Chlamydia Trachomatis Treatment: Chlamydia trachomatis, a bacterial infection often silent in its early stages, is a prevalent sexually transmitted infection (STI) that, if untreated, can lead to significant health issues.
Understanding the nuances of its diagnosis and treatment is crucial for healthcare providers and patients alike.
This article delves into the sophisticated methodologies for identifying Chlamydia trachomatis and the contemporary treatment strategies that promise the best outcomes.
What is Chlamydia Trachomatis?
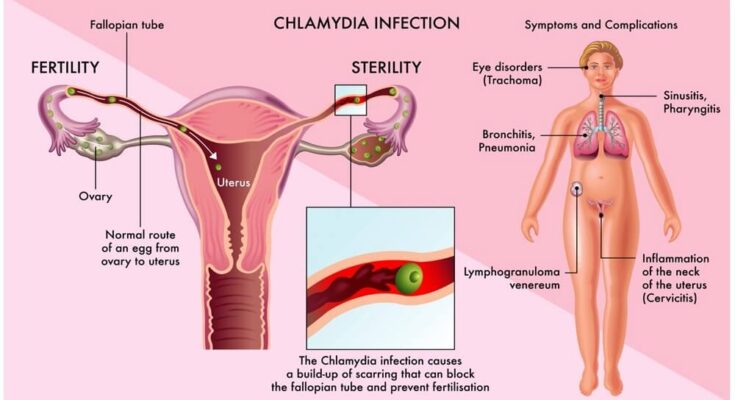
Chlamydia Trachomatis, commonly referred to as Chlamydia, is a type of bacteria that causes one of the most prevalent sexually transmitted infections (STIs) worldwide. It’s known for its stealthy nature, as many individuals who carry the infection may not experience any symptoms at all, making it a silent but significant threat to reproductive health. Understanding Chlamydia Trachomatis is crucial for preventing its spread and mitigating its impact on individuals’ well-being.
Causes and How It Spreads
Chlamydia Trachomatis is primarily spread through sexual contact. This includes vaginal, anal, and oral sex with an infected partner. The bacteria can infect the genital tract, mouth, and rectum of both men and women. It’s important to note that Chlamydia can also be transmitted from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth, leading to complications such as pneumonia or conjunctivitis in the newborn.
Key factors that increase the risk of contracting Chlamydia include having multiple sexual partners, having unprotected sex, having a history of STIs, and being sexually active at a young age. Regular screening and the use of condoms are effective ways to prevent the spread of Chlamydia.
Statistics on Prevalence and Demographics Most Affected
Chlamydia is a global health issue, with millions of new cases reported each year. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), it is the most reported bacterial STI in the United States, with young women between the ages of 15 and 24 being the most affected demographic. This age group is particularly vulnerable due to biological factors that increase their risk and the likelihood of having multiple sexual partners.
The prevalence of Chlamydia underscores the need for targeted public health interventions and education to reduce its spread and protect the health of young individuals.
Symptoms of Chlamydia Trachomatis in Both Men and Women
For those who do experience symptoms, they can differ between men and women but often include:
For Women:
- Abnormal Vaginal Discharge: An increase in quantity or changes in the character of vaginal discharge may be an early sign.
- Pain During Intercourse: Experiencing discomfort or pain during sexual activity is a common symptom.
- Bleeding Between Periods: Spotting or bleeding outside of regular menstrual cycles can indicate an infection.
- Burning Sensation While Urinating: This symptom is not exclusive to chlamydia but is frequently associated with it.
For Men:
- Discharge from the Penis: A clear or cloudy discharge from the tip of the penis is a notable symptom.
- Burning Sensation When Urinating: Similar to women, men may experience pain or a burning feeling during urination.
- Testicular Pain: Swelling and pain in one or both testicles can occur, although it is less common.
It’s essential for sexually active individuals to undergo regular screenings for Chlamydia, especially since the infection can be asymptomatic and go undetected. Early detection and treatment with antibiotics are effective in managing Chlamydia Trachomatis and preventing long-term health issues.
Diagnosis of Chlamydia Trachomatis
Early detection and testing are crucial for effective treatment and preventing long-term complications. Understanding the different types of tests and knowing who should get tested and when can help you take proactive steps toward maintaining your sexual health.
Importance of Early Detection and Testing
Early detection of Chlamydia Trachomatis is key to preventing the spread of the infection and avoiding severe health issues such as infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and an increased risk of contracting other STIs, including HIV. Testing for Chlamydia is straightforward and accessible, making it an essential step for sexually active individuals to include in their routine health check-ups.
Different Types of Tests Used for Diagnosing Chlamydia Trachomatis
Several diagnostic tests are available to detect Chlamydia Trachomatis. Choosing the right test depends on various factors, including accessibility, cost, and personal preference.
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs): NAATs are the most sensitive tests for detecting Chlamydia bacteria. They can be performed on urine samples or swabs taken from the genital area, throat, or rectum. NAATs are highly accurate and are the preferred method for Chlamydia testing.
- Urine Tests: Urine tests are non-invasive and involve collecting a urine sample to test for the presence of Chlamydia DNA. While convenient, urine tests may not be as sensitive as swab tests in certain cases.
- Swab Tests: Swab tests involve taking a sample from the cervix, urethra, throat, or rectum. These tests are particularly useful for detecting the infection in specific sites and can be slightly more accurate than urine tests for certain populations.
Guidelines for Who Should Get Tested and When
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that all sexually active women under the age of 25, as well as older women with risk factors such as new or multiple sex partners, should be tested for Chlamydia annually. Sexually active men who have sex with men (MSM) should also get tested regularly. It’s important for anyone who has unprotected sex or shares injection drug equipment to consider testing, regardless of age or gender.
How to Prepare for a Chlamydia Test and What to Expect
Preparing for a Chlamydia test is simple:
- For urine tests: Avoid urinating for at least one hour before the test to ensure an adequate urine sample.
- For swab tests: There’s no special preparation required, but it’s important to follow any specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
During the test, you may be asked to provide a urine sample or undergo a swab procedure. The process is quick and usually painless. Results can take anywhere from a few days to a week, depending on the lab and the type of test used.
Getting tested for Chlamydia Trachomatis is a crucial component of sexual health. With various testing options available, it’s easier than ever to take charge of your health and prevent the spread of this common STI. If you’re sexually active, talk to your healthcare provider about the best testing schedule for you, and remember, early detection is the key to effective treatment and prevention of long-term health issues.
Chlamydia Trachomatis Treatment
The cornerstone of Chlamydia trachomatis treatment is antibiotics, which are highly effective in eradicating the infection. The most commonly recommended antibiotics include:
- Azithromycin: Typically administered as a single dose.
- Doxycycline: Taken twice daily for a duration of 7 days.
These antibiotics have been proven to be effective in treating Chlamydia trachomatis, with a high success rate when the treatment regimen is followed correctly.
Treatment Duration and Dosage
The duration and dosage of treatment for Chlamydia trachomatis vary depending on the specific antibiotic prescribed. Azithromycin is often favored for its one-time dose, making it easier for patients to complete the treatment. Doxycycline requires a longer commitment, with a twice-daily dosing schedule over a week. Adhering to the prescribed duration and dosage is critical for ensuring the effectiveness of the treatment and reducing the risk of developing antibiotic resistance.
Importance of Completing the Full Course of Treatment
Completing the full course of antibiotic treatment is essential, even if symptoms disappear before the medication is finished. Stopping treatment early can result in the infection not being fully eradicated, leading to a resurgence of symptoms and the potential for spreading the infection to others.
Treatment for Pregnant Women and Potential Complications
Pregnant women diagnosed with Chlamydia trachomatis require special consideration due to the potential risks to the unborn child. Azithromycin is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy. It’s vital for pregnant women to receive treatment promptly to avoid complications such as premature birth and pneumonia in newborns. A healthcare provider will recommend the best treatment plan, taking into account the health of both the mother and the baby.
Addressing the Treatment of Sexual Partners to Prevent Reinfection
Treating Chlamydia trachomatis is not solely an individual concern; it extends to sexual partners as well. To prevent reinfection, it’s crucial for all recent sexual partners of the infected individual to be tested and treated if necessary. This approach helps to break the chain of transmission and reduces the overall prevalence of the infection.
Follow-up Testing and Care After Treatment
Follow-up testing, typically three months after completing treatment, is recommended to ensure the infection has been fully cleared. This step is crucial as it confirms the effectiveness of the treatment and assesses the need for additional care. Regular follow-up also provides an opportunity to discuss preventive measures and address any concerns regarding sexual health.
However, treating Chlamydia trachomatis effectively involves a combination of the right antibiotics, adherence to the treatment regimen, and comprehensive care that includes treating sexual partners and follow-up testing. By understanding and implementing these guidelines, individuals can achieve a full recovery and minimize the risk of health complications associated with Chlamydia trachomatis.
Prevention of Chlamydia Trachomatis
With the right preventive measures, its transmission can be significantly reduced. Understanding and implementing strategies such as safe sex practices, regular screening, limiting sexual partners, and enhancing education and awareness are crucial in preventing this infection.
Safe Sex Practices
One of the most effective ways to prevent Chlamydia Trachomatis infection is through practicing safe sex. This involves the consistent use of condoms during vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Condoms act as a barrier, reducing the risk of transmitting or acquiring STIs, including chlamydia. It is important for individuals to educate themselves on the correct use of condoms and to make condom use a non-negotiable part of their sexual activity.
Regular Screening and Testing
Regular screening for Chlamydia Trachomatis is vital, especially for those who are sexually active with multiple partners. Many people with chlamydia do not exhibit symptoms, making it easy to unknowingly spread the infection. Healthcare professionals recommend annual screenings for sexually active individuals, particularly for women under 25, as they are at a higher risk. Early detection through testing allows for timely treatment, preventing the infection’s spread and avoiding long-term health issues.
Limiting the Number of Sexual Partners
Reducing the number of sexual partners decreases the risk of STI exposure, including chlamydia. Engaging in monogamous relationships or limiting sexual contacts significantly lowers the chances of acquiring or transmitting STIs. It’s crucial for individuals to have open and honest discussions about sexual health with their partners and to make informed decisions about their sexual activities.
Importance of Education and Awareness in Prevention
Education and awareness are powerful tools in the fight against Chlamydia Trachomatis. Comprehensive sexual education programs that cover the risks of STIs, the importance of safe sex, and the benefits of regular testing can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards their sexual health. Public health campaigns and resources should aim to destigmatize STIs, encourage regular screenings, and promote safe sex practices among the wider community.
However, the prevention of Chlamydia Trachomatis requires a multifaceted approach that includes safe sex practices, regular screenings, limiting sexual partners, and the promotion of education and awareness. By adopting these strategies, individuals can protect themselves and others from the transmission of chlamydia and contribute to a healthier community. Remember, proactive prevention and open communication about sexual health are key components in reducing the spread of STIs.
Living with Chlamydia Trachomatis
Living with Chlamydia Trachomatis, a common sexually transmitted infection (STI), can be a challenging experience that requires careful management and support. Understanding how to manage symptoms, maintain your health after diagnosis, seek psychological and emotional support, and discuss your condition with partners is essential for coping effectively and reducing the risk of transmission.
Managing Symptoms and Health After Diagnosis
Upon receiving a diagnosis of Chlamydia Trachomatis, it’s crucial to start treatment promptly. Antibiotics are highly effective in treating the infection, but it’s important to complete the entire course as prescribed, even if symptoms disappear, to ensure the bacteria are fully eradicated.
In addition to following medical advice, adopting a healthy lifestyle can support your immune system and overall well-being. This includes:
- Maintaining a balanced diet: A nutritious diet can boost your immune system and aid in recovery.
- Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps your body flush out toxins.
- Getting adequate rest: Ensure you’re getting enough sleep to allow your body to heal.
- Avoiding sexual activity during treatment: To prevent the spread of the infection to partners and to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment, abstain from sexual activity until you and any affected partners have completed treatment and are cleared by a healthcare provider.
Psychological and Emotional Support
A diagnosis of Chlamydia Trachomatis can also impact your psychological and emotional health. It’s normal to feel a range of emotions, including anxiety, embarrassment, or guilt. Seeking support is vital:
- Professional counseling: A therapist, especially one experienced in sexual health issues, can provide valuable support.
- Support groups: Joining a support group for those living with STIs can offer comfort and reduce feelings of isolation.
- Open communication with healthcare providers: Your doctor or nurse can offer advice and reassurance about managing the condition.
Discussing Chlamydia Trachomatis with Partners
Discussing a Chlamydia Trachomatis diagnosis with current or past sexual partners is essential but can be difficult. Here are some tips to approach these conversations:
- Timing and privacy: Choose a private and comfortable setting for the discussion, ensuring you have enough time to talk things through.
- Be direct and honest: Clearly state your diagnosis, emphasizing that Chlamydia Trachomatis is common and treatable.
- Encourage testing: Advise your partner(s) to get tested and treated to prevent the spread of the infection.
- Use supportive language: Approach the conversation with empathy and understanding, avoiding blame.
Living with Chlamydia Trachomatis requires a proactive approach to treatment, support, and communication. By managing your health, seeking support, and having honest conversations with partners, you can effectively navigate the challenges posed by this condition and lead a healthy life.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions) About Chlamydia Trachomatis
What is Chlamydia Trachomatis?
Chlamydia Trachomatis is a type of bacteria that causes Chlamydia, a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that can affect both men and women. It’s known for its silent nature, as many people infected with the bacteria do not exhibit symptoms, making it a stealthy spreader. When symptoms do occur, they can include pain during urination, unusual discharge from the genitals, and pain in the lower abdomen.
How is Chlamydia Trachomatis transmitted?
Chlamydia Trachomatis is primarily transmitted through sexual contact. This includes vaginal, anal, and oral sex. The infection can be passed even if the penis does not fully enter the vagina or anus. It’s important to note that it can also be transmitted from a pregnant woman to her baby during childbirth, leading to eye infections or pneumonia in the newborn.
Can Chlamydia Trachomatis be cured?
Yes, Chlamydia Trachomatis is curable with antibiotics. The treatment usually involves a short course of antibiotics, such as azithromycin or doxycycline. It’s crucial for both partners to be treated simultaneously to prevent reinfection. Completing the full course of medication, even if symptoms disappear, is important to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
What are the potential complications if left untreated?
If not treated, Chlamydia Trachomatis can lead to serious health issues. In women, it can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can lead to infertility or ectopic pregnancy. In men, it can result in epididymitis, an inflammation of the coiled tube at the back of the testicle that stores and carries sperm, which can also affect fertility. Additionally, untreated chlamydia can increase the risk of acquiring or transmitting HIV.
How can Chlamydia Trachomatis be prevented?
Preventing Chlamydia Trachomatis involves practicing safe sex. This includes using condoms during vaginal, anal, and oral sex, limiting the number of sexual partners, and engaging in mutual monogamy with a partner who has been tested and is known to be uninfected. Regular STI screenings are also crucial, especially for sexually active individuals, to detect and treat infections early.
Should I get tested for Chlamydia Trachomatis?
Yes, regular testing for Chlamydia Trachomatis is recommended for sexually active individuals, particularly those under 25 years old or those with new or multiple sex partners. Testing is simple and usually involves providing a urine sample or a swab from the genitals. Early detection and treatment can prevent complications and transmission to others.
Can you get Chlamydia Trachomatis more than once?
Yes, you can get infected with Chlamydia Trachomatis multiple times. Being treated for chlamydia once does not make you immune to it. This highlights the importance of continued safe sex practices and regular screenings to protect yourself and your partners.
Conclusion:
For sexually active individuals, the importance of regular screenings cannot be overstated. These screenings are a key line of defense in identifying infections early when they are most treatable. Regular check-ups foster a proactive approach to sexual health, enabling individuals to take charge of their well-being and prevent the spread of STIs.
Moreover, this discussion serves as a call to action for everyone to practice safe sex. Using condoms, being in a mutually monogamous relationship where both partners are tested, and having open conversations about STI status and sexual health are all effective strategies for reducing the risk of Chlamydia Trachomatis. These practices not only protect your health but also the health of your partner(s).
If you suspect that you have been exposed to or are exhibiting symptoms of Chlamydia Trachomatis, it is crucial to seek medical advice immediately. Healthcare providers can offer testing, guidance, and treatment to manage and overcome this infection. Remember, early intervention is key to preventing long-term health issues and stopping the spread of Chlamydia Trachomatis.
In conclusion, let’s all take responsible steps towards maintaining our sexual health and ensuring a healthier future for ourselves and our communities. Regular screenings, practicing safe sex, and seeking prompt medical advice are essential actions that contribute to the control and eradication of Chlamydia Trachomatis. Together, we can make a difference in the fight against STIs.