Cervical Spondylosis Treatment: Cervical spondylosis, a condition characterized by age-related wear and tear affecting the spinal disks in your neck, has become increasingly prevalent in today’s aging population.
As the disks dehydrate and shrink, signs of osteoarthritis develop, including the growth of bony projections along the edges of bones (bone spurs).
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment of cervical spondylosis is crucial for maintaining a high quality of life and minimizing the impact of this condition.
What is Cervical Spondylosis?
Cervical spondylosis, commonly known as neck arthritis, is a condition characterized by the wear and tear of the cervical spine’s cartilage and bones. This age-related condition affects the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs of the neck, leading to chronic pain and stiffness. As people age, the effects of aging on the spine can result in the development of cervical spondylosis, making it a common issue among adults over the age of 50. Despite its prevalence, understanding the causes, risk factors, symptoms, and signs of cervical spondylosis is crucial for early detection and management.
Causes and Risk Factors Leading to the Development of Cervical Spondylosis
Cervical spondylosis develops due to the aging process, which causes wear and tear on the cervical spine. However, several factors can accelerate or exacerbate this condition:
- Age: The primary risk factor for cervical spondylosis is age. As people grow older, the discs in the cervical spine gradually break down, lose fluid, and become stiffer.
- Occupational Hazards: Jobs that involve repetitive neck motions, awkward positioning, or a lot of overhead work can increase the risk of developing cervical spondylosis.
- Neck Injuries: Past neck injuries or trauma can lead to premature cervical spondylosis.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of neck pain and spondylosis might increase an individual’s risk.
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to increased neck pain and cervical spine degeneration.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of regular exercise can contribute to the development of cervical spondylosis due to decreased spinal and muscular health.
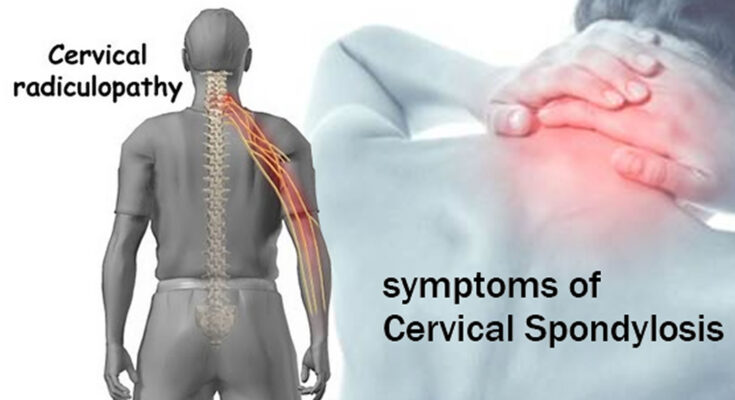
Symptoms and Signs to Watch Out For
Recognizing the symptoms of cervical spondylosis early can lead to a quicker diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Neck Pain and Stiffness: This may worsen with movement and can vary in intensity.
- Headaches: Often originating at the back of the neck and extending towards the forehead.
- Numbness and Weakness: These sensations can occur in the arms, hands, and fingers if nerve roots are compressed.
- Muscle Spasms: Sudden, severe muscle contractions in the neck or shoulder area.
- Reduced Flexibility: Difficulty in moving the head and neck due to stiffness or pain.
It’s important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of these symptoms, especially if they impact your daily life or are accompanied by weakness or numbness in your arms or hands. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the quality of life for those with cervical spondylosis.
By understanding what cervical spondylosis is, the causes and risk factors, and the symptoms to watch out for, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing their neck health. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy posture, and seeking medical advice when symptoms arise can help manage this condition effectively.
Diagnosis of Cervical Spondylosis
An accurate diagnosis is not only crucial for devising an effective treatment plan but also for ensuring a swift return to daily activities without the burden of pain and discomfort. Here, we delve into the diagnostic procedures for cervical spondylosis, emphasizing the significance of a precise diagnosis in shaping the treatment trajectory.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis in the Treatment Plan
Identifying cervical spondylosis accurately is the cornerstone of effective treatment. An incorrect diagnosis can lead to ineffective treatments, prolonging discomfort and potentially causing further complications. A tailored treatment plan, grounded in a precise diagnosis, can alleviate symptoms more effectively, helping patients achieve a better quality of life.
List of Diagnostic Procedures
The diagnostic journey for cervical spondylosis involves a series of steps, each playing a vital role in understanding the condition’s severity and the best course of action.
Physical Examination: What to Expect
The first step in diagnosing cervical spondylosis is a comprehensive physical examination. During this exam, your healthcare provider will assess your neck’s range of motion, check for areas of tenderness, and evaluate any pain triggered by movement. This initial assessment provides valuable insights into your condition’s severity and potential causes.
Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, and CT Scans
Following a physical exam, imaging tests play a pivotal role in visualizing the neck’s structure and identifying any abnormalities.
- X-rays are usually the first imaging test ordered. They can show the alignment of bones in your neck and reveal any degenerative changes, such as bone spurs, that might suggest cervical spondylosis.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scans offer a more detailed view, highlighting issues with discs, muscles, and the spinal cord. MRI is particularly useful in detecting soft tissue damage and nerve-related problems.
- CT (Computed Tomography) scans provide a detailed cross-sectional view of the neck, offering additional insights into the bone structure and potential areas of concern not clearly visible on X-rays.
Nerve Function Tests: EMG and Nerve Conduction Studies
To assess the health of the nerves and muscles in your neck and arms, your doctor might recommend nerve function tests, such as electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies. These tests measure the electrical activity in nerves and muscles, helping to identify nerve damage or compression caused by cervical spondylosis.
Discussing the Results with Your Healthcare Provider
After completing the diagnostic tests, the next crucial step is discussing the results with your healthcare provider. This conversation will focus on understanding the findings, the extent of your cervical spondylosis, and the implications for your treatment plan. Your provider will explain the results in detail, ensuring you have a clear understanding of your condition and the recommended treatment options.
The diagnosis of cervical spondylosis involves a comprehensive evaluation, including a physical examination, imaging tests, and nerve function tests. Each step is vital in accurately identifying the condition, which is essential for developing an effective treatment plan. By actively participating in the diagnostic process and discussing the results with your healthcare provider, you can take an informed role in your care, paving the way for a more comfortable and active life.
Treatment Options for Cervical Spondylosis
Understanding the range of treatment options available is crucial for those affected. This guide explores both non-surgical and surgical treatments for cervical spondylosis, outlining their goals, methods, and when each is appropriate.
Non-surgical Treatment Options
Non-surgical treatments aim to alleviate symptoms without the need for an operation. These approaches are often the first line of treatment and can be very effective in managing pain and improving quality of life.
Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises and physical therapy modalities can significantly relieve symptoms of cervical spondylosis. Physical therapists may employ techniques such as stretching, strengthening exercises, massage, heat therapy, and electrical stimulation to reduce pain and increase flexibility.
Medications: Pain relief is a key component of managing cervical spondylosis. Medications may include over-the-counter pain relievers, prescription non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants to ease muscle spasms, and even corticosteroid injections for severe inflammation.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes: Simple adjustments in daily life can have a profound impact on symptoms. Correcting posture, making ergonomic changes to workstations, and modifying activities to avoid strain on the neck can help manage pain and prevent further degeneration.
Surgical Treatment Options
Surgery may be considered when non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief or if the condition is significantly impacting the patient’s quality of life.
Indications for Surgery: Surgery is typically recommended for patients who experience severe pain, weakness, or numbness that does not improve with conservative treatment, or for those with spinal cord compression.
Common Surgical Procedures for Cervical Spondylosis:
- Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF): A procedure to remove a damaged disc to relieve spinal cord or nerve root pressure and pain, followed by fusion of the vertebrae to stabilize the spine.
- Cervical Artificial Disc Replacement: Instead of fusion, a damaged disc is replaced with an artificial one to preserve more natural movement of the neck.
- Posterior Cervical Decompression: This technique involves relieving pressure on the spinal cord and nerves from the back of the neck, often without the need for fusion.
Risks and Benefits of Surgical Intervention: While surgery can offer significant relief and prevent further degeneration, it comes with risks such as infection, bleeding, and, rarely, nerve damage. The decision to undergo surgery should be made after a thorough discussion with a healthcare professional about the potential benefits and risks.
However, the treatment for cervical spondylosis ranges from conservative non-surgical options to more invasive surgical procedures. The choice of treatment should be personalized, taking into account the severity of symptoms, the patient’s overall health, and their lifestyle. By understanding the available treatments, individuals suffering from cervical spondylosis can make informed decisions about their care, aiming for the best possible outcome and quality of life.
Managing Cervical Spondylosis
Here’s a comprehensive guide on long-term management strategies for cervical spondylosis, emphasizing the importance of regular follow-ups, monitoring, and preventative measures to maintain a healthy neck.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Living with cervical spondylosis requires a proactive approach to manage symptoms and prevent further degeneration. Here are some key strategies:
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in a tailored physical therapy program can help strengthen neck muscles, improve posture, and increase flexibility. This approach can significantly reduce pain and stiffness.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage pain. In some cases, prescription medications may be necessary. Always consult with a healthcare provider for the best course of action.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Simple changes in daily activities can make a big difference. Ergonomic adjustments at the workplace, using a supportive pillow for sleep, and avoiding prolonged periods in one position can help alleviate symptoms.
- Regular Exercise: Incorporating regular, gentle exercises such as walking, swimming, or yoga can improve overall neck health and reduce the risk of further degeneration.
Importance of Regular Follow-Up and Monitoring
Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are crucial for anyone living with cervical spondylosis. These appointments allow for:
- Monitoring Progress: Keeping track of symptoms and the effectiveness of management strategies over time.
- Adjusting Treatments: Healthcare providers can make necessary adjustments to treatment plans based on progress and any new symptoms.
- Early Detection: Regular monitoring helps in detecting any signs of worsening condition early, allowing for prompt intervention.
Tips for Preventing Further Degeneration
While cervical spondylosis is a degenerative condition, there are steps you can take to slow its progression and maintain a healthy neck:
- Maintain Good Posture: Keeping a proper posture, especially while sitting for long periods, can reduce strain on the neck.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity keeps the neck muscles strong and flexible, reducing the risk of further damage.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D promotes bone health, which is vital in managing cervical spondylosis.
- Limit Repetitive Activities: Avoid activities that involve repetitive neck movements or prolonged use of the neck in a fixed position.
- Stay Hydrated: Keeping the body hydrated helps maintain the elasticity of soft tissues and intervertebral discs in the neck.
Implementing these management strategies and tips can significantly improve the quality of life for those living with cervical spondylosis. Remember, it’s essential to work closely with healthcare providers to tailor a management plan that suits your individual needs and circumstances. Regular follow-ups and a commitment to self-care are key to successfully managing this condition and maintaining a healthy, active lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Cervical Spondylosis
What is cervical spondylosis?
Cervical spondylosis is a degenerative condition affecting the cervical spine, which comprises the neck’s vertebrae. It’s often caused by age-related changes in the spine’s discs and joints, leading to symptoms like neck pain, stiffness, and sometimes nerve compression.
How is cervical spondylosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination where a healthcare provider checks for range of motion, reflexes, and muscle strength. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans may also be used to assess the extent of degeneration and the involvement of nerve structures.
What are the common symptoms of cervical spondylosis?
Symptoms may vary but often include neck pain and stiffness, headaches, and sometimes arm pain or numbness if nerve roots are compressed. Some individuals may experience a grinding sensation or noise during neck movement.
Can cervical spondylosis be cured?
While there’s no cure for the degenerative changes that occur with cervical spondylosis, treatment can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Management strategies focus on pain relief, maintaining neck mobility, and preventing further spinal cord or nerve root damage.
What treatments are available for cervical spondylosis?
Treatment options range from conservative to surgical. Conservative treatments include physical therapy, medications (such as anti-inflammatory drugs), and cervical collars. For severe cases, especially those involving nerve compression, surgical interventions may be recommended to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
How can I manage cervical spondylosis at home?
Home management strategies include regular exercise to maintain neck strength and flexibility, applying heat or cold to reduce pain, practicing good posture, and using ergonomic furniture. It’s also important to avoid activities that may exacerbate symptoms.
When should I see a doctor for cervical spondylosis?
You should consult a healthcare provider if you experience persistent neck pain, stiffness that affects your daily activities, or symptoms like arm numbness, weakness, or coordination problems. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Can lifestyle changes help with cervical spondylosis?
Yes, lifestyle changes can play a crucial role in managing cervical spondylosis. Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, avoiding smoking, and practicing good posture can help reduce symptoms and prevent further degeneration.
Conclusion:
Effective management of cervical spondylosis involves a comprehensive approach that may include physical therapy, medication, lifestyle adjustments, and in some cases, surgical interventions. Each treatment plan should be tailored to the individual’s specific symptoms, overall health, and lifestyle, emphasizing the importance of a personalized treatment strategy.
We encourage all readers to take any neck pain or discomfort seriously and to seek professional medical advice. Consulting with healthcare professionals ensures that you receive a diagnosis based on a thorough examination and that your treatment plan is designed to address your unique needs. Remember, early intervention is key to managing symptoms effectively and preventing further complications.
In conclusion, understanding the impact of cervical spondylosis and taking proactive steps towards diagnosis and treatment is essential. By seeking professional guidance and following a personalized treatment plan, individuals can manage their symptoms effectively and maintain an active, healthy lifestyle. Don’t let neck pain hold you back—take action today to support your spinal health for tomorrow.