COPD Symptoms: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease that makes breathing difficult for millions of people worldwide.
This condition is not only debilitating but also significantly impacts the quality of life. Understanding the symptoms and causes of COPD is crucial for early detection and management.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the essential aspects of COPD, aiming to provide valuable information for those affected and their caregivers.
Understanding COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide, with significant implications for both health and quality of life. To fully grasp the impact of COPD, it’s essential to start with a foundational understanding of the respiratory system and how this disease alters its function.
Brief Overview of the Respiratory System and COPD’s Effects
The respiratory system is a complex network designed to supply oxygen to the body’s cells while removing carbon dioxide. It includes the nose, throat, windpipe, and lungs. Air travels down this pathway, reaching the lungs, where oxygen is transferred to the blood, and carbon dioxide is expelled during exhalation.
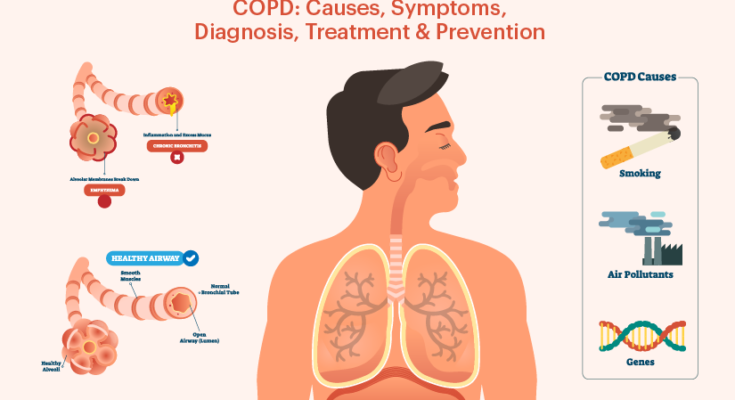
COPD primarily targets the lungs, causing inflammation, damage to the lung tissue, and obstruction of the airways. This results in two main conditions associated with COPD: emphysema, where the air sacs (alveoli) at the end of the airways in the lungs are damaged, making it hard to breathe out; and chronic bronchitis, characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the bronchial tubes, leading to mucus build-up and chronic cough.
The progression of COPD leads to a decrease in the efficiency of the respiratory system. As the disease advances, the lungs struggle to facilitate the exchange of gases, leading to decreased oxygen levels in the blood and difficulty removing carbon dioxide. This inefficiency causes shortness of breath, wheezing, and chronic cough, significantly impacting daily activities and overall quality of life.
Prevalence and Impact of COPD Globally
COPD is a global health concern, with estimates suggesting that millions of people are affected worldwide. The disease is often caused by long-term exposure to harmful particulates or gases, with cigarette smoke being the most common culprit. However, environmental factors such as air pollution and occupational hazards also contribute significantly to its prevalence.
The impact of COPD on individuals and healthcare systems is profound. It is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality globally, placing a substantial burden on economies due to healthcare costs and lost productivity. Individuals with COPD experience a decreased ability to perform routine tasks, often leading to disability and a diminished quality of life. The emotional and psychological toll on patients and their families can be significant, highlighting the need for effective management and support strategies.
However, understanding COPD and its effects on the respiratory system is crucial for recognizing the significance of this disease globally. It underscores the importance of preventive measures, early diagnosis, and management strategies to mitigate the impact of COPD on individuals and society at large. With ongoing research and awareness, there is hope for improved outcomes for those affected by this debilitating condition.
Early Signs and Symptoms of COPD
Recognizing the initial signs of COPD is crucial for prompt treatment and slowing the disease’s progression. In this guide, we’ll explore the detailed list of early COPD symptoms, how to recognize these signs, and the importance of early detection and diagnosis.
Detailed List of Early COPD Symptoms
COPD symptoms often start mild and gradually worsen over time. Early detection can be challenging, as symptoms may be mistaken for a common cold or fatigue. Here are the key early symptoms of COPD:
- Persistent Cough: A cough that lasts for weeks or even months and doesn’t go away can be an early sign of COPD.
- Increased Mucus Production: An increase in the amount of mucus produced, often thicker and more difficult to clear than normal.
- Shortness of Breath: Initially, this might occur during physical activities but can worsen and become noticeable even during rest as the disease progresses.
- Wheezing: A whistling or squeaky sound when breathing, especially during exhalation.
- Frequent Respiratory Infections: An increase in colds, flu, or pneumonia can indicate compromised lung health.
How to Recognize the Initial Signs of COPD
Recognizing COPD in its early stages involves paying close attention to subtle changes in respiratory health. Consider the following:
- Duration and Frequency: Symptoms such as cough and mucus production that persist beyond a typical cold or flu.
- Activity Level Changes: Notice if you’re becoming more easily winded or short of breath during activities that used to be manageable.
- Listening to Your Body: Pay attention to changes in breathing sounds, such as wheezing or struggling to breathe after mild exertion.
Importance of Early Detection and Diagnosis
Early detection of COPD is paramount for several reasons:
- Slows Progression: While COPD is not curable, early intervention can slow the disease’s progression.
- Improves Quality of Life: Early treatment can significantly improve day-to-day functioning and quality of life.
- Reduces Complications: Identifying and managing COPD early can help prevent complications, including exacerbations and hospitalizations.
- Treatment Efficacy: Treatments and lifestyle changes are more effective when implemented early in the disease’s course.
For those at risk, including smokers or individuals exposed to lung irritants, regular check-ups and lung function tests can aid in early detection. Remember, the earlier COPD is caught, the more effective the treatment and management strategies will be.
Major COPD Symptoms: An In-depth Exploration
Understanding its major symptoms is crucial for early detection, management, and differentiation from other respiratory diseases. This comprehensive guide delves into the core symptoms of COPD, their impact on daily life, and how they differ from symptoms of other respiratory conditions.
Chronic Cough
A persistent, chronic cough is a hallmark symptom of COPD. Unlike a common cold cough, this chronic cough is long-lasting and often produces a significant amount of mucus. It’s not just any cough; it’s your body’s response to the blocked airways and inflammation characteristic of COPD.
Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath, medically known as dyspnea, is another significant indicator of COPD. Individuals may experience difficulty breathing during both rest and physical activities. This symptom becomes more pronounced as the disease progresses, severely limiting one’s ability to perform even simple tasks without feeling winded.
Excess Mucus Production
COPD leads to increased mucus production in the respiratory tract. This excess mucus can obstruct the airways, making breathing more difficult and exacerbating the chronic cough. Managing this symptom is a daily challenge for those with COPD, often requiring the use of medications to thin the mucus and ease its clearance.
Wheezing
Wheezing, a high-pitched whistling sound made while breathing, is common in COPD patients. It’s a result of narrowed airways and airflow obstruction. Wheezing can vary in intensity and often worsens during flare-ups or physical exertion.
Fatigue
Fatigue in COPD patients is multifaceted. It arises not just from the effort of breathing with compromised lungs but also from the body’s increased energy expenditure in trying to obtain adequate oxygen. This relentless tiredness affects one’s quality of life, limiting the ability to engage in daily activities and exercise, which are crucial for managing COPD.
Impact on Daily Life
These symptoms significantly impact the quality of life for individuals with COPD. Daily tasks that many take for granted, such as walking, climbing stairs, or even carrying groceries, can become exceedingly challenging. Social activities and hobbies may also be curtailed, contributing to feelings of isolation and depression.
Differentiating COPD from Other Respiratory Conditions
While COPD shares symptoms with other respiratory conditions, certain characteristics help differentiate it. For instance, the chronic cough associated with COPD is typically more persistent than that of asthma, another common respiratory condition. Asthma attacks are often triggered by specific allergens or activities, while COPD symptoms are constant and generally worsen over time. Additionally, COPD is characterized by irreversible airway damage, unlike the reversible airway obstruction seen in asthma.
However, recognizing the major symptoms of COPD is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment. By understanding how these symptoms manifest and affect daily life, individuals can seek appropriate care and management strategies. Differentiating COPD from other respiratory conditions is also crucial, enabling targeted treatment plans that can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected.
Causes and Risk Factors of COPD
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with COPD is crucial for both prevention and early intervention. In this article, we delve into the primary causes and risk factors of COPD, exploring how they contribute to the development of this debilitating disease.
Primary Causes of COPD
- Smoking: The leading cause of COPD is tobacco use. Smoking cigarettes, cigars, pipes, or being exposed to secondhand smoke damages the lungs and airways, leading to COPD. The risk increases with the duration and amount of smoking.
- Environmental Factors: Long-term exposure to harmful pollutants in the environment, including chemical fumes, dust, and other irritants in the workplace, can also cause COPD. Air pollution plays a significant role, especially in urban areas with high levels of outdoor air pollutants.
- Genetic Factors: Although less common, a genetic disorder known as Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (AATD) can lead to the development of COPD even in individuals who have never smoked or been heavily exposed to pollutants. AATD affects the body’s ability to produce alpha-1 antitrypsin, a protein that protects the lungs.
Risk Factors Contributing to COPD
Understanding the risk factors is key to prevention. Besides the primary causes mentioned above, several other factors can increase the likelihood of developing COPD:
- Age: COPD develops slowly over years, so the majority of people are diagnosed after the age of 40.
- Asthma: Individuals with a history of asthma may have an increased risk, especially if they also smoke.
- Exposure to Smoke: Living with a smoker or being exposed to large amounts of secondhand smoke can elevate your risk.
- Occupational Exposures: Jobs that involve inhaling dust, chemicals, and fumes can increase the risk of developing COPD.
- Socioeconomic Status: Studies have shown that people from lower socioeconomic backgrounds are more likely to be exposed to the risk factors associated with COPD.
Discussion on Contribution to COPD Development
Each of these factors contributes to COPD development by damaging the lungs and airways, leading to the characteristic airflow obstruction of the disease. Smoking introduces toxins that inflame and damage lung tissue, while environmental pollutants can cause similar harm over time. In the case of genetic factors like AATD, the lack of protective proteins leaves the lungs vulnerable to damage from even minor irritants.
Moreover, the risk factors interact in complex ways. For example, someone with a genetic predisposition to COPD who also smokes or is frequently exposed to air pollutants is at a significantly higher risk than someone with only one of these risk factors. Thus, understanding and mitigating these risks can play a pivotal role in preventing the onset or progression of COPD.
COPD is a preventable and manageable condition with the right knowledge and precautions. Quitting smoking, avoiding exposure to lung irritants, and understanding personal and genetic risk factors are key steps in preventing COPD or managing its progression. Regular medical check-ups and consultations can also aid in early detection and treatment, helping individuals maintain a better quality of life.
By educating ourselves and making informed lifestyle choices, we can significantly reduce the impact of COPD and its risk factors on our lives and communities.
Diagnosing COPD: Methods and the Importance of Symptom Recognition
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial in managing this disease effectively. This article delves into the primary diagnostic methods for COPD and highlights the pivotal role of symptom recognition in its early diagnosis.
List of Diagnostic Methods for COPD
- Spirometry: The cornerstone of COPD diagnosis, spirometry is a non-invasive test that measures how much and how quickly you can exhale. It helps in assessing lung function and is vital for confirming the presence of airflow obstruction indicative of COPD.
- Chest X-rays: While not diagnostic for COPD on their own, chest X-rays can rule out other lung conditions and show the presence of any complications associated with COPD.
- CT Scans: High-resolution computed tomography (CT) scans provide detailed images of the lungs and can help in detecting emphysema, one of the main components of COPD. They are also useful in assessing the severity of the disease.
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: This test measures the oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in your blood, providing insight into the severity of COPD and its impact on your body’s ability to manage these gases.
- Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Testing: Since Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency is a genetic condition that can lead to COPD, testing for it is crucial, especially if you have a family history of the disease or develop symptoms at a young age.
The Role of Symptom Recognition in Early Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of COPD early on is critical for a timely diagnosis. Symptoms often include chronic cough, sputum production, and shortness of breath, especially during physical activities. However, these symptoms can be subtle and gradually worsen over time, making them easy to overlook or attribute to aging or a lack of fitness.
Early symptom recognition allows individuals to seek medical advice sooner, leading to an early diagnosis. This is essential because the sooner COPD is diagnosed, the more effective the management strategies can be. Early intervention can slow the progression of the disease, improve the quality of life, and reduce the risk of severe complications.
However, a combination of advanced diagnostic methods and keen symptom awareness is key to the early detection and management of COPD. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms related to COPD, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial steps in managing COPD effectively, maintaining lung function, and enhancing overall well-being.
Preventing and Managing COPD Symptoms
Managing and preventing the worsening of COPD symptoms is crucial for maintaining quality of life. This guide offers tips and strategies to help individuals with COPD lead healthier lives.
Tips for Preventing COPD Symptoms from Worsening
- Quit Smoking: Smoking cessation is the most effective step you can take to prevent COPD from getting worse. If you smoke, seek help to quit.
- Avoid Air Pollutants: Stay away from places with dust, fumes, or smoke. Use air purifiers at home to keep the air clean.
- Get Vaccinated: Infections can exacerbate COPD symptoms. Ensure you’re up to date with flu and pneumonia vaccinations.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity can strengthen your respiratory muscles. Talk to your doctor about starting an exercise plan.
- Follow a Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet helps manage COPD by maintaining your strength and immunity.
- Regular Check-ups: Routine visits to your healthcare provider can help monitor your condition and adjust treatments as necessary.
Brief Overview of COPD Management Strategies
Managing COPD involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and therapies to help relieve symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
Medications
- Bronchodilators: These medications help relax the muscles around the airways, making it easier to breathe.
- Steroids: Inhaled corticosteroids can reduce inflammation in the airways.
- Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors: This type of medication can decrease airway inflammation and relax the airways.
- Antibiotics: Occasionally used to treat or prevent lung infections.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Pulmonary rehabilitation is a comprehensive program that combines exercise, education, and support to help people with COPD improve their physical condition and manage their symptoms. It typically includes:
- Exercise training: Tailored to your specific needs and abilities.
- Nutritional advice: To help you maintain an optimal weight.
- Disease management training: To help you manage your condition effectively.
- Psychological counseling: To address the emotional aspects of living with a chronic condition.
Oxygen Therapy
For individuals with severe COPD and low levels of oxygen in their blood, oxygen therapy can be lifesaving. It can be administered via nasal prongs or a mask and is designed to help you breathe easier, sleep better, and stay more active.
However, while COPD is a chronic condition with no cure, adopting the right management strategies can significantly improve your ability to lead an active, fulfilling life. Regular communication with your healthcare provider, adherence to treatment plans, and lifestyle adjustments are key to effectively managing COPD symptoms.
FAQs About COPD
What is COPD and what causes it?
COPD is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. It’s primarily caused by long-term exposure to irritating gases or particulate matter, most often from cigarette smoke. Other factors, such as exposure to air pollution, dust, and chemical fumes in the workplace, can also contribute to developing COPD.
What are the symptoms of COPD?
The most common symptoms of COPD include shortness of breath, wheezing, chest tightness, and a chronic cough that produces a significant amount of mucus. Symptoms often don’t appear until significant lung damage has occurred, and they usually worsen over time.
How is COPD diagnosed?
COPD is diagnosed through a combination of clinical assessment and diagnostic tests. The primary test for COPD is spirometry, which measures the amount of air a person can inhale and exhale, and how quickly they can exhale. Doctors may also recommend chest X-rays, CT scans, and blood tests to determine the severity of the disease and to rule out other respiratory conditions.
Can COPD be treated?
While there is no cure for COPD, treatment can help control symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and generally improve quality of life. Treatments include medication, such as bronchodilators and inhaled steroids, pulmonary rehabilitation, and in severe cases, oxygen therapy or surgery.
Is COPD preventable?
Yes, COPD is largely preventable. The most effective way to prevent COPD is to never start smoking or to quit smoking. Avoiding or minimizing exposure to lung irritants, such as air pollution, chemical fumes, and dust in the workplace, can also significantly reduce the risk of developing COPD.
What lifestyle changes can help manage COPD?
Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage COPD symptoms and improve overall health. These include quitting smoking, staying active through gentle exercise, eating a healthy diet, avoiding air pollution, and getting vaccinated against respiratory infections like the flu and pneumonia.
Can COPD lead to other health problems?
Yes, COPD can increase the risk of other health problems, including respiratory infections, heart disease, lung cancer, and high blood pressure in the lung arteries (pulmonary hypertension). Managing COPD effectively and monitoring for these complications are essential parts of care.
When should I see a doctor?
If you experience symptoms of COPD, especially if you have a history of smoking or long-term exposure to lung irritants, it’s important to see a doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can help slow the progression of the disease and improve quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and recognizing the symptoms of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is crucial for early detection and effective management of the condition. COPD, a progressive lung disease characterized by breathing difficulties, can significantly impact the quality of life if left unaddressed. Symptoms such as persistent cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, and frequent respiratory infections are key indicators that should not be ignored.
Awareness of the causes and risk factors of COPD, including smoking, long-term exposure to air pollutants, and a history of respiratory infections, is essential for prevention and early intervention. Identifying these symptoms early and understanding their potential causes can lead to timely medical advice and treatment, potentially slowing the progression of the disease.
We strongly encourage anyone experiencing symptoms associated with COPD to consult with healthcare providers. Seeking professional advice at the earliest sign of respiratory issues can make a significant difference in managing COPD effectively. Healthcare providers can offer comprehensive evaluations, recommend appropriate treatments, and provide guidance on lifestyle adjustments that can help manage symptoms and improve overall lung health.
Remember, taking proactive steps towards recognizing and addressing the symptoms of COPD is key to maintaining lung health and ensuring a better quality of life. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Your health is paramount, and taking action today can lead to a healthier tomorrow.