.
- Social Withdrawal: Due to the noticeable symptoms and potential misunderstanding of their condition, individuals with ocular rosacea may avoid social interactions, leading to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
- Anxiety and Depression: The chronic nature of ocular rosacea and its effects on appearance and vision can lead to increased anxiety and depression, particularly if the condition is not well-managed.
- Impact on Professional Life: The symptoms of ocular rosacea can interfere with professional activities, especially for those whose jobs require precise visual tasks or public interactions, potentially affecting job performance and career progression.
However, understanding the impact of ocular rosacea on both physical and mental health is crucial. Effective management and treatment strategies can help mitigate these effects, improving both eye health and quality of life.
Managing and Treating Ocular Rosacea
Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to handle ocular rosacea, including treatment options, tips for managing symptoms at home, and advice on when to seek professional medical help.
Treatment Options for Ocular Rosacea
Treating ocular rosacea often involves a multifaceted approach, combining prescription medications with routine eye care practices. Here is a list of common treatment options:
- Prescribed Eye Drops: Doctors often prescribe antibiotic or steroid eye drops that help reduce inflammation and control flare-ups.
- Oral Antibiotics: For more severe cases, oral antibiotics like doxycycline or tetracycline may be recommended to help reduce symptoms.
- Omega-3 Supplements: These can help improve tear quality and reduce dryness, which is beneficial for those suffering from ocular rosacea.
- Lid Hygiene Products: Daily eyelid cleaning with prescribed solutions can help manage symptoms by removing debris and controlling bacterial growth.
- Artificial Tears: Over-the-counter lubricating eye drops can provide relief from dryness and irritation.
- Punctal Plugs: In cases where tear evaporation is a problem, your doctor might suggest punctal plugs to help retain moisture in the eyes.
- Intense Pulsed Light Therapy (IPL): Some specialists might recommend IPL to reduce redness and inflammation in severe cases.
Tips for Managing Ocular Rosacea Symptoms at Home
Managing ocular rosacea at home is crucial for comfort and to prevent exacerbation of symptoms. Consider the following tips:
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress to the eyes daily can help soften hardened oils in the gland ducts, easing irritation.
- Gentle Eye Cleansing: Use baby shampoo or doctor-recommended cleansers to gently clean eyelids and keep the area free from irritants.
- Avoid Known Triggers: Common triggers include hot drinks, spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol. Identifying and avoiding these can reduce flare-ups.
- Wear Sunglasses: Protecting your eyes from wind and sunlight can help reduce symptoms.
- Maintain a Humid Environment: Using a humidifier, especially in dry climates or seasons, can help maintain moisture levels around the eyes.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps maintain overall hydration and supports eye health.
When to Seek Professional Medical Advice
While many aspects of ocular rosacea can be managed at home, certain situations require professional medical advice:
- Persistent Symptoms: If symptoms persist despite regular use of over-the-counter treatments and home remedies, consult a healthcare professional.
- Vision Changes: Any changes in vision or intense pain in the eyes are serious symptoms that necessitate immediate medical attention.
- Frequent Flare-Ups: If flare-ups become more frequent or severe, it might indicate that your current management strategy isn’t effective.
- Complications: Symptoms like sensitivity to light or blurry vision could suggest complications that require professional treatment.
By understanding the available treatments, employing useful home management tips, and recognizing when to seek professional advice, individuals suffering from this condition can significantly improve their quality of life.
Prevention Tips for Ocular Rosacea
While there’s no cure, understanding how to manage and prevent flare-ups can significantly enhance your quality of life. Below, we explore some effective preventative measures and lifestyle tips to help you minimize the risk or severity of ocular rosacea symptoms.
Preventative Measures to Reduce the Risk or Severity of Symptoms
- Protect Your Eyes from the Elements: Wind and ultraviolet (UV) light can exacerbate symptoms. Wear sunglasses with UV protection whenever you are outdoors, regardless of the season. Choose glasses with wraparound frames to shield your eyes from wind and debris.
- Maintain Good Eyelid Hygiene: Regularly clean your eyelids with gentle, baby shampoo or doctor-recommended cleansers. Keeping the eyelid area clean can prevent the buildup of oils and debris that can worsen ocular rosacea.
- Manage Dry Eyes: Use artificial tears to keep your eyes moist and relieve dryness. Opt for preservative-free drops to avoid potential irritants. In dry or windy weather, increase the frequency of application.
- Avoid Known Triggers: Identify and avoid triggers that cause flare-ups. Common triggers include hot drinks, spicy foods, alcohol, and extreme temperatures. Keeping a symptom diary can help you track and avoid these triggers.
- Use Anti-inflammatory Medications: Consult your healthcare provider about medications that can help manage inflammation. Oral or topical antibiotics are sometimes prescribed to reduce inflammation and other symptoms of ocular rosacea.
Lifestyle and Dietary Tips That May Help Prevent Flare-ups
- Adopt a Rosacea-Friendly Diet: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as flaxseeds, walnuts, and cold-water fish like salmon, can help reduce inflammation. Avoid foods that are known to trigger rosacea symptoms, such as hot and spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps maintain skin hydration and health, potentially reducing rosacea flare-ups.
- Practice Stress Management: Stress can trigger or worsen rosacea symptoms. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise can be effective in managing stress.
- Maintain a Cool Environment: Heat can exacerbate rosacea symptoms. Try to stay cool by using fans or air conditioning during hot weather, and avoid hot baths and saunas.
- Limit Exposure to Harsh Chemicals: Skin and eye care products with alcohol, witch hazel, fragrance, menthol, and eucalyptus oil can irritate sensitive skin. Choose gentle, fragrance-free products specifically designed for sensitive skin.
By integrating these preventative and lifestyle adjustments into your daily routine, you can effectively manage ocular rosacea and lead a more comfortable life. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment or altering your diet.
FAQs about Ocular Rosacea Treatment
1. What is ocular rosacea?
Ocular rosacea is a condition related to skin rosacea, affecting the eyes. It can cause redness, irritation, and swollen eyelids. People with skin rosacea are more likely to develop ocular symptoms, though it can occur independently.
2. What are the symptoms of ocular rosacea?
Symptoms include persistent redness in the eyes, itchy or burning sensations, blurred vision, sensitivity to light, and visible blood vessels on the whites of the eyes. Swollen eyelids and recurrent styes are also common.
3. How is ocular rosacea diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a thorough examination by an eye specialist (ophthalmologist) who will assess the symptoms and may conduct tests to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms, such as conjunctivitis or dry eyes.
4. What treatments are available for ocular rosacea?
Treatment options focus on managing symptoms and may include prescription eye drops or ointments, oral antibiotics, and managing underlying skin rosacea. Keeping the eyelid area clean and avoiding known irritants can also help.
5. Can lifestyle changes help manage ocular rosacea?
Yes, certain lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve symptoms. These include wearing sunglasses to protect eyes from UV light, avoiding spicy foods and hot drinks, using a humidifier to moisten indoor air, and maintaining good facial and eyelid hygiene.
6. Is ocular rosacea curable?
While there is no cure for ocular rosacea, the condition can be effectively managed with the right treatment and lifestyle changes. Regular check-ups with an eye care professional are crucial to monitor the condition and adjust treatments as necessary.
7. When should I see a doctor for ocular rosacea?
You should consult an eye care professional if you experience any of the symptoms of ocular rosacea, especially if these symptoms persist or worsen. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications such as vision impairment.
Conclusion
In summary, ocular rosacea presents a unique set of challenges due to its symptoms, which include red, irritated eyes, and the sensation of having something gritty within them. These discomforts often accompany or precede the more recognized symptoms of facial rosacea, such as redness and visible blood vessels. The causes of ocular rosacea are not fully understood but are believed to be linked to a combination of hereditary and environmental factors.
Given the complexities of this condition and its potential to impact daily life significantly, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. An expert can provide a proper diagnosis and tailor a treatment plan that addresses both the ocular and dermatological aspects of rosacea. Early and effective treatment can help manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. If you notice any of the symptoms mentioned, don’t hesitate to seek professional advice.
References
For further reading and validation of the information provided on the treatment of Ocular Rosacea, please consult the following reputable sources:
- American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) – Provides comprehensive guidelines and latest research on the treatment of various forms of rosacea, including ocular rosacea. Visit their site here.
- National Rosacea Society (NRS) – Offers detailed patient resources and treatment options for all rosacea symptoms, focusing significantly on ocular issues. Explore more here.
- Mayo Clinic – Features expert advice on the symptoms, causes, and treatment modalities for ocular rosacea. Learn more by clicking here.
- PubMed Central – A reliable resource for accessing peer-reviewed scientific papers on ocular rosacea treatments. Access studies here.
These sources provide well-researched and credible information that can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about treating ocular rosacea.