COPD Treatment: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung condition that poses significant health challenges globally.
Recognized by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation due to airway and/or alveolar abnormalities, COPD’s diagnosis and treatment require a comprehensive approach to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
This article aims to provide an in-depth overview of the diagnostic processes and treatment modalities for COPD, leveraging the latest research and clinical guidelines.
Understanding COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a significant health concern globally, affecting millions of individuals and posing substantial challenges to healthcare systems. This article delves into the prevalence and impact of COPD, its causes and risk factors, common symptoms, and progression. By understanding COPD, individuals can take proactive steps toward management and prevention, improving their quality of life.
Statistics on Prevalence and Impact
COPD is not just a health issue; it’s a global burden. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), COPD is the third leading cause of death worldwide, affecting more than 384 million people. The prevalence of COPD varies by region, with higher rates often observed in countries with higher smoking rates or exposure to COPD risk factors. The economic impact is equally staggering, with billions of dollars spent annually on direct healthcare costs, lost productivity, and disability. These statistics underscore the urgent need for effective prevention strategies and treatments.
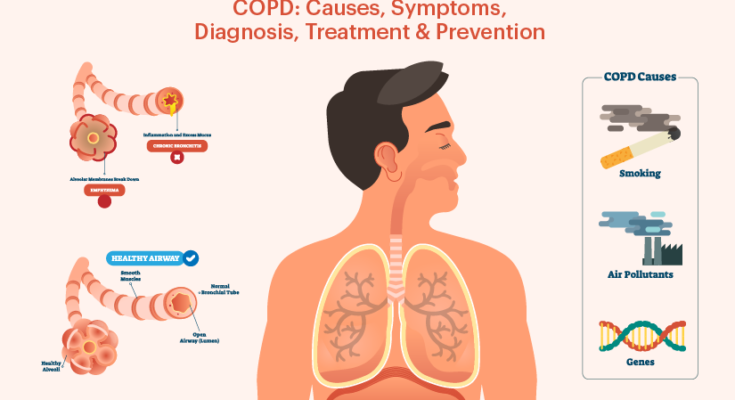
Causes and Risk Factors of COPD
Understanding the causes and risk factors of COPD is crucial for prevention and early intervention. The primary cause of COPD is long-term exposure to irritants that damage the lungs and airways. Key risk factors include:
- Smoking: The leading cause of COPD, accounting for about 85% of cases. This includes cigarettes, cigars, and other forms of tobacco.
- Environmental Exposure: Long-term exposure to air pollution, dust, and chemical fumes in the workplace or environment.
- Genetic Factors: A deficiency in the protein Alpha-1 antitrypsin can cause COPD, especially if the individual smokes.
- Asthma: Individuals with asthma who smoke are at a higher risk of developing COPD.
Common Symptoms and Progression
COPD symptoms often don’t appear until significant lung damage has occurred, and they usually worsen over time. Early diagnosis and management are key to slowing the progression. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent cough: Often referred to as a smoker’s cough.
- Shortness of breath: Especially during physical activities.
- Wheezing: A whistling or rattling sound when breathing.
- Chest tightness.
COPD progresses through stages from mild to very severe, impacting individuals’ ability to breathe over time. The progression can be slowed with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, especially if smoking cessation is achieved.
Diagnosing COPD: A Comprehensive Guide
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung condition that necessitates early detection for effective management. Understanding the importance of early diagnosis, familiarizing oneself with the diagnostic tests and procedures, interpreting diagnosis results accurately, and differentiating COPD from other respiratory conditions are crucial steps in the management of this disease.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of COPD is pivotal in slowing down the progression of the disease, improving the quality of life, and potentially extending life expectancy. Recognizing symptoms early—such as persistent cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, and frequent chest infections—can lead to prompt intervention, reducing the risk of severe lung damage and associated health complications. Early intervention strategies can include lifestyle changes, medication, and pulmonary rehabilitation, highlighting the critical nature of early diagnosis in COPD management.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Several diagnostic tests and procedures are employed to confirm the presence of COPD and assess its severity. These include:
- Spirometry: The most common test for COPD diagnosis, measuring how much and how quickly you can exhale.
- Chest X-Ray: Helps rule out other lung conditions and shows the extent of any lung damage.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the lungs and can help detect emphysema, one of the main conditions of COPD.
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: Assesses the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood.
- Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs): A series of tests to measure lung function and capacity.
Understanding these tests and what they entail is crucial for patients undergoing diagnosis for COPD.
Interpreting Diagnosis Results
Interpreting the results of diagnostic tests requires a nuanced understanding of the data. For example, spirometry results are expressed in terms of FEV1 (Forced Expiratory Volume in one second) and FVC (Forced Vital Capacity). An FEV1/FVC ratio below 70% typically indicates COPD. Pulmonologists use these results in conjunction with clinical symptoms and other test outcomes to make a comprehensive diagnosis. Understanding these results can help patients better comprehend their condition and the severity of their COPD.
Differentiating COPD from Other Respiratory Conditions
COPD often presents symptoms similar to other respiratory diseases, making differential diagnosis essential. Conditions such as asthma, bronchiectasis, and pulmonary fibrosis share symptoms with COPD but require different management strategies. Key differentiators include the nature of symptoms (such as variability in asthma symptoms compared to the persistent symptoms of COPD), response to treatment, and specific findings on diagnostic tests (like CT scans and spirometry). A detailed medical history, coupled with comprehensive diagnostic testing, aids healthcare providers in distinguishing COPD from other respiratory conditions.
However, diagnosing COPD involves a detailed understanding of the diagnostic process, from recognizing the importance of early diagnosis to differentiating COPD from other respiratory ailments. By undergoing the appropriate diagnostic tests and accurately interpreting the results, individuals can embark on a tailored treatment path that mitigates the impacts of COPD, thereby enhancing their quality of life. Awareness and education on these fronts are essential for patients and their families to navigate the complexities of COPD management effectively.
COPD Treatment Overview
Effective management of COPD involves a comprehensive treatment plan aimed at reducing symptoms, improving quality of life, and slowing the progression of the disease. This article provides an overview of COPD treatment goals, the crucial role of lifestyle changes, and specific strategies such as smoking cessation, nutritional advice, and exercise, including pulmonary rehabilitation.
Overview of COPD Treatment Goals
The primary goals of COPD treatment are to alleviate symptoms, prevent and treat complications, and halt the disease’s progression. Treatment strategies are tailored to individual needs, based on the severity of the disease and the presence of other health conditions. By adopting a personalized treatment plan, individuals with COPD can achieve better control over their symptoms, enhance their ability to perform daily activities, and improve their overall quality of life.
The Role of Lifestyle Changes in Managing COPD
Lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role in managing COPD. These changes not only help in reducing the severity of symptoms but also contribute to a slower progression of the disease. Key lifestyle adjustments include smoking cessation, adopting a healthy diet, and engaging in regular physical activity tailored to one’s capabilities.
Smoking Cessation
Quitting smoking is the most effective way to halt the progression of COPD. Smoking is the leading cause of COPD and continuing to smoke can accelerate the disease’s progression. Smoking cessation can significantly improve lung function and decrease the severity of symptoms. Various resources, including counseling, nicotine replacement therapies, and prescription medications, can support individuals in their journey to quit smoking.
Nutritional Advice
Good nutrition is essential for individuals with COPD. A well-balanced diet can help maintain a healthy weight, provide the energy needed for daily activities, and support immune function. People with COPD may need more calories due to the extra effort required to breathe. Consulting a dietitian to create a personalized nutrition plan can be beneficial, focusing on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
Exercise and Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Regular exercise is crucial for individuals with COPD, as it helps improve cardiovascular health, muscle strength, and overall stamina. Pulmonary rehabilitation, a program tailored for lung health, combines exercise, education, and support to help people with COPD breathe as efficiently as possible and improve their quality of life. These programs are designed by healthcare professionals and cater to the specific needs and limitations of each individual.
Managing COPD requires a multifaceted approach that includes medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and the support of a healthcare team. By focusing on smoking cessation, nutritional improvements, and regular exercise through pulmonary rehabilitation, individuals with COPD can significantly improve their health outcomes and quality of life. Adopting these lifestyle modifications is a proactive step towards managing COPD effectively and enjoying a more active and fulfilling life.
Medical Treatments for COPD
The treatment for COPD aims to relieve symptoms, slow the progression of the disease, and improve quality of life. Here are some of the most effective medical treatments for COPD.
Bronchodilators and Inhaled Steroids
Bronchodilators are medications that help open up the airways in your lungs, making it easier to breathe. They are usually taken using an inhaler or a nebulizer. There are two main types of bronchodilators: short-acting and long-acting. Short-acting bronchodilators provide quick relief from symptoms, while long-acting bronchodilators are used daily to control symptoms.
Inhaled steroids, also known as corticosteroids, can reduce inflammation in the airways and help improve breathing. They are often prescribed for people with moderate to severe COPD, especially those who have frequent exacerbations. In some cases, doctors may prescribe a combination inhaler that includes both a bronchodilator and an inhaled steroid to manage COPD symptoms more effectively.
Long-term Oxygen Therapy
For people with severe COPD and low levels of oxygen in their blood, long-term oxygen therapy may be necessary. This treatment involves breathing in oxygen through a mask or nasal prongs from a portable oxygen tank or a machine in your home. Long-term oxygen therapy can help increase oxygen levels in the bloodstream, reduce the strain on the heart, improve sleep and mood, and increase life expectancy.
Surgery Options for Advanced COPD
In advanced stages of COPD, when other treatments have not been effective, surgery may be an option to improve breathing and quality of life.
Lung Volume Reduction Surgery
Lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS) involves removing diseased, emphysematous lung tissue, which can improve the function of the remaining, healthier lung tissue. This surgery can reduce breathlessness, improve the ability to exercise, and enhance overall quality of life for certain patients with emphysema, a form of COPD.
Lung Transplant
A lung transplant may be considered for individuals with very severe COPD when all other treatments have failed. This surgery involves replacing one or both diseased lungs with healthy lungs from a donor. A lung transplant can significantly improve lung function and quality of life but involves major surgery and a lifelong commitment to taking immunosuppressive medications to prevent organ rejection.
For individuals living with COPD, it’s crucial to avoid triggers that can worsen symptoms, such as tobacco smoke, air pollution, and respiratory infections. Regular check-ups, vaccinations, and following a treatment plan can help manage the disease effectively.
Emerging Treatments and Therapies for COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) remains a significant health challenge worldwide, affecting millions of people and impairing their quality of life. However, the landscape of COPD treatment is evolving rapidly, thanks to ongoing research and the development of innovative therapies. This article explores recent advances in COPD treatment, the critical role of research in developing new therapies, and the future prospects in the management of this condition.
Recent Advances in COPD Treatment
The last few years have seen remarkable progress in the treatment of COPD. Traditional treatments like bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids remain staples in managing the disease. Still, newer modalities are providing additional options for patients and healthcare providers. Among these are the introduction of biologic therapies targeted at reducing inflammation and the use of dual bronchodilators that work to improve lung function more effectively than single medications. Furthermore, advances in pulmonary rehabilitation techniques and non-invasive ventilation methods have significantly improved the quality of life for many COPD sufferers.
Technological advancements, including smart inhalers equipped with digital health technology, have made it easier for patients to manage their condition and adhere to treatment regimens. These devices can track medication usage, monitor symptoms, and even remind patients when it’s time to take their medication, thus enhancing treatment efficacy.
The Role of Research in Developing New Therapies
Behind these advancements lies a vast expanse of research and clinical trials aimed at understanding COPD’s complexities. Research in COPD spans from basic science exploring the molecular and genetic bases of the disease to clinical studies testing new drugs and therapies. This research is critical for identifying novel targets for treatment and understanding how the disease progresses, which in turn, informs the development of new therapeutic strategies.
One of the most promising areas of research is the exploration of anti-inflammatory treatments that can address one of the core mechanisms of COPD. Researchers are also investigating the potential of regenerative medicine, including stem cell therapy, to repair lung tissue damaged by COPD. Such therapies could offer hope for a more definitive solution to a disease currently considered incurable.
Future Prospects in COPD Treatment
The future of COPD treatment is bright, with numerous innovative therapies in the pipeline. Personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the genetic makeup and specific characteristics of an individual’s disease, holds particular promise. This approach could revolutionize COPD treatment by ensuring that patients receive the most effective therapies for their unique condition.
Moreover, ongoing advancements in telemedicine and remote patient monitoring offer the potential to further improve disease management. These technologies can facilitate better communication between patients and healthcare providers, timely interventions to prevent exacerbations, and more personalized care plans.
However, the landscape of COPD treatment is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by advances in medical research and technology. While challenges remain, the prospects for more effective treatments and ultimately a cure for COPD are more promising than ever before. As research continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible, patients with COPD can look forward to a future with better management options and improved quality of life.
Managing COPD: A Holistic Approach
Understanding the importance of a comprehensive management plan, participating in pulmonary rehabilitation programs, and acknowledging the role of support groups and mental health considerations are pivotal in effectively managing COPD. This holistic approach can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals living with this condition.
Importance of a Comprehensive Management Plan
A comprehensive management plan is essential for anyone living with COPD. This plan should be personalized, taking into account the severity of the disease, the patient’s lifestyle, and their overall health. It typically includes medication management, lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, regular physical activity, and dietary adjustments. Additionally, it’s crucial to monitor lung function and have regular check-ups with healthcare providers to adjust the treatment plan as necessary. This proactive and inclusive strategy aims to minimize symptoms, reduce the frequency of flare-ups, and slow the progression of the disease.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation Programs
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs are a cornerstone of COPD management. These programs are designed to improve the physical and emotional well-being of people with COPD. They usually include exercise training, education on managing COPD, nutritional advice, and psychological support. The goal is to enhance the overall stamina, reduce symptoms, and increase the capacity for daily activities. Studies have shown that participants of pulmonary rehabilitation experience significant improvements in their quality of life and a reduction in the need for hospitalization.
Support Groups and Mental Health Considerations
Living with COPD can be challenging not just physically but also emotionally and mentally. Support groups play a vital role in providing emotional comfort, practical advice, and a sense of community for individuals with COPD. Sharing experiences and coping strategies with others who understand what you’re going through can be incredibly reassuring and empowering.
Furthermore, addressing mental health is crucial in COPD management. Conditions such as anxiety and depression are more common in individuals with COPD than in the general population. Recognizing and treating these conditions with the help of healthcare professionals can significantly improve the overall well-being and management of COPD.
However, managing COPD effectively requires a holistic approach that encompasses a comprehensive management plan, participation in pulmonary rehabilitation programs, and attention to mental health and support networks. By integrating these elements, individuals with COPD can lead more fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by the disease.
Living with COPD: Tips and Strategies
Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) can be challenging, but with the right strategies and modifications to your daily life, you can manage your symptoms more effectively and lead a fulfilling life. In this guide, we’ll explore practical tips and strategies for living with COPD, focusing on daily life modifications, prevention of exacerbations, and emergency planning.
Daily Life Modifications for Better Living with COPD
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke, quitting is the most significant step you can take to improve your COPD symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
- Stay Active: Regular, gentle exercise can help improve your breathing, increase your energy levels, and enhance your overall quality of life. Consider activities like walking, swimming, or cycling, and consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: A nutritious diet can help you maintain your strength and improve your energy levels. Focus on a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Stay hydrated and consider eating smaller, more frequent meals if you find it difficult to breathe while eating.
- Avoid Air Pollutants: Stay indoors on days when air quality is poor, and avoid exposure to irritants like dust, chemical fumes, and smoke that can worsen COPD symptoms.
How to Prevent Exacerbations
- Take Your Medications as Prescribed: Adherence to your prescribed medication regimen is crucial in managing COPD and preventing exacerbations.
- Get Vaccinated: Influenza and pneumonia vaccinations can help reduce your risk of COPD flare-ups.
- Monitor Your Symptoms: Be vigilant about changes in your symptoms and learn to recognize early signs of an exacerbation, such as increased shortness of breath, coughing, or changes in mucus production.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Regular hand washing and avoiding close contact with people who are sick can help prevent respiratory infections that may lead to exacerbations.
Emergency Planning and When to Seek Help
- Create an Action Plan: Work with your healthcare provider to develop a clear action plan for managing exacerbations. This plan should include when to use rescue medications, when to call your doctor, and when to seek emergency care.
- Recognize the Signs of an Emergency: Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe shortness of breath, have trouble speaking or walking due to breathing difficulties, or if your lips or fingernails turn blue or gray.
- Keep Emergency Contacts Handy: Have a list of emergency contacts, including your healthcare provider’s phone number, readily available.
By implementing these daily life modifications and strategies, you can effectively manage your COPD symptoms, prevent exacerbations, and be prepared for emergencies. Remember, working closely with your healthcare team is essential in managing COPD, so keep them informed about any changes in your condition or symptoms.
Living with COPD requires adaptation and adjustments, but with the right approach, you can maintain an active, healthy lifestyle. Focus on what you can do, stay positive, and seek support from family, friends, and support groups to help you navigate the challenges of COPD.
FAQs about COPD Treatment
What is the best treatment for COPD?
The best treatment for COPD varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual patient’s health. Generally, treatment includes quitting smoking, medications like bronchodilators and corticosteroids, pulmonary rehabilitation, and in severe cases, oxygen therapy. It’s crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to tailor a treatment plan that’s best for you.
Can COPD be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for COPD. However, treatment can help control symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and improve the ability to lead an active life. Early diagnosis and following a treatment plan can significantly impact the progression of the disease.
How can I improve my lung function with COPD?
Improving lung function with COPD involves several lifestyle changes and treatments. Quitting smoking is the most effective step you can take. Engaging in regular, moderate exercise can help improve your overall strength and endurance. Pulmonary rehabilitation programs offer tailored exercise and education to help manage COPD symptoms. Following your prescribed medication regimen is also crucial for improving lung function.
Is walking good for COPD?
Yes, walking is an excellent exercise for individuals with COPD. It helps strengthen the cardiovascular system and muscles without overstraining the lungs. Walking can improve endurance, reduce symptoms, and enhance the quality of life. Start with short walks and gradually increase the duration and intensity based on your comfort and ability.
What foods should be avoided with COPD?
Certain foods can worsen COPD symptoms or lead to discomfort. It’s advisable to avoid highly processed foods, foods with a lot of salt, dairy products (if they cause mucus build-up), and fried or greasy foods. Instead, focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains to help manage your symptoms and improve overall health.
Can stress affect COPD?
Yes, stress can have a significant impact on COPD. Stress can lead to breathlessness and exacerbate COPD symptoms. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga, can help alleviate symptoms. It’s also important to seek support from friends, family, or support groups to cope with the emotional challenges of living with COPD.
How often should I see my doctor for COPD management?
The frequency of doctor visits for COPD management depends on the severity of your condition and how well your symptoms are controlled. Typically, people with COPD should see their healthcare provider at least once a year for a check-up. However, if your symptoms worsen or you experience frequent exacerbations, more frequent visits may be necessary.
Conclusion:
We strongly encourage patients and their loved ones to foster a collaborative relationship with their healthcare providers. Open communication, regular check-ups, and a proactive approach to managing COPD can make a substantial difference in the course of the disease. It’s about creating a partnership where patient empowerment and professional guidance converge to tailor a treatment plan that acknowledges individual needs and lifestyle considerations.
Moreover, the medical field is continually evolving, with research bringing to light new insights and advancements in the treatment of COPD. Staying informed about these developments is more important than ever. By keeping abreast of the latest treatment options, therapies, and management strategies, patients and healthcare providers can work together to explore new avenues for care that may offer additional benefits.
As we conclude, let this be a call to action for everyone impacted by COPD to stay informed, engaged, and proactive in their care journey. Whether you are a patient, a loved one, or a healthcare professional, your role in recognizing, diagnosing, and treating COPD is invaluable. Together, by harnessing knowledge, compassion, and the latest in medical advancements, we can face COPD with resilience and hope for a brighter, healthier future.