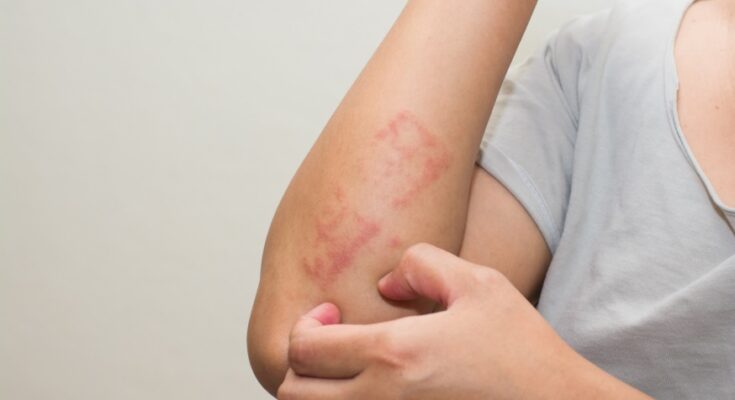
Contact Dermatitis Symptoms: Contact dermatitis is a prevalent skin condition characterized by redness, itching, and sometimes blisters, resulting from direct skin contact with an irritant or allergen.
This condition can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, causing discomfort and, in severe cases, leading to complications if not properly addressed.
Understanding the symptoms, causes, and effective management strategies is crucial for those affected by contact dermatitis.
What is Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis is a common skin condition characterized by redness, itching, and inflammation. It occurs when the skin comes into contact with a substance that either irritates it directly or triggers an allergic reaction. Understanding contact dermatitis is crucial, not only for those who suffer from the condition but also for anyone looking to maintain healthy skin.
Irritant vs. Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Irritant Contact Dermatitis is the more prevalent form of the condition. It results from direct damage to the skin by harsh substances like detergents, solvents, or acids. This type does not involve the immune system and can occur in anyone, even after a single exposure to the irritant. Symptoms typically include dry, cracked skin that may feel sore or burn.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis, on the other hand, is an immune system reaction to an allergen. This type requires prior sensitization to the substance; in other words, your skin must have been exposed to the allergen at least once before. Common allergens include nickel, fragrances, and certain plants like poison ivy. Symptoms are similar to irritant dermatitis but also include severe itching and potentially blisters.
However, while both types of contact dermatitis result in uncomfortable skin reactions, they differ significantly in their causes and underlying mechanisms. Irritant dermatitis is a direct reaction to a substance, whereas allergic dermatitis involves an immune response to an allergen. Recognizing the distinction between these types is a key step in managing symptoms and avoiding triggers.
Symptoms of Contact Dermatitis
Understanding the symptoms of contact dermatitis is crucial for identifying and managing this condition effectively. This article outlines the common symptoms associated with contact dermatitis, highlights how symptoms can vary between individuals, and provides guidance on when it might be time to consult a doctor.
Common Symptoms Associated with Contact Dermatitis
The symptoms of contact dermatitis can vary in severity and may include:
- Redness: One of the first signs of contact dermatitis is often red, inflamed skin at the site of contact with the irritant or allergen.
- Itching: This is a prevalent symptom, which can range from mild to severe and can be particularly discomforting.
- Swelling: Affected areas may become swollen, especially if the reaction is intense.
- Dryness, Flaking, or Scaling: The skin may become dry and flaky as the condition progresses, leading to scaling.
- Blisters: In more severe cases, blisters may form. These blisters can sometimes leak fluid and crust over.
- Burning sensation: Some individuals may experience a burning sensation on the affected skin.
How Symptoms Can Vary Between Individuals
The intensity and nature of contact dermatitis symptoms can vary significantly between individuals. Factors influencing these variations include the type of substance involved, the duration of exposure, and the individual’s sensitivity to the allergen or irritant. Some people might experience mild redness and itching, while others could have severe swelling and blistering. Additionally, the location on the body where symptoms appear can affect the severity and type of symptoms experienced.
Signs That Indicate It’s Time to See a Doctor
While mild cases of contact dermatitis can often be managed at home, there are certain signs that indicate the need for professional medical advice:
- Persistent Symptoms: If symptoms persist for more than a few weeks despite home care and avoidance of the suspected irritant or allergen.
- Severe Symptoms: Intense itching, pain, widespread redness, or swelling that significantly affects your daily activities or sleep.
- Infection Signs: If you notice signs of infection, such as increased pain, warmth, yellow or green pus, or fever, it’s crucial to seek medical attention.
- Facial or Genital Involvement: Dermatitis affecting the face or genital area can be particularly problematic and warrants a doctor’s evaluation.
- Difficulty Breathing: Though rare, if you experience difficulty breathing or swelling of the face, lips, or eyes, seek immediate medical care as it may indicate a severe allergic reaction.
However, recognizing the symptoms of contact dermatitis and understanding how they can vary between individuals are essential steps in managing this condition. Knowing when to seek medical advice can prevent complications and lead to more effective treatment options. If you’re uncertain about your symptoms or how to manage them, consulting with a healthcare professional is always the best course of action.
Causes of Contact Dermatitis
Understanding the causes of contact dermatitis is essential for both prevention and treatment. This article delves into the common irritants and allergens responsible for contact dermatitis, explains the underlying mechanisms of these reactions, and highlights the differences between irritant and allergic contact dermatitis.
Common Irritants and Allergens
Several substances can act as irritants or allergens, leading to contact dermatitis. Common irritants include soaps, detergents, solvents, acids, and abrasive materials. These substances can directly damage the outer layer of the skin, leading to irritant contact dermatitis. On the other hand, allergens responsible for allergic contact dermatitis include nickel (found in jewelry and metal items), latex, certain fragrances, and components of skin care and beauty products. Allergens cause a reaction because the immune system mistakenly identifies these harmless substances as threats.
How and Why These Reactions Occur
The reactions occur due to the skin’s direct contact with irritants or allergens, leading to two main types of contact dermatitis: irritant and allergic.
- Irritant Contact Dermatitis: This is the most common form and occurs when a substance damages the skin’s outer protective layer. Chemicals in detergents or soaps can strip away oils and moisture from the skin, leading to dryness, cracks, and inflammation.
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis: This form arises from an immune system reaction to a substance. Upon first exposure, the skin may not react, but it becomes sensitized to the allergen. Subsequent exposures lead to an allergic reaction, as the body’s immune system releases chemicals to combat the perceived threat, causing itching, redness, and swelling.
Differences Between Irritant and Allergic Contact Dermatitis
The primary difference between irritant and allergic contact dermatitis lies in the body’s response to the substance.
- Irritant Dermatitis is an immediate reaction that does not involve the immune system. It can occur in anyone upon sufficient exposure to an irritant, and the severity is dose-dependent.
- Allergic Dermatitis involves a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. It only occurs in individuals who are sensitized to specific allergens, and even minimal contact can trigger a significant reaction.
Understanding these differences is crucial for identifying the cause of contact dermatitis and determining the appropriate treatment strategy. Avoiding known irritants and allergens, using protective barriers, and maintaining skin hydration are key preventive measures.
However, contact dermatitis is a condition with diverse causes, including exposure to various irritants and allergens. By recognizing the substances that trigger this condition and understanding the differences between irritant and allergic contact dermatitis, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this uncomfortable skin reaction.
Identifying Contact Dermatitis Triggers
Identifying the triggers of contact dermatitis is a crucial step towards managing and preventing flare-ups of this skin condition. Contact dermatitis, a type of eczema, arises when the skin reacts to substances it comes into contact with, leading to symptoms such as itching, redness, and blisters. Understanding what triggers your contact dermatitis can significantly improve your quality of life by allowing you to avoid these irritants or allergens. Here, we will explore tips for identifying your personal triggers and discuss the role of patch testing in diagnosis.
Tips for Identifying Personal Triggers
- Keep a Symptom Diary: Start by documenting your daily activities, the products you use, and your diet. When symptoms occur, note them down alongside these details. Over time, you may start to see patterns that can help identify potential triggers.
- Review Your Products: Household cleaners, cosmetics, skincare products, and even your laundry detergent can contain irritants or allergens. Check the ingredients for common culprits like fragrances, preservatives, and certain metals.
- Consider Your Environment: Environmental factors such as pollen, pet dander, and certain fabrics (like wool or synthetic fibers) can trigger contact dermatitis. Reflect on whether your flare-ups coincide with specific environmental exposures.
- Food Allergies and Sensitivities: Although less common, certain foods can exacerbate contact dermatitis in some individuals. Pay attention to your diet and consider consulting an allergist if you suspect food-related triggers.
- Professional Patch Testing: If identifying triggers through elimination and observation is challenging, patch testing can be an invaluable diagnostic tool.
Discussion on Patch Testing and Diagnosis
Patch testing is a specialized procedure conducted by dermatologists to diagnose allergic contact dermatitis. During this test, small patches containing potential allergens are applied to the skin, typically on the back, and left in place for 48 hours. After this period, the patches are removed, and the skin is evaluated for reactions. A follow-up examination may occur several days later to check for delayed reactions. This method can precisely identify specific substances causing your skin reactions.
Patch Testing Process:
- Pre-Test Consultation: Your dermatologist will review your medical history and symptom diary to select the appropriate allergens for testing.
- Application: Small patches with different allergens are applied to your back.
- Initial Evaluation: After 48 hours, the patches are removed, and the skin is assessed for reactions.
- Final Evaluation: A subsequent check, typically after another 48 to 72 hours, is performed to identify delayed reactions.
Benefits of Patch Testing:
- Accurate Identification: Helps pinpoint specific allergens causing your symptoms.
- Personalized Avoidance Strategies: Allows for tailored advice on avoiding identified allergens.
- Improved Management: Leads to better control and prevention of contact dermatitis symptoms.
Keeping a detailed symptom diary, being mindful of product ingredients, considering environmental factors, and undergoing patch testing are all valuable strategies in pinpointing your personal triggers. By taking these steps, you can achieve greater comfort and reduce the frequency of contact dermatitis flare-ups.
Prevention Strategies for Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a common skin condition that results from either direct contact with irritants or an allergic reaction to certain substances. The key to managing this condition lies in effective prevention strategies that help avoid common irritants and allergens. In this guide, we’ll explore practical steps you can take to reduce the risk of contact dermatitis, ensuring your skin remains healthy and irritation-free.
How to Avoid Common Irritants and Allergens
- Identify Your Triggers: The first step in preventing contact dermatitis is to identify what triggers your skin reactions. Common irritants include soaps, detergents, solvents, and certain metals like nickel. Allergens might include fragrances, latex, and certain plants like poison ivy. Keeping a diary of your flare-ups can help pinpoint specific substances to avoid.
- Use Gentle Skincare Products: Opt for skincare products that are free from fragrances, dyes, and other potential allergens. Look for labels indicating the product is suitable for sensitive skin or is hypoallergenic.
- Wear Protective Clothing: When dealing with chemicals, cleaning agents, or any known allergens, wear protective clothing such as gloves, long sleeves, and pants. This barrier can significantly reduce your skin’s exposure to irritants.
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping your skin well-moisturized helps maintain its natural barrier function, making it less susceptible to irritants. Choose a moisturizer that is free from fragrances and irritants, and apply it regularly, especially after washing your hands or bathing.
- Practice Safe Hand Hygiene: Frequent hand washing can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation. Use lukewarm water and mild, fragrance-free soap, and always moisturize afterward. Consider using alcohol-based hand sanitizers as a less irritating alternative when soap and water are not available.
- Be Mindful of Jewelry and Clothing: Nickel is a common allergen found in jewelry and the buttons of jeans. Opt for nickel-free or hypoallergenic options. Similarly, choose clothing made from natural fibers, such as cotton, which is less likely to irritate the skin compared to synthetic fibers.
Protective Measures to Reduce Risk of Contact Dermatitis
- Educate Yourself and Others: Awareness of what substances can cause contact dermatitis is crucial. Educate yourself, family members, and coworkers about the importance of avoiding known irritants and allergens, especially if they are common in your living or work environment.
- Use Protective Barriers: For jobs or tasks that involve exposure to irritants, use barrier creams and protective equipment like gloves. Ensure that these barriers are suitable for the type of substances you’re handling.
- Implement Safe Work Practices: Employers should ensure that workplaces are safe from common irritants and allergens by adopting safer work practices. This includes providing appropriate protective gear and training employees on how to avoid skin exposure to harmful substances.
- Regular Skin Checks: Regularly inspect your skin for signs of contact dermatitis, such as redness, itching, or blisters. Early detection can prevent further aggravation and facilitate timely treatment.
- Consult a Dermatologist: If you suspect you have contact dermatitis, or if you’re struggling to identify your triggers, consulting a dermatologist can provide you with personalized advice and treatment options. They can perform patch tests to identify specific allergens you should avoid.
By adopting these prevention strategies, you can significantly reduce your risk of contact dermatitis. Remember, the key to managing this condition is awareness, protection, and early intervention. Keep your skin healthy and protected by being mindful of your environment and the products you use daily.
Treatment Options for Contact Dermatitis
There are several treatment options available that can help manage the symptoms and prevent future outbreaks. Below, we explore over-the-counter remedies, prescription treatments, home remedies, and lifestyle changes that can provide relief.
Over-the-Counter Remedies and When to Use Them
Over-the-counter (OTC) remedies are widely available and can be effective in managing mild to moderate symptoms of contact dermatitis. These include:
- Hydrocortisone Creams: These topical steroids can reduce inflammation and itching. They are suitable for short-term use on small areas of affected skin.
- Oral Antihistamines: Medications such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) can relieve itching and reduce allergic reactions. They’re especially helpful for nighttime use to improve sleep.
- Moisturizers and Emollients: Products that are fragrance-free and designed for sensitive skin can help restore the skin’s barrier and prevent dryness.
It’s important to use these remedies as directed and consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen.
Prescription Treatments and Therapies
In cases where OTC remedies are not sufficient, a healthcare provider may recommend prescription treatments, including:
- Topical Steroids: Stronger than OTC options, prescription steroids can more effectively reduce inflammation and itching.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Medications like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are non-steroidal and can treat inflammation and itching without the side effects of steroids.
- Phototherapy: This involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural sunlight or artificial UV light, beneficial for severe cases.
A dermatologist can provide guidance on the most appropriate prescription treatment based on the severity and extent of your condition.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes for Managing Symptoms
In addition to medical treatments, certain home remedies and lifestyle adjustments can help alleviate symptoms of contact dermatitis:
- Avoid Known Irritants: Identify and steer clear of substances that trigger your symptoms. This may involve changing skincare products, detergents, or fabrics.
- Cool Compresses: Applying a cool, damp cloth to the affected area can reduce itching and inflammation.
- Oatmeal Baths: A colloidal oatmeal bath can soothe the skin and provide relief from itching.
- Wear Protective Clothing: If your job or daily activities expose you to irritants, wearing gloves or protective clothing can prevent skin contact.
By incorporating these treatments and adjustments, individuals with contact dermatitis can significantly improve their quality of life and manage their symptoms effectively. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment to ensure it’s suitable for your specific condition.
Managing Contact Dermatitis in Daily Life
Managing it effectively requires a holistic approach, focusing on daily skin care routines, selecting the right products, and managing stress. Here’s how you can navigate life with contact dermatitis while minimizing flare-ups and maintaining healthy skin.
Daily Skin Care Routines
- Gentle Cleansing: Opt for mild, fragrance-free cleansers. Harsh soaps can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation. Use lukewarm water and gently pat the skin dry with a soft towel.
- Moisturizing: After cleansing, apply a fragrance-free moisturizer to help maintain the skin’s barrier. Look for products with ceramides, glycerin, or hyaluronic acid, which can provide deep hydration without irritating the skin.
- Protective Barriers: When handling detergents or chemicals, wear protective gloves to avoid direct contact with irritants. Similarly, for outdoor activities, use clothing and accessories to protect your skin from environmental factors.
Product Recommendations
- Hypoallergenic Products: These are formulated to minimize the risk of allergic reactions. Hypoallergenic skincare and household cleaning products can be safer alternatives.
- Patch Testing: Before fully integrating a new product into your routine, perform a patch test on a small skin area. This can help identify potential reactions without widespread exposure.
- Ingredients to Avoid: Stay clear of products containing alcohol, fragrances, and certain preservatives, as these can be common irritants. Reading labels and being informed about irritant-free products is crucial.
Stress Management
- Mindfulness and Relaxation: Stress can exacerbate contact dermatitis. Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can reduce stress levels, potentially minimizing flare-ups.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you’re getting enough rest. Sleep plays a vital role in stress reduction and overall skin health.
- Seek Support: Dealing with chronic skin conditions can be stressful. Consider joining support groups or consulting a mental health professional for coping strategies.
However, managing contact dermatitis involves a comprehensive approach that includes meticulous skin care, careful selection of products, and stress management. By integrating these practices into your daily life, you can help control flare-ups and maintain healthier, more comfortable skin. Remember, each individual’s skin can react differently, so it may take some time to find the right routine that works for you. Consulting with a dermatologist can provide tailored advice and treatment options suited to your specific condition.
When to Seek Professional Help
Contact dermatitis can often be managed at home with over-the-counter remedies and lifestyle modifications. However, certain symptoms and situations require professional medical intervention to prevent complications and ensure proper treatment. Understanding when to seek help is crucial for your health and well-being.
Symptoms That Warrant a Visit to a Healthcare Provider
It’s time to consult a healthcare provider if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Severe or Persistent Symptoms: If the rash is severe, covers a large area of your body, or doesn’t improve with home care within a few weeks.
- Signs of Infection: Symptoms such as increased redness, warmth, swelling, pus, or if you develop a fever.
- Impact on Daily Activities: When the rash affects your sleep, work, or daily activities.
- Sensitive Areas: If the rash appears on sensitive areas of your body, such as the face or genitals.
- Difficulty Breathing: Although rare, if you experience difficulty breathing or swelling of the face, lips, or eyes, seek immediate medical attention as it may indicate a severe allergic reaction.
What to Expect During the Consultation
During your consultation, your healthcare provider will:
- Review Your Medical History: Discuss any known allergies, recent exposures to potential irritants, and previous episodes of contact dermatitis.
- Conduct a Physical Examination: Examine the affected areas to assess the severity and pattern of the rash.
- Discuss Management Strategies: Offer advice on avoiding triggers, skin care routines, and prescribe medications if necessary. This may include topical corticosteroids or oral medications for more severe cases.
- Consider Further Testing: In some cases, patch testing might be recommended to identify specific allergens causing your symptoms.
Importance of Following Professional Medical Advice
Following your healthcare provider’s advice is paramount for several reasons:
- Preventing Complications: Proper treatment can prevent infections and other complications.
- Avoiding Worsening Symptoms: Professional guidance helps in avoiding substances that may exacerbate your condition.
- Long-term Management: Learning how to manage your condition can reduce the likelihood of future flare-ups and improve your quality of life.
However, while mild cases of contact dermatitis can often be treated at home, it’s important to recognize when professional help is needed. Early intervention by a healthcare provider can ensure effective treatment, prevent complications, and provide guidance on managing your condition for long-term relief. By understanding the signs that warrant professional consultation and the importance of following medical advice, you can take proactive steps towards managing contact dermatitis effectively.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions) About Contact Dermatitis
What is contact dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis is a type of skin inflammation that occurs when the skin comes into contact with a substance that either irritates it directly or triggers an allergic reaction. This condition can result in redness, itching, and blisters, depending on the severity and type of contact dermatitis.
What causes contact dermatitis?
Several substances can cause contact dermatitis, including soaps, detergents, skin care products, perfumes, jewelry (especially nickel), plants like poison ivy, and certain chemicals used in the workplace. Each person may react differently to these substances.
Are there different types of contact dermatitis?
Yes, there are primarily two types: irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type and occurs when a substance damages your skin’s outer protective layer. Allergic contact dermatitis, however, is an immune system reaction to a substance that your body is sensitive to.
How can I tell if I have contact dermatitis?
Symptoms of contact dermatitis include redness, itching, swelling, flaking, and in severe cases, blisters. If you suspect you have contact dermatitis, it’s important to note when the symptoms appeared and what substances you’ve been in contact with that might have caused the reaction.
How is contact dermatitis diagnosed?
A healthcare provider can often diagnose contact dermatitis by examining your skin and asking about your symptoms and potential exposure to irritants or allergens. Patch testing may be recommended to identify specific allergies.
Can contact dermatitis be treated?
Yes, treatment usually involves avoiding the irritant or allergen that caused the reaction, applying topical steroids to reduce inflammation and itching, and keeping the skin moisturized. In more severe cases, oral medications or phototherapy may be recommended.
How can I prevent contact dermatitis?
Preventing contact dermatitis involves avoiding known irritants and allergens. Wearing protective gloves, using mild soaps and skin care products, and applying moisturizers regularly can help protect your skin. It’s also helpful to be aware of materials and substances that trigger your skin reactions and avoid them.
Is contact dermatitis contagious?
No, contact dermatitis is not contagious. It cannot be spread from person to person. The skin reaction is a personal immune response to an irritant or allergen.
When should I see a doctor for contact dermatitis?
You should see a doctor if your symptoms are severe, if the rash doesn’t improve with home care, or if the rash is widespread. You should also seek medical attention if you experience signs of infection, such as fever, pus, or increased redness and pain in the affected area.
Can contact dermatitis go away on its own?
Yes, contact dermatitis often clears up on its own once the irritant or allergen is identified and avoided. However, treatments can help relieve symptoms and speed up recovery.
Conclusion:
In wrapping up our exploration of contact dermatitis, it’s clear that understanding the symptoms and causes of this condition is more than just a matter of skin deep. Recognizing the redness, itching, and possible blistering as signals from your body can guide you towards identifying the culprits behind these reactions—whether they’re chemical, environmental, or related to personal care products.
We encourage you to not let the discomfort and annoyance of contact dermatitis linger without action. By staying vigilant about your skin’s reactions and being mindful of the substances you come into contact with, you can navigate a path to relief and comfort. Remember, your skin is a reflection of your overall health, and taking care of it is a step towards a happier, healthier you.
Let this guide serve as a starting point in your journey to understand and combat contact dermatitis. With the right knowledge and proactive measures, you can achieve not just temporary relief but long-term skin health and comfort.