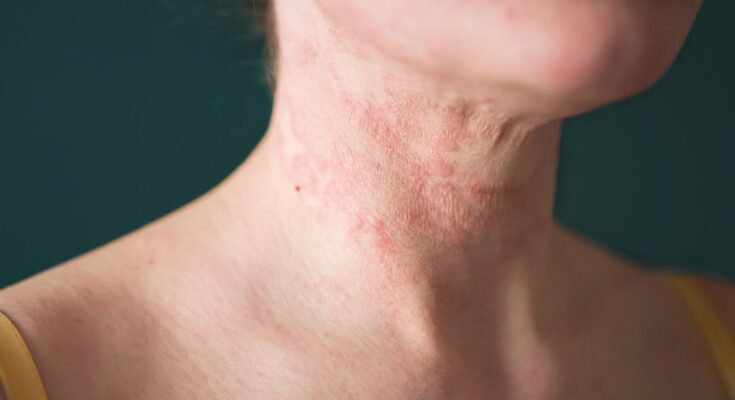
Dermatitis Symptoms: Dermatitis, a broad term that encompasses a range of skin conditions, manifests as inflamed, itchy, and often red skin.
This common ailment affects individuals of all ages, making understanding its symptoms and causes crucial for effective management and treatment.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of dermatitis, offering insights into its various forms, symptoms, and underlying causes, with the goal of empowering readers with the knowledge needed to navigate this condition.
What is Dermatitis?
Dermatitis is a common skin condition that causes the skin to become inflamed, itchy, and often red. Think of it as your skin throwing a bit of a tantrum, reacting to something it doesn’t like or can’t handle. This reaction can result from various factors, including allergies, irritants, genetic makeup, and even stress. In simple terms, if your skin is irritated, red, and itchy, you might be dealing with dermatitis.
Different Types of Dermatitis
Dermatitis comes in several forms, each with its triggers and symptoms. Understanding the different types can help you identify what might be causing your skin’s unhappy response and how to soothe it.
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): This type is like the sensitive artist of the dermatitis family, often starting in childhood and affecting those with a family history of the condition. It’s characterized by dry, itchy skin that can blister or peel. Common in the creases of elbows, behind the knees, and on the face, it’s a long-term condition that flares up periodically.
- Contact Dermatitis: Imagine your skin as a detective, reacting when it touches something it doesn’t like. This type can be caused by irritants like harsh soaps or chemicals, leading to irritated skin, or by allergens like nickel or poison ivy, causing an itchy, blistering rash. It’s your skin’s way of saying, “Please don’t touch that again!”
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: This type targets your oil-producing areas like the scalp, face, and chest. It’s like your skin is overproducing oil and then getting mad about it, leading to red, scaly patches. Often seen in infants as cradle cap or in adults as dandruff, it’s both common and manageable.
- Dyshidrotic Dermatitis: This type focuses on your hands and feet, presenting as small, itchy blisters. It’s like your skin is protesting against sweat or stress. It’s more common in warmer months and can be quite uncomfortable.
- Nummular Dermatitis: This form is characterized by coin-shaped spots on the skin that can be itchy and scaly. Think of it as your skin minting its currency but not in a fun way. It can result from dry skin or an injury to the skin, like a bug bite or scrape.
- Stasis Dermatitis: This one is a bit like your skin getting fed up with your circulatory system’s performance, leading to itchy and swollen lower legs. It’s often related to blood flow issues and is more common in older adults.
Each type of dermatitis has its nuances, but they all share the common thread of being an inflammatory response of the skin. Identifying your specific type can be key to managing your symptoms and keeping your skin happy and healthy.
Common Symptoms of Dermatitis
The symptoms of dermatitis can vary widely among individuals, but there are several common indicators that are frequently observed:
- Itching: This is perhaps the most common and discomforting symptom associated with dermatitis. The intensity of the itch can range from mild to severe, often becoming worse at night.
- Redness: Affected areas of the skin may appear red and irritated, which is a clear sign of inflammation.
- Dry Skin: Many people with dermatitis experience extremely dry skin, which can lead to cracking, peeling, or flaking.
- Rashes: Dermatitis often causes rashes that can appear on any part of the body, but are most commonly found on the face, inside the elbows, behind the knees, and on the hands and feet.
- Swelling: In some cases, the affected areas may swell up and become tender to the touch.
- Blisters: Certain types of dermatitis can cause blisters that ooze and form crusts, adding to the discomfort.
Variations Between Different Types of Dermatitis
While the symptoms mentioned above are common across various forms of dermatitis, it’s important to note that specific types of this condition can present unique characteristics:
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): Primarily seen in children, this type can persist into adulthood. It is characterized by chronic, itchy rashes that can become very sore from scratching.
- Contact Dermatitis: This type results from direct contact with allergens or irritants, leading to localized redness, itching, and sometimes blistering.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Commonly affecting the scalp, face, and chest, this type presents with scaly, greasy patches of skin.
- Dyshidrotic Dermatitis: This type affects the hands and feet, characterized by small, itchy blisters.
The Importance of Recognizing Symptoms for Diagnosis and Treatment
Recognizing the symptoms of dermatitis early on is essential for timely and accurate diagnosis. Dermatologists can often diagnose the condition based on a physical examination and review of medical history. In some cases, patch testing or skin biopsies may be necessary to identify the specific type of dermatitis and rule out other skin conditions.
Understanding the nuances of dermatitis symptoms is also vital for effective treatment. While there is no cure for dermatitis, symptoms can be managed with a combination of lifestyle changes, skincare routines, and, when necessary, medication prescribed by a healthcare provider. Treatments may include moisturizers to combat dryness, corticosteroid creams to reduce inflammation, and antihistamines to alleviate itching.
However, being well-informed about the common symptoms of dermatitis and how they vary among the different types of the condition is fundamental to seeking appropriate care. Early recognition and treatment can significantly improve quality of life for those affected by dermatitis, minimizing discomfort and preventing complications.
Causes of Dermatitis
Understanding the causes and triggers of dermatitis is crucial for effective management and treatment. This article explores the various factors that contribute to dermatitis, shedding light on how and why these causes lead to symptoms.
Common Causes and Triggers of Dermatitis
- Allergic Reactions: Allergens such as pollen, pet dander, certain foods, and metals like nickel can trigger allergic contact dermatitis. The immune system’s reaction to these allergens results in skin inflammation.
- Irritants: Everyday substances like soaps, detergents, shampoos, and cleaning agents can cause irritant contact dermatitis. These chemicals can damage the outer layer of the skin, leading to irritation and inflammation.
- Genetic Factors: Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, often has a genetic component. Individuals with a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop this condition.
- Environmental Factors: Extreme temperatures, humidity changes, and exposure to UV radiation can exacerbate dermatitis symptoms. These environmental stressors can disrupt the skin’s barrier, leading to dryness and irritation.
- Stress: Emotional stress doesn’t directly cause dermatitis but can worsen the symptoms. Stress can trigger flare-ups in people with existing skin conditions.
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can also lead to dermatitis. The skin’s reaction to these pathogens can cause inflammation and rash.
How and Why These Causes Lead to Dermatitis Symptoms
The primary mechanism behind dermatitis is the skin’s reaction to various internal or external factors. When the skin comes into contact with irritants, allergens, or undergoes stress due to environmental changes, it can lead to an inflammatory response. This response is the body’s way of protecting itself, resulting in symptoms such as redness, itching, swelling, and the formation of blisters or crusts.
Allergic reactions occur when the immune system mistakenly identifies a harmless substance as a threat, releasing chemicals that cause skin symptoms. In the case of irritant contact dermatitis, the chemicals directly damage the skin’s protective barrier, making it more susceptible to inflammation.
Genetic factors in conditions like atopic dermatitis influence how the skin develops and its ability to retain moisture and protect against allergens, irritants, and pathogens. This compromised skin barrier function leads to increased sensitivity and susceptibility to dermatitis.
Environmental factors and stress affect the skin’s condition by either directly causing damage, drying out the skin, or affecting its immune response, which can exacerbate dermatitis symptoms.
However, understanding the causes and triggers of dermatitis is essential for managing the condition effectively. Avoiding known irritants and allergens, maintaining skin moisture, and managing stress levels can help minimize flare-ups and improve the quality of life for those affected by dermatitis.
Diagnosing Dermatitis
Understanding the Need for Professional Diagnosis
When it comes to skin conditions like dermatitis, seeking a professional diagnosis is paramount. Dermatitis, characterized by swollen, red, and itchy skin, can be caused by various factors, including allergies, genetic predisposition, or environmental triggers. A professional diagnosis not only ensures accurate identification of the type of dermatitis but also rules out other skin conditions that may mimic dermatitis symptoms. Dermatologists use their expertise to evaluate the symptoms, consider your medical history, and apply specialized diagnostic tests. This professional assessment is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual’s specific needs, thereby preventing potential complications and improving the quality of life.
Common Diagnostic Methods for Dermatitis
- Physical Examination: The first step in diagnosing dermatitis involves a thorough physical examination. Dermatologists meticulously inspect the affected skin, noting the appearance, distribution, and pattern of the rash. They may also inquire about the duration of symptoms, any known triggers, and whether there’s a family history of skin conditions. This initial assessment provides vital clues about the nature of the dermatitis.
- Patch Tests: Patch testing is a specialized diagnostic method used to identify specific allergens responsible for contact dermatitis. During this test, small amounts of potential allergens are applied to patches, which are then placed on the skin, typically on the back, for a set period, usually 48 hours. After removal, the skin is examined for signs of an allergic reaction. Patch tests are instrumental in pinpointing the exact substances causing allergic contact dermatitis, enabling individuals to avoid these allergens and manage their condition effectively.
- Other Diagnostic Tests: Depending on the suspected cause or type of dermatitis, additional tests may be conducted. These can include skin biopsies, where a small sample of skin is removed for microscopic examination, or blood tests to check for underlying health issues that might contribute to the skin condition. For instance, individuals with atopic dermatitis may undergo allergy tests to identify food or environmental allergens exacerbating their symptoms.
This tailored approach ensures that individuals receive the most appropriate treatment, helping to alleviate symptoms and improve their overall well-being. If you suspect you have dermatitis, consulting a dermatologist is a critical first step towards understanding your condition and finding relief.
Treatment Options for Dermatitis
Various treatment options are available to manage and alleviate its symptoms. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the effective strategies for treating dermatitis, including medications, home remedies, lifestyle modifications, and preventive measures.
Medications for Dermatitis
Medication plays a crucial role in the management of dermatitis, aimed at reducing inflammation, itching, and preventing infections. The following are the most commonly prescribed medications for dermatitis:
- Topical Steroids: These are the cornerstone of dermatitis treatment, effective in reducing skin inflammation and irritation. They come in various strengths and are applied directly to the affected areas.
- Antihistamines: Useful in relieving itching, antihistamines can help improve sleep when dermatitis symptoms flare up at night.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Prescribed for short-term use, these non-steroidal creams and ointments can help to repair the skin and reduce inflammation.
- Antibiotics: If the skin becomes infected, antibiotics may be necessary to fight the infection and heal the skin.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medication, several home remedies and lifestyle modifications can significantly improve dermatitis symptoms:
- Moisturizing Regularly: Keeping the skin hydrated is essential. Use fragrance-free moisturizers immediately after bathing to lock in moisture.
- Gentle Skin Care: Use mild, fragrance-free soaps and avoid harsh skin products that can irritate your skin.
- Cool Compresses: Applying a cool, damp cloth to the affected area can help soothe the skin and reduce itching.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate dermatitis, so incorporating stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial.
Preventive Measures
Preventing dermatitis flare-ups is equally important as treating them. Here are some strategies to help avoid triggers:
- Avoid Known Irritants: Identify and steer clear of substances that trigger your dermatitis. This could include certain fabrics, soaps, and detergents.
- Wear Protective Clothing: When dealing with irritants or allergens, wear gloves or protective clothing to shield your skin.
- Maintain a Skin-Friendly Diet: Some foods may trigger dermatitis in certain individuals. Keeping a food diary can help identify potential food triggers.
- Keep Your Environment Humidified: Dry air can worsen dermatitis. Using a humidifier, especially in winter, can help maintain skin moisture.
Combining these treatment options and preventive measures can significantly reduce the symptoms of dermatitis, improve skin health, and enhance overall well-being. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and conditions.
Managing Dermatitis Symptoms at Home
Below, you’ll find practical tips and tricks to help you take control of your dermatitis at home, focusing on the importance of moisturizing, avoiding irritants, and making lifestyle adjustments.
1. Prioritize Moisturizing
Moisturizing is not just beneficial; it’s essential for managing dermatitis. The right moisturizers can help restore the skin’s barrier, prevent moisture loss, and reduce the itchiness and flaking associated with dermatitis.
- Choose the Right Moisturizer: Look for products labeled “for sensitive skin” or “fragrance-free,” as these are less likely to irritate your skin. Creams and ointments are generally more effective than lotions.
- Apply After Bathing: Lock in moisture by applying moisturizer within a few minutes of bathing or showering. Pat your skin dry gently before applying.
- Frequent Application: Apply moisturizer several times a day, especially after washing your hands or any other part of your body.
2. Avoid Irritants
Identifying and avoiding irritants is a crucial step in managing dermatitis symptoms. Common irritants include soaps, detergents, fragrances, and certain fabrics.
- Use Gentle Skincare Products: Opt for soap-free cleansers, hypoallergenic products, and avoid using scented lotions or soaps.
- Protect Your Skin: Wear gloves when using cleaning agents, solvents, or gardening. Choose clothing made of soft, breathable fabrics like cotton.
- Be Mindful of Your Environment: Dust, pet dander, and pollen can exacerbate symptoms. Keep your living space clean and consider using an air purifier to reduce airborne irritants.
3. Lifestyle Adjustments
Making small changes to your daily routine can significantly impact your comfort and symptom severity.
- Manage Stress: Stress can trigger or worsen dermatitis symptoms. Incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises into your routine.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: While food allergies can contribute to dermatitis flare-ups, a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can support skin health. Consider foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, like fish, flaxseed, and walnuts.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain your skin’s hydration from the inside out.
Remember, if your symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options. Making moisturizing a priority, avoiding known irritants, and adjusting your lifestyle can empower you to manage dermatitis effectively and live comfortably.
When to See a Doctor for Dermatitis
Recognizing when to seek professional medical advice is crucial. Early intervention not only alleviates discomfort but also prevents potential complications that can arise from untreated or improperly managed dermatitis.
Key Indicators for Seeking Medical Attention
- Persistent Symptoms: If symptoms persist despite over-the-counter treatments or home care, it’s time to see a doctor. Continuous itching and skin irritation can lead to more serious conditions, such as infections.
- Severe Symptoms: Severe redness, swelling, blistering, or oozing are signs that your dermatitis needs medical evaluation. Such symptoms can indicate an acute reaction or infection that requires professional treatment.
- Impact on Daily Life: When dermatitis symptoms interfere with your daily activities or sleep patterns, professional guidance can help you manage your condition more effectively and improve your quality of life.
- Infection Signs: If you notice signs of infection, such as increased pain, warmth at the site, yellowish crusts, or pus-filled blisters, seek medical attention promptly. Infections can escalate quickly and may require antibiotics.
- No Known Cause: If you cannot identify a cause for your dermatitis, such as a new skincare product or an allergen, a doctor can help determine the underlying cause through tests or allergy screenings.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention is key to managing dermatitis effectively. A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and tailor a treatment plan to your specific condition. This may include prescription medications, such as topical corticosteroids or immunomodulators, and advice on skincare routines and lifestyle adjustments to avoid triggers. By addressing dermatitis early, you can prevent the condition from worsening or leading to long-term skin damage and infections.
Furthermore, a doctor can offer insights into coping strategies and preventative measures, empowering you to take control of your dermatitis. They can also provide guidance on when to follow up or adjust treatment plans based on your response to therapy.
FAQs on Dermatitis: Symptoms and Causes
What is dermatitis?
Dermatitis is an umbrella term that refers to a group of conditions characterized by skin inflammation. It can present in various forms, such as atopic dermatitis (eczema), contact dermatitis, and seborrheic dermatitis, among others. Symptoms typically include redness, itching, swelling, and sometimes blistering or peeling of the skin.
What causes dermatitis?
The causes of dermatitis vary depending on the type. For example, atopic dermatitis is often linked to genetic factors, allergies, and environmental triggers. Contact dermatitis results from direct skin exposure to irritants or allergens, while seborrheic dermatitis may be associated with a yeast that lives on the skin’s surface. Stress and hormonal changes can also play a role in triggering or worsening the condition.
How can I tell if I have dermatitis?
Identifying dermatitis usually involves looking for common symptoms such as skin redness, itching, dryness, and discomfort. These can vary in intensity and may appear on different body parts. If you suspect you have dermatitis, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Can dermatitis be cured?
While there is no cure for dermatitis, many effective treatments can manage symptoms and significantly improve quality of life. Treatment options may include topical creams and ointments, oral medications, light therapy, and lifestyle modifications to avoid known triggers. Your healthcare provider can help determine the best treatment approach for your specific condition.
Is dermatitis contagious?
No, dermatitis is not contagious. It cannot be spread from person to person through direct contact or other means. The condition is related to the body’s immune response and skin sensitivity, not infectious agents.
How can I prevent dermatitis flare-ups?
Preventing flare-ups involves identifying and avoiding your personal triggers, which may include certain soaps, detergents, fabrics, foods, or environmental factors. Keeping the skin moisturized, following a gentle skincare routine, and managing stress levels can also help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Can dietary changes improve dermatitis?
For some individuals, dietary changes may help manage dermatitis, especially if food allergies or sensitivities are contributing to the condition. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet. They can guide you on the best approach based on your specific situation.
Conclusion
Managing dermatitis often requires a multifaceted approach, including avoiding known irritants, maintaining skin hydration, using prescribed medications, and implementing lifestyle changes. While over-the-counter treatments can offer relief for mild symptoms, it’s important to remember that these measures may not address the root cause of the condition.
We strongly encourage anyone experiencing persistent or severe symptoms of dermatitis to seek professional medical advice. A healthcare provider can offer a comprehensive evaluation, accurate diagnosis, and a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and condition. Professional guidance is invaluable in navigating the complexities of dermatitis, ensuring effective management, and improving your quality of life.
Remember, each individual’s skin is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Seeking professional advice is a critical step towards understanding your skin condition and finding the most effective treatment plan for you. Don’t let dermatitis control your life—help is available, and with the right approach, you can manage your symptoms and enjoy healthier skin.