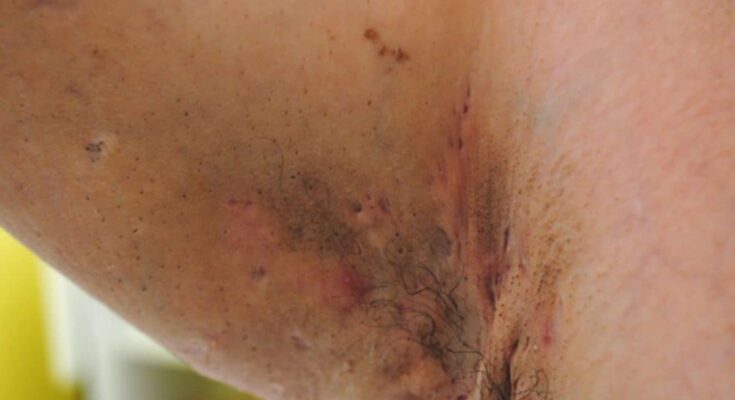
Hidradenitis Suppurativa Treatment: Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is a chronic skin condition characterized by the presence of lumps under the skin.
These lumps are typically painful and may open up as abscesses, causing scarring. HS primarily affects areas where skin rubs together, such as the armpits, groin, buttocks, and breasts.
Understanding the symptoms and early signs of HS is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management.
What is Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is a chronic skin condition characterized by the occurrence of painful lumps under the skin. These lumps typically form where the skin rubs together, such as the armpits, groin, buttocks, and breasts. The lumps are caused by inflammation of the hair follicles and can lead to abscesses, scarring, and tunneling under the skin. HS is often painful and can significantly impact the quality of life of those affected.
Statistics on Prevalence and Demographics Affected
Hidradenitis Suppurativa affects approximately 1 to 4% of the global population. It is most commonly diagnosed in individuals between the ages of 20 and 30, although symptoms can start in adolescence. Women are more likely to develop HS than men, with a female to male ratio of about 3:1. The condition is also more prevalent among people of African descent and those who have a family history of HS, suggesting a genetic component.
List of Symptoms of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
The symptoms of Hidradenitis Suppurativa vary in severity and may include:
- Painful lumps: These are often the first sign of HS and can be very tender.
- Abscesses and drainage: Lumps may become infected, leading to the formation of abscesses that drain pus.
- Scarring and skin changes: Repeated episodes of lumps and drainage can cause significant scarring and skin thickening.
- Odor: Infections and drainage may produce a noticeable odor.
- Tunneling: Over time, tracts or tunnels can develop under the skin connecting different lumps.
- Restricted movement: Severe cases may impair the range of motion, especially when the disease affects areas like the armpits or groin.
Stages of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis Suppurativa progresses in three stages:
- Stage I (Mild): This stage is characterized by the presence of blackheads and small, isolated abscesses without scarring or tunneling.
- Stage II (Moderate): In this stage, individuals experience recurrent abscesses, single or multiple widely separated lesions, and begin to see evidence of scarring and tunneling.
- Stage III (Severe): The most advanced stage, where patients suffer from widespread abscesses and scarring. Multiple interconnected tunnels and subcutaneous tracts are common.
However, understanding the stages of Hidradenitis Suppurativa can help in managing the condition more effectively and targeting treatment to slow its progression and alleviate symptoms.
Causes and Risk Factors of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Understanding the causes and risk factors can help manage and possibly prevent severe symptoms. This section delves into the genetic predispositions, common triggers, lifestyle and environmental factors, and the role of hormones and immune system dysfunction in HS.
Genetic Predispositions and Common Triggers
HS has a notable genetic component, as it often runs in families. Research indicates that individuals with a family history of HS are at a higher risk of developing the condition. Specific genes related to immune system function and inflammation might play a role, although the exact genetic markers are still under investigation.
Common triggers that may exacerbate HS include:
- Friction from clothing: Tight clothing can irritate the skin and cause friction, leading to flare-ups.
- Excessive sweating: Areas prone to sweating, like the armpits and groin, are common sites for HS lesions.
- Smoking: Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes can affect immune response and skin health, worsening HS symptoms.
- Stress: Emotional stress can trigger the immune system and exacerbate skin conditions, including HS.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lifestyle choices and environmental factors can significantly influence the severity and frequency of HS flare-ups. Key factors include:
- Diet: High-glycemic diets and dairy products have been linked to increased inflammation, potentially triggering HS symptoms.
- Obesity: Excess weight increases skin friction and sweat, creating an ideal environment for HS lesions to develop.
- Hygiene: Poor hygiene can exacerbate skin conditions, although over-washing sensitive areas might also irritate the skin and worsen symptoms.
Environmental factors such as heat and humidity can also contribute to the severity of HS, as they promote sweating and friction.
The Role of Hormones and Immune System Dysfunction
Hormonal fluctuations are closely tied to HS, particularly in women. Changes in hormone levels during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, or menopause can trigger or worsen HS symptoms. Androgens (male hormones present in both sexes) can increase the production of sebum and sweat, exacerbating HS.
Immune system dysfunction plays a crucial role in HS. The immune system may mistakenly attack healthy tissue in the hair follicles and sweat glands, leading to inflammation and abscess formation. This chronic inflammation can trigger further immune responses, creating a vicious cycle that perpetuates the condition.
However, understanding these causes and risk factors allows individuals and healthcare providers to develop more effective management strategies for Hidradenitis Suppurativa, potentially improving quality of life for those affected.
Diagnosing Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Diagnosing HS can be complex due to its resemblance to other skin conditions. Here’s a comprehensive guide to the diagnostic tests and procedures for HS, as well as the challenges faced in diagnosing it early.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures for Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Clinical Examination: The first step in diagnosing HS is a thorough clinical examination by a dermatologist. The doctor will look for the telltale signs of HS, such as blackheads in a double-barreled pattern, red bumps, and abscesses that drain pus.
- Patient History: Understanding the patient’s medical and family history is crucial. Doctors often inquire about the duration of the symptoms, frequency of flare-ups, and any family history of similar symptoms.
- Hurst Stage Classification: HS is often classified using the Hurley staging system, which helps in assessing the severity of the condition. This system ranges from Stage I (mild) to Stage III (severe).
- Biopsy: In uncertain cases, a skin biopsy might be performed to rule out other conditions like cancer or deep fungal infections. The biopsy involves taking a small sample of skin tissue for laboratory analysis.
- Ultrasound: High-frequency ultrasound can be used to assess the structure of the skin and underlying tissues, helping to identify tunnels beneath the skin surface, which are common in later stages of HS.
- Blood Tests: While there are no specific blood tests to diagnose HS, tests may be conducted to rule out other conditions or to check for related complications like anemia or inflammation.
Challenges in Diagnosing Hidradenitis Suppurativa Early
- Symptom Similarity: Early symptoms of HS often mimic those of other skin disorders, such as acne, folliculitis, or cysts, leading to misdiagnosis.
- Lack of Awareness: Both patients and healthcare providers may lack awareness about HS, resulting in delays in seeking or providing appropriate care.
- Variable Presentation: Symptoms of HS can vary widely from one patient to another, and even in the same patient over time, complicating the diagnosis.
- Stigma and Patient Reluctance: The placement of lesions in private areas can lead to embarrassment, causing patients to delay seeking medical advice.
- Stage of Presentation: Many patients present in the later stages of the disease, when complications such as scarring and tunneling have already developed, making early diagnosis challenging.
Early and accurate diagnosis of HS is crucial for managing symptoms effectively and improving the quality of life for sufferers. Patients experiencing symptoms consistent with HS are encouraged to consult a dermatologist for a thorough evaluation.
Treatment Options for Hidradenitis Suppurativa
The treatment approach typically includes medications and, in more severe cases, surgical interventions. Understanding these options can help patients manage the condition more effectively.
Medications for Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Medications are the first line of defense in the treatment of HS and aim to reduce inflammation, prevent new flare-ups, and manage pain. Here are some commonly prescribed medications:
- Antibiotics: These are often used to treat and prevent infections associated with HS. They can be taken orally or applied topically. Long-term use might be necessary to manage the condition.
- Corticosteroids: Injected directly into the lesions, corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and pain in the affected areas. However, their usage is usually limited due to potential side effects with long-term use.
- Hormonal Therapies: Hormonal treatments, such as oral contraceptives or anti-androgens, may be effective in some patients, especially when the condition is influenced by hormonal fluctuations.
- Biologics: Biologic drugs, particularly those that block tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, can be prescribed for patients with moderate to severe HS. Adalimumab (Humira) is currently the only FDA-approved biologic for the treatment of HS and has shown significant effectiveness in reducing symptoms.
- Pain Relief Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage the pain associated with HS. For more severe pain, stronger medications may be necessary under a doctor’s supervision.
Surgical Interventions for Hidradenitis Suppurativa
In cases where medication is insufficient to alleviate symptoms or where there is significant scarring, surgical options may be considered:
- Incision and Drainage: This is a short-term solution aimed at relieving pain by draining pus from the severe flare-ups. However, this procedure does not prevent the recurrence of the nodules.
- Excision of Lesions: Complete excision, or surgical removal, of the affected skin areas can be more effective in reducing recurrence but comes with a higher risk of scarring and longer recovery times.
- Laser Surgery: Laser therapy can be used to remove hair follicles that contribute to the blockage and inflammation. It’s less invasive and may require several sessions to achieve significant results.
- Tissue-sparing Techniques: Newer methods, such as deroofing, which involves removing the skin over the tunnels connecting the abscesses, can preserve more healthy tissue and reduce recovery time.
- CO2 Laser: This advanced laser technique is employed to vaporize tissue in affected areas, promoting healing with less damage to surrounding tissues.
However, it’s essential for patients to work closely with a dermatologist experienced in treating HS to find the most effective treatment strategy. Regular follow-ups and adjustments to the treatment plan may be necessary to manage this chronic condition effectively.
Emerging Treatments and Research in Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is a chronic skin condition that causes painful lumps under the skin. Recent years have seen promising developments in the treatment and management of HS. This article explores the latest advancements, ongoing clinical trials, and the future outlook for managing this challenging condition.
Latest Advancements in HS Treatment
The treatment landscape for Hidradenitis Suppurativa is evolving, with new medications and therapeutic approaches showing potential. One of the significant breakthroughs has been the use of biologic drugs, which target specific parts of the immune system that fuel inflammation. Adalimumab, a TNF-alpha inhibitor, is currently the only FDA-approved biologic for HS, but others are being tested in clinical trials.
Laser therapy and radiotherapy are also gaining attention as effective treatments for reducing the severity and frequency of flare-ups. These methods work by targeting affected tissues and reducing the follicular occlusion that characterizes HS. Furthermore, advancements in pain management and wound care continue to improve quality of life for patients.
Clinical Trials and Research Highlights
Clinical trials are pivotal in advancing HS treatment. Researchers are currently investigating several promising therapies, including:
- New Biologics: Drugs that inhibit interleukin-1 (IL-1) and interleukin-17 (IL-17) are being tested, which are crucial in controlling inflammation and have shown promise in early trials.
- JAK Inhibitors: These are small molecule medications that block certain pathways important in the inflammatory process. Early results suggest they could be a powerful tool against HS.
- Microbiome Treatments: Understanding the role of skin bacteria in HS has led to the development of treatments aimed at modifying the skin microbiome to reduce inflammation.
These trials not only help in developing new treatments but also in understanding the underlying mechanisms of the disease, which can lead to more targeted and effective therapies.
The Future of HS Management
The future of HS management looks promising, driven by a combination of technological advancements and a deeper understanding of the disease. Personalized medicine, which tailors treatment based on individual genetic profiles, may play a significant role. This approach could help predict treatment response and optimize therapy choices, reducing the trial and error currently associated with managing HS.
Moreover, there is a growing emphasis on comprehensive care models that integrate dermatologists, surgeons, pain specialists, and psychologists to address all aspects of the disease. This holistic approach ensures that both the physical and psychological impacts of HS are managed effectively.
However, while Hidradenitis Suppurativa remains a challenging condition, the ongoing research and emerging treatments offer hope for better management and improved outcomes for patients. As research continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible, it is an exciting time for both patients and healthcare providers involved in the treatment of HS.
Managing Hidradenitis Suppurativa at Home
Managing this condition at home involves a combination of lifestyle changes, diet adjustments, and specialized skin care routines. Below, we explore effective strategies to help mitigate symptoms and improve the quality of life for those living with HS.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
- Wear Loose Clothing: Tight clothing can irritate the skin and exacerbate HS symptoms. Opt for loose, breathable fabrics that minimize friction and allow air circulation.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is linked to the severity of HS symptoms. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce flare-ups and improve overall skin health.
- Stress Management: Stress is a known trigger for HS flare-ups. Engage in stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises to help manage stress levels.
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regular washing can help reduce the risk of infections, which can worsen HS symptoms. However, it’s important to be gentle and avoid irritating the affected areas.
- Heat Therapy: Applying warm compresses to the affected areas can help reduce pain and swelling associated with HS.
Diet and Exercise Recommendations
- Anti-inflammatory Diet: Adopting a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help manage HS symptoms. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and flaxseeds. Avoid inflammatory foods such as dairy, refined sugars, and processed foods.
- Weight Management: Excess weight can exacerbate HS symptoms by increasing skin friction. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help manage symptoms.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity improves blood circulation and helps reduce inflammation. Choose low-impact exercises such as swimming or cycling, which are easier on the skin.
Skin Care Tips Specifically for HS
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a gentle, fragrance-free cleanser to clean affected areas. Avoid scrubbing, which can irritate the skin and worsen symptoms.
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin moisturized can prevent dryness and reduce irritation. Look for non-comedogenic moisturizers that won’t clog pores.
- Avoid Irritants: Skin care products containing alcohol, perfumes, or dyes can irritate the skin. Opt for hypoallergenic and non-irritating products specifically designed for sensitive skin.
- Consider Medicated Products: Products containing resorcinol, zinc, or clindamycin prescribed by a healthcare provider can help manage HS by reducing bacteria and inflammation.
By incorporating these management strategies, individuals with Hidradenitis Suppurativa can help control flare-ups and reduce discomfort, leading to a better quality of life. Remember, while home management is beneficial, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for a tailored treatment plan.
Psychological Impact of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is not just a skin condition—it deeply affects the emotional and psychological well-being of those diagnosed with it. Living with HS often brings a unique set of challenges, including managing painful physical symptoms and coping with the emotional distress that can accompany visible skin flare-ups.
Emotional and Psychological Toll of HS
The chronic nature of HS can lead to significant emotional distress. Patients frequently report feelings of anxiety and depression due to the unpredictability of flare-ups, which can occur without warning and may be difficult to treat effectively. The visibility of the condition can also lead to self-consciousness and social withdrawal, as sufferers may feel embarrassed by their appearance or fear negative reactions from others.
The pain associated with HS can be debilitating, affecting daily activities and quality of life. This constant discomfort can lead to increased stress levels, which can in turn exacerbate the condition, creating a vicious cycle of physical symptoms and emotional distress.
Importance of Mental Health Support and Resources
Recognizing the psychological impact of HS is crucial in the treatment and management of the disease. Mental health support should be an integral part of the care plan for anyone with HS. Dermatologists and healthcare providers should not only focus on the physical symptoms but also on the emotional needs of their patients.
Mental health professionals can help manage the stress, anxiety, and depression that often accompany HS. Support groups, whether online or in person, can also provide a valuable network for sharing experiences and coping strategies. Such communities help lessen the feeling of isolation by connecting sufferers with others who understand their struggles firsthand.
Patient Stories and Coping Strategies
Sharing personal stories can be a powerful way for patients to connect and learn from each other. Many find solace in hearing others’ experiences with HS, which can provide practical advice and emotional comfort. Common coping strategies shared among HS sufferers include:
- Routine Management: Developing a daily skincare routine that helps manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Implementing stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises to help reduce the impact of stress on the body.
- Dietary Adjustments: Some patients find that certain foods exacerbate their symptoms, so experimenting with dietary changes can sometimes lead to improvements in flare-ups.
However, effective management of HS requires a holistic approach that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of the disease. By providing comprehensive care and support, healthcare professionals can help improve the overall quality of life for those living with hidradenitis suppurativa.
FAQs about Hidradenitis Suppurativa Treatment
What is Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS)?
Hidradenitis Suppurativa is a chronic skin condition characterized by the occurrence of painful lumps under the skin, typically where skin rubs together such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts. These lumps can break open or cause tunnels under the skin.
How is Hidradenitis Suppurativa treated?
Treatment for HS varies depending on the severity of the condition. Options include medications like antibiotics and biologics, lifestyle changes such as weight management and wearing loose clothing, and in severe cases, surgery to remove affected skin areas.
Are there any home remedies for HS?
While home remedies are not a substitute for medical treatment, they can complement it. Applying warm compresses can reduce swelling and pain. Maintaining good hygiene and avoiding irritants can also help manage symptoms.
Can diet affect Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Yes, diet can impact HS. Foods that cause inflammation, such as dairy products and refined sugars, might worsen symptoms. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fish, leafy greens, and whole grains may help manage flare-ups.
Is there a cure for HS?
Currently, there is no cure for Hidradenitis Suppurativa, but with proper treatment, most people can manage their symptoms effectively and lead active lives. Regular consultations with a healthcare provider specializing in skin conditions are crucial.
Can HS go away on its own?
HS is a chronic condition, and while symptoms may improve with treatment, they typically do not disappear completely without medical intervention. It’s important to seek ongoing care and follow a tailored treatment plan.
Conclusion
In summing up the discussion on Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS), it is crucial to reiterate the significance of recognizing and addressing this chronic skin condition. HS is more than just a cosmetic concern; it can profoundly impact an individual’s quality of life, causing significant pain and discomfort. Early detection and treatment are vital to managing the symptoms, preventing progression, and reducing complications associated with the disease.
If you suspect that you or someone you know might be suffering from HS, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. Dermatologists, in particular, are well-equipped to diagnose and treat this condition, offering a range of therapies that can help manage flare-ups and improve overall skin health. Remember, seeking professional help is a step towards healing and should never be delayed.
In encouraging you to take proactive steps towards managing HS, we hope to foster a better understanding of the condition and promote more effective treatment outcomes. With the right support and medical advice, individuals with HS can lead a more comfortable and fulfilling life.
References
For further reading and to validate the information provided on the treatment of Hidradenitis Suppurativa, consider exploring the following reputable sources. These references offer in-depth knowledge and the latest research findings to help readers gain a comprehensive understanding of this condition and its management strategies.
- American Academy of Dermatology Association (AAD) – This resource offers detailed guidelines and treatment strategies for Hidradenitis Suppurativa, backed by dermatological expertise. Learn more about treatment options on the AAD website.
- Mayo Clinic – Known for its patient-centered approach, the Mayo Clinic provides insights into the symptoms, causes, and treatments of Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Visit the Mayo Clinic’s section on Hidradenitis Suppurativa.
- National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD) – NORD provides comprehensive information on rare diseases, including Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Their resources are great for understanding the broader context of the disease. Explore patient and caregiver resources at NORD.
- PubMed Central – An invaluable resource for accessing peer-reviewed scientific papers, PubMed Central offers extensive research articles on the latest treatments and studies related to Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Search for Hidradenitis Suppurativa on PubMed Central.
These sources are essential for patients, healthcare professionals, and researchers interested in the latest and most reliable information on Hidradenitis Suppurativa. They provide a solid foundation for understanding the disease and keeping abreast of new developments in its treatment.