Constipation Treatment: Constipation is a common health condition that affects individuals across all ages, impacting quality of life and overall health. Understanding the diagnosis and treatment options is essential for managing this condition effectively.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of constipation, including its causes, diagnosis methods, and a variety of treatment strategies to help alleviate symptoms.
What is Constipation?
Constipation is a common digestive condition marked by infrequent bowel movements or difficulty passing stools. It occurs when the colon absorbs too much water from the waste, making it dry and hard to pass. This can lead to discomfort, bloating, and a sense of incomplete evacuation.
Common Symptoms
The symptoms of constipation include:
- Fewer than three bowel movements per week.
- Straining during bowel movements more than 25% of the time.
- Hard or lumpy stools.
- A sensation of blockage in the rectum preventing bowel movements.
- The need to assist the removal of stool manually.
- Feeling of incomplete evacuation after a bowel movement.
Statistics on Prevalence
Constipation is a widespread issue affecting individuals of all ages, with significant variations in prevalence worldwide. According to research, about 16% of adults globally experience constipation, with rates rising to over 33% in individuals aged 60 and above. This highlights the commonality and relevance of the condition, underscoring the importance of understanding and addressing it.
Short-term vs. Long-term Constipation
Short-term constipation is usually temporary and can be resolved with simple lifestyle changes or over-the-counter remedies. It often results from changes in diet, lack of exercise, or dehydration.
Long-term constipation, also known as chronic constipation, persists for several weeks or longer. It may signify underlying health issues such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), thyroid disorders, or specific medications’ side effects. Chronic constipation requires a comprehensive approach for management, including medical intervention and lifestyle modifications.
However, understanding the nature of your constipation, whether short-term or long-term, is crucial for determining the most effective treatment and management strategies to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
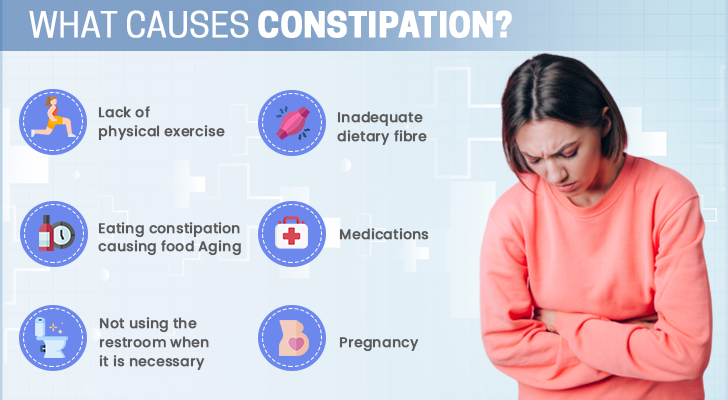
Causes of Constipation
Understanding the causes of constipation can help you take proactive steps to alleviate this uncomfortable condition. Here, we explore the main causes of constipation, focusing on dietary factors, physical inactivity, medications and supplements, medical conditions, and psychological factors.
Dietary Factors
One of the primary causes of constipation is related to diet, particularly fiber intake and hydration. Fiber is an essential component of a healthy diet, aiding in digestion and ensuring smooth bowel movements. A diet low in fiber can lead to harder stools that are difficult to pass. Sources of fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Similarly, hydration plays a crucial role in preventing constipation. Insufficient water intake can result in dry, hard stools. It’s recommended to drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain proper digestion and bowel function.
Physical Inactivity
Lack of physical activity is another significant factor contributing to constipation. Regular exercise helps stimulate intestinal activity, facilitating easier passage of stools. In contrast, sedentary lifestyles can slow down the digestive process, leading to constipation. Incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine, such as walking, yoga, or swimming, can help prevent and relieve constipation.
Medications and Supplements
Certain medications and supplements can also lead to constipation as a side effect. These include, but are not limited to, iron supplements, narcotics, some antidepressants, and anticonvulsants. If you suspect that your medication is causing constipation, consult with your healthcare provider. They may adjust your dosage or recommend an alternative that is less likely to affect your bowel movements.
Medical Conditions
Various medical conditions can cause constipation, including Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), thyroid issues, and diabetes. These conditions can affect the body’s ability to digest food properly and expel waste, leading to constipation. If you have a chronic condition and experience constipation, it’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to manage both your condition and its gastrointestinal symptoms.
Psychological Factors
Lastly, psychological factors such as stress and anxiety can impact bowel movements. When you’re stressed or anxious, your body can respond by slowing down or speeding up the digestive process, which can lead to constipation or diarrhea. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or counseling can help mitigate its impact on your digestive health.
However, constipation can be caused by a variety of factors, including dietary habits, physical inactivity, medications, medical conditions, and psychological stress. By understanding these causes, you can take steps to prevent or alleviate constipation, improving your overall digestive health. If constipation persists or is accompanied by severe pain or other symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice to rule out underlying conditions.
Diagnosing Constipation
It can be uncomfortable and sometimes painful, but it’s usually manageable with the right approach. Understanding when to seek medical advice, who to turn to, and what diagnostic tests might be involved is crucial for effective treatment.
When to See a Doctor
While occasional constipation is normal, it’s important to know when to seek medical help. Consult a doctor if you experience any of the following:
- Persistent constipation lasting more than three weeks
- Severe pain during bowel movements
- Blood in your stool
- Unexplained weight loss
- Constipation that alternates with diarrhea
- Difficulty in passing stools despite the urge
These symptoms could indicate a more serious condition that requires prompt medical attention.
Types of Medical Professionals Who Diagnose and Treat Constipation
Constipation can be evaluated and treated by various healthcare providers, including:
- Primary Care Physicians (PCPs): Your first point of contact, PCPs can assess your symptoms, provide initial treatment options, and refer you to a specialist if necessary.
- Gastroenterologists: Specialists in digestive system disorders, gastroenterologists have advanced training in diagnosing and treating conditions like constipation.
- Pediatricians: For children experiencing constipation, pediatricians are trained to diagnose and treat young patients in a way that’s appropriate for their age and development.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
To diagnose constipation and its underlying causes, healthcare providers may recommend one or more of the following tests:
- Physical Examination: A comprehensive evaluation, including a discussion of your medical history and lifestyle factors that could contribute to constipation.
- Blood Tests: To check for a systemic condition such as hypothyroidism.
- Colonoscopy: Allows doctors to examine the colon for blockages, abnormalities, or signs of cancer.
- Anorectal Manometry: Measures the muscle strength of the rectum and anus, and the coordination of bowel movements.
- Transit Study: Involves swallowing a capsule containing markers that show up on X-rays taken over several days, indicating how well food moves through the colon.
- Defecography: An X-ray of the area around the anus and rectum that shows how well you can hold and release stool.
Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing constipation effectively and preventing complications. If you’re experiencing signs of constipation that concern you, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider for a proper evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes for Constipation
Constipation can be an uncomfortable condition, but with some simple home remedies and lifestyle adjustments, you can help ease the symptoms and encourage regular bowel movements.
Dietary Adjustments: Increase Fiber and Fluids
One of the first steps to combat constipation is to look at your diet. Increasing your intake of fiber can significantly help. Fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, add bulk to your stool and make it easier to pass. Aim for at least 25 to 30 grams of fiber per day.
In addition to fiber, increasing your fluid intake is crucial. Drinking plenty of water and other hydrating fluids, like herbal teas, can help soften your stool. Try to drink at least eight glasses of water a day, more if you’re active or live in a hot climate.
Physical Activity Recommendations
Regular physical activity is another key factor in alleviating constipation. Exercise helps by decreasing the time it takes food to move through the large intestine, thus limiting the amount of water absorbed from the stool into your body. Simple activities, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, for 30 minutes a day, can significantly improve symptoms.
Over-the-Counter Treatments
For those who need a little extra help, over-the-counter treatments like bulk-forming agents and stool softeners can be beneficial. Bulk-forming agents, such as psyllium, methylcellulose, and polycarbophil, help by adding bulk and moisture to the stool, making it easier to pass. Stool softeners, like docusate, work by moistening the stool and making it softer. While these treatments can be effective, it’s important to use them as directed and to consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Importance of Routine and Stress Management
Establishing a regular bowel movement routine can also aid in preventing constipation. Try to go at the same time each day, giving yourself enough time to use the bathroom without rushing. Managing stress is another crucial aspect. High stress levels can lead to changes in your digestive system, so incorporating stress-reduction techniques like deep breathing, yoga, or meditation can be beneficial.
However, making dietary adjustments to increase your intake of fiber and fluids, staying physically active, considering over-the-counter treatments when necessary, and managing your routine and stress levels can all play a significant role in alleviating constipation. Remember, if constipation persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional.
Medical Treatments for Constipation
We’ll explore the options for prescription medications, the potential side effects and considerations, and the role of probiotics and dietary supplements in managing constipation.
Prescription Medications
Prescription medications play a pivotal role in the treatment of constipation, especially for cases that do not respond to lifestyle changes or over-the-counter solutions. These medications can be classified into several categories:
- Laxatives: These are among the most commonly prescribed solutions for constipation. They work in various ways, such as softening the stool, stimulating bowel movements, or increasing stool bulk. Examples include bulk-forming agents, stimulant laxatives, and osmotic laxatives.
- Stool Softeners: These medications, such as docusate, make the stool softer and easier to pass by increasing the amount of water absorbed by the stool.
- Motility Agents: For individuals with constipation due to slow transit through the colon, motility agents can be prescribed. These medications help increase the movement of the intestines to facilitate easier bowel movements.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
While prescription medications are effective in managing constipation, they come with potential side effects and considerations. Common side effects include bloating, gas, and, ironically, diarrhea. Long-term use of certain laxatives can lead to dependency, making it difficult for the bowel to function normally without medication. It’s crucial to use these medications under the guidance of a healthcare provider to minimize risks and ensure they are used effectively and safely.
Role of Probiotics and Dietary Supplements
In addition to prescription medications, probiotics and dietary supplements have gained attention for their role in improving gut health and alleviating constipation.
- Probiotics: These are live bacteria and yeasts that are beneficial for digestive health. Probiotics can help balance the gut microbiota, which can improve bowel movement regularity. Common sources include yogurt, fermented foods, and supplements.
- Dietary Supplements: Fiber supplements, such as psyllium, methylcellulose, and polycarbophil, can also help manage constipation. They increase the bulk of the stool and encourage passage through the digestive system. It’s important to increase water intake when using fiber supplements to prevent worsening constipation.
When considering the use of probiotics and dietary supplements, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider. They can offer guidance on the appropriate type and dosage, ensuring these supplements are integrated safely into your treatment plan.
However, the medical treatment of constipation involves a comprehensive approach, including prescription medications, with consideration for potential side effects, and the supportive role of probiotics and dietary supplements. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most effective and safe treatment plan for your specific needs.
Advanced Treatment Options for Constipation
We will explore the advanced treatment options for constipation, focusing on biofeedback therapy, surgical interventions for chronic cases, and emerging treatments and research that promise new hope for sufferers.
Biofeedback Therapy
Biofeedback therapy is a non-invasive treatment option that teaches patients how to control physiological functions that are usually involuntary. For constipation, biofeedback therapy is particularly useful for those with anorectal disorders, such as dyssynergic defecation, where the muscles of the pelvic floor do not work well together. During biofeedback sessions, sensors are attached to the body to measure muscle activity, and these measurements are displayed on a screen for both the patient and therapist to see. This real-time feedback helps patients learn how to contract and relax their pelvic floor muscles correctly, improving bowel movement frequency and consistency. Studies have shown that biofeedback therapy can be highly effective, especially for individuals who have not responded to conventional treatments.
Surgical Interventions (for Chronic Cases)
Surgery may be considered for chronic constipation cases that do not respond to other treatments. Surgical options vary based on the underlying cause of constipation but may include procedures to remove a section of the colon that is not working properly. One common surgical intervention is subtotal colectomy with ileorectal anastomosis, which involves removing the affected portion of the colon and connecting the remaining parts to improve bowel movement regularity. While surgery can offer significant relief, it is typically considered a last resort due to the risks and potential complications associated with invasive procedures. Patients considering surgery should discuss the benefits and risks with their healthcare provider to make an informed decision.
Emerging Treatments and Research
The field of gastroenterology is continuously evolving, with new treatments and research offering hope to those with constipation. Emerging therapies such as intestinal pacemakers, which use electrical stimulation to promote bowel activity, are currently under investigation. Additionally, advancements in pharmaceuticals, including new classes of laxatives and motility agents, aim to provide more effective and targeted relief for various types of constipation. Genetic research is also underway to better understand the underlying causes of constipation, which may lead to personalized treatment approaches in the future.
However, while constipation can be a challenging condition to manage, there are several advanced treatment options available for those who do not find relief from standard therapies. From biofeedback therapy and surgical interventions to cutting-edge research and emerging treatments, patients have reasons to be optimistic about managing their symptoms more effectively. As always, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual needs and circumstances.
Prevention of Constipation
Here, we’ll delve into some effective strategies to help you maintain regular bowel movements, emphasize the importance of consistent medical check-ups, and discuss when it might be necessary to adjust your treatment plans.
Lifestyle and Dietary Tips to Prevent Constipation
To keep your digestive system functioning smoothly, consider the following tips:
- Increase Fiber Intake: Incorporating more fiber into your diet is one of the most effective ways to prevent constipation. Foods rich in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can help increase stool bulk and promote movement through the digestive system.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, helps soften the stool, making it easier to pass. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water a day, and consider adding in fluids like herbal teas and fruit-infused water for variety.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can stimulate the muscles in the intestines, aiding in bowel movements. Even a daily 30-minute walk can make a significant difference.
- Mind Your Meals: Eating regular, balanced meals helps maintain a consistent bowel routine. Avoid skipping meals, and try to eat at the same times each day to help regulate your digestive system.
- Limit Low-Fiber Foods: While increasing high-fiber foods, it’s also important to reduce intake of low-fiber foods such as meat, dairy products, and processed foods, which can contribute to constipation.
Importance of Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can play a crucial role in preventing constipation, especially if you have a history of digestive issues or are taking medications that might affect bowel movements. During these visits, your doctor can:
- Review Your Medications: Some medications can contribute to constipation. Your doctor can suggest alternatives or adjustments to your current medication regimen.
- Identify Underlying Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or diabetes, can cause constipation. Early detection and treatment can help manage these conditions and prevent related constipation.
- Provide Personalized Advice: Based on your health history and lifestyle, your doctor can offer tailored recommendations to prevent constipation.
When to Adjust Treatment Plans
It’s essential to recognize when your prevention strategies might need a reevaluation. Consider adjusting your treatment plan if:
- You Experience Persistent Symptoms: If constipation becomes a regular issue despite following preventative measures, it may be time to consult your doctor for a more targeted approach.
- You Notice Changes in Bowel Habits: Any significant changes in your bowel habits, such as consistently hard stools, difficulty passing stools, or needing to strain, should prompt a visit to your healthcare provider.
- Your Current Plan Causes Discomfort: If your dietary changes or medications are causing side effects or discomfort, don’t hesitate to discuss alternative options with your doctor.
By adopting a proactive approach to your diet and lifestyle, staying vigilant about your health, and maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider, you can significantly reduce your risk of constipation. Regular adjustments to your plan, based on your body’s responses, will help you maintain digestive health and overall well-being.
FAQ Section: Common Questions About Constipation
What is constipation?
Constipation is a condition characterized by infrequent bowel movements, typically less than three times a week, or difficulty passing stool. It occurs when the colon absorbs too much water from the waste, making the stool hard and difficult to pass through the digestive tract.
What causes constipation?
Constipation can be caused by a variety of factors, including a low-fiber diet, inadequate water intake, lack of physical activity, certain medications, and ignoring the urge to have a bowel movement. Stress, changes in routine, and underlying health conditions can also contribute to constipation.
How can I relieve constipation?
To relieve constipation, consider increasing your fiber intake through fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Drinking plenty of water and other fluids can also help soften the stool. Regular physical activity encourages bowel movements. If necessary, over-the-counter laxatives may be used, but it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication.
Are there any home remedies for constipation?
Yes, there are several home remedies that can offer relief from constipation:
- Warm Liquids: Starting your day with warm water or herbal tea can stimulate digestion.
- Fiber-rich Foods: Incorporating more fiber into your diet helps bulk up your stool, making it easier to pass.
- Prunes and Prune Juice: These are natural laxatives due to their high sorbitol content.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps increase muscle activity in your intestines.
When should I see a doctor for constipation?
While occasional constipation is common, you should see a doctor if you experience persistent constipation that lasts for several weeks, severe pain with bowel movements, blood in your stool, or unexplained weight loss. These symptoms could indicate a more serious underlying condition.
Can constipation be prevented?
Yes, constipation can often be prevented by:
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids
- Exercising regularly
- Listening to your body and going to the bathroom when you feel the urge
Is constipation more common in certain age groups?
Yes, constipation can affect individuals of all ages but is more common in older adults. This is due to factors like a slower metabolism, decreased physical activity, and the use of certain medications that may affect bowel movements.
Conclusion
In summarizing the critical nature of recognizing and addressing constipation promptly and effectively, it’s paramount to underline the far-reaching benefits of proper management. Constipation, albeit common, should not be overlooked or underestimated due to its potential impact on overall health and well-being. Addressing this condition proactively can significantly enhance one’s quality of life, prevent complications, and contribute to maintaining a healthy digestive system.
We strongly encourage individuals experiencing persistent or severe symptoms of constipation to seek professional medical advice. Consulting a healthcare provider can ensure a tailored approach to treatment, considering the unique needs and circumstances of each individual. Professional guidance is invaluable in navigating the myriad of available treatments and interventions, ensuring both safety and effectiveness.
In closing, it is essential to recognize the importance of addressing constipation as part of a broader commitment to one’s health. By taking proactive steps towards diagnosis and treatment, individuals can safeguard their digestive health, which is a cornerstone of overall physical and mental well-being. Let this be a reminder that health, in its entirety, demands attention to even the most seemingly minor issues, as they play a crucial role in the larger picture of our health journey.