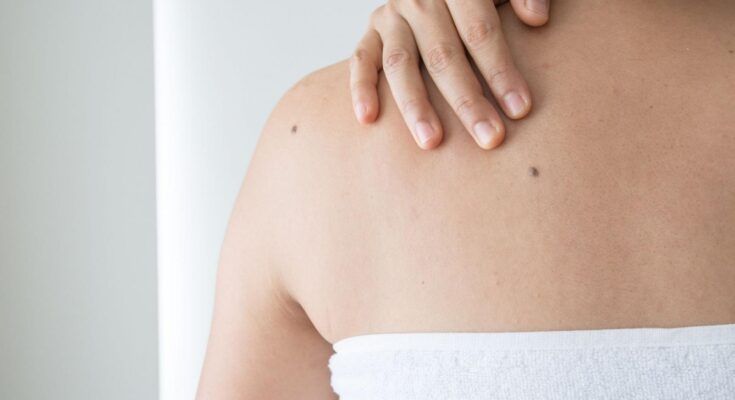
Melanoma Symptoms: Melanoma, one of the most serious types of skin cancer, arises when the pigment-producing cells that give color to the skin become cancerous.
Understanding its symptoms and causes is crucial for early detection and treatment, which significantly improves the prognosis.
What is Melanoma?
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that originates in the cells known as melanocytes, which are responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. Unlike other forms of skin cancer, melanoma is more likely to spread to other parts of the body if not detected and treated early. It can develop anywhere on the skin and is frequently characterized by the uncontrolled growth of pigment-producing cells. Melanomas can appear as new spots on the skin, or they may evolve from existing moles that become cancerous.
Differentiation between Melanoma and Other Types of Skin Cancer
Melanoma is distinguished from other types of skin cancers in several key ways:
- Appearance: Melanoma typically presents as a dark mole with irregular borders, varying colors, and an asymmetrical shape. It often changes in size, color, or shape.
- Growth: Melanoma tends to grow more quickly than other types of skin cancer such as basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
- Spread: Unlike BCC and SCC, which are more likely to remain localized, melanoma has a higher potential to metastasize, or spread to other parts of the body, including the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, brain, and bones.
- Risk: While sun exposure is a risk factor for all types of skin cancer, the risk of melanoma is also significantly influenced by genetics, the number of moles on the skin, and skin type.
Statistics on Melanoma Incidence and Mortality Rates
Melanoma accounts for only about 1% of skin cancer cases but causes the majority of skin cancer deaths. The incidence of melanoma has been rising steadily over the past few decades, making it one of the most rapidly increasing forms of cancer globally.
- Incidence Rates: In the United States, the American Cancer Society estimates that in 2023, about 99,780 new melanomas will be diagnosed (about 57,180 in men and 42,600 in women).
- Mortality Rates: Annually, it’s estimated that 7,650 deaths (5,080 men and 2,570 women) from melanoma will occur in the U.S. alone.
- Survival Rates: The overall 5-year survival rate for patients whose melanoma is detected early is about 99%. However, the survival rate falls to 66% when the disease reaches the lymph nodes and 27% when the disease metastasizes to distant organs.
However, regular skin checks and protective measures against UV radiation can significantly reduce the risk of developing melanoma.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Melanoma
Being aware of the key symptoms can help you recognize this type of skin cancer before it advances. Below are the early signs and symptoms of melanoma to watch out for:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole does not match the other half in terms of size, shape, color, or thickness.
- Border Irregularity: The edges of the mole are ragged, notched, or blurred. The pigment may spread into the surrounding skin.
- Color Changes: The mole does not have a uniform color and may include shades of brown or black, or sometimes patches of pink, red, white, or blue.
- Diameter: The suspicious mole is larger than 6mm across (about the size of a pencil eraser), although melanomas can sometimes be smaller than this.
- Evolving: Any change in size, shape, color, elevation, or another trait, or any new symptom such as bleeding, itching, or crusting points to danger.
- New Moles: The appearance of a new mole after the age of 30 may also be a sign of melanoma.
- Pain or Tenderness: Moles that are painful, tender, or sensitive to touch.
- Elevation: A mole that is raised above the skin and has an uneven surface.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult with a dermatologist promptly. Early detection and treatment are the keys to a successful outcome in battling melanoma.
Causes and Risk Factors for Melanoma
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with melanoma can help in early detection and preventive strategies.
Causes of Melanoma
The primary cause of melanoma is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which can come from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds. Here are the key contributors:
- Sun Exposure: Intense, intermittent sun exposure that leads to sunburns significantly increases melanoma risk, especially if sunburns occurred during childhood.
- Tanning Beds: The use of indoor tanning beds before the age of 30 increases the risk of developing melanoma by 75%. Tanning lamps and booths are also potent sources of UV radiation.
- Rare Genetic Conditions: Conditions like xeroderma pigmentosum, which prevent the skin from repairing damage caused by UV light, can increase melanoma risk.
Risk Factors for Melanoma
While anyone can develop melanoma, certain factors increase the likelihood:
- Skin Type: Individuals with fair skin, light hair, and blue or green eyes have a higher risk because their skin has less melanin, which helps protect against UV radiation.
- Personal History of Sunburn: Experiencing one or more severe, blistering sunburns as a child or teenager increases the risk of melanoma as an adult.
- Family History of Melanoma: If a close relative (such as a parent or sibling) has had melanoma, the risk is significantly higher due to shared genetic susceptibilities and possibly shared behavioral patterns related to sun exposure.
- Age: Older individuals are more likely to develop melanoma, although it’s one of the most common cancers in young adults, particularly young women.
- Moles: People with numerous moles or unusual (atypical) moles are at a heightened risk.
- Immune System Function: Individuals with weakened immune systems, including those undergoing treatments that suppress immune function, are at increased risk.
By being aware of these causes and risk factors, individuals can take proactive measures such as using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding peak sun hours. Early detection through regular skin checks is also critical in managing melanoma risk effectively.
Prevention Tips for Melanoma
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are essential tips to help you prevent melanoma by protecting your skin effectively.
Sun Safety Measures
- Use Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 to all exposed skin, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Opt for long-sleeved shirts, pants, and a wide-brimmed hat to cover as much skin as possible. Clothes with UV protection offer additional safety.
- Seek Shade: Especially during the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. when the sun’s rays are strongest, make use of shade or create your own with an umbrella.
- Use Sunglasses: Protect your eyes and the sensitive skin around them by wearing sunglasses that block 99% to 100% of both UVA and UVB light.
Regular Skin Checks and Dermatologist Visits
- Perform Monthly Self-Exams: Learn the patterns of moles, freckles, and other skin marks. Use a mirror to check hard-to-see areas and look for new changes or unusual growths.
- Schedule Annual Skin Exams: Visit a dermatologist yearly for a professional skin examination. This is crucial for detecting early signs of melanoma that might be missed during self-exams.
- Follow Dermatologist Recommendations: If you have a higher risk of melanoma due to family history or past skin cancers, follow any additional recommendations from your dermatologist, which may include more frequent checks.
Avoiding Tanning Beds and Direct Sun Exposure
- Steer Clear of Tanning Beds: Avoid tanning beds and sunlamps, which increase the risk of skin damage and melanoma. Embrace your natural skin tone as a sign of health.
- Limit Midday Sun Exposure: Try to stay indoors or in the shade during peak sunlight hours (between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.). Plan outdoor activities for early morning or late afternoon.
- Use Extra Caution Near Water, Snow, and Sand: These surfaces can reflect and intensify the damaging rays of the sun, increasing your risk of sunburn and skin damage.
By integrating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing melanoma. Remember, taking a few simple steps today can lead to a healthier tomorrow.
Diagnosing Melanoma
Below, we explore the diagnostic process, the importance of biopsies and skin examinations, and highlight new technologies enhancing melanoma detection.
The Diagnostic Process for Melanoma
- Initial Skin Examination: The process often begins with a thorough skin check by a healthcare professional. This examination involves looking for moles or growths that have irregular shapes, multiple colors, or have changed in appearance.
- Dermoscopic Analysis: A dermatoscope, a tool that provides a magnified, illuminated view of the skin, allows doctors to observe the microscopic structures of a mole or growth.
- Digital Monitoring: For patients with multiple moles, digital images are taken over time to track changes and detect early signs of melanoma development.
- Biopsy: If a suspicious mole is identified, a biopsy is performed where all or part of the mole is removed and sent to a lab for pathological examination.
- Pathological Examination: A pathologist examines the tissue under a microscope to determine if cancer cells are present and, if so, the type and severity of the melanoma.
- Further Testing: If melanoma is diagnosed, additional tests may be conducted to determine the cancer’s spread (metastasis), such as lymph node biopsies and imaging tests.
Importance of Biopsy and Skin Examinations
- Early Detection: Regular skin exams and biopsies help catch melanoma in its earliest stages when it is most treatable.
- Accurate Diagnosis: Biopsies provide definitive evidence of melanoma, helping to distinguish it from less harmful types of skin lesions.
- Treatment Planning: The detailed information from a biopsy helps oncologists develop a tailored treatment plan, potentially improving patient outcomes.
New Technologies and Techniques in Melanoma Detection
- Genetic Testing: Advanced tests can now identify specific genetic mutations associated with melanoma, guiding personalized treatment options.
- AI and Machine Learning: Artificial intelligence systems are being trained to recognize patterns in mole changes that might be indicative of melanoma, potentially increasing the accuracy and speed of diagnosis.
- High-Resolution Ultrasound Imaging: This non-invasive technique allows for deeper examination of skin layers to detect melanoma without the need for a biopsy.
- Confocal Microscopy: This imaging technique provides real-time, cellular-level examination of the skin, aiding in the precise identification of malignant cells.
However, regular skin checks combined with these innovative techniques contribute significantly to successful outcomes in melanoma treatment.
FAQs About Melanoma Symptoms
What are the common symptoms of melanoma?
Melanoma typically manifests as a new spot on the skin or a change in an existing mole. Key signs include asymmetry, border irregularities, color changes, a diameter larger than a pencil eraser, and evolving size, shape or color. These characteristics are remembered easily as the ABCDEs of melanoma.
Can melanoma appear on skin not exposed to the sun?
Yes, melanoma can develop on any part of the skin, even areas that are not typically exposed to the sun, such as the soles of the feet, under nails, and on the scalp.
Is melanoma painful?
Melanoma is not usually painful in the early stages. However, as it progresses, a melanoma can become sore, itchy, or may bleed. Any discomfort or change in a mole should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
How quickly does melanoma progress?
The rate at which melanoma progresses can vary widely. Some melanomas grow slowly over years, while others can develop rapidly within months. Early detection and treatment are crucial to manage the progression effectively.
Are there different types of melanoma?
Yes, there are several types of melanoma, including superficial spreading melanoma, nodular melanoma, lentigo maligna melanoma, and acral lentiginous melanoma. Each type has distinct characteristics and patterns of growth.
Conclusion
In summary, melanoma is characterized by several key symptoms, including new or unusual growths on the skin, changes in existing moles, and the appearance of irregular patches that may be asymmetrical, have uneven borders, or vary in color. Causes of melanoma include excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, a history of sunburns, genetic factors, and having a fair complexion, among others.
It’s crucial for everyone to remain vigilant about their skin health. Regular self-examinations and being aware of any changes in your skin’s appearance can be lifesaving. If you notice any suspicious changes, such as new moles or changes in existing ones, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider promptly. Early detection and treatment significantly improve the prognosis for melanoma. Stay proactive about your skin health and seek professional advice when necessary to ensure early intervention and care.
References
For further reading and to validate the information provided on melanoma symptoms, consider exploring the following reputable sources:
- American Cancer Society – Offers comprehensive details on melanoma symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures. Visit the American Cancer Society.
- Mayo Clinic – Provides a detailed overview of melanoma, including symptoms, causes, and diagnostic procedures. Learn more at Mayo Clinic.
- National Cancer Institute – Features extensive information on melanoma including symptom descriptions, research, and patient care resources. Read about Melanoma at the National Cancer Institute.
- WebMD – Offers easy-to-understand information on the symptoms of melanoma and other useful health-related content. Check symptoms on WebMD.
- Healthline – Provides insights into the early signs of melanoma, preventative tips, and health advice. Explore Healthline for more information.
Each of these resources has been chosen for their reliability and authority in the field of health and oncology. They serve as excellent starting points for those looking to deepen their understanding of melanoma symptoms.