Lupus Symptoms: Lupus, known medically as Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), is a chronic autoimmune disease that can cause severe inflammation and damage to various parts of the body.
It is a complex and multifaceted condition that primarily affects women, especially those in their childbearing years.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of lupus is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
What is Lupus?
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. This can lead to inflammation and damage across various parts of the body, including the joints, skin, kidneys, heart, lungs, blood vessels, and brain.
Types of Lupus
Lupus manifests in several forms, each affecting the body in different ways:
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): This is the most common type of lupus, which affects multiple systems within the body and can range from mild to severe.
- Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus: Primarily affects the skin, causing rashes and lesions, often triggered by exposure to sunlight.
- Drug-induced Lupus Erythematosus: Caused by certain prescription drugs, this type is typically temporary and subsides once the medication is discontinued.
- Neonatal Lupus: A rare condition that affects newborns, likely caused by antibodies from the mother that affect the infant, leading to skin rashes and, rarely, more serious complications.
Demographics Most Affected by Lupus
Lupus can affect anyone, but certain demographics are more commonly affected:
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop lupus than men, with females comprising about 90% of adult cases.
- Age: Although lupus can be diagnosed at any age, it is most often diagnosed between the ages of 15 and 44.
- Race and Ethnicity: Lupus is more prevalent and tends to be more severe in people of African American, Hispanic, Asian, and Native American descent compared to Caucasians.
However, understanding these demographics helps in early diagnosis and management of the disease, crucial for improving the quality of life for those affected.
Common Symptoms of Lupus
Understanding the common symptoms can lead to quicker detection and management. Below, we delve into the typical early signs of lupus and explain how these symptoms can range from mild to severe.
Detailed List of Early Lupus Symptoms
- Fatigue: One of the most prevalent symptoms, fatigue affects about 90% of people with lupus. This isn’t just ordinary tiredness but a deep exhaustion that can hinder daily activities and doesn’t improve with rest.
- Fever: Mild fevers without an apparent cause can be an early indicator of lupus, often fluctuating between 98.5°F to 101°F (36.9°C to 38.3°C). These fevers may come and go and are sometimes overlooked as symptoms of common viral infections.
- Joint Pain and Stiffness: Many individuals with lupus experience joint issues, including pain and swelling, particularly in the morning. This symptom often affects smaller joints, like those in the hands, wrists, and knees.
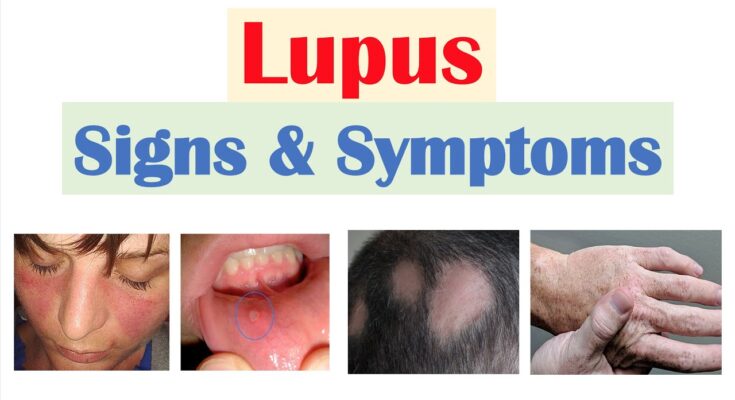
- Skin Rash: A distinctive sign of lupus is a butterfly-shaped rash (malar rash) that spreads across the cheeks and the bridge of the nose. Additionally, the skin may be sensitive to sunlight, with rashes developing or worsening after exposure.
- Kidney Involvement: Lupus nephritis, which affects the kidneys, can develop early in the disease. Early signs include swelling in the legs and feet and around the eyes, high blood pressure, and darker urine.
- Photosensitivity: Exposure to sunlight or even artificial lighting can cause skin lesions or trigger a lupus flare. This symptom necessitates rigorous sun protection measures.
- Hair Loss: Thinning hair is common due to inflammation and scarring on the scalp. Hair may come out in clumps or gradually thin, often becoming more noticeable after washing or brushing.
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon: Many with lupus experience this condition where fingers and toes turn white or blue and feel numb in response to cold temperatures or stress.
- Dry Eyes and Mouth: These symptoms align with Sjögren’s syndrome, which often overlaps with lupus, causing decreased moisture production in glands.
Variability in Severity
The severity of lupus symptoms can vary widely among individuals:
- Mild Symptoms: Some people may experience only mild joint pain, fatigue, and occasional rashes. These symptoms can be intermittent and might not significantly interfere with daily activities.
- Moderate Symptoms: In more moderate cases, symptoms such as persistent fever, frequent flares of joint pain and skin rashes, and more consistent fatigue can affect quality of life and require systematic treatment to manage.
- Severe Symptoms: In severe cases, lupus can cause significant health issues, including major kidney damage (lupus nephritis), neurological problems (such as seizures and psychosis), and increased risk of infections or cardiovascular disease.
If you notice any of these signs persistently, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and possible diagnosis.
Diagnosing Lupus
Understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. Here, we’ll explore the steps involved in diagnosing lupus and discuss the challenges associated with its symptom overlap with other diseases.
The Diagnostic Process for Lupus
1. Patient History: The first step in diagnosing lupus involves a detailed review of the patient’s medical history. Doctors look for a pattern of symptoms that fit the profile of lupus and consider any family history of lupus or other autoimmune diseases.
2. Physical Examination: A thorough physical exam is conducted to check for typical signs of lupus. This includes examining skin rashes, joint swelling, and any other physical manifestations of the disease.
3. Laboratory Tests:
- Antinuclear Antibody Test (ANA): Almost all people with lupus have a positive ANA test. However, a positive result alone isn’t enough for a lupus diagnosis as other autoimmune diseases also show positive ANA tests.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test measures the levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Lupus patients often have abnormalities in these counts.
- Urinalysis: This test helps detect kidney involvement by identifying protein or red blood cells in the urine.
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) and C-reactive Protein (CRP): These tests measure the level of inflammation in the body. Elevated levels might suggest the presence of an inflammatory process such as lupus.
4. Imaging Tests: Doctors may recommend imaging tests like X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRIs to look for organ involvement in lupus, especially in the kidneys and heart.
5. Biopsy: In certain cases, a biopsy of affected tissues (like the kidney or skin) can help confirm the diagnosis. This involves taking a small sample of tissue to look for disease indicators under a microscope.
Challenges in Diagnosing Lupus
- Symptom Overlap: Lupus symptoms often overlap with those of other diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, fibromyalgia, and thyroid disorders. This similarity can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis.
- Variability of Symptoms: Symptoms of lupus can vary widely from person to person and can change over time. This variability makes it difficult to establish a clear diagnosis based solely on symptom presentation.
- Laboratory Test Limitations: While tests like the ANA are helpful, they are not definitive for lupus. Many people without lupus can have a positive ANA, and conversely, some lupus patients might have a negative ANA during their disease course.
- Intermittent Nature of Disease: Lupus can be episodic, with periods of flare-ups and remission. Catching the disease in a non-active phase can complicate the diagnosis process.
However, the diagnosis of lupus involves combining clinical evaluation with laboratory and imaging tests, requiring a careful and comprehensive approach by healthcare professionals.
Treatment Options for Lupus
Effective management of lupus involves a combination of medications tailored to address specific symptoms and the severity of the condition. Here, we explore the current treatment methods available for lupus and highlight the importance of individualized treatment plans.
Current Treatment Methods for Lupus
1. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, are commonly used to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with lupus.
2. Antimalarial Drugs: Medications like hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) are routinely prescribed not only for malaria but also for lupus, especially to manage fatigue, joint pain, and skin rashes. They can also help reduce lupus flares.
3. Corticosteroids: Powerful anti-inflammatory drugs, such as prednisone, are effective in controlling severe lupus symptoms. However, due to potential long-term side effects, their usage is carefully monitored.
4. Immunosuppressants: For more severe cases of lupus, drugs like methotrexate, azathioprine, and cyclophosphamide might be used to suppress the immune system’s activity, thereby reducing damage to healthy tissues.
5. Biologics: Newer biological treatments, such as belimumab, are designed to target specific components of the immune system. They offer a more targeted approach to managing lupus and can be beneficial for those who do not respond to traditional therapies.
6. Lifestyle Adjustments: In addition to medication, lifestyle changes—such as diet modifications, regular exercise, and adequate sun protection—are crucial in managing lupus symptoms and improving overall well-being.
Importance of a Personalized Treatment Plan
The diversity in lupus symptoms and their severity across patients makes a personalized treatment plan essential. A tailored approach ensures that the treatment addresses the unique manifestations of the disease in each patient, which can vary widely from skin and joint issues to organ involvement. Collaborating closely with healthcare providers, patients can develop a treatment strategy that effectively mitigates symptoms, reduces flare-ups, and maintains quality of life.
Effective lupus management requires ongoing assessment and adjustments by healthcare professionals. Regular monitoring helps in adapting the treatment plan to changes in the patient’s condition, optimizing therapy effectiveness, and minimizing potential side effects.
However, understanding the available treatment options and the importance of a personalized approach can empower patients with lupus to take an active role in managing their health. It underscores the necessity of patient-centered care in achieving the best possible outcomes in lupus treatment.
Living with Lupus
With effective management strategies and strong support systems, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are practical tips for managing everyday life with lupus and understanding the importance of support from healthcare providers and groups.
Tips for Managing Everyday Life with Lupus
- Establish a Routine: Having a consistent daily routine can help manage fatigue and stress, common lupus symptoms. Plan regular rest periods to prevent overexertion.
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: Nutrition plays a crucial role in managing lupus. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can help reduce inflammation and support overall health.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in gentle exercises like walking, yoga, or swimming. Regular physical activity can improve strength and flexibility while also boosting mental health.
- Monitor Your Symptoms: Keep a daily log of your symptoms to identify triggers and patterns. This record can be invaluable for your healthcare provider in managing your treatment plan effectively.
- Protect Yourself from the Sun: UV rays can trigger lupus flares. Wear protective clothing, use sunscreen with a high SPF, and avoid direct sunlight during peak hours.
- Prioritize Mental Health: Living with a chronic illness can be emotionally taxing. Consider therapy or counseling to help cope with the psychological aspects of lupus.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Understanding lupus and educating those around you can help manage expectations and foster a supportive environment.
Importance of Support from Healthcare Providers and Support Groups
- Healthcare Providers: Regular consultations with your healthcare provider are crucial. They can adjust your treatment as needed and help manage side effects. Specialists in rheumatology, nephrology, and dermatology can provide targeted care.
- Support Groups: Joining a lupus support group can provide emotional support and valuable information. Connecting with others who understand what you’re going through can be incredibly reassuring and helpful.
- Comprehensive Care: Some healthcare facilities offer multidisciplinary care teams to manage lupus comprehensively. These teams typically include doctors, nurses, psychologists, and social workers who collaborate on your care.
- Educational Resources: Many organizations offer educational materials and resources that help you understand your condition better and keep informed about new treatments and research.
By implementing these management tips and utilizing available support resources, individuals with lupus can maintain their quality of life and take proactive steps towards managing their condition effectively.
FAQs about Lupus Symptoms
What are the common symptoms of lupus?
Lupus symptoms vary widely but often include joint pain, skin rashes, and extreme fatigue. Other common signs are fever, hair loss, and sensitivity to the sun. Since lupus can affect various body systems, some people may also experience kidney issues, inflammation in the lungs, and cardiovascular problems.
Can lupus symptoms appear suddenly?
Yes, lupus symptoms can flare up suddenly and vary in intensity. These flares can be triggered by various factors, including stress, sun exposure, and infections. It’s important for patients to monitor their symptoms closely and consult with their healthcare provider to manage flares effectively.
How do lupus symptoms differ from person to person?
Lupus symptoms can differ significantly between individuals due to the disease’s complexity and how it affects different parts of the body. While some may experience mild joint pain and fatigue, others may suffer from severe organ damage and systemic issues, making personalized medical attention crucial.
Are lupus symptoms constant?
No, lupus symptoms can come and go. Patients may experience periods of flare-ups followed by times when the symptoms improve or even disappear temporarily, known as remission. Managing stress, maintaining a balanced diet, and following treatment plans are vital for managing these fluctuations.
When should someone seek medical advice for lupus symptoms?
It’s advisable to seek medical advice if you experience persistent symptoms like unexplained rashes, ongoing fever, persistent joint pain, or fatigue that interferes with daily life. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the management of the condition.
Conclusion
Understanding the symptoms and causes of lupus is crucial for managing this complex autoimmune disease. Recognizing signs such as joint pain, skin rashes, and fatigue can prompt timely medical intervention, potentially mitigating severe health complications.
If you suspect you or someone you know might be exhibiting symptoms of lupus, it’s imperative to consult with a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are key to improving quality of life for those affected by lupus.
Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice—your health is too important to wait.
References
For those seeking more detailed information on Lupus symptoms and the science behind them, the following reputable sources are recommended. These articles and studies offer extensive insights and are pivotal for validating the information discussed:
- The Lupus Foundation of America – Provides comprehensive guides and articles on the symptoms of Lupus, treatment options, and ongoing research.
Visit the Lupus Foundation of America - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Offers detailed information on Lupus, including statistics, research updates, and symptom management.
Explore CDC Resources on Lupus - Mayo Clinic – Features in-depth articles on the diagnosis and treatment of Lupus, written by medical experts.
Read more at Mayo Clinic - Johns Hopkins Lupus Center – Provides articles and resources that cover everything from Lupus symptoms to advanced treatment options.
Learn from Johns Hopkins Lupus Center
These sources are critical for anyone looking to understand more about Lupus, from patients and families to medical professionals. They ensure that the information you read is accurate, current, and scientifically validated.