Cryoglobulinemia Treatment: Cryoglobulinemia is a rare but significant medical condition characterized by the presence of abnormal proteins in the blood, known as cryoglobulins, which can precipitate at low temperatures.
This condition can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, from mild to life-threatening.
In this article, we delve into the essential aspects of diagnosing and treating cryoglobulinemia, providing healthcare professionals and patients with a detailed guide to managing this complex condition.
Understanding Cryoglobulinemia
Cryoglobulinemia is a rare medical condition characterized by the presence of abnormal proteins in the blood, known as cryoglobulins, which can precipitate or clump together at low temperatures. This unique behavior of cryoglobulins can lead to various health complications, primarily affecting the skin, joints, kidneys, and nervous system. Understanding the types of cryoglobulinemia, its epidemiology and risk factors, alongside the symptoms and complications associated with the condition, is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers.
Types of Cryoglobulinemia
Cryoglobulinemia is classified into three main types, each with distinct characteristics and implications for patient management:
- Type I Cryoglobulinemia: This type is often associated with hematologic disorders, such as multiple myeloma or Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. It involves a single type of immunoglobulin, usually IgM or IgG, and is the least common form.
- Type II Cryoglobulinemia: Also known as mixed cryoglobulinemia, this type involves a mixture of IgM and IgG antibodies. IgM acts against IgG, forming immune complexes. It is frequently associated with chronic infections, such as hepatitis C.
- Type III Cryoglobulinemia: Similar to type II, this form involves immune complexes of polyclonal IgG and antibodies but is often linked with autoimmune diseases rather than infections.
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
Cryoglobulinemia is considered a rare condition, with its prevalence varying geographically, largely due to the distribution of associated risk factors such as infections and autoimmune diseases. Key risk factors include:
- Infections: Chronic hepatitis C infection is a significant risk factor, especially for type II cryoglobulinemia.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis increase the risk of developing type III cryoglobulinemia.
- Hematologic Disorders: Diseases affecting blood cells, such as leukemia, increase the risk for type I cryoglobulinemia.
Symptoms and Complications Associated with Cryoglobulinemia
The symptoms of cryoglobulinemia can vary widely, depending on the type and severity of the condition, but often include:
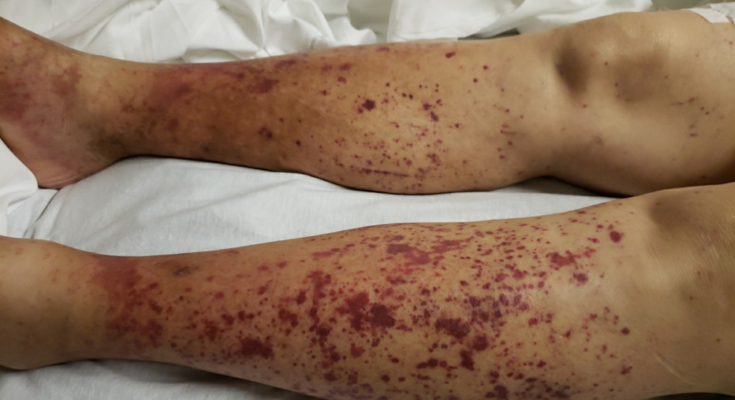
- Skin Manifestations: Purple spots or rashes, particularly on the lower legs, caused by blood vessel inflammation.
- Joint Pain: Arthralgia or arthritis, especially in the knees and hands, can occur.
- Renal Involvement: Kidney damage can manifest as proteinuria or nephritic syndrome, potentially leading to chronic kidney disease.
- Neurological Symptoms: Peripheral neuropathy, manifesting as numbness or tingling in the extremities, is common.
- Systemic Complications: More severe cases can lead to widespread inflammation affecting multiple organs, including the liver and lungs.
Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to managing cryoglobulinemia effectively and preventing serious complications. If you suspect you have symptoms of cryoglobulinemia, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and appropriate management.
Diagnosing Cryoglobulinemia
Cryoglobulinemia, a complex condition characterized by the presence of cryoglobulins in the blood, which precipitate at cold temperatures, poses significant diagnostic challenges. Achieving an accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and management of the condition. This article delves into the critical role of diagnostic tests, including blood tests, laboratory diagnostics, imaging, and biopsies, in identifying cryoglobulinemia. Furthermore, it addresses the obstacles encountered during diagnosis and offers strategies to overcome them, ensuring patients receive the timely and effective care they need.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis in Effective Cryoglobulinemia Treatment
An accurate diagnosis of cryoglobulinemia is foundational to developing an effective treatment plan. This condition, if left undiagnosed or misdiagnosed, can lead to severe complications, including organ damage and systemic inflammation. Early detection through precise diagnostic methods enables healthcare providers to tailor treatment strategies that can mitigate symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life for patients.
Blood Tests and Laboratory Diagnostics: Role in Identifying Cryoglobulins
Blood tests play a pivotal role in the diagnosis of cryoglobulinemia. These tests are designed to detect the presence of cryoglobulins in the blood, which are proteins that clump together at low temperatures. The process involves collecting a blood sample and allowing it to cool, then observing whether cryoglobulins precipitate. Comprehensive laboratory diagnostics further analyze these cryoglobulins, determining their type and concentration, which is essential for guiding treatment decisions.
Imaging and Biopsies: Additional Diagnostic Tools
Beyond blood tests, imaging studies and biopsies serve as vital diagnostic tools in identifying cryoglobulinemia and assessing its impact on the body. Imaging tests, such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI, can reveal the extent of organ involvement and damage. Biopsies, particularly of affected tissues, can provide definitive evidence of cryoglobulinemic vasculitis, thereby confirming the diagnosis and informing the therapeutic approach.
Challenges in Diagnosing Cryoglobulinemia and How to Overcome Them
Diagnosing cryoglobulinemia is fraught with challenges, primarily due to its rarity, the variability of symptoms, and the risk of cryoglobulins dissolving before analysis if the blood sample is not handled properly. To overcome these obstacles, it is crucial to follow strict protocols for blood collection and handling, ensuring samples are kept at the correct temperature to prevent the dissolution of cryoglobulins. Additionally, a high index of suspicion and awareness among healthcare providers is essential for recognizing potential cases and pursuing appropriate diagnostic evaluations.
However, the diagnosis of cryoglobulinemia requires a multifaceted approach involving accurate blood tests, detailed laboratory diagnostics, imaging, and biopsies. Facing and overcoming the diagnostic challenges is crucial for ensuring patients receive the necessary care to manage their condition effectively. Early and precise diagnosis paves the way for targeted treatments, significantly enhancing outcomes for those affected by cryoglobulinemia.
Cryoglobulinemia Treatment Options
There are several effective treatments available for managing this condition. This article explores the primary cryoglobulinemia treatment options, focusing on medications, blood purification methods, and the importance of lifestyle changes and supportive care.
Medications for Cryoglobulinemia
The cornerstone of cryoglobulinemia treatment involves the use of medications designed to reduce inflammation, suppress the immune system’s abnormal response, and tackle the underlying causes of the condition.
- Corticosteroids and Immunosuppressants: Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. Immunosuppressants, including cyclophosphamide and rituximab, may also be used to control the production of cryoglobulins. These medications can be effective in reducing symptoms, but they also come with potential side effects, such as increased susceptibility to infections, which require careful monitoring.
- Antiviral Therapy: For cases of cryoglobulinemia associated with viral infections, such as hepatitis C, antiviral therapy plays a critical role. Direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs) have revolutionized the treatment of hepatitis C, offering a cure for the infection and, consequently, reducing or eliminating the associated cryoglobulinemia.
Blood Purification Methods
In addition to medication, blood purification methods such as plasmapheresis can be beneficial for some patients. Plasmapheresis involves filtering the blood to remove cryoglobulins and other harmful substances. This process can help alleviate symptoms, especially in severe cases or during flare-ups. However, plasmapheresis is usually considered a short-term solution or used in conjunction with other treatments.
Lifestyle Changes and Supportive Care
While medications and medical procedures are critical, lifestyle changes and supportive care also play a vital role in managing cryoglobulinemia. Patients are advised to:
- Avoid Cold Exposure: Keeping warm can help prevent the clumping of cryoglobulins in the blood, reducing symptoms. Dressing in layers and avoiding cold environments are simple yet effective strategies.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking can improve overall health and potentially reduce the severity of symptoms.
- Seek Support: Living with a chronic condition like cryoglobulinemia can be challenging. Support groups, counseling, and education about the disease can provide valuable emotional support and practical advice for managing the condition.
However, the treatment of cryoglobulinemia involves a multifaceted approach that includes medications, blood purification methods, and supportive care. By working closely with healthcare providers, patients can develop a treatment plan that effectively manages symptoms and improves quality of life. Remember, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for the best outcomes in managing cryoglobulinemia.
Advanced Therapies for Cryoglobulinemia
With advancements in medical research, new therapies have emerged, offering hope and improved quality of life for patients. This article delves into the latest research on cryoglobulinemia treatment, focusing on biologics and targeted therapies, and explores the clinical trials and emerging treatments that represent the future prospects of managing this challenging condition.
Biologics and Targeted Therapies: A New Dawn in Cryoglobulinemia Treatment
Biologic therapies, which are derived from living organisms, and targeted therapies, which aim at specific molecular targets associated with the disease, have shown promising results in the treatment of cryoglobulinemia. These advanced therapies are designed to interfere with specific pathways in the immune system, reducing inflammation and the production of cryoglobulins.
Biologics, such as Rituximab, a monoclonal antibody that targets CD20-positive B lymphocytes, have been pivotal in treating patients with cryoglobulinemia, especially those who have not responded well to traditional treatments. Rituximab has demonstrated effectiveness in reducing symptoms and improving the quality of life for patients, making it a cornerstone of therapy for cryoglobulinemia.
On the other hand, targeted therapies, including Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, have emerged as valuable options. These therapies target specific enzymes or pathways involved in the pathogenesis of cryoglobulinemia, offering a more focused approach to treatment. The precision of these therapies can lead to better outcomes and fewer side effects compared to conventional treatments.
Clinical Trials and Emerging Treatments: Mapping the Future
The landscape of cryoglobulinemia treatment is rapidly evolving, with numerous clinical trials underway to evaluate the efficacy and safety of new biologics and targeted therapies. These trials are critical for discovering the next generation of treatments that can offer even more significant benefits to patients.
Emerging treatments, such as new monoclonal antibodies targeting novel immune checkpoints and cell signaling pathways, are on the horizon. Additionally, small molecule inhibitors that can be taken orally and offer a convenient alternative to intravenous therapies are also in development. These advancements represent a beacon of hope for patients with cryoglobulinemia, promising more effective and less invasive treatment options in the future.
Moreover, the integration of personalized medicine into the treatment of cryoglobulinemia is a promising trend. By understanding the genetic and molecular landscape of each patient’s disease, therapies can be tailored to provide the most benefit, minimizing side effects and optimizing outcomes.
However, the field of cryoglobulinemia treatment is witnessing an exciting era of innovation, with biologics and targeted therapies leading the way. As research progresses and new treatments emerge from clinical trials, the future looks brighter for patients with cryoglobulinemia. These advances not only offer the prospect of more effective management of the disease but also open the door to personalized treatment approaches, ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate therapy for their specific condition.
Managing Cryoglobulinemia: Patient Care and Monitoring
Managing cryoglobulinemia effectively requires a comprehensive approach that focuses on regular monitoring, managing treatment side effects, and improving the patient’s quality of life. It is crucial for patients and healthcare providers to work closely together to ensure optimal care and management of this condition.
Importance of Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up Care
Regular monitoring and follow-up care are paramount in managing cryoglobulinemia. This condition, characterized by the presence of abnormal proteins (cryoglobulins) in the blood that clump together at low temperatures, can lead to various complications if not monitored closely. Healthcare providers should schedule regular appointments to track the patient’s symptoms, blood work, and organ function. These check-ups allow for timely adjustments in treatment plans to prevent or mitigate complications such as kidney damage, blood vessel inflammation, and skin ulcers. Patients should be encouraged to report new symptoms or changes in their condition immediately, as early intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Managing Side Effects of Treatment and Improving Quality of Life
Treatment for cryoglobulinemia often involves medications that suppress the immune system, which can lead to side effects such as increased susceptibility to infections, fatigue, and mood changes. Managing these side effects is crucial for improving the patient’s quality of life. Healthcare providers should provide comprehensive care, including strategies to minimize side effects, such as adjusting medication dosages, prescribing additional treatments to counteract side effects, and recommending lifestyle changes. Support groups and counseling may also be beneficial to help patients cope with the emotional and psychological impact of living with a chronic condition.
Patient Education: Understanding Cryoglobulinemia and Self-Care Strategies
Educating patients about cryoglobulinemia and empowering them with self-care strategies are essential components of effective management. Understanding the nature of the disease, its potential complications, and the importance of treatment adherence can motivate patients to take an active role in their care. Healthcare providers should offer resources on how to manage symptoms at home, such as avoiding cold temperatures to prevent cryoglobulin clumping, recognizing signs of complications early, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support overall health. Additionally, teaching patients about the importance of a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can further enhance their quality of life and disease outcomes.
However, managing cryoglobulinemia involves a multifaceted approach that includes regular monitoring, effective management of treatment side effects, and comprehensive patient education. By fostering a collaborative relationship between patients and healthcare providers, individuals living with cryoglobulinemia can achieve better health outcomes and improved quality of life.
FAQs About Cryoglobulinemia Treatment
What is cryoglobulinemia?
Cryoglobulinemia is a rare condition characterized by the presence of abnormal proteins (cryoglobulins) in the blood that clump together at low temperatures. These clumps can block blood vessels, leading to a range of symptoms including skin ulcers, joint pain, and kidney problems.
What causes cryoglobulinemia?
The exact cause of cryoglobulinemia can vary. It may be associated with certain infections, immune system disorders, and cancers. Hepatitis C is one of the most common infections linked to cryoglobulinemia.
How is cryoglobulinemia diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a combination of blood tests to detect cryoglobulins, along with tests to assess liver function, kidney function, and the immune system. Your doctor may also recommend a biopsy of affected tissue.
What are the treatment options for cryoglobulinemia?
Treatment typically focuses on managing symptoms and treating the underlying cause, if known. Options may include medications to suppress the immune system, antiviral therapy for infections, and treatments specific to complications like skin ulcers or kidney disease.
Can cryoglobulinemia be cured?
While there’s no cure for cryoglobulinemia, effective management of the underlying cause and symptoms can significantly improve quality of life. In cases where cryoglobulinemia is caused by an infection, treating the infection can lead to remission of the condition.
What lifestyle changes can help manage cryoglobulinemia?
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage symptoms. This includes avoiding cold temperatures, which can trigger symptom flare-ups, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding tobacco and alcohol.
Are there any new treatments for cryoglobulinemia?
Research into cryoglobulinemia is ongoing, and new treatments are being explored. This includes targeted therapies that focus on the underlying mechanisms of the disease. Always consult with a healthcare provider for the most current treatment options.
Is cryoglobulinemia contagious?
Cryoglobulinemia itself is not contagious. However, if the condition is associated with an infectious disease like hepatitis C, the infection can be contagious.
When should I see a doctor for cryoglobulinemia?
If you experience symptoms such as unexplained rashes, joint pain, weakness, or any signs of kidney problems, it’s important to see a doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications.
How can I support a loved one with cryoglobulinemia?
Supporting a loved one with cryoglobulinemia involves understanding their condition, encouraging adherence to treatment plans, and helping them manage symptoms. Emotional support and helping them avoid triggers, like cold exposure, can also be beneficial.
Conclusion
Looking ahead, the future of cryoglobulinemia treatment is promising, with innovations and improvements on the horizon. Advances in medical research are paving the way for new therapeutic options, including targeted therapies and biologics that offer the potential for more effective and personalized treatment approaches. These advancements are expected to improve the quality of life for patients with cryoglobulinemia significantly.
For patients navigating this condition and healthcare providers managing their care, staying informed about the latest developments in treatment and research is crucial. The medical community is continually gaining a deeper understanding of cryoglobulinemia, leading to more effective diagnosis methods and treatments. Patients and their caregivers are encouraged to engage with support groups and professional societies that focus on cryoglobulinemia, as these platforms provide valuable resources and updates on cutting-edge research.
In conclusion, while cryoglobulinemia presents its set of challenges, the outlook is increasingly optimistic thanks to ongoing research and innovation in treatment methods. By staying informed and proactive, patients and healthcare providers can navigate this journey with hope and access the best care possible.