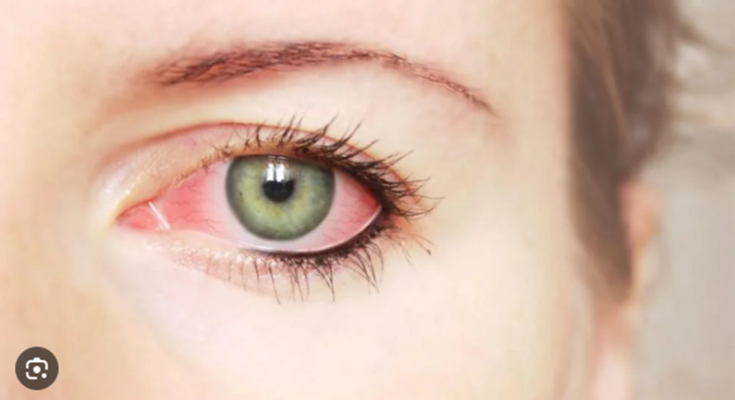
Ocular Rosacea Symptoms: Ocular Rosacea is a chronic condition that primarily affects the eyes, manifesting as part of the broader spectrum of rosacea, a skin disease that leads to redness and pimples on the face.
This specific subtype of rosacea can cause significant discomfort and, if untreated, may lead to serious eye health issues.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of ocular rosacea is essential for effective management and treatment.
What is Ocular Rosacea?
Ocular rosacea is a condition closely related to the skin disorder known as rosacea, which typically affects the face. However, ocular rosacea specifically targets the eyes, leading to symptoms that can include redness, irritation, and dryness of the eyes and eyelids. People with this condition may experience feelings of grittiness or foreign bodies in the eyes, and in severe cases, it can lead to blurred vision and sensitivity to light. Understanding this condition is crucial as it often requires different management strategies compared to other forms of rosacea.
Differences Between Ocular Rosacea and Other Forms of Rosacea
Ocular rosacea and other forms of rosacea share some similarities, mainly their association with chronic inflammation, but there are key differences:
- Location of Symptoms: While classic rosacea primarily affects the skin of the face with symptoms like flushing, pimples, and visible blood vessels, ocular rosacea primarily affects the eyes and eyelids.
- Symptoms: Ocular rosacea sufferers commonly experience red and irritated eyes, swollen eyelids, and symptoms akin to conjunctivitis. This is distinct from the skin symptoms seen in other types of rosacea.
- Complications: In severe cases, ocular rosacea can lead to more serious eye conditions such as keratitis, which can impair vision if not treated properly.
Statistics on Prevalence and Demographics Affected
Ocular rosacea is a prevalent condition, particularly among those who already suffer from other types of rosacea. Here are some statistics and demographic data:
- Prevalence: It is estimated that about 20% of people with rosacea also develop ocular symptoms, though the incidence can vary widely depending on the population and diagnostic criteria used.
- Age Group: Ocular rosacea most commonly affects adults between the ages of 30 and 50.
- Gender: While rosacea, in general, is more common in women, ocular rosacea shows a more balanced gender distribution, affecting men and women nearly equally.
- Risk Factors: Individuals with fair skin, light hair, and light eye colors are at a higher risk, although ocular rosacea can affect all ethnicities and skin types.
By understanding ocular rosacea, including how it differs from other forms of rosacea and the demographics it affects, individuals can better seek appropriate treatment and management strategies.
Symptoms of Ocular Rosacea
Understanding these symptoms is crucial for diagnosis and effective management. Here, we’ll explore the common and less common symptoms of ocular rosacea, and how they differ from those of similar eye conditions.
Common Symptoms of Ocular Rosacea
The most frequent symptoms of ocular rosacea include:
- Redness of the Eyes and Eyelids: A persistent reddening similar to that seen in rosacea-affected skin.
- Eye Dryness: A sensation of gritty, dry eyes that can be uncomfortable and irritating.
- Burning or Stinging Sensation: Many individuals report a burning or stinging feeling that exacerbates discomfort.
- Teariness: Excessive tearing that does not correlate with emotional crying.
- Swollen Eyelids: Swelling or edema of the eyelids, which can be painful or tender to the touch.
- Recurrent Styes: Frequent development of styes, which are painful, pimple-like bumps on the eyelid.
Less Common Symptoms of Ocular Rosacea
While the symptoms listed above are frequently reported, some individuals may experience less common signs such as:
- Blurred Vision: Vision may become blurred sporadically, affecting daily activities.
- Sensitivity to Light: Increased discomfort in bright light or when viewing screens.
- Corneal Damage: In severe cases, the cornea (the clear front surface of the eye) may become involved, leading to corneal damage which could affect vision.
How Symptoms of Ocular Rosacea Differ from Similar Eye Conditions
Ocular rosacea can be mistaken for other eye conditions, such as conjunctivitis or blepharitis. However, there are key differences:
- Association with Skin Rosacea: Ocular rosacea is often accompanied by the facial redness and acne-like eruptions characteristic of skin rosacea.
- Chronic Symptoms: Unlike conjunctivitis, which tends to be acute, the symptoms of ocular rosacea are chronic and often flare in response to certain triggers like heat or spicy foods.
- Response to Treatment: Symptoms of ocular rosacea may respond to treatments that reduce overall inflammation and manage rosacea, unlike those of simple conjunctivitis or allergies.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, consulting with a healthcare provider who specializes in eye care or dermatology is advisable for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Causes and Risk Factors of Ocular Rosacea
Ocular rosacea is a condition that affects the eyes, characterized by redness, irritation, and swelling, often associated with the skin condition known as rosacea. Understanding the causes and risk factors can help in managing or even preventing this condition.
Causes of Ocular Rosacea
The exact cause of ocular rosacea remains unclear, but it is thought to be linked to a combination of hereditary and environmental factors. Here are some potential causes:
- Meibomian Gland Dysfunction: This is a common issue in ocular rosacea, where the glands in the eyelids that produce a vital component of tears become blocked.
- Microbial Flora Changes: Alterations in the bacteria or mites (such as Demodex) on the eyelids might contribute to inflammation.
- Systemic Inflammation: People with rosacea often have heightened levels of systemic inflammation, which can also affect the eyes.
- Helicobacter pylori Infection: Some researchers believe that this common stomach bacteria might play a role in triggering rosacea symptoms, including those affecting the eyes.
Risk Factors of Ocular Rosacea
Several factors may increase the risk of developing ocular rosacea, including:
- Age and Gender: Ocular rosacea is most frequently diagnosed in individuals between the ages of 30 and 50, and while it can affect anyone, women are more often diagnosed with rosacea. However, men may experience more severe symptoms.
- Skin Type: Individuals with fair skin, particularly those who blush easily, are at a higher risk.
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of rosacea or ocular rosacea increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to sunlight, extreme temperatures, wind, and humidity can exacerbate the symptoms.
- Lifestyle Choices: Consumption of alcohol, spicy foods, and hot beverages has been linked to flare-ups of rosacea symptoms.
- Health Conditions: Other health issues such as hypertension and cardiovascular diseases are seen more commonly in people with rosacea.
How Ocular Rosacea Develops: A Look at the Pathophysiology
The development of ocular rosacea involves several pathophysiological mechanisms:
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is a core component of ocular rosacea, affecting the eyelids, conjunctiva, and sometimes the cornea.
- Blood Vessel Changes: Abnormalities in blood vessel function and an increase in vascular growth factors lead to dilation and increased visibility of blood vessels in and around the eyes.
- Immune System Response: An altered immune response can also play a role, where the body’s immune system may react excessively to normal bacteria or Demodex mites on the skin.
- Lipid Abnormalities: Dysfunctional lipid production by the meibomian glands can lead to poor tear film quality, resulting in dry eyes and irritation.
However, regular consultations with a healthcare provider specializing in eye health and dermatology can help mitigate the symptoms and improve quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Diagnosing Ocular Rosacea
Accurate diagnosis is crucial as it guides the subsequent treatment strategies and helps in managing the symptoms efficiently.
Common Diagnostic Procedures and Criteria
- Clinical Examination: The initial step in diagnosing ocular rosacea involves a detailed clinical examination by an eye care professional. They look for common signs such as redness, swelling, and irritation in the eyes and eyelids.
- Patient History: Understanding the patient’s medical history, including any previous diagnosis of skin rosacea, is vital. Patients may report symptoms such as eye dryness, sensitivity to light, blurred vision, or a gritty sensation in the eyes.
- Ophthalmologic Tests: Specific tests like the Schirmer test to measure tear production and slit-lamp examinations to inspect the eyelids, cornea, and conjunctiva are commonly used.
- Skin Tests: Since ocular rosacea is often associated with skin rosacea, dermatological assessments can also be part of the diagnostic process.
- Response to Treatment: In some cases, the response to typical anti-rosacea treatments may help confirm the diagnosis, particularly when typical symptoms are present.
Role of Healthcare Professionals in Diagnosing Ocular Rosacea
A multi-disciplinary approach is often necessary for diagnosing and managing ocular rosacea:
- Ophthalmologists play a pivotal role in the direct assessment and management of eye symptoms.
- Dermatologists may be involved to treat and diagnose related skin symptoms.
- Primary Care Physicians often serve as the first point of contact and can refer patients to specialists.
These professionals work collaboratively to ensure a comprehensive evaluation and to manage the condition holistically.
Importance of Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is critical in distinguishing ocular rosacea from other eye conditions that can present with similar symptoms, such as:
- Conjunctivitis: Commonly known as pink eye, it shares the redness and irritation seen in ocular rosacea.
- Blepharitis: Inflammation of the eyelids, which can also occur in rosacea, needs to be identified separately.
- Dry Eye Syndrome: This condition mimics the dryness and discomfort associated with ocular rosacea.
- Meibomian Gland Dysfunction: Often co-occurs with ocular rosacea, making it essential to differentiate the primary cause of the symptoms.
By employing comprehensive diagnostic strategies and leveraging the expertise of various healthcare professionals, patients can achieve better outcomes and improved quality of life.
Impact of Ocular Rosacea on Daily Life
This condition can significantly impact daily life through both physical and psychological challenges. Understanding these effects can help individuals seek appropriate treatment and manage their symptoms more effectively.
How Ocular Rosacea Can Affect Vision and Eye Health
- Chronic Dry Eyes: One of the most common symptoms of ocular rosacea is persistent dryness in the eyes. This can lead to discomfort, redness, and a gritty sensation, making it difficult to carry out everyday activities like reading or using digital devices.
- Photophobia (Light Sensitivity): Individuals with ocular rosacea often experience increased sensitivity to light. This can result in discomfort in bright environments, complicating outdoor activities and driving during sunny days.
- Blurred Vision: Inflammation of the cornea, known as keratitis, can occur in more severe cases of ocular rosacea. This inflammation can cause blurred vision, which can affect the ability to perform tasks that require sharp eyesight.
- Frequent Eye Infections: The inflammation associated with ocular rosacea can lead to an increased risk of eye infections, such as conjunctivitis or blepharitis. These infections can cause additional symptoms, including eyelid swelling and soreness.
- Potential Vision Loss: In rare instances, if ocular rosacea is not adequately treated, it can lead to corneal damage and potentially permanent vision loss. Regular consultations with healthcare providers are crucial for monitoring and managing the condition.
Psychological and Social Implications of Living with Ocular Rosacea
- Self-Consciousness and Anxiety: The visible symptoms of ocular rosacea, such as red and irritated eyes, can make individuals feel self-conscious and anxious about their appearance. This can impact social interactions and reduce confidence in public settings.
- Social Withdrawal: Due to the discomfort and appearance of their symptoms, some people with ocular rosacea might avoid social gatherings or public places. This social withdrawal can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
- Impact on Professional Life: The symptoms of ocular rosacea can interfere with professional activities, especially for those whose jobs require precision vision or extensive use of digital screens. Frequent eye discomfort and the need for medical appointments can also lead to reduced productivity.
- Emotional Distress: Living with a chronic condition that affects one’s appearance and daily functioning can lead to depression and anxiety. It’s important for individuals with ocular rosacea to seek support from mental health professionals and support groups to manage these challenges effectively.
Ocular rosacea poses significant challenges, but with proper medical care and support, individuals can manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. Awareness and understanding of the condition’s impact are vital for improving quality of life for those affected.
Managing and Treating Ocular Rosacea
Ocular rosacea is a challenging condition, but with the right management strategies and treatments, individuals can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve their quality of life. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to manage and treat ocular rosacea effectively.
Treatment Options for Ocular Rosacea
1. Prescribed Medications:
- Antibiotics: Oral antibiotics like doxycycline or tetracycline can help reduce inflammation and eyelid swelling.
- Steroid Eye Drops: These can be used temporarily to reduce eye inflammation.
- Immunosuppressive Drugs: In severe cases, drugs like cyclosporine eye drops are prescribed to control inflammation.
2. Laser Therapy: Intense pulsed light (IPL) or other laser treatments can help manage visible blood vessels and reduce redness and irritation.
3. Eyelid Hygiene: Regular cleaning of the eyelids with prescribed solutions or baby shampoo can help maintain eyelid hygiene and prevent flare-ups.
3. Artificial Tears: Over-the-counter lubricating eye drops can help relieve dryness and irritation.
Tips for Managing Symptoms at Home
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm, damp cloth to the eyes can help soothe irritation and loosen crusts.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid triggers such as hot drinks, spicy foods, alcohol, and extreme temperatures, which can exacerbate symptoms.
- Protect Your Eyes: Wear sunglasses to protect your eyes from wind and UV rays, which can irritate the condition.
- Maintain a Clean Environment: Keep your living and working areas dust-free and avoid smoke and pollutants that could irritate your eyes.
- Diet and Hydration: Stay hydrated and consider increasing your intake of omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce inflammation.
When to Seek Professional Medical Advice
- Persistent Symptoms: If symptoms persist despite home management, consult a healthcare provider.
- Worsening Condition: If the condition worsens or if you experience severe pain, blurred vision, or sensitivity to light, seek medical attention immediately.
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular appointments with an eye specialist or dermatologist are crucial for monitoring the condition and adjusting treatment as necessary.
By following these treatment options and management tips, you can control the symptoms and lead a more comfortable life. Always consult a healthcare professional for a treatment plan tailored to your specific condition.
Prevention Tips for Ocular Rosacea
Fortunately, several preventative measures can be taken to reduce the risk or severity of symptoms. Additionally, certain lifestyle and dietary changes may help prevent flare-ups, contributing to overall eye health and comfort.
Preventative Measures to Reduce Risk or Severity of Symptoms
- Protect Your Eyes from the Elements: Wear sunglasses that block UVA and UVB rays whenever you are outdoors. This can protect your eyes from wind and sunlight, which may exacerbate symptoms.
- Maintain Good Eyelid Hygiene: Regularly clean your eyelids with a gentle, diluted baby shampoo or doctor-recommended cleansers. Keeping the eyelid area clean can help prevent blockages of the oil glands around the eyes.
- Use Artificial Tears: Lubricating eye drops can help manage dryness and irritation. Opt for preservative-free artificial tears to avoid potential irritants.
- Manage Indoor Environments: Use a humidifier in dry indoor environments to help maintain moisture levels, which can soothe and protect your eyes.
- Be Mindful of Screen Time: Limit exposure to computer screens and take frequent breaks to rest your eyes. Practicing the 20-20-20 rule—every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds—can be beneficial.
- Consult with Healthcare Professionals: Regular check-ups with an ophthalmologist or dermatologist can help monitor your condition and adjust your treatment plan as necessary.
Lifestyle and Dietary Tips to Prevent Flare-Ups
- Follow an Anti-inflammatory Diet: Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, and plenty of fruits and vegetables to help reduce inflammation.
- Avoid Known Triggers: Common triggers for rosacea include hot beverages, spicy foods, alcohol, and caffeine. Keeping a food diary can help you identify and avoid your personal triggers.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps maintain hydration and supports overall eye health.
- Practice Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate rosacea symptoms. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, or regular exercise can reduce stress levels and potentially lessen the frequency of flare-ups.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Both very hot and very cold weather can trigger rosacea symptoms. Dressing appropriately for the weather and avoiding sudden temperature changes can help manage your condition.
However, keeping a proactive approach to treatment and daily care plays a crucial role in managing this chronic condition effectively.
FAQs about Ocular Rosacea Symptoms
What are the common symptoms of ocular rosacea?
Ocular rosacea primarily affects the eyes and eyelids. Symptoms often include red, irritated eyes, a gritty feeling almost like there is sand in the eyes, and swollen eyelids. Many people also experience dry eyes, tearing, and sensitivity to light.
Can ocular rosacea cause vision problems?
Yes, if left untreated, ocular rosacea can lead to more serious complications, including blurred vision and, in rare cases, corneal damage which can affect the clarity of your vision. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider if you experience any changes in your vision.
How is ocular rosacea different from regular rosacea?
Ocular rosacea is a subtype of rosacea that affects the eyes, whereas regular rosacea typically affects the skin of the face with symptoms like redness, pimples, and visible blood vessels. Some individuals may experience both ocular and cutaneous symptoms simultaneously.
Is ocular rosacea contagious?
No, ocular rosacea is not contagious. It is a chronic inflammatory condition related to the immune system and environmental triggers, not caused by an infectious agent.
What triggers ocular rosacea flare-ups?
Triggers vary among individuals but often include factors such as stress, hot or spicy foods, alcohol, extreme temperatures, sunlight, and certain cosmetics or skin care products. Identifying and avoiding personal triggers is key to managing symptoms.
How can ocular rosacea be treated?
Treatment typically involves a combination of good eyelid hygiene, prescription medications like antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs, and sometimes artificial tears to help manage dryness. For severe cases, ophthalmic therapies or surgery might be required. Always follow a treatment plan advised by your healthcare provider.
Can lifestyle changes help manage ocular rosacea symptoms?
Yes, lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing ocular rosacea. These include wearing sunglasses to protect eyes from UV light, avoiding known dietary and environmental triggers, using gentle skin care products, and managing stress levels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ocular rosacea is a complex condition characterized by symptoms such as red, irritated eyes, swollen eyelids, and the sensation of having something gritty in the eyes. These symptoms can significantly impact daily life and are often accompanied by facial rosacea, which includes redness and visible blood vessels on the face. The exact causes of ocular rosacea are not fully understood, but factors like environmental triggers, genetic predisposition, and issues related to blood vessel function and the immune system are believed to play a role.
If you experience any of the symptoms associated with ocular rosacea, it’s crucial to seek professional medical advice. A healthcare provider can offer a proper diagnosis and recommend effective treatment strategies tailored to your specific needs. Early intervention is key to managing symptoms effectively and preventing further complications. Remember, while ocular rosacea can be challenging, you don’t have to face it alone.
References
For those seeking additional information or validation regarding the symptoms of ocular rosacea, several reputable sources are available. These resources offer detailed insights and further exploration into the condition:
- American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO): Provides comprehensive guidelines and research articles on ocular rosacea. Learn more by visiting their official website at American Academy of Ophthalmology.
- National Rosacea Society: Offers a wealth of information about all types of rosacea, including ocular manifestations. Explore their resources at National Rosacea Society.
- Mayo Clinic: A trusted medical resource that offers detailed descriptions of symptoms, causes, and treatment options for ocular rosacea. Further information can be found on their page dedicated to the condition at Mayo Clinic – Ocular Rosacea.
- PubMed Central: An invaluable database for accessing scientific studies and clinical trials related to ocular rosacea. Visit PubMed Central to search for relevant research articles.
These resources are excellent starting points for anyone looking to understand more about ocular rosacea, its symptoms, and treatment options.