Lupus Treatment: Lupus, formally known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a complex and multifaceted autoimmune disease that presents a significant challenge in both diagnosis and treatment.
This chronic condition not only impacts the immune system but also affects various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, brain, and other organs.
Understanding the intricacies of lupus is crucial for effective management and treatment strategies.
Understanding Lupus
Lupus is a complex and multifaceted autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the body’s own tissues and organs. Understanding the different types of lupus and recognizing common symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and management. Here, we will explore the various forms of lupus and discuss how its symptoms can affect patients.
Types of Lupus
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): The most common form of lupus, SLE can affect many parts of the body, including joints, skin, kidneys, heart, lungs, blood vessels, and the brain.
- Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus: This type primarily affects the skin and can cause rashes and lesions, often on areas exposed to sunlight.
- Drug-induced Lupus: Triggered by certain prescription drugs, this type of lupus is typically temporary and resolves once the medication is stopped.
- Neonatal Lupus: Although rare, this type affects newborns and is usually transient. It can cause skin rashes and other symptoms, which are often resolved within several months without any lasting effects.
Common Symptoms of Lupus and Their Impact
Lupus symptoms can vary widely from person to person, and they can be intermittent, with periods of illness (flares) and periods of wellness. Some common symptoms include:
- Fatigue: One of the most common symptoms, fatigue can severely impact daily functioning and quality of life.
- Joint Pain and Swelling: Many lupus patients experience arthritis-like symptoms which can limit mobility and impair daily activities.
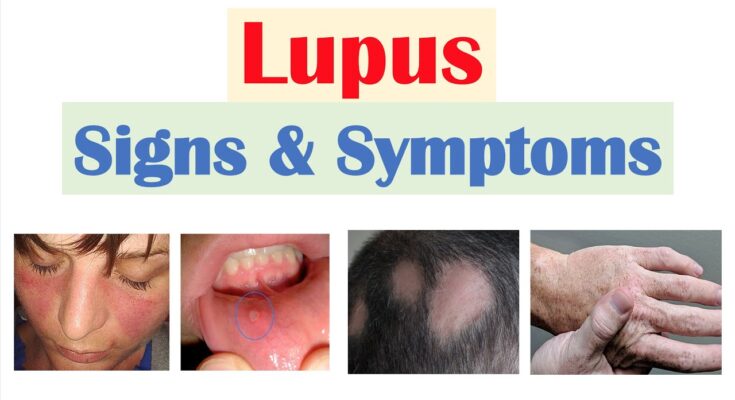
- Skin Rashes: Particularly the “butterfly rash” across the cheeks and nose, which can be sensitive to sunlight and cause emotional distress due to visible marks.
- Fever: Recurrent fevers are common and can often complicate the diagnosis process.
- Kidney Problems: Lupus can lead to nephritis, affecting kidney function and overall health.
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon: Exposure to cold or stress can cause fingers and toes to turn white or blue, indicating circulation problems.
- Respiratory and Cardiac Issues: Lupus can cause inflammation of the heart and lungs, leading to chest pain, shortness of breath, and other severe conditions.
However, early recognition and treatment can help manage the symptoms of lupus and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Diagnosis of Lupus
Lupus, a complex autoimmune disease, presents significant challenges for accurate diagnosis due to its diverse and often overlapping symptoms with other conditions. This variability can delay diagnosis and treatment, impacting patient outcomes.
Challenges in Diagnosing Lupus
- Symptom Variability: Lupus symptoms can range widely from joint pain and fatigue to rashes and kidney dysfunction, which can vary over time and from one person to another.
- Overlap with Other Conditions: Many lupus symptoms are not unique to the disease, overlapping with other autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, complicating the diagnostic process.
- Fluctuating Symptoms: The symptoms of lupus can change in severity and type, sometimes disappearing temporarily, a phenomenon known as flares and remissions.
Diagnostic Criteria and Medical Tests
To diagnose lupus effectively, healthcare providers rely on a combination of clinical criteria and specialized tests:
- Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) Test: This is a primary test used in the diagnosis of lupus as most lupus patients have a positive ANA test result, indicating the presence of autoantibodies.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test measures the levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, which can help identify the presence of anemia or other blood abnormalities common in lupus.
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) and C-Reactive Protein (CRP): These tests measure inflammation levels, which are often elevated in lupus patients.
- Kidney and Liver Assessment: Tests such as urinalysis, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and creatinine tests assess kidney function, while liver function tests help evaluate the health of the liver, both commonly affected by lupus.
- Skin and Kidney Biopsy: In cases where lupus affects the skin or kidneys, a biopsy can be crucial for confirming the diagnosis by showing typical disease patterns in tissue samples.
Role of Healthcare Professionals in the Diagnosis Process
The diagnosis of lupus involves a multidisciplinary approach due to its complexity:
- Primary Care Physicians: Often the first point of contact, they perform initial assessments and refer patients to specialists when lupus is suspected.
- Rheumatologists: Specialists in autoimmune diseases, rheumatologists are central to diagnosing and managing lupus, often coordinating care with other specialists.
- Dermatologists and Nephrologists: These specialists are involved when lupus presents with skin issues or kidney involvement, respectively, contributing critical insights into the overall diagnosis and treatment plan.
- Nurses and Physician Assistants: Support the diagnostic process by managing patient history information, conducting preliminary tests, and providing patient education and follow-up care.
However, understanding the challenges, utilizing a comprehensive range of diagnostic tests, and involving a team of healthcare professionals are critical for accurately diagnosing lupus and initiating effective treatment strategies.
Treatment Options for Lupus
Below is a detailed exploration of the treatment options available for lupus, including medications, and lifestyle and home remedies that support medical treatment.
Goals of Lupus Treatment
The treatment goals for lupus are designed to:
- Reduce inflammation: Since lupus causes significant inflammation that can affect different parts of the body, reducing this inflammation is crucial.
- Control symptoms: Lupus symptoms can range from mild to severe and controlling these effectively improves quality of life.
- Prevent flares: Treatment aims to lengthen the periods between active episodes, or flares, of the disease.
- Minimize organ damage: Lupus can affect major organs; treatments strive to protect these organs from damage.
- Improve overall well-being: Enhancing the overall health and well-being of patients is a key component of lupus treatment.
Medications Used in Lupus Treatment
A variety of medications are used to treat lupus, depending on the specific symptoms and severity of the disease:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These are used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Common examples include ibuprofen and naproxen.
- Antimalarial Drugs: Medications like hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) are used to manage skin and joint symptoms. They also help prevent lupus flares.
- Corticosteroids: Drugs like prednisone can control severe inflammation rapidly but come with potential side effects if used long-term.
- Immunosuppressants: These are used for more severe forms of lupus. Medications like methotrexate, azathioprine, and cyclophosphamide help control the immune system to reduce damage to tissues and organs.
- Biologics: Newer therapeutic options, such as belimumab (Benlysta), are targeted treatments that help reduce autoantibody levels and control the immune response.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies Supporting Medical Treatment
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes and home remedies can support the management of lupus:
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can help manage inflammation and maintain overall health.
- Exercise Regularly: Moderate exercise can help maintain joint flexibility, reduce stress, and improve overall physical health.
- Protect Against Sun Exposure: UV light can trigger lupus flares, so wearing protective clothing and using sunscreen is essential.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can exacerbate lupus symptoms and increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Get Adequate Rest: Lupus can lead to fatigue; thus, ensuring sufficient sleep is important to manage energy levels and recovery.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or therapy can help manage stress, which may exacerbate symptoms.
However, regular consultations with healthcare providers ensure that the treatment plan remains effective and adapted to any changes in the condition.
Advanced Therapies and Research in Lupus Treatment
Understanding the latest therapies, ongoing research, and future prospects is essential for those impacted by this complex condition.
Latest Advancements in Lupus Treatment Options
- Biologic Therapies: Recent years have witnessed the emergence of biologic drugs tailored to target specific parts of the immune system involved in lupus. Medications like belimumab and anifrolumab have been approved for use, showing promise in reducing disease activity.
- JAK Inhibitors: Janus kinase inhibitors, a newer class of medication, are currently under investigation for their effectiveness in treating lupus. These drugs, which include tofacitinib and baricitinib, work by blocking specific pathways that contribute to immune system activity.
- Peptide Therapeutics: Research into short peptides that can modulate the immune system’s response has opened a new avenue for lupus treatment, potentially leading to therapies that are both effective and have fewer side effects.
Ongoing Research and Clinical Trials Focused on Lupus
- Stem Cell Therapy: Clinical trials are exploring the use of stem cell therapy as a treatment for severe cases of lupus. This approach aims to reset the immune system, thereby reducing the autoimmunity at the core of the disease.
- Microbiome and Lupus: Investigators are studying the relationship between the gut microbiome and lupus activity. This research could lead to probiotic treatments aimed at modifying the microbiome to help manage lupus symptoms.
- Genetic Studies: Ongoing research is focused on understanding the genetic foundations of lupus, which could lead to personalized treatment strategies and improved diagnosis.
Future Prospects in the Treatment of Lupus
- Personalized Medicine: Advances in genetic research are paving the way for personalized medicine in lupus treatment, where therapies are tailored to the individual’s genetic makeup, potentially improving treatment efficacy and reducing side effects.
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being integrated into research to better predict disease patterns, treatment responses, and patient outcomes. This could lead to more sophisticated and individualized treatment plans.
- Immunotherapy Innovations: Future treatments may include advanced immunotherapies that more precisely target the immune dysfunctions in lupus without compromising the body’s overall ability to fight infections.
By keeping abreast of these developments, patients and healthcare providers can better navigate the complexities of lupus treatment and look forward to a future with more effective and personalized options.
Living with Lupus: Managing Day-to-Day Life
Lupus, a chronic autoimmune disease, presents unique challenges to those diagnosed. Managing day-to-day life effectively is crucial for maintaining quality of life. Here are key areas to focus on:
Diet, Exercise, and Stress Management
- Diet: Maintaining a well-balanced diet is essential for people with lupus. Anti-inflammatory foods like fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help manage inflammation. It’s also beneficial to avoid foods that can trigger flare-ups, such as processed foods and those high in saturated fats and sugars.
- Exercise: While strenuous activity might exacerbate symptoms, gentle exercises like walking, yoga, or swimming can improve strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular health without overtaxing the body. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting a new exercise regimen.
- Stress Management: Stress can trigger lupus symptoms. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can be valuable tools for managing stress levels. Regular engagement in hobbies and activities that bring joy can also help alleviate stress.
Importance of Mental Health Support and Community Resources
- Mental Health Support: Managing lupus isn’t just about physical health; mental and emotional well-being are equally important. Counseling or therapy can provide support for coping with the emotional challenges of living with a chronic illness. Support groups, whether online or in-person, can offer a network of peers who understand the unique struggles of living with lupus.
- Community Resources: Many organizations offer resources specifically for lupus patients, including educational materials, workshops, and seminars that provide valuable information on managing the disease. Leveraging these resources can empower patients to take an active role in their health management.
Patient Stories: Treatment Successes and Challenges
Case Study 1: Jane, a 34-year-old diagnosed with lupus three years ago, found that a tailored treatment plan including medication, a refined diet, and routine exercise helped her manage her symptoms effectively. However, navigating flare-ups and medication side effects continues to be a challenge, highlighting the importance of ongoing medical support and personal resilience.
Case Study 2: Michael, a 45-year-old with severe lupus, experienced significant improvement in his quality of life after joining a support group and beginning biologic treatments. His story illustrates the potential impact of combining medical innovations with strong community support in overcoming the obstacles posed by lupus.
Living with lupus involves continuous adaptation and management. By focusing on diet, exercise, and stress management, and seeking mental health support and community resources, individuals can lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges of the disease.
FAQs about Lupus Treatment
1. What is the first line of treatment for lupus?
The first line of treatment for lupus typically includes anti-inflammatory medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and antimalarial drugs like hydroxychloroquine. Corticosteroids may also be used to reduce inflammation. Each treatment plan is tailored to the individual’s symptoms and severity of the disease.
2. Are there any new treatments for lupus?
Recently, there have been advances in lupus treatment, including biologics like belimumab, which targets specific parts of the immune system. Additionally, ongoing research is focused on developing more targeted therapies that aim to treat lupus with fewer side effects.
3. Can lifestyle changes impact lupus symptoms?
Yes, lifestyle changes can significantly impact lupus symptoms. Patients are advised to maintain a balanced diet, get regular exercise, and avoid excessive exposure to sunlight. Stress management techniques, such as yoga and meditation, can also help manage flare-ups.
4. Is lupus treatment covered by insurance?
Most health insurance plans cover lupus treatment, but coverage can vary significantly. It’s important for patients to review their health insurance policy and speak with their insurance provider to understand what treatments and medications are covered.
5. How long do I need to continue treatment?
Lupus is a chronic condition, and its treatment may be lifelong. However, the intensity of treatment can vary depending on the disease’s activity. Regular consultations with healthcare providers are essential to adjust the treatment plan as needed.
6. Can lupus go into remission?
Yes, with appropriate treatment, many lupus patients can achieve a state of remission, where symptoms are minimal or absent. However, even in remission, ongoing monitoring and occasional treatment might be necessary to manage the condition effectively.
7. What are the side effects of lupus medications?
Common side effects of lupus medications can include gastrointestinal issues, increased risk of infections, and mood changes. More severe side effects might involve organ damage from prolonged use of certain steroids. It’s crucial to discuss potential side effects with a healthcare provider.
8. Can alternative therapies be used to treat lupus?
While alternative therapies such as acupuncture and herbal supplements can complement traditional treatment, they should not replace conventional medical treatment. It’s important to consult healthcare professionals before starting any alternative therapies to ensure they do not interfere with standard treatments.
9. What should I do during a lupus flare-up?
During a lupus flare-up, it’s vital to rest, take prescribed medications, and contact your healthcare provider. They might adjust your medications to better control the symptoms during a flare-up.
10. How can I find a specialist in lupus treatment?
You can find a specialist in lupus treatment by asking for a referral from your primary care physician, checking with local hospitals, or visiting websites of organizations dedicated to lupus research and advocacy.
Conclusion
In summary, diagnosing and treating lupus effectively requires a comprehensive understanding of its diverse symptoms and the individual patient’s health background. We’ve explored the key diagnostic tools such as blood tests, imaging, and clinical evaluations, which are essential for confirming lupus. Treatment strategies include medications like anti-inflammatory drugs and immunosuppressants, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing monitoring to manage this complex autoimmune disorder.
For those living with lupus and their families, it’s crucial to engage closely with healthcare professionals. Tailored treatment plans are vital, as they consider the unique aspects of each patient’s condition. Therefore, consulting with a knowledgeable healthcare provider ensures that treatment approaches are both effective and appropriate for your specific situation.
Finally, the importance of ongoing research cannot be overstressed. Advances in medical research continue to shed light on lupus, improving the ways it can be managed and treated. Moreover, patient advocacy plays a critical role in driving this research forward and ensuring that the needs of lupus patients are met. Together, through continued learning and advocacy, there is hope for better management strategies and ultimately, a cure for lupus.
References
For further reading and to validate the information provided on Lupus treatment, we recommend the following reputable sources:
- The Lupus Foundation of America – Offers comprehensive resources on Lupus, including detailed discussions on the latest treatment options and ongoing research. Visit the Lupus Foundation of America.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Provides robust information on Lupus symptoms, treatments, and statistical data about its prevalence. Access CDC resources on Lupus.
- Mayo Clinic – A respected medical institution that offers a depth of information on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of Lupus. Explore Mayo Clinic’s Lupus section.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Includes extensive research articles and updates on Lupus, helping patients and healthcare providers stay abreast of advancements. Read more at NIH’s Lupus pages.
- Johns Hopkins Lupus Center – Known for specialized Lupus treatment and research, their site provides valuable insights into managing this complex condition. Learn from Johns Hopkins Lupus Center.
Each of these resources has been selected for their authority and the quality of information they provide on Lupus, ensuring that readers have access to the most accurate and up-to-date information available.