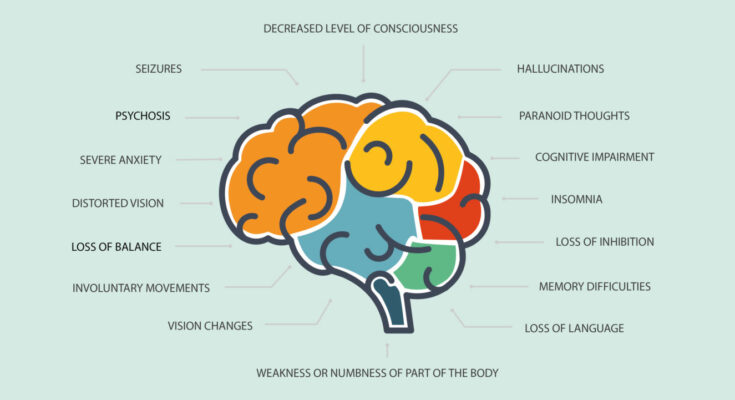
Encephalitis Symptoms: Encephalitis is a severe medical condition characterized by the inflammation of the brain. This inflammation can result from a variety of causes, including viral infections, autoimmune diseases, and sometimes even unknown factors.
The condition can affect individuals of any age, background, or health status, making it a universal health concern.
What is Encephalitis?
Encephalitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the brain. This inflammation can be caused by various factors, including infections (viral, bacterial, or fungal), autoimmune diseases, or as a secondary response to other health complications. Encephalitis is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention to prevent potential long-term complications or even death.
How Encephalitis Affects the Brain
When encephalitis occurs, the brain’s inflammation leads to swelling, which can disrupt the normal function of the brain. Symptoms can range from mild, such as fever and headache, to severe, including seizures, confusion, difficulty speaking or hearing, and loss of consciousness. The swelling can damage or destroy nerve cells, potentially leading to lasting brain damage. The brain’s ability to communicate with the rest of the body can be compromised, affecting the individual’s cognitive, physical, and emotional functions.
Types of Encephalitis
There are several types of encephalitis, each with its causes and implications:
- Viral Encephalitis: The most common type, caused by various viruses such as herpes simplex virus (HSV), enteroviruses, and arboviruses like the West Nile virus. Treatment typically involves antiviral medications.
- Autoimmune Encephalitis: Occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy brain cells. It can be associated with certain cancers or occur in isolation.
- Bacterial and Fungal Encephalitis: Less common than viral encephalitis, these types are caused by bacterial or fungal infections. They are treated with antibiotics or antifungal medications, respectively.
- Primary Encephalitis: This occurs when a virus or other agent directly infects the brain. The infection may be focal or diffuse.
- Secondary Encephalitis: Results from a faulty immune system response to an infection elsewhere in the body. Instead of fighting off the infection, the immune system mistakenly attacks the brain, leading to inflammation.
Each type of encephalitis has its specific treatment protocols, emphasizing the importance of accurate diagnosis and swift medical intervention. Awareness and understanding of encephalitis are crucial for early detection and effective treatment, potentially minimizing the long-term impacts on those affected.
Common Symptoms of Encephalitis
Understanding these common symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment. This comprehensive guide outlines the key symptoms associated with encephalitis, emphasizing the variability in symptom presentation based on the underlying cause and infection severity.
Mild Symptoms
Mild symptoms of encephalitis often resemble those of the flu and can include:
- Fever: A slight to moderate increase in body temperature.
- Fatigue: General feelings of tiredness and a lack of energy.
- Headache: Persistent or severe headaches not alleviated by over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Joint Pain: Discomfort or pain in the joints.
- Muscle Aches: General muscle discomfort which can be widespread or localized.
- Sore Throat: Irritation or pain in the throat, often accompanied by difficulty swallowing.
Severe Symptoms
In more severe cases, encephalitis symptoms can escalate, necessitating immediate medical attention. These include:
- Seizures: Uncontrolled electrical disturbances in the brain leading to convulsions, which can be focal or generalized.
- Paralysis: Partial or complete loss of muscle function in one or more parts of the body.
- Sensory Changes: Alterations in vision, smell, or taste, such as blurred vision, double vision, or hallucinations.
- Confusion and Disorientation: Difficulty with concentration, memory lapses, or profound disorientation.
- Personality Changes: Sudden changes in mood, behavior, or personality, including agitation or aggression.
- Problems with Speech or Hearing: Difficulty understanding speech, speaking, or hearing issues.
- Loss of Consciousness: From brief fainting spells to prolonged comas.
Variation by Type and Severity
The symptoms of encephalitis can vary significantly based on the type of virus or bacteria causing the infection, as well as the severity of the inflammation. For instance, encephalitis caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV) may present more abruptly and severely than encephalitis resulting from other causes. Additionally, individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or those receiving immunosuppressive therapies, may experience more severe symptoms and complications.
Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes, reducing the risk of long-term complications associated with encephalitis. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms consistent with encephalitis, contact a healthcare provider immediately for a comprehensive evaluation.
Causes of Encephalitis
Encephalitis, a condition characterized by the inflammation of the brain, can stem from various origins. Understanding the causes is crucial for both prevention and treatment. This section delves into the general causes of encephalitis, highlighting viral infections as the predominant factor, alongside other significant causes such as autoimmune conditions and less common origins like bacterial and parasitic infections.
Viral Infections: The Forefront of Encephalitis Causes
The leading cause of encephalitis is viral infections. Various viruses have been identified as culprits, capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier to infect the brain. Among these, the herpes simplex virus (HSV) stands out due to its severity and prevalence. HSV can lead to herpes simplex encephalitis, a serious condition that requires prompt treatment.
Another noteworthy virus is the West Nile virus, transmitted through mosquito bites. It can cause West Nile encephalitis, showcasing how vector-borne diseases play a role in the spread of viruses leading to encephalitis. Other viruses, such as enteroviruses, varicella-zoster virus (responsible for chickenpox and shingles), and the measles virus, also contribute to the array of viral agents capable of causing encephalitis.
Autoimmune Conditions: When the Body Attacks Itself
Apart from viral causes, autoimmune conditions represent a significant segment of encephalitis cases. In these scenarios, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy brain cells, leading to inflammation. Conditions such as autoimmune encephalitis highlight the complex interplay between the immune system and the brain, underscoring the importance of recognizing and treating autoimmune triggers to manage encephalitis effectively.
Less Common Causes: Beyond Viruses and Autoimmunity
While viruses and autoimmune responses account for a considerable portion of encephalitis cases, it’s essential to acknowledge less common causes. Bacterial infections, though rarer, can lead to encephalitis. Specific bacteria, including those responsible for Lyme disease or syphilis, have been implicated in certain cases.
Parasitic infections, too, play a role, albeit a smaller one, in the landscape of encephalitis causes. Parasites like Toxoplasma gondii, which can be contracted from undercooked meat or contaminated water, can cause encephalitis, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems.
However, understanding these causes is pivotal for effective prevention, diagnosis, and treatment strategies. By addressing the wide range of potential triggers, healthcare professionals can better safeguard against the diverse manifestations of encephalitis.
Diagnosing Encephalitis
Understanding the symptoms and causes of encephalitis is crucial, but the real challenge often lies in its diagnosis. Encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain, requires timely recognition and treatment to prevent potentially severe outcomes. This article delves into the significance of early diagnosis and outlines the common diagnostic tests and procedures utilized in identifying this condition.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of encephalitis is paramount for several reasons. Primarily, it allows for the prompt initiation of treatment, which can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve the prognosis. Early therapeutic interventions can mitigate the severity of symptoms, prevent the spread of infection, and safeguard against long-term neurological damage. Given the rapid progression of encephalitis in some cases, the window for effective intervention may be narrow, underscoring the necessity for swift action.
Detecting encephalitis early also facilitates the identification of the underlying cause, whether it be viral, bacterial, or autoimmune. This determination is crucial, as it directs the treatment strategy, ensuring that it is tailored to combat the specific agent responsible for the inflammation. Furthermore, early diagnosis helps in monitoring the disease’s progression and adjusting treatment plans as needed, offering the best chance for recovery.
Common Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
The diagnosis of encephalitis involves a combination of clinical evaluation and specific tests, aimed at confirming the presence of brain inflammation and identifying its cause. Here are the most common diagnostic tests and procedures employed:
- Neurological Examination: A thorough neurological exam helps assess brain function and identify areas affected by inflammation. This may involve testing reflexes, strength, sensation, coordination, and cognitive functions.
- Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap): This procedure involves collecting a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the spinal canal. CSF analysis can reveal signs of inflammation and detect pathogens responsible for the condition.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI of the brain can provide detailed images, revealing areas of inflammation, swelling, or damage. It’s instrumental in ruling out other conditions that might mimic encephalitis.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): By measuring the electrical activity in the brain, an EEG can identify patterns that suggest inflammation or dysfunction in brain activity, common in encephalitis cases.
- Blood Tests: Blood samples may be analyzed for evidence of infection or immune responses that indicate encephalitis. These tests can also help identify the infectious agent or autoimmune markers.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Testing: This test can detect the DNA or RNA of viruses in various samples (CSF, blood, or tissue), offering a direct method to identify viral causes of encephalitis.
- Biopsy: Although rarely performed, a brain biopsy (taking a small tissue sample) can be conclusive in diagnosing encephalitis when other tests are inconclusive.
Timely and accurate diagnosis of encephalitis is a critical step in managing the disease effectively. The use of these diagnostic tests, combined with a comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals, ensures the best possible outcomes for those affected. By recognizing the importance of early diagnosis and employing the appropriate diagnostic procedures, medical practitioners can pave the way for effective treatment and recovery.
Treatment Options for Encephalitis
Encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain, requires immediate medical attention. Treatment options vary based on the cause of the inflammation but aim to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and address the underlying cause. Here is a comprehensive list of treatment approaches for encephalitis:
Antiviral Medications
For encephalitis caused by viruses, antiviral medications are the frontline treatment. Drugs such as acyclovir are commonly prescribed for herpes simplex virus, the most frequent cause of encephalitis. It’s crucial to start antiviral treatment as soon as possible to enhance effectiveness.
Antibiotic Treatments
Although encephalitis is more often caused by viruses, when a bacterial infection is suspected, antibiotics are administered. Identifying the specific bacterial cause is essential for selecting the most effective antibiotic.
Steroids
Steroids, such as dexamethasone, may be used to reduce brain swelling and inflammation. This treatment approach is particularly relevant when the encephalitis causes significant swelling that could damage the brain.
Supportive Care
Supportive care in a hospital setting is critical for individuals with encephalitis. This can include:
- Fluid Management: To maintain hydration and electrolyte balance.
- Pain Management: Using medications to alleviate headaches and body aches.
- Anti-Seizure Medications: To prevent or control seizures that might occur due to brain inflammation.
- Rest and Rehabilitation: Cognitive and physical therapy may be necessary during recovery to regain lost functions.
Immunotherapy
For encephalitis caused by an autoimmune response or not responsive to antiviral medications, immunotherapy can be effective. This includes treatments that modify the immune system’s response, such as intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) or plasma exchange (plasmapheresis).
Surgical Intervention
In rare cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to relieve pressure within the brain or to remove a source of infection or inflammation.
The treatment of encephalitis is multifaceted, often requiring a combination of medications, supportive care, and sometimes surgery. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for the best outcomes. It’s important to consult healthcare professionals if encephalitis is suspected, as they can provide the most appropriate care based on the cause and severity of the condition.
Preventing Encephalitis: Essential Strategies and Tips
Encephalitis, a serious condition that causes inflammation of the brain, can result from various causes, including viral infections. Fortunately, there are effective strategies for prevention, focusing on vaccinations, avoiding mosquito and tick bites, and maintaining personal hygiene and sanitation.
Vaccinations and Their Role in Prevention
Vaccinations stand as the frontline defense against encephalitis. They prepare the immune system to fight off specific viruses known to cause the condition, such as Japanese encephalitis, tick-borne encephalitis, and certain forms of herpes simplex virus. Staying up-to-date with recommended vaccines is crucial for individuals living in or traveling to areas where these viruses are prevalent. It’s essential to consult healthcare providers about the necessary vaccinations based on travel plans and local health recommendations.
Tips for Avoiding Mosquito and Tick Bites
Mosquitoes and ticks are common vectors for the viruses that lead to encephalitis. Reducing exposure to these insects significantly lowers the risk of infection. Here are practical tips to avoid bites:
- Use Insect Repellent: Apply insect repellent that contains DEET, picaridin, IR3535, or oil of lemon eucalyptus on exposed skin and clothing.
- Wear Protective Clothing: When outdoors, especially in wooded or grassy areas, wear long-sleeved shirts, pants, and hats to cover the body as much as possible.
- Secure Living Spaces: Install screens on windows and doors to keep mosquitoes out. Use air conditioning when available.
- Be Mindful of Peak Activity Times: Mosquitoes are most active during dusk and dawn, while ticks thrive in warm months. Plan outdoor activities accordingly to avoid peak times.
- Check for Ticks: After spending time in tick-prone areas, thoroughly check your body, children, and pets for ticks. Remove any ticks found promptly and correctly.
Importance of Personal Hygiene and Sanitation
Good personal hygiene and proper sanitation can also play a vital role in preventing encephalitis. Viruses that cause encephalitis can spread through respiratory droplets or fecal contamination. Thus, regular handwashing with soap and water, especially before eating or after visiting the bathroom, is essential. Keeping living environments clean and free from pests helps reduce the risk of infection.
Ensuring access to clean water and proper disposal of waste further contributes to preventing the spread of infections that could lead to encephalitis. In areas where sanitation infrastructure is lacking, using water purification methods and ensuring safe food preparation practices are critical steps.
Preventing encephalitis involves a combination of proactive measures, including getting vaccinated, minimizing exposure to mosquito and tick bites, and adhering to good hygiene and sanitation practices. These strategies not only reduce the risk of encephalitis but also contribute to overall health and well-being. Always stay informed about local health advisories and consult healthcare professionals to take appropriate preventive measures based on individual risk factors and geographic location.
When to See a Doctor
Recognizing the symptoms of encephalitis and understanding the urgency of seeking medical attention are critical steps in ensuring your health and well-being. Encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain, requires immediate medical evaluation due to its potential severity and the speed at which it can progress. This section provides advice on when to see a doctor if you suspect you or someone you know might have encephalitis.
Recognizing Symptoms of Encephalitis
Encephalitis presents a range of symptoms that can vary from mild to severe. These symptoms can develop over several days or can appear suddenly. Key symptoms to be aware of include:
- High fever
- Severe headache
- Confusion or altered consciousness
- Seizures
- Stiff neck
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Unusual behavior or personality changes
- Severe fatigue
- Problems with speech or hearing
- Difficulty moving or coordination issues
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other medical conditions, making it crucial to seek professional medical advice for an accurate diagnosis.
Urgency of Seeking Medical Attention
If you or someone you know exhibits symptoms of encephalitis, it is imperative to seek medical attention immediately. Encephalitis is a condition that can rapidly worsen, leading to more serious complications such as loss of consciousness, long-term neurological issues, or even death if not treated promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to improving outcomes and reducing the risk of long-term complications.
When to seek emergency medical care:
- If the person experiences a seizure for the first time
- If there’s a sudden change in mental status or consciousness
- If severe headache, fever, and stiff neck are accompanied by nausea and vomiting
- If any symptoms of encephalitis appear suddenly and severely
If you suspect encephalitis, do not wait to see if symptoms improve on their own. Contact a healthcare provider or go to the nearest emergency department to ensure the best possible care and treatment. Remember, encephalitis is a medical emergency, and early intervention is key to recovery.
FAQs About Encephalitis Symptoms and Causes
What is Encephalitis?
Encephalitis is an inflammation of the brain, often caused by an infection. This condition can lead to symptoms ranging from mild flu-like signs to severe brain damage. Understanding encephalitis is crucial for early detection and treatment.
What Causes Encephalitis?
The primary causes of encephalitis are viral infections. However, bacteria, fungi, and parasites can also lead to this condition. In some cases, encephalitis can occur as a secondary immune response to an infection elsewhere in the body.
What are the Symptoms of Encephalitis?
Symptoms of encephalitis can vary widely. Mild symptoms may include fever, headache, and fatigue, while severe cases can present with confusion, seizures, sensory changes, and even loss of consciousness. Recognizing these symptoms early is key to effective treatment.
How is Encephalitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing encephalitis typically involves a combination of methods, including medical history, physical exams, brain imaging tests like MRI or CT scans, lumbar punctures to test cerebrospinal fluid, and blood tests to identify the infection causing the inflammation.
Can Encephalitis be Treated?
Yes, encephalitis can be treated, though the approach depends on the underlying cause. Treatments may include antiviral medications, antibiotics (if a bacterial infection is the cause), corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and supportive care to relieve symptoms.
Is Encephalitis Contagious?
Encephalitis itself is not contagious, but the infections causing it can be. Viral forms of encephalitis, like those caused by the herpes simplex virus, are spread through direct contact with infected individuals or surfaces.
How Can I Prevent Encephalitis?
Preventive measures include practicing good hygiene, staying up to date on vaccinations, and using insect repellent to protect against mosquito-borne viruses. Maintaining a strong immune system through a healthy lifestyle can also reduce your risk.
When Should I See a Doctor?
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of encephalitis, especially severe headache, fever, confusion, or seizures, seek medical attention immediately. Early intervention is crucial for a positive outcome.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of encephalitis and understanding its causes holds paramount importance for our health and well-being. This condition, marked by the inflammation of the brain, can lead to severe complications if left untreated. By being aware of the early signs, such as fever, headache, confusion, and seizures, individuals can seek timely medical intervention, significantly improving the chances of recovery.
It is crucial to acknowledge the various causes of encephalitis, which range from viral infections to autoimmune diseases and even environmental factors. This knowledge not only aids in the diagnosis and treatment but also underscores the importance of preventive measures. Vaccinations, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding exposure to known viruses and bacteria can play a significant role in preventing the occurrence of encephalitis.
We encourage everyone to take these preventive steps seriously and to not hesitate in consulting healthcare professionals when experiencing symptoms indicative of encephalitis. Early medical advice and intervention can make a substantial difference in outcomes, offering a clearer path to recovery.
Taking action towards understanding and preventing encephalitis is a critical step in safeguarding our health. Let’s commit to staying informed and proactive in recognizing the signs of this condition, embracing preventive measures, and seeking medical advice when necessary. Together, we can minimize the impact of encephalitis and ensure a healthier future for all.
References
For those seeking further information on encephalitis symptoms and desiring reputable sources for validation, the following references are invaluable. These links lead to trusted medical resources and organizations dedicated to providing accurate and up-to-date health information.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – The CDC’s comprehensive overview on encephalitis covers causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies. This resource is pivotal for understanding the complexity of encephalitis and its impact on health. Read more about encephalitis at CDC.
- World Health Organization (WHO) – WHO provides a global perspective on encephalitis, including statistics, research findings, and international health guidelines. Their documentation is crucial for those looking to understand the global impact of encephalitis. Explore WHO’s encephalitis resources.
- Mayo Clinic – Renowned for patient care and research, the Mayo Clinic offers an in-depth look at encephalitis symptoms, diagnosis methods, and treatment options. Their resource is patient-friendly and includes advice on managing the condition. Visit Mayo Clinic’s encephalitis guide.
- MedlinePlus – A service of the U.S. National Library of Medicine, MedlinePlus provides accessible information on encephalitis, including an overview of the condition, details on symptoms, and links to clinical trials. Learn more about encephalitis on MedlinePlus.
- The Encephalitis Society – A leading organization focused on encephalitis, offering support, education, and resources for those affected by the condition. Their website includes personal stories, professional advice, and the latest research findings. Connect with The Encephalitis Society.
By consulting these reputable sources, readers can gain a thorough understanding of encephalitis symptoms, enhancing their knowledge and ability to seek appropriate care. Remember, while these resources provide valuable information, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.