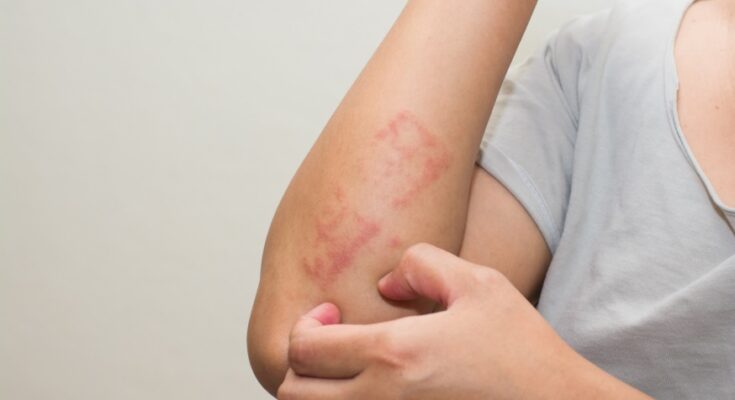
Contact Dermatitis Treatment: Contact Dermatitis is a common skin condition characterized by an itchy rash that occurs after direct contact with a substance.
It can lead to redness, itching, and sometimes blistering or peeling. This condition is not contagious or life-threatening but can be uncomfortable for those affected.
What is Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis is a type of skin inflammation that occurs when the skin comes into contact with a substance that either irritates it or triggers an allergic reaction. This condition can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender, and can manifest anywhere on the body. Understanding contact dermatitis is crucial for effective management and prevention, as it can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life.
Types of Contact Dermatitis
There are two main types of contact dermatitis, each with distinct causes and mechanisms:
- Irritant Contact Dermatitis (ICD): This is the most common form and is caused by direct damage to the skin from a substance. It can result from a single exposure to a strong irritant or repeated exposures to milder irritants.
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis (ACD): This occurs when the skin develops an allergy to a specific substance. Unlike ICD, ACD requires previous exposure to the allergen for sensitization to occur, and subsequent exposures lead to allergic reactions.
Common Causes and Triggers
Contact dermatitis can be triggered by a wide range of substances. Common irritants and allergens include:
- Chemicals found in cleaning products, detergents, and solvents.
- Metals, especially nickel, which is often found in jewelry and clothing fasteners.
- Plants, such as poison ivy, poison oak, and poison sumac.
- Cosmetics, including perfumes, hair dyes, and skin care products.
- Environmental factors, such as extreme temperatures, can exacerbate symptoms.
Symptoms and Signs to Look Out For
The symptoms of contact dermatitis can vary depending on the type and severity but commonly include:
- Redness and Rash: Often the first sign, appearing in the area of contact.
- Itching: This can range from mild to severe and is more common in allergic contact dermatitis.
- Dryness, Flaking, or Scaling: The skin may become dry and flaky as it heals.
- Blisters and Oozing: In more severe cases, especially with allergic contact dermatitis, blisters can form and may ooze.
- Swelling: Areas of skin exposed to the allergen or irritant may swell.
Recognizing these symptoms early is key to managing contact dermatitis effectively. If you suspect you have contact dermatitis, it’s important to identify the cause and avoid further exposure. For persistent or severe symptoms, consulting a healthcare provider or dermatologist is recommended for proper diagnosis and treatment.
By understanding the types, causes, and symptoms of contact dermatitis, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this condition. Remember, the key to dealing with contact dermatitis is identifying and avoiding the triggers whenever possible.
Diagnosis of Contact Dermatitis
Its diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and management. In this guide, we’ll explore the importance of an accurate diagnosis, outline the steps involved in diagnosing contact dermatitis, and discuss how to distinguish it from other skin conditions.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
An accurate diagnosis of contact dermatitis is essential for several reasons:
- Targeted Treatment: Identifying the type and cause of contact dermatitis enables healthcare providers to recommend the most effective treatments, reducing symptoms more quickly.
- Avoidance of Triggers: Understanding what triggers your contact dermatitis helps in avoiding those substances, preventing future outbreaks.
- Minimizing Complications: Early and accurate diagnosis can prevent complications such as infections, which can occur if the skin is broken and becomes more susceptible to bacteria.
Steps in Diagnosing Contact Dermatitis
Diagnosing contact dermatitis involves several key steps to ensure an accurate understanding of the condition. Here’s a step-by-step approach used by healthcare professionals:
- Medical History Review: The process begins with a thorough review of the patient’s medical history, including any previous skin conditions, allergies, and exposure to potential irritants.
- Physical Examination: A detailed examination of the skin helps identify the characteristic signs of contact dermatitis, such as redness, itching, and blistering.
- Patch Testing: For allergic contact dermatitis, patch testing may be conducted. This involves applying small amounts of various substances to the skin to see if a reaction occurs, identifying specific allergens.
- Elimination of Irritants: Patients may be advised to eliminate certain products or substances from their environment to see if their condition improves, helping to pinpoint potential irritants.
- Skin Biopsy: In some cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary to rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis of contact dermatitis.
Differential Diagnosis: Distinguishing Contact Dermatitis from Other Skin Conditions
Contact dermatitis often presents symptoms similar to other skin conditions, making differential diagnosis important. Conditions that can mimic contact dermatitis include:
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): While both conditions cause itching and redness, eczema is usually more chronic and may be associated with a family history of allergies.
- Psoriasis: Psoriasis can cause red, scaly patches that might look similar to contact dermatitis but often appears on the elbows, knees, and scalp.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: This condition causes flaky scales and redness, primarily on the scalp and face, differing from the localized reactions typical of contact dermatitis.
- Fungal Infections: These can cause rash and itching similar to contact dermatitis but usually have a distinct ring shape and may respond to antifungal treatments.
Distinguishing contact dermatitis from these and other skin conditions often requires a combination of medical history, physical examination, and sometimes additional testing.
Accurately diagnosing contact dermatitis is the first step toward effective management and treatment. Understanding the steps involved in diagnosis and the importance of distinguishing it from other skin conditions can empower patients and healthcare providers alike to address this uncomfortable condition more effectively.
Contact Dermatitis Treatment Strategies
Managing contact dermatitis effectively involves a comprehensive approach that ranges from home care and lifestyle adjustments to medical treatments and exploring emerging therapies. Below, we detail strategies that can help alleviate symptoms, speed up recovery, and prevent future flare-ups.
Home Care and Lifestyle Modifications
The foundation of treating contact dermatitis is often through simple home care measures and modifications to your daily routine. These steps are aimed at reducing irritation and avoiding exposure to allergens or irritants:
- Avoid Known Irritants: The most critical step is identifying and steering clear of the substances that trigger your symptoms. This might mean changing your skincare products, laundry detergents, or even wearing gloves to protect your skin from irritants.
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin moisturized helps repair the skin barrier and reduces dryness and itching. Use fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizers immediately after bathing to lock in moisture.
- Cool Compresses: Applying cool, wet compresses to the affected areas can soothe irritation and reduce itching.
- Protect Affected Skin: Cover the skin with protective clothing or dressings, especially if you’re engaging in activities that might expose you to irritants.
- Bathing Habits: Short, lukewarm baths or showers can help your skin. Avoid hot water and harsh soaps, opting for mild, fragrance-free cleansers instead.
Medical Treatments
When home remedies are not enough, medical treatments can offer relief:
- Topical Corticosteroids: These are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching. It’s important to use them as directed by your healthcare provider to avoid potential side effects.
- Oral Medications: For severe cases, oral corticosteroids, antihistamines, or antibiotics (if an infection is present) may be prescribed.
- Barrier Creams and Ointments: Products designed to protect the skin from irritants can also be beneficial, especially for individuals frequently in contact with water or irritants.
Emerging Treatments and Therapies
Research into contact dermatitis is ongoing, and new treatments are being developed:
- Biologics: These are a new class of drugs that target specific parts of the immune system. They hold promise for treating severe cases of dermatitis that don’t respond to traditional treatments.
- Phototherapy: This involves exposing the skin to certain types of ultraviolet light, helping to reduce itching and inflammation in some patients.
- Topical Immunomodulators: These non-steroidal creams and ointments can help treat inflammation and symptoms with potentially fewer side effects than corticosteroids.
However, managing contact dermatitis requires a multi-faceted approach tailored to the severity of your symptoms and the specific triggers involved. Home care and lifestyle changes are essential for all sufferers, while medical treatments and emerging therapies offer hope for more severe or persistent cases. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for your situation.
Managing Contact Dermatitis: Practical Tips and Advice
With the right strategies, you can effectively manage and even prevent flare-ups. Below, we offer practical tips and advice to help you navigate through the complexities of contact dermatitis, focusing on identifying common irritants, using protective measures, and understanding the role of stress management.
Tips for Identifying and Avoiding Common Irritants and Allergens
Understanding what triggers your contact dermatitis is crucial in managing the condition. Common irritants include soaps, detergents, and certain metals like nickel. Allergens could range from fragrances in cosmetics to plants such as poison ivy.
- Keep a Diary: Track your daily activities and products used. Over time, you may notice patterns that help identify triggers.
- Patch Testing: Consider seeing a dermatologist for patch testing, which can pinpoint specific allergens causing your reactions.
- Choose Products Wisely: Opt for hypoallergenic and fragrance-free personal care products. Reading labels can help you avoid known irritants.
Recommendations for Protective Clothing and Products
Protective measures can significantly reduce your exposure to irritants and allergens.
- Protective Clothing: Wear gloves when using cleaning agents or gardening. If you’re allergic to certain fabrics, opt for natural fibers like cotton.
- Barrier Creams: These can provide a protective layer on your skin. Look for products specifically designed to block irritants.
- Moisturize: Keeping your skin well-moisturized helps maintain its barrier function, making it less susceptible to irritants.
Stress Management and Its Role in Symptom Reduction
Stress doesn’t just affect your mental health; it can also exacerbate skin conditions, including contact dermatitis. Managing stress is a key component in reducing symptoms.
- Regular Exercise: Activities like walking, yoga, or swimming can help reduce stress levels.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help calm the mind and body.
- Seek Support: Talking to a therapist or joining a support group can provide emotional support and practical advice on managing dermatitis.
By implementing these practical tips and strategies, you can effectively manage contact dermatitis, reducing both the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Remember, understanding your triggers, protecting your skin, and managing stress are key steps in living comfortably with contact dermatitis.
When to See a Doctor
Recognizing when to seek medical advice for skin concerns is crucial. Whether it’s an unusual rash, persistent irritation, or signs of infection, understanding the indicators can guide you to timely and effective treatment. Here’s what you need to know about when to see a dermatologist and what to expect from your visit.
Identifying Signs of Infection or Severe Contact Dermatitis
Infections and severe contact dermatitis can manifest through various symptoms, making it essential to monitor your skin closely. Key signs that warrant a doctor’s visit include:
- Persistent Redness or Swelling: If redness or swelling doesn’t improve with over-the-counter treatments or persists for more than a week, it’s time to consult a doctor.
- Pain or Discomfort: Pain, especially if it’s severe or interferes with your daily activities, indicates the need for professional evaluation.
- Pus or Discharge: The presence of pus or a significant discharge is a clear sign of infection.
- Fever: A fever accompanying skin issues can signal a more serious infection requiring immediate attention.
Expectations from a Dermatology Visit
A dermatology visit typically involves a thorough assessment of your skin condition. Here’s what to expect:
- Medical History Review: Be prepared to discuss your medical history, including any previous skin conditions, allergies, and medications you’re taking.
- Skin Examination: Your dermatologist will examine the affected area and may use a dermatoscope to get a closer look.
- Diagnosis and Treatment Plan: Based on the examination, your doctor will diagnose the condition and recommend a treatment plan. This may include prescriptions, lifestyle modifications, or further testing.
The Importance of Follow-up and Managing Chronic Conditions
Follow-up appointments play a vital role in managing skin conditions, especially chronic ones like eczema, psoriasis, or acne. These visits help your dermatologist:
- Monitor Progress: To ensure the treatment is effective and make adjustments if necessary.
- Manage Flare-ups: Early intervention can prevent conditions from worsening.
- Long-term Care: Chronic conditions require ongoing management to keep symptoms at bay and improve the quality of life.
However, knowing when to seek medical advice and what to expect from a dermatology visit are key steps in addressing skin conditions effectively. Timely consultation, accurate diagnosis, and a tailored treatment plan, coupled with regular follow-up, are essential for managing both acute and chronic dermatological issues. Always prioritize your health by paying attention to your skin’s needs and seeking professional care when necessary.
FAQs Section on Contact Dermatitis
What is Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis is a type of skin inflammation that occurs when the skin comes into contact with a foreign substance, causing an allergic reaction or irritation. It results in a rash that can be itchy, red, and sometimes blistered or dry and cracked.
What Causes Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis can be caused by a wide variety of substances. Allergic contact dermatitis is triggered by an immune response to a substance like nickel, latex, or certain preservatives in cosmetics. Irritant contact dermatitis, on the other hand, is caused by direct damage to the skin by substances like detergents, solvents, or acids.
What are the Symptoms of Contact Dermatitis?
Symptoms of contact dermatitis include redness, itching, swelling, blistering, dryness, and cracking of the skin. The severity of symptoms can vary depending on the cause and the individual’s sensitivity.
How is Contact Dermatitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination of the affected skin and a review of your medical history. Patch testing may also be conducted to identify specific allergens responsible for allergic contact dermatitis.
How Can Contact Dermatitis be Treated?
Treatment for contact dermatitis focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing future reactions. This may include the application of topical steroids to reduce inflammation, moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated, and avoiding contact with identified irritants or allergens.
Can Contact Dermatitis Spread?
Contact dermatitis is not contagious and cannot spread from person to person. However, the rash can spread to other areas of the body if the irritant or allergen comes into contact with them.
How Can I Prevent Contact Dermatitis?
Preventing contact dermatitis involves identifying and avoiding substances that trigger your symptoms. Protective measures such as wearing gloves, using gentle skin care products, and applying barrier creams can also help reduce the risk of developing contact dermatitis.
Is Contact Dermatitis Permanent?
Contact dermatitis is usually not permanent. With proper treatment and avoidance of known irritants or allergens, most people can expect their symptoms to improve. However, some individuals may experience recurring episodes if they come into contact with the triggering substance again.
When Should I See a Doctor?
You should see a doctor if your symptoms are severe, if the rash does not improve with over-the-counter treatments, or if you suspect an infection. A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend an effective treatment plan.
Conclusion:
In summarizing our comprehensive guide on diagnosing and treating contact dermatitis, it’s vital to revisit the key points that pave the way for effective management and recovery. Contact dermatitis, a prevalent skin condition, emerges as a reaction to substances that irritate the skin or trigger an allergic response. Identifying the root cause, whether it’s an irritant or an allergen, is the cornerstone of diagnosis. This process often involves patch testing, a reliable method that pinpoints specific substances your skin reacts to.
Treatment strategies for contact dermatitis are multifaceted, focusing on alleviating symptoms and preventing future outbreaks. Key approaches include avoiding known irritants, applying topical steroids to reduce inflammation, and maintaining skin hydration through emollients. For more severe cases, advanced treatments such as phototherapy or systemic medications may be recommended under professional guidance.
However, the journey to recovery transcends clinical treatments. It’s a collaborative effort that requires your active participation. Being informed about your condition, understanding the triggers, and adhering to the care plan are instrumental in managing contact dermatitis effectively. Your engagement in lifestyle adjustments, skincare routines, and follow-up consultations plays a pivotal role in mitigating symptoms and enhancing your quality of life.
We encourage you to view this journey not just as a path to symptom relief but as an opportunity for empowerment. By taking an active role in your care plan, you contribute significantly to the healing process. Remember, managing contact dermatitis is a dynamic process that benefits immensely from your involvement and adaptability.
In closing, contact dermatitis, while challenging, is a condition that can be managed successfully with the right approach and mindset. Armed with knowledge, the right treatments, and a proactive stance, you can navigate the complexities of this condition and move towards a healthier, more comfortable skin state.