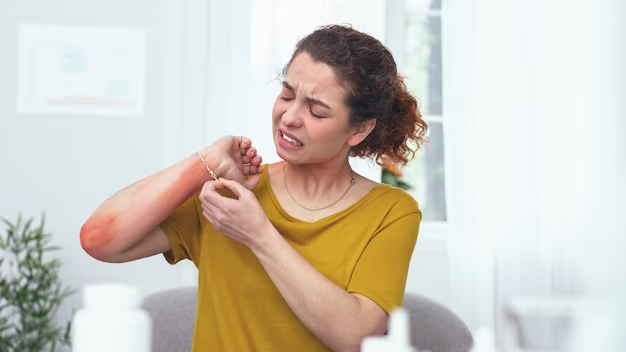
Nickel Allergy Symptoms: Nickel allergy is one of the most common causes of allergic contact dermatitis, a condition that can cause skin irritation when nickel, a ubiquitous metal found in many everyday items, comes into contact with the skin.
This comprehensive guide explores the symptoms, causes, and management of nickel allergy, providing valuable information for those affected.
What is Nickel Allergy?
Nickel allergy is one of the most common causes of allergic contact dermatitis, a skin reaction that occurs when an individual who is allergic to nickel comes into contact with it. This allergy develops when the immune system views nickel as a harmful substance and triggers an allergic reaction. Symptoms can include itching, redness, rash, dry patches, and blisters at the site of contact. Common sources of nickel exposure include jewelry, coins, cell phones, eyeglass frames, zippers, and certain types of food.
Statistics on Prevalence and Demographic Most Affected
Nickel allergy affects approximately 10-20% of the general population, making it a prevalent concern worldwide. The condition is notably more common in women than men, with studies suggesting that up to 17% of women and 3% of men may be allergic to nickel. This disparity is often attributed to the higher frequency of ear piercings among females, which can increase exposure to nickel-containing metals from a young age.
The prevalence of nickel allergy is also significant among children and adolescents, particularly those with pierced skin. Studies have shown that early exposure to nickel through body piercings can increase the likelihood of developing a nickel allergy. Additionally, certain occupations that involve frequent exposure to metal items, such as hairdressers, retail workers, and healthcare professionals, are at a higher risk for this type of allergy.
Common Symptoms of Nickel Allergy
Here’s a detailed look at the primary symptoms, their manifestations, and severe symptoms that require immediate medical attention.
Primary Symptoms of Nickel Allergy
- Skin Redness and Rash: Often appearing at the site of contact with nickel-containing objects, the skin may become red and irritated, developing a rash that is itchy and uncomfortable.
- Itching: One of the most persistent symptoms, itching can range from mild to severe and usually accompanies the rash.
- Blisters and Skin Lesions: Severe reactions may lead to the formation of blisters or small bumps on the skin that can ooze and become crusty over time. These lesions can be particularly painful and prone to infection.
- Dry Patches of Skin: Resembling eczema, these dry, scaly patches can develop in the area of contact and may persist long after the initial exposure.
Variability of Symptoms
The intensity and appearance of nickel allergy symptoms can vary widely among individuals:
- Duration of Contact: Longer exposure to nickel can exacerbate symptoms, leading to more severe skin reactions.
- Sensitivity Levels: Individuals with higher sensitivity may experience symptoms with minimal contact, whereas others may require prolonged exposure to trigger a reaction.
- Location of Contact: Symptoms typically appear where the nickel-containing item touches the skin, such as ears from earrings or wrists from watches, but they can spread beyond the contact area in severe cases.
Severe Symptoms That Require Medical Attention
While most symptoms of nickel allergy are manageable with over-the-counter treatments and avoiding contact with nickel, some severe symptoms necessitate immediate medical intervention:
- Widespread Rash: If the rash covers a large area of the body or spreads rapidly, it may require professional medical treatment.
- Infection Signs: Symptoms like increased pain, swelling, warmth, or pus near the affected areas can indicate an infection that needs medical attention.
- Respiratory Issues: Although rare, some individuals might experience respiratory problems if they inhale nickel particles, which is an emergency requiring urgent care.
- Swelling of Face and Limbs: Significant swelling, especially around the eyes, face, or limbs, can be a sign of a severe allergic reaction known as angioedema, which requires immediate emergency care.
If you suspect you have a nickel allergy, consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Causes of Nickel Allergy
Understanding how and why this allergy develops, alongside recognizing common sources and potential genetic and environmental triggers, can help manage and mitigate its effects.
How and Why Nickel Allergy Develops
Nickel allergy develops when the immune system identifies nickel as a harmful substance, leading to an allergic reaction. This typically occurs after repeated or prolonged exposure to nickel-containing items, causing sensitization. Once sensitized, even brief contact can trigger symptoms such as itching, redness, and rashes. This allergic response is primarily a delayed hypersensitivity reaction, where the body’s immune defenses are activated hours to days after nickel contact.
Common Sources of Nickel Exposure in Everyday Life
Nickel is ubiquitous in everyday objects, which makes avoiding it challenging for those with sensitivities. Common sources include:
- Jewelry and Watches: Nickel is often used in earrings, necklaces, bracelets, and watch bands.
- Coins and Keys: Many coins and keys contain nickel, which can wear off onto skin with handling.
- Mobile Phones and Electronic Gadgets: Nickel is used in the metallic parts of these devices.
- Clothing Fasteners: Items like zippers, buttons, and belt buckles are frequent culprits for causing nickel allergy reactions.
- Kitchen Utensils and Cutlery: Stainless steel often contains nickel, which can leach out when cooking acidic foods.
Genetic Factors and Environmental Triggers
The likelihood of developing a nickel allergy can be influenced by genetic factors. Individuals with a family history of allergies or allergic conditions such as eczema, asthma, or hay fever are at a higher risk. Environmental triggers also play a critical role. Factors such as increased use of nickel-containing products, occupational exposure (like in metalworking industries), and even certain dietary choices can enhance the risk of sensitization and allergy development.
By understanding these factors and sources of nickel, individuals can better manage their exposure and symptoms, reducing the impact of nickel allergy on their daily lives.
Diagnosis of Nickel Allergy
Proper diagnosis is crucial for managing and treating nickel allergy effectively. Here, we explore the diagnostic methods for nickel allergy, the role of medical history, and the importance of differential diagnosis.
Diagnostic Methods for Nickel Allergy
The diagnosis of nickel allergy primarily relies on specific tests and evaluations, including:
- Patch Test: The most definitive method for diagnosing nickel allergy is the patch test. Small amounts of nickel and other allergens are applied to the skin, typically on the back, and covered with patches. These are left in place for 48 hours before the first evaluation, and the skin’s reaction is assessed again at 72 or 96 hours. A positive reaction, typically a localized rash, confirms sensitivity to nickel.
- Dimethylglyoxime (DMG) Test: This is a less common test where a chemical solution is applied to an object suspected of containing nickel. A pink color change indicates the presence of nickel, suggesting a potential source of allergy, though it does not confirm skin sensitivity.
Role of Medical History in Diagnosing Nickel Allergy
A thorough medical history plays a pivotal role in diagnosing nickel allergy:
- Personal and Family History of Allergies: Information about personal or familial tendencies toward allergies can guide the diagnosis.
- Previous Reactions: Details of past reactions to metal-containing items, such as jewelry, watches, and zippers, can be indicative of nickel allergy.
- Onset and Duration: The timing and duration of symptoms following exposure to suspected nickel-containing items help in correlating the cause and effect.
Importance of Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is essential to rule out other conditions that may mimic the symptoms of nickel allergy:
- Other Dermatological Conditions: Conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and other types of contact dermatitis need to be considered.
- Infections: Skin infections can sometimes resemble the rashes caused by allergic reactions.
- Reaction to Other Metals: Patients may react to metals other than nickel, such as cobalt or chromium, which often co-exist in metal alloys.
By distinguishing nickel allergy from these conditions, healthcare providers can ensure appropriate management and avoid ineffective treatments.
Managing and Treating Nickel Allergy Symptoms
If you’re dealing with nickel allergy, managing your symptoms involves a combination of avoiding nickel exposure, seeking medical treatments, and making lifestyle adjustments. Here’s how you can effectively manage and treat nickel allergy symptoms.
Strategies for Avoiding Nickel Exposure
- Choose Nickel-Free Jewelry and Accessories: Opt for jewelry that is specifically labeled as “nickel-free.” Be cautious of items labeled “hypoallergenic” as they can sometimes still contain nickel.
- Check Clothing Fasteners: Avoid clothing with metal fasteners that contain nickel. Look for plastic snaps or buttons instead, or coat metal fasteners with clear nail polish to create a barrier between the metal and your skin.
- Use Nickel Testing Kits: These kits can help you identify items in your household that contain nickel, allowing you to avoid direct contact.
- Opt for Stainless Steel or Glass Cookware: Replace cookware that contains nickel, such as certain stainless steel alloys, with options like high-grade stainless steel (nickel-free), glass, or enamel.
- Be Cautious with Personal Devices: Mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and other personal devices may contain nickel. Use covers or cases to minimize skin contact.
Medical Treatments Available
- Topical Corticosteroids: These creams or ointments can reduce inflammation and treat rashes caused by nickel allergy.
- Oral Antihistamines: These medications can help alleviate itching and other allergic reactions.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: For severe cases, doctors may prescribe medications such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus to reduce the immune system’s response.
- Desensitization: In some cases, a dermatologist might recommend a process called desensitization, where small amounts of nickel are gradually introduced to the body to build up tolerance.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Home Remedies
- Keep Skin Clean and Dry: This prevents the build-up of sweat and dirt, which can exacerbate skin reactions.
- Moisturize Regularly: Using a good moisturizer can help protect the skin barrier and prevent irritation.
- Wear Protective Barriers: If you must handle nickel-containing items, wear gloves or protective clothing to reduce skin contact.
- Diet Considerations: Some foods are high in nickel, such as nuts, chocolate, and canned foods. If you notice a worsening of symptoms after consuming these foods, consider limiting them in your diet.
However, always consult with a healthcare professional to develop a treatment plan that is suitable for your specific condition.
Prevention Tips for Nickel Allergy
Nickel allergies can be inconvenient and uncomfortable, but with the right knowledge and strategies, you can prevent reactions effectively. Understanding how to identify nickel in products and choosing nickel-free alternatives are key steps in managing this allergy.
Tips for Identifying Nickel in Products
- Check Product Labels: Always read the labels on jewelry, clothing, and other metal items. Products labeled as “nickel-free,” “hypoallergenic,” or “surgical stainless steel” are generally safer choices.
- Use a Nickel Testing Kit: These kits are available online or at pharmacies. They come with a solution that, when applied to a metal object, will turn pink if nickel is present.
- Know Common Nickel Carriers: Items like keys, coins, mobile phones, and glasses often contain nickel. Be cautious with metal buttons, zippers, and snaps on clothing as well.
- Consult with Manufacturers: If unsure, contact the manufacturer to confirm whether a product contains nickel. This is especially useful for larger purchases like kitchen utensils or electronics.
Recommendations for Nickel-Free Products and Alternatives
- Jewelry: Opt for jewelry made from platinum, sterling silver, or at least 18K gold. Polymer clay and glass jewelry are stylish, affordable, and completely nickel-free.
- Clothing Fasteners: Look for plastic or polymer alternatives to traditional metal snaps, buttons, and zippers. These are readily available and can be a simple switch to make.
- Kitchenware: Stainless steel alloys without nickel are available, although they may be more expensive. Ceramic, glass, and silicone kitchen tools are excellent alternatives.
- Personal Items: Choose glasses with plastic or titanium frames, and opt for leather or cloth belts instead of those with metal buckles.
- Electronics: When purchasing electronics, look for ones that specify “nickel-free” components, especially in areas like earbuds or phone casings that come into direct contact with your skin.
However, always stay informed and proactive about the materials in the products you use to best manage your nickel allergy.
FAQs about Nickel Allergy Symptoms
1. What are the common symptoms of a nickel allergy?
Nickel allergy symptoms typically manifest as a skin reaction known as allergic contact dermatitis. Common signs include itching, redness, rash, dry patches resembling a burn, and blisters that may drain fluid if severe.
2. How long does it take for symptoms to appear after exposure to nickel?
Symptoms can appear within 12 to 48 hours after contact with a nickel-containing item, though some reactions may be immediate, particularly if you have a pre-existing allergy.
3. Can nickel allergy symptoms occur on parts of the body not in direct contact with nickel?
Typically, symptoms appear at the point of contact. However, in severe cases, they can spread beyond the contact area, especially if the allergen is transferred by the hands.
4. Are there any systemic symptoms associated with nickel allergies?
While rare, systemic nickel allergy syndrome (SNAS) can occur, leading to more widespread symptoms like headache, fatigue, nausea, and respiratory problems in addition to dermatitis.
5. How can I manage and treat nickel allergy symptoms?
Management includes avoiding direct contact with nickel-containing objects. Treatments often involve topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and oral antihistamines to ease itching. For persistent or severe reactions, consult a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of a nickel allergy is crucial for managing this common skin condition effectively. As we’ve discussed, being aware of the potential triggers and familiarizing oneself with the typical signs—such as skin redness, itching, and blistering—can significantly enhance your quality of life.
If you suspect you have a nickel allergy, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide a definitive diagnosis and tailor a management plan that helps you avoid exposure and treat symptoms effectively.
Remember, early detection and professional advice are your best tools for living comfortably with a nickel allergy.
References
For further reading and validation of the information provided on Nickel Allergy Symptoms, the following reputable sources are recommended:
1. American Academy of Dermatology Association: Explore comprehensive insights into the symptoms and management of nickel allergies at the American Academy of Dermatology Association. Their detailed guides offer practical advice and the latest dermatological research. Visit the AAD website
2. National Eczema Association: The National Eczema Association provides resources specifically tailored to understanding and managing contact dermatitis, of which nickel allergy is a common cause. Their articles are vetted by medical professionals and offer strategies for reducing exposure to irritants. Read more at the National Eczema Association
3. Mayo Clinic: Mayo Clinic offers a thorough overview of nickel allergy, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Their content is authored by a team of experts in the field of allergies and immune response. Learn more at Mayo Clinic
These sources are authoritative and provide evidence-based information that can help individuals understand and manage their nickel allergy symptoms effectively.