Genital Warts Treatment: Genital warts, clinically known as condyloma acuminata, are one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), these growths can affect both men and women and are particularly noted for their appearance on the genital and anal areas.
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment of genital warts is crucial for effective management and prevention of transmission.
Symptoms of Genital Warts
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to more effective management and treatment. Here’s a detailed look at the signs and symptoms of genital warts, including their appearance, common locations, and when to seek medical advice.
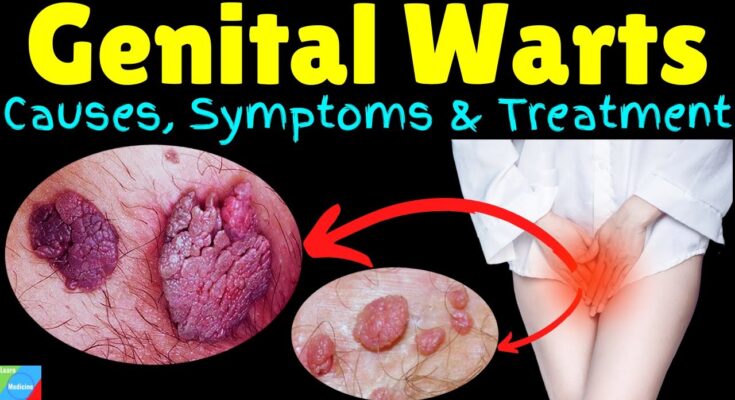
Description of the Appearance of Genital Warts
Genital warts typically appear as small, flesh-colored or gray swellings in your genital area. They can be raised or flat, small or large, and sometimes they cluster together to form a cauliflower-like shape. These warts may not cause pain or discomfort, but they can be itchy or feel tender when touched.
Common Locations on the Body for Genital Warts
Genital warts can appear on several different areas of the body, including:
- In females: Warts may occur on the vulva, the walls of the vagina, the area between the external genitals and the anus, the anal canal, and the cervix.
- In males: Warts are commonly found on the penis, scrotum, or around or inside the anus. Rarely, they can also appear in the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body.
- In both genders: Warts may also develop in the mouth or throat of individuals who have had oral sexual contact with an infected person.
Signs That You Should Seek Medical Advice
It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider if you notice any of the following:
- Persistence of warts: If you observe any bumps or lesions in your genital area that do not go away over time, it’s advisable to get them checked.
- Discomfort or symptoms: Any itching, discomfort, or bleeding from warts, especially during sexual intercourse, should prompt a visit to the doctor.
- After unprotected sex: If you’ve had unprotected sex and suspect you might have been exposed to HPV, it’s wise to seek medical evaluation.
- If you are pregnant: Pregnant women with genital warts should seek advice because the condition can complicate the pregnancy or be transmitted to the baby during delivery.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment of genital warts can help manage the symptoms and reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to others. It’s important to remember that while treatments can remove warts, they do not cure the virus itself. Thus, management of the condition involves regular medical follow-up.
Diagnosing Genital Warts
Here’s how healthcare providers typically diagnose genital warts, the role of visual inspection and medical tests, and the importance of differential diagnosis.
How Healthcare Providers Diagnose Genital Warts
- Visual Inspection: The first step in diagnosing genital warts involves a thorough visual examination by a healthcare provider. Genital warts usually appear as small, flesh-colored or gray swellings in the genital area. They can be raised or flat, single or multiple, and sometimes they cluster together forming a cauliflower-like shape. Healthcare providers can often diagnose genital warts based on their distinctive appearance.
- Medical History: Providers will review the patient’s medical history, including any previous incidents of warts, sexual history, and overall health status. This information helps in understanding the risk factors and potential complications.
- Physical Examination: In addition to looking at the visible warts, a detailed physical examination of the genital area is conducted to check for any other abnormalities that might suggest different conditions.
The Role of Visual Inspection and Possible Medical Tests
While visual inspection is pivotal, sometimes further tests are necessary to confirm the diagnosis of genital warts, especially if the lesions are atypical:
- Acetic Acid Application: A diluted acetic acid solution may be applied to the genital area during the examination. This solution causes the warts to whiten, making them more visible. This test is simple and can be performed during the physical examination.
- Biopsy: In cases where the diagnosis is uncertain, or if the lesions do not respond to standard treatment, a biopsy may be performed. A small sample of the tissue is taken and examined under a microscope. This is particularly important to rule out other conditions, such as cancer.
Importance of Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is vital because several other conditions can mimic the appearance of genital warts, including:
- Molluscum Contagiosum: Another viral infection that leads to small, pearly bumps on the skin.
- Genital Herpes: Characterized by painful sores and unlike the warts caused by HPV.
- Syphilis: Presents with a sore initially, which can sometimes be confused with warts if not properly examined.
Correctly distinguishing genital warts from these and other conditions is crucial as it affects treatment options and outcomes. It also helps in providing the correct advice on sexual health and preventing the spread of infections.
However, diagnosing genital warts involves a combination of visual inspection, medical history, physical examination, and occasionally, confirmatory tests. Differential diagnosis plays a critical role in ensuring appropriate treatment and in differentiating genital warts from other conditions that can present with similar symptoms. Early and accurate diagnosis helps in managing the condition more effectively and reduces the risk of complications.
Professional Treatments for Genital Warts
Managing this condition effectively often requires professional medical treatments. These treatments can be broadly categorized into topical treatments and surgical options, each with its own set of benefits and risks. Here’s a detailed look at the available professional treatments for genital warts:
Topical Treatments for Genital Warts
Topical treatments are medications applied directly to the skin. They are often the first line of treatment due to their ease of use and non-invasive nature. Here are some commonly prescribed topical treatments:
- Imiquimod Cream: Boosts the immune system to fight the virus. It’s used primarily for external warts.
- Podofilox Solution: Destroys wart tissue and is applied directly by the patient at home.
- Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA): Applied by a healthcare provider, this chemical burns off the warts.
These medications can vary in their effectiveness, and they may cause side effects such as skin irritation or mild pain.
Surgical Options for Genital Warts
For persistent, larger, or internally located warts, surgical interventions may be recommended. The following are the main surgical options:
- Cryotherapy: This method freezes the warts with liquid nitrogen. It’s effective for both external and internal warts and has minimal side effects, though repeat treatments are often necessary.
- Electrosurgery: Involves burning off the warts with high-frequency electrical currents. This is particularly effective for large clusters of warts and is usually done under local anesthesia.
- Laser Treatment: Utilizes intense beams of light to destroy wart tissue. It’s a good option for extensive or tough-to-treat warts and can be used when other treatments fail.
- Surgical Excision: The warts are cut out with a scalpel, which offers immediate results. This is usually performed under local anesthesia and is suitable for large or resistant warts.
Benefits and Risks Associated with Each Treatment Method
Each treatment method for genital warts has its advantages and potential drawbacks:
Topical Treatments:
- Benefits: Non-invasive, can be applied in the privacy of your home.
- Risks: May cause local skin reactions, require prolonged treatment periods to achieve effectiveness.
Cryotherapy:
- Benefits: Quick procedure, relatively low pain, effective with potentially fewer sessions than topical treatments.
- Risks: Can cause discomfort during the procedure, potential for mild scarring.
Electrosurgery:
- Benefits: Effective for removing large warts quickly.
- Risks: Requires local anesthesia, can cause pain and has a higher risk of scarring.
Laser Treatment:
- Benefits: Highly effective for extensive and recurrent warts.
- Risks: More expensive, may require anesthesia, and carries a risk of scarring.
Surgical Excision:
- Benefits: Immediate results, effective for large and stubborn warts.
- Risks: Invasive, risk of scarring, requires anesthesia.
When choosing a treatment for genital warts, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider who can assess the specific situation and recommend the most appropriate option based on the size, location, and number of warts, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Home Care and Alternative Treatments for Genital Warts
Genital warts, a common condition caused by the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), can be distressing and uncomfortable. While professional medical treatment is crucial, understanding self-care practices and exploring over-the-counter products can support your healing process. However, it’s essential to be aware of the limitations and risks associated with unverified treatments.
Self-Care Practices That Complement Professional Treatments
When managing genital warts, self-care practices can play a supportive role alongside prescribed treatments. Here are a few strategies that can aid comfort and recovery:
- Maintain Hygiene: Keep the affected area clean and dry. Use mild soap and lukewarm water to gently wash the area, avoiding any harsh scrubbing that could irritate the warts.
- Avoid Irritants: Steer clear of perfumed soaps, bubble baths, and colored or scented toilet paper, as these can aggravate symptoms.
- Wear Comfortable Clothing: Opt for loose, breathable garments that allow air circulation and reduce moisture buildup, which can exacerbate the condition.
- Boost Your Immune System: A strong immune system can help your body fight off the virus. Focus on a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, get regular exercise, and ensure adequate sleep.
Over-the-Counter Products and Their Effectiveness
Several over-the-counter (OTC) products claim to treat genital warts, but their effectiveness can vary:
- Salicylic Acid: This common wart treatment helps peel away the wart layer by layer. It’s more suitable for warts on other parts of the body and should be used with caution on genital warts due to the sensitive nature of the skin.
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antiviral properties, tea tree oil may reduce wart symptoms when applied topically. However, it should be used diluted and with care, as it can cause irritation or allergic reactions.
- Aloe Vera: Often used for its soothing properties, aloe vera gel can help relieve irritation, although it does not eliminate warts.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any over-the-counter treatment to ensure it’s appropriate for your specific situation.
Warning About the Limitations and Risks of Unverified Treatments
While exploring alternative treatments, it’s crucial to be cautious. Here are a few points to consider:
- Unverified Treatments: Many products and remedies available online or over the counter are not backed by scientific research and may be ineffective or even harmful.
- Risk of Misdiagnosis: Self-diagnosing and treating what you believe to be genital warts could lead to overlooking a more serious condition. Always consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
- Potential for Worsening Symptoms: Incorrect treatments can aggravate the condition, leading to increased discomfort or more complex health issues.
However, while self-care practices and some OTC products can offer relief and complement professional treatments, it is essential to approach the treatment of genital warts with caution. Always seek guidance from a healthcare provider to choose the safest and most effective treatment strategy.
Prevention of Genital Warts
Preventing genital warts is crucial not only for personal health but also for reducing the spread of HPV in the population. Here are effective strategies to prevent genital warts:
Vaccination Against the HPV Virus
One of the most effective methods to prevent genital warts is through vaccination. The HPV vaccine is designed to protect against the most common types of viruses that cause genital warts and cervical cancer. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends HPV vaccination for preteens aged 11 to 12 years, but it can be administered as early as age 9 and up to age 45 in some cases. Getting vaccinated before becoming sexually active significantly increases the effectiveness of the vaccine. It is important to complete the entire vaccination series for optimal protection.
Safe Sex Practices to Prevent the Spread of HPV
Practicing safe sex is another key strategy in the prevention of genital warts. Using latex condoms every time you engage in sexual intercourse can greatly reduce the risk of transmitting HPV. However, it is important to note that HPV can also infect areas not covered by a condom, so condoms may not fully protect against HPV. Maintaining a monogamous relationship and reducing the number of sexual partners can also decrease the risk of HPV infection and the subsequent development of genital warts.
Importance of Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular health check-ups play a vital role in preventing genital warts by ensuring early detection and treatment of any HPV infection. Routine screenings, such as Pap tests for women, can detect HPV-related health issues before they develop into more serious conditions. Men and women who are sexually active should discuss their risk factors with their healthcare provider and seek advice on the frequency of health check-ups. Early intervention can prevent complications and reduce the spread of the virus.
By following these preventive measures—vaccination, safe sex practices, and regular health check-ups—you can protect yourself and others from genital warts and help control the spread of HPV. Stay informed and take proactive steps towards your sexual health.
Living with Genital Warts: Understanding the Emotional Impact and Managing Symptoms
Living with genital warts can be challenging, not just physically but also emotionally and psychologically. This common condition, caused by certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV), often carries a stigma that can significantly affect your mental health and well-being. It’s important to understand the impact of genital warts and to know how to effectively manage symptoms and prevent transmission.
Emotional and Psychological Impact of Having Genital Warts
Being diagnosed with genital warts can lead to a range of emotional responses, including anxiety, embarrassment, and distress. The visibility of the condition can make you feel self-conscious and may negatively impact your intimate relationships. It’s crucial to acknowledge these feelings and consider seeking support from a counselor or a support group who can provide a safe space to express these concerns. Remember, genital warts are a medical condition—they do not define your worth or character.
Advice on Managing Symptoms and Preventing Transmission to Partners
Managing the symptoms of genital warts effectively can help reduce the risk of transmission and alleviate some of the stress associated with the condition. Here are some practical tips:
- Follow Treatment Plans: Use prescribed medications, such as topical creams, as directed by your healthcare provider. These treatments can help control outbreaks and reduce the visibility of warts.
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regular washing and keeping the affected area dry can prevent further irritation or infection.
- Use Protection: While not 100% effective at preventing HPV transmission, using condoms can significantly reduce the risk of spreading genital warts to your partner.
Open communication with your partner about your condition is also essential. Discussing your health status not only promotes trust but also allows you both to make informed decisions about precautions and testing.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider for Ongoing Management
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for managing genital warts effectively. Schedule visits if:
- You notice new warts appearing after treatment
- Existing warts grow larger or become painful
- You experience psychological distress that affects your daily life
Healthcare providers can offer solutions for managing outbreaks and can also provide resources for emotional support. Remember, early intervention and consistent management can greatly improve your quality of life.
By understanding the emotional impacts and employing strategies to manage symptoms and communication, you can maintain a fulfilling life even with genital warts. Remember, you’re not alone, and professional help is always available to guide you through this journey.
FAQs on Genital Warts Treatment
What are the treatment options for genital warts?
Genital warts can be treated in several ways, depending on their size, location, and your overall health. Common treatments include topical medications like imiquimod, podophyllin, and podofilox, which are applied directly to the warts. Other options include cryotherapy (freezing the warts off), electrocautery (burning the warts with electric current), surgical removal, and laser treatments. Your healthcare provider will recommend the best treatment based on your specific case.
Can genital warts be treated at home?
While some topical treatments can be applied at home, it’s crucial to first consult with a healthcare provider. Over-the-counter remedies for other types of warts should not be used for genital warts due to the sensitive nature of the skin involved. Home treatments without professional guidance can lead to skin damage and other complications.
How long does it take to see results from treatment?
The duration of treatment for genital warts varies depending on the method used and individual factors like the immune system’s strength and the size and number of warts. Some treatments, like topical creams, may show improvements in a few weeks, while procedures like cryotherapy might show results immediately. However, multiple treatment sessions are often necessary, and warts can recur.
Are genital wart treatments covered by insurance?
Many insurance plans cover treatments for genital warts, but coverage can vary based on the specific plan and treatment method. It is advisable to check with your insurance provider to understand what treatments are covered and any out-of-pocket costs you might incur.
Do genital wart treatments have side effects?
Yes, treatments for genital warts can have side effects. Topical medications may cause skin irritation, redness, and discomfort. Procedures like cryotherapy and surgical removal can sometimes result in pain, swelling, and scarring. Discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider to fully understand the risks and benefits of each treatment option.
Can genital warts be completely cured?
While treatments can effectively remove visible warts and alleviate symptoms, genital warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), which may remain in your system. This means warts can recur, and ongoing monitoring and additional treatments may be necessary. Vaccines are available to help prevent some types of HPV that cause genital warts and can reduce the risk of recurrence.
Conclusion
In summary, the recognition, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment of genital warts are crucial for managing this common yet often distressing condition. It’s essential to understand the potential risks and complications associated with genital warts, including their impact on physical and psychological well-being.
If you suspect that you or someone you know might have genital warts, it is important to seek professional medical advice. While home remedies may seem appealing, they are not a substitute for professional treatment. Medical professionals can offer proven therapies that are safe and effective, tailored to your specific needs. They can also provide necessary guidance on how to prevent the spread of the virus and manage symptoms.
We encourage everyone to prioritize health and not delay consulting a healthcare provider for any concerns about genital warts. Remember, early intervention is key to successful management and can significantly improve your quality of life. Don’t rely solely on unverified treatments—professional help is readily available and is the best course of action for health and safety.
References
For those seeking additional information on genital warts treatment and wishing to explore reputable sources for validation and further reading, the following references are invaluable. Each listed source provides comprehensive insights and reliable information on the management and treatment of genital warts.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – The CDC offers up-to-date information on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of genital warts, focusing on medical guidelines and public health policies. CDC Genital Warts Resources
- World Health Organization (WHO) – WHO provides a global perspective on the healthcare strategies for managing genital warts, including prevention techniques and treatment options available worldwide. WHO Information on HPV and Genital Warts
- Mayo Clinic – A respected healthcare organization, Mayo Clinic offers detailed articles on symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatments for genital warts, written by medical professionals. Mayo Clinic on Genital Warts
- WebMD – WebMD provides accessible, peer-reviewed health information on genital warts, including a breakdown of treatment options and preventative measures. WebMD Guide to Genital Warts
- Healthline – Known for its clear, authoritative content, Healthline discusses the latest treatments for genital warts and offers guidance on living with HPV. Healthline on Treating Genital Warts
These resources are essential for anyone looking to understand more about genital warts, from basic facts and prevention to advanced treatment options. They provide readers with credible and thorough information, helping them make informed health decisions.