Diarrhea Symptoms: Diarrhea, characterized by the frequent passage of loose, watery stools, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding its symptoms and causes is crucial for effective management and treatment.
This article delves into the intricacies of diarrhea, providing a detailed examination of its symptoms, causes, and insights into preventive measures.
What is Diarrhea?
Diarrhea is a common condition characterized by loose, watery stools that occur more frequently than your usual bowel movements. Individuals experiencing diarrhea may find themselves needing to use the bathroom more often than normal, typically more than three times a day. This condition can affect anyone, from young children to the elderly, and while it often resolves on its own within a few days, it can sometimes indicate a more serious underlying health issue.
How Diarrhea Affects the Digestive System
Diarrhea impacts the digestive system by speeding up the movement of food through the digestive tract. This rapid transit prevents the colon from absorbing water from the food waste as it normally would, leading to the production of loose or watery stools. The condition can also be caused by an infection from bacteria, viruses, or parasites, an intolerance to certain foods, medications, or diseases affecting the stomach, small intestine, or colon. In addition to causing discomfort and inconvenience, significant loss of fluids and salts through diarrhea can lead to dehydration, especially in young children and older adults, making it important to maintain fluid intake during episodes.
However, understanding the causes and effects of diarrhea on the digestive system is crucial for managing symptoms effectively and preventing complications. If diarrhea persists for more than a few days, or if it’s accompanied by symptoms like fever, severe pain, or dehydration, seeking medical advice is recommended to identify and treat any underlying conditions.
Common Symptoms of Diarrhea
Understanding its symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment. Here, we delve into the most common symptoms of diarrhea and how to recognize signs of dehydration associated with it.
Detailed Description of Diarrhea Symptoms
The primary symptom of diarrhea is the frequent evacuation of loose, watery stools, often occurring more than three times a day. However, this condition can be accompanied by several other symptoms, which include:
- Abdominal Cramps and Pain: The movement of stool through the irritated or inflamed gut can cause discomfort or sharp pain.
- Bloating: A feeling of fullness or swelling in the abdomen is common.
- Urgency: An immediate and uncontrollable need to have a bowel movement.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms may occur in certain cases, contributing to the loss of fluids.
- Fever: A high temperature may indicate an infection or inflammation as the cause of diarrhea.
Understanding these symptoms can help individuals seek timely medical advice, especially if diarrhea persists for more than two days, is accompanied by severe pain, or results in significant fluid loss.
How to Recognize Dehydration Signs Related to Diarrhea
Dehydration is a serious complication of diarrhea, especially in young children and the elderly. Recognizing the signs of dehydration early can be life-saving. Key indicators include:
- Thirst: An increased need for fluids, which may not always be a reliable early indicator, especially in infants and the elderly.
- Reduced Urination: Less frequent urination or in smaller amounts than usual; urine may also be dark yellow.
- Dry Mouth and Tongue: Look for a sticky or parched feeling in the mouth.
- Fatigue or Irritability: Especially in children, these can be early signs of dehydration.
- Sunken Eyes or Cheeks: This symptom indicates severe dehydration, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Skin Elasticity: Gently pinch the skin; if it doesn’t quickly return to its normal position, dehydration may be present.
If you or someone you are caring for shows signs of dehydration, it’s important to increase fluid intake and seek medical advice. Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) are especially effective in replacing lost fluids and electrolytes.
However, recognizing the common symptoms of diarrhea and the signs of dehydration related to it are crucial steps in managing the condition effectively. Early detection and appropriate hydration strategies can mitigate the risks associated with diarrhea, including severe dehydration. If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional is strongly advised.
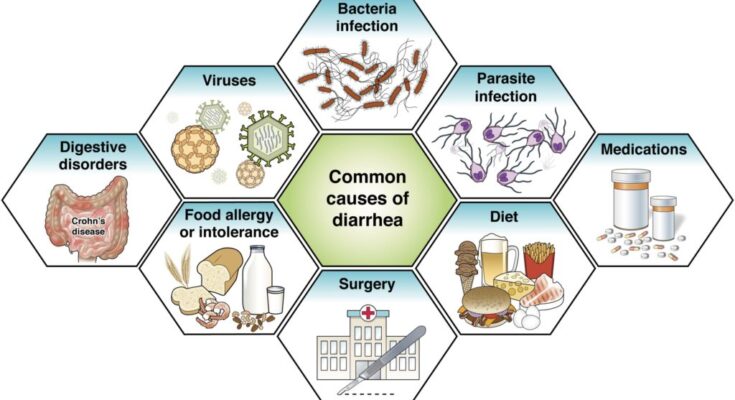
Potential Causes of Diarrhea
Understanding its potential causes is the first step towards effective management and prevention. Here, we explore the common triggers of diarrhea, from infections to dietary factors.
Infections: Bacterial, Viral, and Parasitic
Infections are among the leading causes of diarrhea. These can be bacterial, such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter; viral, including norovirus and rotavirus; or parasitic, with Giardia lamblia being a common culprit. These pathogens often enter the body through contaminated food or water and can cause severe gastrointestinal symptoms.
Food Intolerances and Allergies
Certain foods can trigger diarrhea in people with specific intolerances or allergies. Lactose intolerance, where the body cannot properly digest lactose found in dairy products, is a common example. Similarly, allergies to foods like nuts, gluten (celiac disease), and shellfish can also lead to digestive distress and diarrhea.
Medications and Antibiotics
Some medications, particularly antibiotics, can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the gut, leading to diarrhea. Antibiotics can indiscriminately kill both harmful and beneficial bacteria, sometimes resulting in an overgrowth of toxin-producing bacteria like Clostridium difficile. Other medications, such as antacids containing magnesium, can also cause diarrhea as a side effect.
Digestive Disorders
Chronic digestive conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis are notable for causing diarrhea. These disorders affect the digestive tract in various ways, leading to inflammation, pain, and altered bowel habits. Managing these conditions often requires a comprehensive approach, including dietary changes and medication.
Contaminated Water or Food
Consuming contaminated water or food is a common way pathogens causing diarrhea are ingested. This can occur through the consumption of undercooked meats, improperly washed fruits and vegetables, or drinking water contaminated with pathogens. It underscores the importance of food safety practices, such as proper cooking and handling of food and ensuring safe drinking water sources.
However, understanding the potential causes of diarrhea is crucial for identifying the appropriate treatment and preventive measures. If you’re experiencing persistent or severe diarrhea, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
When to See a Doctor for Diarrhea
Understanding when to seek professional help is crucial for your health. This guide will highlight the symptoms that warrant a doctor’s visit and discuss the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms That Warrant Medical Attention
It’s essential to be vigilant and recognize when diarrhea is more than just a minor inconvenience. Here are key symptoms that should prompt you to see a doctor:
- Persistent Diarrhea: If your diarrhea lasts more than two days without any signs of improvement, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional. Prolonged diarrhea can lead to dehydration and other complications.
- Severe Pain or Discomfort: Severe abdominal or rectal pain, especially if it’s persistent or particularly intense, can be a sign of a more serious condition.
- Blood in the Stool: The presence of blood or black, tarry stools indicates bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, which requires immediate medical attention.
- High Fever: A fever higher than 102°F (39°C) accompanying diarrhea can signify an infection or inflammatory conditions that need treatment.
- Signs of Dehydration: Symptoms of dehydration, including thirst, dry mouth, limited urine output, dark urine, fatigue, and dizziness, are red flags, especially in young children and the elderly.
- Weight Loss: Unintended weight loss along with diarrhea could indicate an underlying health issue that needs evaluation.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Seeking medical help early is vital for several reasons. First, it can help identify the underlying cause of diarrhea, whether it’s an infection, a chronic disease like inflammatory bowel disease, or a dietary issue such as intolerance to certain foods. Early diagnosis allows for prompt and appropriate treatment, which can mitigate symptoms, prevent complications, and improve your overall quality of life.
Moreover, early treatment is crucial for preventing dehydration, one of the most serious complications of diarrhea. Dehydration can be particularly dangerous for young children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems. By addressing diarrhea early, you can avoid emergency situations and ensure a smoother recovery.
However, while diarrhea is often a mild condition, certain symptoms should not be ignored. Recognizing when to seek medical attention can lead to early diagnosis and treatment, preventing complications and ensuring your well-being. Always listen to your body and consult with a healthcare provider if you experience any symptoms that concern you.
Diagnostic Approaches for Diarrhea
Diagnosing the underlying cause of diarrhea is crucial for effective treatment. This section delves into the various methods and medical tests used to diagnose diarrhea.
List of Diagnostic Methods:
Medical History and Physical Examination: Initially, healthcare providers will review the patient’s medical history and symptoms. Questions may cover the duration of diarrhea, presence of blood in the stool, recent travel, diet, and medication use. A physical examination can help rule out certain conditions.
Stool Tests: Laboratory analysis of stool samples can detect infections caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Special tests can identify toxins produced by bacteria such as Clostridium difficile.
Blood Tests: Blood tests, including complete blood count (CBC) and others, can help identify inflammatory or infectious conditions, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalances.
Colonoscopy or Sigmoidoscopy: These procedures involve the use of a flexible tube equipped with a camera to visually inspect the colon and rectum. They can detect inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, and are useful if symptoms are severe or persistent.
Imaging Tests: Radiologic tests, including X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans, can identify complications or causes of chronic diarrhea, such as bowel obstructions or tumors.
Breath Tests: To diagnose conditions like lactose intolerance or bacterial overgrowth, breath tests measure the production of gas by bacteria in the intestine.
Endoscopy: Beyond colonoscopy, an upper endoscopy may be performed to examine the stomach and small intestine if disorders in these areas are suspected.
Each diagnostic method has its unique role and may be chosen based on the suspected underlying cause of diarrhea and the patient’s overall condition. Accurate diagnosis is key to formulating an effective treatment plan, which may involve medications, dietary adjustments, or other interventions tailored to address the specific cause of diarrhea.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Adjustments
Preventive measures and lifestyle adjustments are key to reducing the risk of developing diarrhea and managing symptoms when they occur. Here are essential strategies that can help:
Hygiene Practices to Prevent Infections
- Handwashing: Regularly wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after using the bathroom, before eating, and after handling pets or waste. This simple practice can dramatically reduce the risk of infection.
- Food Safety: Ensure food is cooked thoroughly and stored at the correct temperatures to prevent bacterial growth. Avoid raw or undercooked meats and eggs, and wash fruits and vegetables before eating.
- Water Safety: Drink water from safe sources. If you’re unsure about the water quality, opt for bottled water or boil tap water before drinking.
- Avoiding Contaminated Sources: Be cautious of swimming in or drinking water from lakes, rivers, or swimming pools that might be contaminated.
Dietary Changes to Manage or Prevent Symptoms
- BRAT Diet: In cases of diarrhea, the BRAT diet (Bananas, Rice, Applesauce, Toast) can help in managing symptoms due to its bland nature and the ability to firm up stools.
- Limiting Irritants: Reduce or eliminate foods that can irritate the digestive system, such as spicy foods, fatty foods, and dairy products if you’re lactose intolerant.
- Probiotics: Consuming foods rich in probiotics, such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, can help restore the natural balance of bacteria in your gut and improve digestive health.
The Role of Hydration in Preventing Dehydration
Hydration is critically important when managing diarrhea, as the body loses fluids rapidly. To prevent dehydration:
- Fluid Intake: Increase your intake of fluids such as water, broths, and oral rehydration solutions. These liquids help replenish electrolytes and prevent dehydration.
- Avoiding Certain Beverages: Steer clear of alcohol, caffeine, and sugary drinks, as they can exacerbate dehydration.
- Monitoring Symptoms: Pay close attention to signs of dehydration, including thirst, dry mouth, reduced urination, and dizziness. Seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen.
Remember, while these tips are beneficial for managing mild to moderate cases, consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial if you experience severe or persistent symptoms.
Treatment Options for Diarrhea
These treatments can range from simple home remedies to prescription medications, depending on the severity and underlying cause of the diarrhea. Let’s explore some of the common methods used to manage this uncomfortable condition.
List of Treatment Methods
- Hydration: One of the first and most crucial steps in treating diarrhea is to stay hydrated. Diarrhea can lead to dehydration, so drinking plenty of fluids such as water, broth, or oral rehydration solutions is vital.
- Diet Adjustments: Consuming a bland diet can help ease diarrhea. Foods like bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast (often referred to as the BRAT diet) are recommended due to their soothing effect on the digestive system.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: For immediate relief, over-the-counter medications like loperamide (Imodium) or bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) can be effective. These medications work by slowing down the movement of the gut, helping to reduce the frequency of bowel movements.
- Probiotics: These beneficial bacteria can help restore the natural balance of your gut flora, which may be upset during a bout of diarrhea. Probiotics can be found in yogurt with live cultures, fermented foods, or as supplements.
When Prescription Medications Are Necessary
There are scenarios where over-the-counter treatments and home remedies might not be enough to manage diarrhea. In such cases, prescription medications may be necessary, particularly if the diarrhea is caused by a bacterial infection or a more serious underlying condition. Antibiotics can be prescribed to target bacterial infections, while other medications may be used to treat specific causes of diarrhea, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional if your diarrhea is severe, persistent, or accompanied by symptoms such as high fever, blood in the stool, or signs of dehydration. A doctor can determine the underlying cause of the diarrhea and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan for you.
By understanding and utilizing these treatment options, you can effectively manage diarrhea and mitigate its impact on your daily life. Remember, staying hydrated and consulting with a healthcare professional when necessary are key steps in the treatment process.
Managing Diarrhea Symptoms at Home
Managing diarrhea symptoms at home requires a blend of practical dietary adjustments and ensuring adequate hydration. Here’s how you can find relief and support your body’s recovery:
Practical Tips for Symptom Relief
- BRAT Diet: Embrace the BRAT diet, which includes Bananas, Rice, Applesauce, and Toast. These foods are bland, low in fiber, and can help make your stools firmer. Due to their simplicity, they’re less likely to irritate your stomach.
- Avoid Irritants: Steer clear of caffeine, dairy products, and foods that are fatty, spicy, or high in fiber. These can exacerbate diarrhea by irritating your digestive system or accelerating bowel movements.
- Consider Probiotics: Probiotics found in yogurt and fermented foods can help restore the natural balance of your gut flora, potentially reducing the duration of diarrhea. However, if dairy worsens your symptoms, seek dairy-free probiotic supplements instead.
Importance of Staying Hydrated
Diarrhea can lead to dehydration, making it crucial to drink plenty of fluids. However, not all fluids are equal in this context:
- Water: The best choice for staying hydrated. It’s gentle on your stomach and effective in replacing lost fluids.
- Oral Rehydration Solutions (ORS): These are specifically designed to replenish fluids and electrolytes. ORS can be particularly beneficial for severe cases of diarrhea.
- Avoid Sugary or Carbonated Drinks: Beverages like sodas or fruit juices can make diarrhea worse due to their high sugar content, which can draw more water into the intestines.
By incorporating these tips into your self-care routine, you can help manage diarrhea symptoms more effectively at home. Remember, while these measures can provide relief, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider if your symptoms persist or worsen, as they could indicate a more serious condition. Prioritizing a gentle diet and adequate hydration can significantly aid in your recovery and comfort.
FAQs: Understanding Diarrhea Symptoms
What are common symptoms of diarrhea?
Common symptoms of diarrhea include loose, watery stools, frequent need to evacuate your bowels, abdominal cramps, and sometimes nausea. Depending on the cause, you might also experience fever, bloating, and the presence of blood or mucus in your stool.
How long does diarrhea usually last?
Most cases of diarrhea last two to three days. However, when caused by infections or more serious health issues, it can persist longer. Chronic diarrhea, lasting more than four weeks, may indicate underlying disorders such as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) or Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).
Can diarrhea be a sign of something serious?
While diarrhea is often caused by minor infections or dietary factors, persistent or severe diarrhea can indicate a more serious condition. If you experience symptoms like dehydration, blood in the stool, severe abdominal pain, or diarrhea lasting more than two days without improvement, seek medical advice.
What should I eat if I have diarrhea?
It’s recommended to eat bland, easy-to-digest foods like toast, rice, bananas, and applesauce. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids, including water, broth, and oral rehydration solutions. Avoid dairy products, fatty foods, high fiber foods, and spicy foods until your symptoms improve.
When should I see a doctor for diarrhea?
Consult a healthcare provider if you have diarrhea that lasts more than two days, severe pain in the abdomen or rectum, a fever of 102°F (39°C) or higher, signs of dehydration, or if you notice blood or black, tarry stools. These could be signs of a more serious condition requiring medical intervention.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes of diarrhea is crucial for maintaining our health and well-being. By being aware of the various triggers and manifestations of this condition, individuals can take proactive steps to manage mild episodes at home through proper hydration and diet. However, it’s vital to remember that persistent or severe cases of diarrhea may signal underlying health issues that require professional medical advice.
Seeking the guidance of a healthcare provider is essential in such scenarios to ensure a correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Medical professionals can offer valuable insights and solutions tailored to individual needs, helping to alleviate symptoms and address the root cause of the problem effectively.
Let’s prioritize our health by staying informed about our bodies’ signals and when in doubt, consulting with a healthcare professional to ensure our well-being. Persistent or severe symptoms should never be ignored, as early intervention can prevent complications and lead to a quicker recovery.