Head and Neck Cancers Symptoms: Head and neck cancers are a group of biologically similar cancers originating in the squamous cells that line the mucosal surfaces of the head and neck.
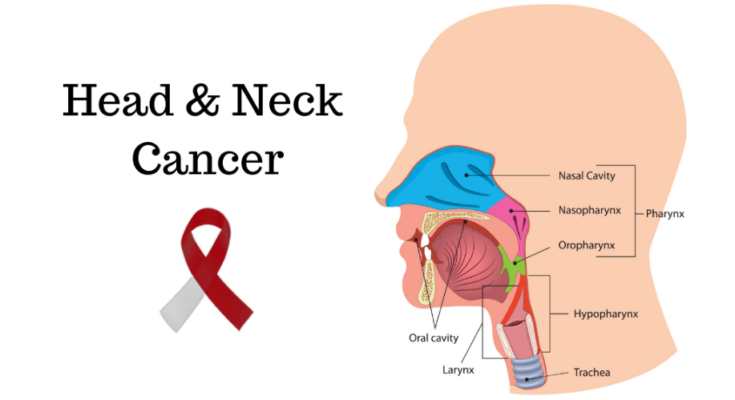
These cancers can affect the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, sinus and nasal cavity, and salivary glands.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of these cancers is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
What are Head and Neck Cancers?
Head and neck cancers primarily refer to a group of malignancies that arise in the tissues and organs of the head and neck region. These cancers typically originate from the squamous cells that line the moist, mucosal surfaces inside the head and neck, such as the mouth, nose, and throat. Some of the main types of cancers classified under this category include oral cavity cancer, oropharyngeal cancer, laryngeal cancer, and nasopharyngeal cancer.
Common Locations for Development
The most common locations where head and neck cancers develop include:
- Oral Cavity: This includes cancers of the lips, tongue, gums, and the inner lining of the cheeks.
- Pharynx: Cancers here may affect the nasopharynx (upper part of the throat behind the nose), oropharynx (middle part of the throat including the base of the tongue and tonsils), and hypopharynx (lower part of the throat).
- Larynx: Also known as the voice box, this is where vocal cord cancers occur.
- Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses: These cancers affect the spaces around the nose and can cause symptoms similar to sinus infections.
Prevalence and Demographics
Head and neck cancers account for approximately 4% of all cancers in the United States. They are more commonly diagnosed in people over the age of 50, with a higher prevalence among men compared to women. Risk factors include tobacco use, heavy alcohol consumption, and exposure to human papillomavirus (HPV). According to recent statistics, over 65,000 individuals in the U.S. are diagnosed with head and neck cancers each year. Globally, these cancers are more prevalent in regions where tobacco and alcohol use are more widespread, and where there are higher incidences of certain viral infections such as HPV.
Symptoms of Head and Neck Cancers
Recognizing the early symptoms of these cancers can significantly enhance the effectiveness of treatment. Here’s a detailed guide to understanding the common signs and when it might be time to consult a medical professional.
Early and Common Symptoms
The symptoms of head and neck cancers can vary, but some are more prevalent. Noticing these early signs can be crucial for timely diagnosis:
- Persistent sore throat: A sore throat that does not go away could be a warning sign, especially if it’s accompanied by difficulty swallowing.
- Change in voice: Hoarseness or changes in the voice that persist for more than two weeks can indicate laryngeal cancer.
- Unexplained weight loss: Significant weight loss without trying could be a symptom of several types of cancer, including those of the head and neck.
- Persistent cough: A cough that doesn’t resolve, particularly if it’s accompanied by blood, is something that needs medical attention.
- Swelling or lumps in the neck: Any lumps on the neck that last for more than two weeks should be evaluated.
- Ear pain: Persistent ear pain, especially on one side, could be associated with throat cancers.
- Trouble breathing or speaking: Any persistent difficulty with breathing or vocalizing should be assessed.
Variability by Location and Type
The symptoms of head and neck cancers can vary significantly depending on the specific location and type of the cancer:
- Oral cavity: Includes cancers of the lips, tongue, gums, and the inside lining of the cheeks. Look for red or white patches in the mouth or lips, mouth sores that don’t heal, and bleeding in the mouth.
- Pharyngeal (throat) cancer: Symptoms can include trouble swallowing, pain when swallowing, and a feeling of something stuck in the throat.
- Laryngeal (voice box) cancer: Watch for breathing difficulties, voice changes, and hoarseness.
- Nasal cavity and sinus cancer: These cancers might present with blocked sinuses that do not clear, sinus infections that do not respond to treatment, and nosebleeds.
When to See a Doctor: Recognizing Alarming Signs
If you experience any of the symptoms listed above, particularly if they have persisted for more than two weeks, it is advisable to see a doctor. Early detection is crucial. Here are some alarming signs that require immediate medical consultation:
- A lump in the neck: Any new growths or a persisting lump in the neck can indicate a need for prompt medical evaluation.
- Persistent hoarseness or voice changes: These symptoms, especially if accompanied by difficulty swallowing or unexplained weight loss, could signal throat or laryngeal cancer.
- Unexplained bleeding: Bleeding from the mouth, nose, or throat that is not due to a known cause should be examined as soon as possible.
Regular check-ups and being aware of the changes in your body are key to early detection of head and neck cancers. If in doubt, it’s always better to err on the side of caution and consult your healthcare provider.
Causes and Risk Factors for Head and Neck Cancers
Understanding the causes and risk factors for these cancers is crucial for prevention and early detection. Below, we delve into the primary causes and risk factors associated with head and neck cancers.
Tobacco Use
Tobacco use is the most significant risk factor for developing head and neck cancers. Both smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes and chewing tobacco can lead to these cancers. Tobacco smoke exposes the mucous membranes of the mouth, throat, and larynx to harmful chemicals that can cause mutations in the DNA of cells, leading to cancer. Similarly, the direct contact of chewing tobacco with the oral tissues can lead to similar damage.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol consumption is another prominent risk factor for head and neck cancers, particularly those in the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx. The risk increases significantly for those who consume alcohol heavily on a regular basis. Alcohol acts as an irritant; it damages cells in the mouth and throat, which can lead to cancerous changes when the body attempts to repair that damage.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
The Human Papillomavirus (HPV), especially HPV16, is strongly linked to oropharyngeal cancers (cancers of the middle part of the throat, including the tonsils and base of the tongue). HPV-related oropharyngeal cancers are distinct from those caused by tobacco and alcohol but are increasing in incidence, particularly among younger populations in developed countries. The virus can be transmitted through oral sex and other forms of close contact, and vaccination against HPV can significantly reduce the risk of these cancers.
Other Risk Factors
Several other factors can increase the risk of developing head and neck cancers, including:
- Prolonged Sun Exposure: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun can cause skin cancer, including cancers of the lip and, less commonly, the face and neck.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Poor dental care and chronic gum disease have been linked to cancers of the oral cavity.
- Exposure to Certain Chemicals: Certain occupational exposures to wood dust, asbestos, synthetic fibers, and other chemicals have been associated with a higher risk of developing nasopharyngeal and laryngeal cancers.
- Epstein-Barr Virus: Particularly relevant in nasopharyngeal cancers among populations in East Asia and North Africa.
Genetic Predispositions and Other Less Common Causes
While less common, genetic factors can predispose individuals to head and neck cancers. Family history of cancer can increase risk, pointing to possible genetic mutations shared among family members. Additionally, certain genetic syndromes like Fanconi anemia and dyskeratosis congenita are known to increase the risk of developing these cancers.
However, understanding these risk factors is essential for individuals and healthcare providers to implement preventative measures and to promote early detection strategies, which can significantly improve outcomes in head and neck cancer cases. Regular dental check-ups, moderating alcohol consumption, avoiding tobacco products, and considering HPV vaccination are practical steps that can help reduce the risk of these serious diseases.
Diagnosing Head and Neck Cancers
The diagnosis of head and neck cancers typically begins with a thorough physical examination. During this initial assessment, doctors look for physical signs of cancer such as lumps, abnormal growths, and asymmetries in the head and neck region. If symptoms or abnormalities are identified, further specialized tests are conducted to confirm the presence of cancer.
Key Medical Tests
1. Imaging Tests:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI scan uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the head and neck. This test is particularly useful for viewing soft tissues and assessing the extent to which the cancer has spread.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: CT scans provide a more detailed look at the area than regular X-rays, using multiple X-ray measurements to create cross-sectional images. They help in identifying the size and location of the tumor.
2. Biopsy Procedures:
- A biopsy is the most definitive way to diagnose cancer. During this procedure, a small sample of tissue is removed from the suspected area and examined under a microscope for cancer cells. Types of biopsies for head and neck cancers include fine needle aspirations, core biopsies, and incisional biopsies, depending on the tumor’s location and nature.
Role of Healthcare Professionals
Various healthcare professionals are involved in the diagnosis of head and neck cancers:
- Dentists: Often the first to notice abnormalities during routine dental check-ups, especially for cancers in the mouth or throat.
- Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) Specialists: These specialists, also known as otolaryngologists, play a pivotal role in diagnosing cancers of the head and neck region. They perform detailed examinations, including endoscopic evaluations of the nasal passages, throat, and voice box.
Early detection remains a key factor in improving the prognosis and quality of life for patients affected by head and neck cancers.
Prevention and Early Detection of Head and Neck Cancers
Preventing head and neck cancers involves implementing strategies that not only reduce the risk of development but also facilitate early detection, which is crucial for successful treatment outcomes. Here are some key approaches to consider:
Lifestyle Changes
Making positive lifestyle changes is one of the most significant steps in preventing head and neck cancers. Here are a few specific actions you can take:
- Quit Smoking: Smoking tobacco significantly increases the risk of various types of cancers, including those in the head and neck area. Quitting smoking can drastically reduce this risk. Numerous resources and support systems are available to help with cessation.
- Reduce Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption is another risk factor for head and neck cancers. By limiting alcohol intake, you can lower your cancer risk substantially.
Regular Medical and Dental Check-Ups
Regular check-ups play a vital role in the early detection of head and neck cancers:
- Medical Screenings: Regular visits to your doctor for physical examinations can help catch signs of cancer early. Discussing any persistent symptoms like a sore throat, hoarseness, or unexplained weight loss can lead to early diagnosis.
- Dental Check-Ups: Dentists can often spot the early signs of oral cancers during routine dental exams. Regular dental visits, at least twice a year, are recommended for maintaining oral health and potentially catching cancerous changes early.
Importance of HPV Vaccination
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is linked to several types of cancers, including some forms of head and neck cancers. Vaccination against HPV can significantly reduce the risk of these cancers:
- HPV Vaccination: The HPV vaccine is effective in preventing the types of HPV that are most often associated with cancer. Vaccination is recommended for preteens, but older individuals can also benefit from it as part of a cancer prevention strategy.
Incorporating these strategies into your daily life can significantly reduce the risk of developing head and neck cancers and improve the chances of catching any potential cancers early when they are most treatable. Regular consultations with healthcare providers, lifestyle adjustments, and vaccinations are key components of a proactive approach to cancer prevention.
FAQs about Head and Neck Cancer Symptoms
What are the common symptoms of head and neck cancers?
The most common symptoms of head and neck cancers include a persistent sore throat, difficulty swallowing, unexplained weight loss, and changes in voice, such as hoarseness. Some people may also experience a lump or mass in the neck area, persistent ear pain, or sores that do not heal.
Can head and neck cancers cause symptoms in other parts of the body?
Yes, head and neck cancers can cause symptoms in other parts of the body. For example, cancers that spread to lymph nodes can cause swelling in the neck or jaw area. Additionally, advanced cancers may lead to symptoms like fatigue, pain, or general ill health due to their impact on the body’s overall functioning.
Are there any early warning signs of head and neck cancers?
Early warning signs of head and neck cancers include persistent sores on the neck, face, or mouth that bleed easily and do not heal within two weeks, white or red patches inside the mouth, and unusual bleeding or numbness in the oral cavity. Early detection of these signs is crucial for effective treatment.
Do all head and neck cancer symptoms mean I have cancer?
Not all symptoms of head and neck cancers necessarily indicate cancer. Many symptoms can be caused by less severe conditions such as infections or inflammation. However, if you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
How are symptoms of head and neck cancers diagnosed?
Symptoms of head and neck cancers are typically diagnosed using a combination of physical examinations, imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs, and biopsy procedures where a small sample of tissue is removed for laboratory analysis. These diagnostic tools help determine the presence and extent of cancer.
What should I do if I notice symptoms of head and neck cancer?
If you notice any symptoms associated with head and neck cancer, it is important to seek medical advice promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. Schedule a visit with your doctor, who may refer you to a specialist in oncology or otolaryngology (ear, nose, and throat) for further evaluation and management.
Conclusion
In summary, recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes of head and neck cancers are crucial steps towards effective management and treatment. These cancers, if caught early, can often be treated successfully, emphasizing the importance of awareness and knowledge.
We encourage everyone to not overlook any persistent changes or discomfort in the head and neck regions. Regular medical advice and screening can be life-saving, offering the best chance for early detection.
Take proactive steps towards your health by scheduling regular check-ups and discussing any concerns with your healthcare provider. Your vigilance could make a significant difference in your health outcomes. Remember, early intervention is key in the fight against head and neck cancers.
References
For those looking to delve deeper into the topics discussed or seeking validation of the information provided on head and neck cancer symptoms, the following resources are invaluable. These sources are reputable and offer comprehensive insights into the complexities of head and neck cancer:
- American Cancer Society (ACS) – Provides detailed information on the types, symptoms, and treatments of head and neck cancers. Visit their site for thorough educational resources and updates on the latest research: American Cancer Society – Head and Neck Cancer.
- National Cancer Institute (NCI) – A part of the U.S. National Institutes of Health, NCI offers a wealth of information on cancer symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment options. Their page on head and neck cancers is an excellent starting point for in-depth research: National Cancer Institute – Head and Neck Cancers.
- Mayo Clinic – Known for its patient-friendly approach to complex medical information, Mayo Clinic provides an overview of symptoms, causes, and treatments of head and neck cancers. Check their resource for a comprehensive understanding: Mayo Clinic – Head and Neck Cancer.
- PubMed Central – An excellent resource for accessing peer-reviewed scientific papers, PubMed Central offers a plethora of articles on recent studies and reviews concerning head and neck cancer. Explore their extensive database for scholarly articles: PubMed Central.
By consulting these resources, readers can enhance their understanding of head and neck cancer symptoms, empowering them with knowledge crucial for early detection and effective management.