Constipation Symptoms: Constipation is a common gastrointestinal issue affecting individuals globally, characterized by infrequent bowel movements or difficulty passing stools.
Understanding its symptoms and causes is crucial for effective management and prevention.
What is Constipation?
Constipation is a common digestive issue that affects individuals of all ages. It is characterized by infrequent bowel movements, difficulty passing stools, or the sensation of incomplete evacuation. To understand constipation, it’s essential to first grasp what constitutes normal bowel movements.
Normal Bowel Movements
Normal bowel movements vary widely among individuals. Some may have bowel movements several times a day, while others might only have them a few times a week. What’s considered normal is dependent on each person’s diet, lifestyle, and bodily functions. Generally, a normal bowel movement should be pain-free and require minimal strain. The stools themselves should be soft and easy to pass.
Constipation Compared
In contrast, constipation deviates from one’s regular pattern, leading to less frequent bowel movements. Typically, having fewer than three bowel movements per week indicates constipation. The condition often involves hard, dry stools that are difficult to pass. This difficulty can lead to straining during bowel movements, discomfort, and the feeling that not all stool has been passed.
Several factors contribute to constipation, including inadequate fiber intake, insufficient hydration, lack of physical activity, certain medications, and underlying health conditions. Understanding these factors is crucial in managing and preventing constipation.
By recognizing the differences between normal bowel movements and constipation, individuals can better identify when they might need to adjust their diet, lifestyle, or seek medical advice to maintain digestive health.
Identifying Constipation Symptoms
It can be uncomfortable, and sometimes painful, but recognizing its symptoms early can help manage the condition effectively. This guide provides a detailed list of constipation symptoms and advises when it’s essential to see a doctor.
Detailed List of Constipation Symptoms
- Infrequent Bowel Movements: Less than three bowel movements per week is a clear sign of constipation.
- Hard, Dry, or Lumpy Stools: Stools that are difficult to pass and look dry or lumpy indicate constipation.
- Straining to Have Bowel Movements: If you need to strain or exert a lot of effort to have a bowel movement, it’s a symptom of constipation.
- Feeling of Incomplete Evacuation: The sensation that you haven’t emptied your bowel fully after a toilet visit.
- Discomfort in the Abdomen: This can include bloating, pain, or cramps in the abdominal area.
- Reduced Appetite: Experiencing a decrease in appetite could be related to the discomfort or bloating caused by constipation.
- Feeling Lethargic: Constipation can make you feel tired or lethargic due to the body’s overall discomfort.
When to See a Doctor: Recognizing Severe Symptoms
While constipation is often manageable with diet and lifestyle adjustments, certain symptoms indicate a need for medical consultation. Seek a doctor’s advice if you experience:
- Persistent Pain or Severe Abdominal Cramps: Pain that doesn’t subside with a bowel movement or continues for several days.
- Blood in Stool: Noticing red blood on the toilet paper or in the stool itself is a sign to consult a doctor.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying, especially if you’re also experiencing constipation, could indicate a more serious condition.
- Constipation that Lasts More than Two Weeks: If dietary and lifestyle changes don’t relieve your symptoms after two weeks, it’s time to see a doctor.
- Difficulty Passing Gas: Alongside constipation, if you’re unable to pass gas, this could signal an obstruction.
Listening to your body and responding to its signals can help maintain digestive health and overall well-being. If you’re experiencing any severe symptoms or if your constipation persists, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider.
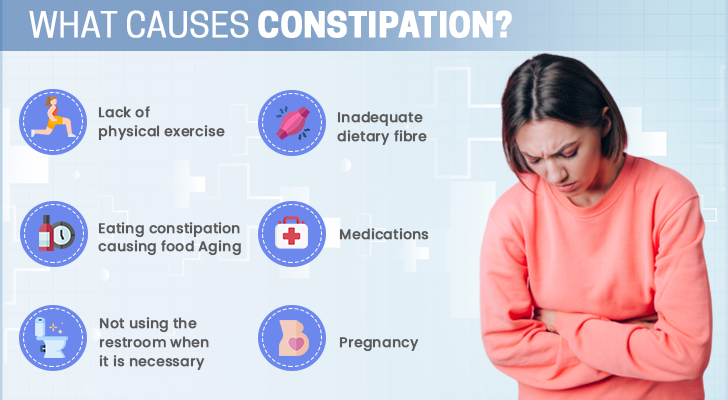
Common Causes of Constipation
Understanding the common causes of constipation is essential for effectively managing and preventing it. This article delves into the key factors contributing to constipation, ranging from dietary habits to psychological factors.
Dietary Factors
One of the most significant contributors to constipation is diet, particularly a diet low in fiber. Fiber is crucial for bowel health, aiding in the formation of bulkier and softer stools that are easier to pass. Foods rich in fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. An inadequate intake of these foods can lead to harder stools and reduced bowel movement frequency.
Equally important is water intake. Dehydration can make stools hard and difficult to pass, as the body absorbs more water from waste, which is why it’s essential to drink enough fluids throughout the day. The recommended daily water intake varies depending on age, sex, and activity level, but a general guideline is to aim for 8-10 glasses a day.
Physical Inactivity
A sedentary lifestyle is another key factor that can lead to constipation. Regular physical activity helps stimulate intestinal movements, making it easier for stools to move through the colon. Lack of exercise can slow down this process, leading to constipation. Incorporating moderate exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, into your daily routine can help maintain regular bowel movements.
Medications
Certain medications can also cause constipation as a side effect. These include, but are not limited to, opioids (used for pain relief), antacids containing aluminum or calcium, antispasmodic drugs, antidepressants, iron supplements, and some blood pressure medications. If you suspect that your medication is causing constipation, consult with your healthcare provider for possible alternatives or solutions.
Medical Conditions
Several medical conditions can predispose individuals to constipation. These include neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis, endocrine disorders like hypothyroidism, and gastrointestinal conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and intestinal obstructions. In such cases, managing the underlying condition is crucial for alleviating constipation.
Psychological Factors
Stress and anxiety can significantly impact digestive health, leading to symptoms like constipation. During periods of high stress, the body’s natural digestive processes can slow down, resulting in delayed bowel movements. Managing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, and counseling can help improve overall digestive health and alleviate constipation.
However, constipation can result from a variety of factors, including dietary habits, physical inactivity, certain medications, medical conditions, and psychological stress. Understanding these causes is the first step toward effective management and prevention. Incorporating a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, maintaining regular physical activity, managing stress, and consulting with healthcare providers about medication side effects and underlying medical conditions can all contribute to alleviating constipation and improving digestive health.
Risk Factors for Constipation
Understanding the risk factors associated with constipation is essential for prevention and effective management. This article explores age-related risks, lifestyle choices, and the role of hydration in preventing constipation, providing insights into how individuals can mitigate these risks.
Age-related Risks
Age plays a significant role in the likelihood of experiencing constipation. As people age, the digestive system naturally slows down, which can lead to increased instances of constipation. Older adults are particularly at risk due to several factors, including reduced physical activity, decreased muscle strength in the digestive tract, and the use of medications that may exacerbate constipation. It’s crucial for seniors to monitor their digestive health closely and seek appropriate interventions to manage constipation effectively.
Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices significantly influence the risk of developing constipation. A diet low in fiber is a primary culprit, as fiber helps to bulk up stools and promotes regular bowel movements. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes into one’s diet can significantly reduce the risk of constipation.
Physical activity is another critical factor; regular exercise helps stimulate the digestive system and can prevent constipation. Sedentary behavior, in contrast, can increase the likelihood of experiencing this uncomfortable condition. Making conscious lifestyle modifications, such as improving diet and increasing physical activity, can be highly effective in preventing constipation.
The Role of Hydration in Preventing Constipation
Hydration plays a pivotal role in preventing constipation. Adequate fluid intake helps to soften stools, making them easier to pass. Water is particularly beneficial, but other fluids like herbal teas can also contribute to maintaining hydration levels. Individuals who consume a high-fiber diet should pay extra attention to their hydration levels, as fiber absorbs water during digestion. Failing to drink enough fluids can lead to hard stools and constipation, undermining the benefits of a fiber-rich diet.
However, understanding and addressing the risk factors for constipation—such as age-related changes, lifestyle choices, and hydration levels—can significantly reduce the likelihood of experiencing this common digestive issue. By making informed decisions about diet, exercise, and fluid intake, individuals can maintain a healthy digestive system and improve their overall quality of life.
Complications Associated with Constipation
While occasional constipation might not be a cause for concern, chronic constipation can lead to several health complications. Understanding these potential issues and recognizing the importance of early intervention can significantly improve one’s quality of life.
Health Issues Caused by Chronic Constipation
- Hemorrhoids: Prolonged straining during bowel movements can lead to swollen blood vessels in the rectum and anus, known as hemorrhoids. These can be extremely painful and may cause bleeding.
- Anal Fissures: Chronic constipation can also lead to the development of small tears in the skin around the anus, known as anal fissures. These fissures can be painful and may bleed during bowel movements.
- Fecal Impaction: When hard stool packs the intestine and rectum so tightly that the normal pushing action of the colon is not enough to expel the stool, it leads to fecal impaction. This condition may require intervention from a healthcare professional.
- Rectal Prolapse: Straining to have a bowel movement may cause a small amount of the rectum to stretch and protrude from the anus, a condition known as rectal prolapse, which can be uncomfortable and may require surgical treatment.
- Increased Risks of Colon Cancer: Although the link is not fully understood, some studies suggest that chronic constipation may increase the risk of colon cancer.
The Importance of Addressing Symptoms Early
Early intervention in the case of constipation is crucial. Addressing constipation promptly can prevent the development of the more severe complications listed above. Simple lifestyle changes, such as increasing fiber intake, drinking more water, and engaging in regular physical activity, can often alleviate constipation. Over-the-counter remedies may also be effective. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider if constipation persists, as it may indicate a more serious underlying condition.
Moreover, recognizing and treating constipation early can improve overall digestive health and well-being. It can prevent the progression to more serious conditions and enhance the quality of life. Individuals should not hesitate to seek medical advice when experiencing persistent or severe symptoms related to constipation.
However, while constipation is a common issue, chronic constipation can lead to significant health complications. Understanding these potential complications and the importance of early intervention can help prevent long-term health issues. Adopting healthy lifestyle habits and seeking medical advice when necessary are key steps in managing constipation effectively.
Preventing Constipation
Below, we explore dietary recommendations, the importance of regular exercise, and proper hydration to help keep constipation at bay.
Dietary Recommendations: Embrace High-Fiber Foods
A diet rich in high-fiber foods is crucial for preventing constipation. Fiber helps by adding bulk to your stool and promoting regular bowel movements. Adults should aim to consume between 25 to 30 grams of fiber daily from a variety of sources. High-fiber foods include:
- Fruits: such as apples, pears, and berries.
- Vegetables: including broccoli, carrots, and leafy greens.
- Whole Grains: options like oatmeal, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread.
- Legumes: beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of fiber.
Incorporating these foods into your diet not only aids digestion but also contributes to overall health and well-being.
The Importance of Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity is another key component in preventing constipation. Exercise helps by increasing blood flow to the digestive system and stimulating intestinal muscles, thereby facilitating easier and more frequent bowel movements. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities can include walking, cycling, swimming, or any other form of exercise that you enjoy and can maintain regularly.
Hydration: How Much Water Should You Drink?
Staying well-hydrated is essential for softening stool and preventing constipation. Water helps to dissolve fiber and enables it to move smoothly through your digestive system. The amount of water each person needs can vary based on factors such as climate, physical activity levels, and overall health. However, a general guideline is to drink at least 8 glasses (about 2 liters or half a gallon) of water per day. Remember, if you’re increasing your fiber intake, you should also increase your water intake to help manage fiber’s bulking action.
In addition to water, other fluids like herbal teas can contribute to your daily hydration needs. However, it’s best to limit beverages that can lead to dehydration, such as those high in caffeine or alcohol.
Meanwhile, these lifestyle adjustments not only aid in digestion but also contribute to your overall health and well-being. Start incorporating these tips into your daily routine for a happier, healthier digestive system.
When to Seek Medical Help for Constipation
Understanding when to seek medical help for constipation is crucial for your health and well-being. This guide will help you identify the symptoms that warrant a doctor’s attention and outline what to expect during the doctor’s visit.
Symptoms That Require a Doctor’s Attention
Constipation might seem like a straightforward condition, but certain symptoms accompanying it can signal more serious health issues. Here are the key signs that you should consult a healthcare professional:
- Persistent Constipation: If you’ve experienced constipation for three weeks or more, despite making dietary and lifestyle adjustments, it’s time to see a doctor.
- Blood in Stool: The presence of blood in your stool, whether bright red or dark, is a red flag that needs immediate medical evaluation.
- Severe Pain: Experiencing severe pain during bowel movements or abdominal pain that doesn’t go away could indicate complications such as blockages or other underlying conditions.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss combined with constipation is a symptom you should never ignore, as it could suggest more serious health issues.
- Changes in Bowel Movements: Sudden changes in the frequency, consistency, or ease of bowel movements can be a sign of underlying health problems.
- Additional Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, and a noticeable decrease in appetite alongside constipation are symptoms that require a doctor’s attention.
What to Expect During the Doctor’s Visit
Understanding what to expect during your visit can help alleviate any anxiety and prepare you for a productive consultation. Here’s a general overview:
- Medical History Review: Be prepared to discuss your medical history, including any previous instances of constipation, your diet, exercise habits, and any medications you’re taking.
- Physical Examination: Your doctor may perform a physical examination, including an abdominal exam, to check for any tenderness or blockages. In some cases, a rectal examination may also be conducted to evaluate the muscle tone and detect any abnormalities.
- Diagnostic Tests: Depending on the initial findings, your doctor might order additional tests such as blood tests, a colonoscopy, or an X-ray of the colon, to identify the cause of constipation.
- Treatment Plan: After diagnosing the cause, your doctor will suggest a treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. This may include dietary recommendations, lifestyle changes, over-the-counter or prescription medications, and, in rare cases, surgical intervention.
By paying attention to the symptoms that require a doctor’s attention and knowing what to expect during the visit, you can take proactive steps toward your health and well-being. Always remember, early intervention can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes.
FAQs About Constipation
What is constipation?
Constipation is a condition where an individual has difficulty emptying their bowels, typically associated with hard or infrequent stools. It occurs when bowel movements become less frequent and stools become difficult to pass.
What causes constipation?
Several factors can lead to constipation, including a low-fiber diet, inadequate water intake, lack of physical activity, certain medications, and ignoring the urge to have a bowel movement. Stress and changes in routine can also contribute to constipation.
How can I prevent constipation?
Preventing constipation involves lifestyle and diet changes. Increase your fiber intake by eating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Drink plenty of water, engage in regular physical activity, and don’t ignore the urge to go to the bathroom. These steps can help maintain regular bowel movements.
How often should I have a bowel movement?
Bowel movement frequency varies greatly among individuals. While some may have bowel movements several times a day, others might only have them a few times a week. Generally, less than three bowel movements per week may indicate constipation.
When should I see a doctor for constipation?
You should consult a doctor if constipation lasts longer than three weeks, is accompanied by blood in your stools, severe pain, or unexpected weight loss. Also, seek medical advice if constipation starts suddenly and is significantly disrupting your life.
Are there any effective home remedies for constipation?
Yes, many find relief through home remedies. Increasing fiber intake, drinking more water, and exercising regularly can be effective. Warm liquids in the morning, such as herbal tea or warm water with lemon, can also stimulate bowel movements.
Can children get constipated?
Yes, children can also experience constipation. It’s often related to diet, insufficient fluid intake, toilet training issues, or reluctance to use the bathroom at school. Encouraging a balanced diet and regular bathroom breaks can help manage constipation in children.
Is it safe to use laxatives for constipation?
While laxatives can provide relief, they should not be used as a long-term solution without consulting a healthcare provider. Overuse of laxatives can lead to dependency and affect bowel function. If you’re considering laxatives, it’s best to discuss this with your doctor to choose the right type for your situation.
Conclusion
Adopting a healthier lifestyle is a proactive step towards preventing constipation. Incorporating a diet rich in fiber, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular physical activity can greatly improve bowel function. It’s also important to listen to your body and not ignore the urge to go, as doing so can exacerbate symptoms.
Remember, making small, consistent changes to your daily habits can have a profound impact on preventing constipation and improving your overall well-being. If you’re experiencing persistent issues, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for tailored advice and treatment options.
By prioritizing your digestive health, you’re not just addressing constipation but also contributing to a healthier, more vibrant life. Let’s embrace these changes with optimism and commitment to our health.
With the right knowledge and lifestyle adjustments, we can all take meaningful steps towards preventing and managing constipation, ensuring a smoother path to digestive health and overall wellness.