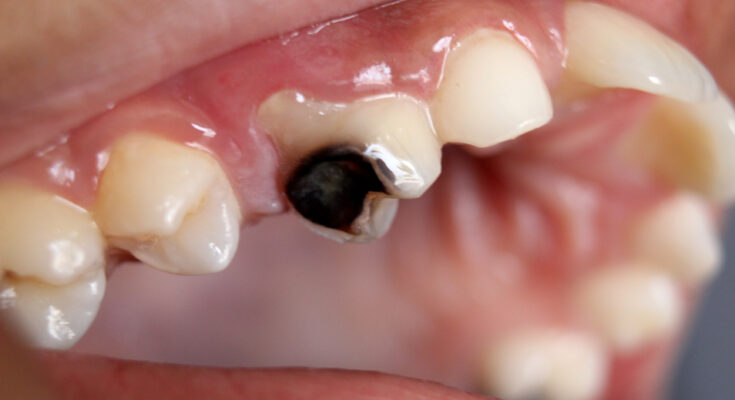
Cavities and Tooth Decay Treatment: Cavities, also known as tooth decay, are a prevalent health issue impacting individuals globally.
This dental condition occurs when tooth enamel, the hard outer layer of your teeth, is eroded, leading to tiny openings or holes. Without timely and effective intervention, cavities can lead to severe toothache, infection, and even tooth loss.
This article delves into the diagnosis and treatment of cavities, offering comprehensive insights for maintaining optimal oral health.
What are Cavities and Tooth Decay?
Cavities, also known as dental caries or tooth decay, are permanently damaged areas in the hard surface of your teeth that develop into tiny openings or holes. They are caused by a combination of factors, including bacteria in your mouth, frequent snacking, sipping sugary drinks, and not cleaning your teeth well. Cavities and tooth decay are among the world’s most common health problems. They can affect anyone with teeth, including infants.
Causes and Risk Factors
The process of tooth decay involves several steps:
- Plaque Formation: Dental plaque is a clear sticky film that coats your teeth. It’s due to eating a lot of sugars and starches and not cleaning your teeth well. When sugars and starches aren’t cleaned off your teeth, bacteria quickly begin feeding on them and forming plaque.
- Plaque Attack: The acids in plaque remove minerals in your tooth’s hard, outer enamel. This erosion causes tiny openings or holes in the enamel — the first stage of cavities. Once areas of enamel are worn away, the bacteria and acid can reach the next layer of your teeth, called dentin.
- Continued Decay: Dentin is softer than enamel and less resistant to acid. The bacteria and acid continue their march through the teeth, moving next to the inner tooth material (pulp) that contains nerves and blood vessels. The pulp becomes swollen and irritated from the bacteria. Because there’s nowhere for the swelling to expand inside a tooth, the nerve becomes pressed, causing pain.
Risk factors for cavities include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Not brushing your teeth regularly allows plaque to build up and attack the tooth enamel.
- Foods and Drinks: Foods that cling to your teeth for a long time — like milk, ice cream, honey, sugar, soda, dried fruit, cake, cookies, hard candy, breath mints, dry cereal, and chips — are more likely to cause decay than foods that are easily washed away by saliva.
- Frequent Snacking or Sipping: This gives the acid more time to erode the tooth.
- Bedtime Infant Feeding: When babies are given bottles filled with milk, formula, or juice at bedtime, the sugars can linger on teeth, leading to decay.
- Inadequate Fluoride: Fluoride, a naturally occurring mineral, helps prevent cavities and can even reverse the earliest stages of tooth damage.
Statistics on Prevalence and Impact
Tooth decay and cavities are extremely common. According to the World Health Organization:
- Nearly 100% of adults have at least one dental cavity.
- Between 60-90% of school children worldwide have at least one cavity.
- Dental cavities are a major health concern in most industrialized countries, affecting 60-90% of schoolchildren and the vast majority of adults.
- Cavities and tooth decay are a significant public health problem globally. They can cause pain, discomfort, disfigurement, and even lead to death.
The impact of tooth decay goes beyond just dental health. It can affect a person’s overall health, quality of life, and even their economic productivity due to time lost at work or school. Regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene practices, and reducing sugar intake are essential steps in preventing tooth decay and cavities.
Symptoms and Signs of Cavities and Tooth Decay
Early Signs of Tooth Decay
Recognizing these early signs is crucial for timely intervention and avoiding more serious complications. Here are some early indicators of tooth decay:
- Tooth Sensitivity: One of the first signs of decay is a noticeable sensitivity in one or more teeth. This sensitivity often occurs when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks.
- Mild Toothache: An occasional or mild toothache may indicate the beginning of tooth decay. This pain might come and go but tends to persist over time.
- White Spots on Teeth: The appearance of white spots on the surface of teeth can signal the loss of minerals and the onset of decay.
- Visible Pits or Holes: In some cases, small pits or holes might appear on the teeth, which are areas where the tooth enamel has started to break down.
Progression of Symptoms
If not addressed, the symptoms of tooth decay can worsen. As the decay progresses, the signs become more pronounced and may include:
- Increased Tooth Sensitivity and Pain: As decay reaches deeper layers of the tooth, it can cause more severe pain and sensitivity. The discomfort may become constant and interfere with daily activities.
- Dark Spots or Holes on Teeth: These spots or holes become larger and more visible as the decay progresses. They are clear indicators that the enamel has been significantly compromised.
- Bad Breath or Taste: Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth, despite good oral hygiene, can be a sign of advancing tooth decay.
- Swelling Gums: In some cases, the gums around the affected tooth may swell or bleed, indicating a possible infection.
When to Seek Dental Advice
It’s essential to consult a dentist if you notice any of the above symptoms. Early intervention can prevent further damage and more invasive treatments. Here are some guidelines on when to seek dental advice:
- Persistent Pain: If tooth pain persists for more than a day or two, it’s important to see a dentist.
- Visible Decay or Damage: Any visible changes in the tooth’s structure, like holes or dark spots, warrant a dental check-up.
- Long-term Sensitivity: Sensitivity that doesn’t resolve after a few days or occurs with every exposure to hot or cold should be evaluated.
- Swollen Gums or Abscesses: Swelling, particularly if accompanied by fever or severe pain, could indicate an abscess or infection that requires immediate dental care.
Remember, early detection and treatment of tooth decay can save your teeth and prevent more serious health issues. Regular dental check-ups are a key part of maintaining good oral health.
Diagnosis of Cavities and Tooth Decay
Professional Dental Examination
The first step in identifying cavities and tooth decay is a comprehensive dental examination. During this check-up, a dentist uses their expertise to evaluate the health of your teeth and gums. This process involves visually inspecting the mouth for signs of decay, such as discoloration, holes in the teeth, and other abnormalities. A professional dental examination is crucial as it allows for early detection of cavities, often before they become painful or visible to the naked eye.
Tools and Techniques Used in Diagnosis
Dentists employ various tools and techniques to diagnose cavities and tooth decay accurately:
- X-rays: Dental X-rays are among the most effective tools for detecting cavities. They can reveal decay that isn’t visible during a regular examination, particularly cavities between teeth or under existing fillings. X-rays can also help in assessing the extent of the decay and planning the appropriate treatment.
- Dental Probes: These are instruments used to gently explore the mouth and teeth. Dentists use them to check for soft areas, a common sign of tooth decay. Dental probes help in assessing the health of tooth enamel and in identifying cavities at their early stages.
- Other Diagnostic Tools: Dentists may also use additional tools like cavity-detecting dyes, which help in identifying decayed areas, and intraoral cameras that provide detailed images of the teeth and gums.
The Role of Patient History in Diagnosis
Understanding a patient’s dental history plays a vital role in diagnosing cavities and tooth decay. Dentists often inquire about:
- Previous dental issues and treatments.
- Dietary habits, especially sugar intake.
- Oral hygiene practices, including brushing and flossing routines.
- Family history of dental diseases.
This information helps dentists in making a more accurate diagnosis. For instance, a history of frequent cavities may prompt a more thorough investigation for hidden decay. Similarly, knowledge of a patient’s dietary habits can assist in identifying the potential causes of tooth decay and in advising preventative measures.
However, the diagnosis of cavities and tooth decay is a multifaceted process involving professional dental examinations, the use of specialized tools and techniques, and a thorough understanding of a patient’s dental history. Early detection and treatment of cavities can prevent more serious dental issues and ensure the maintenance of good oral health.
Treatment Options for Cavities and Tooth Decay
Dealing with cavities and tooth decay is crucial for maintaining oral health and overall well-being. Fortunately, modern dentistry offers a variety of treatment options tailored to the severity and stage of the decay. Here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding these treatments.
1. Fluoride Treatments
Fluoride is a mineral that can help repair tooth enamel and reverse early signs of tooth decay. When cavities are just beginning to form, a professional fluoride treatment may be enough to restore the tooth’s enamel and fend off further decay.
2. Dental Fillings
Dental fillings are the most common treatment for cavities that have progressed beyond the earliest stage. The decayed part of the tooth is removed, and the cavity is filled with various materials such as composite resins, porcelain, or dental amalgam.
3. Dental Crowns
For more extensive decay or weakened teeth, a dental crown may be necessary. Crowns are custom-fitted coverings that replace the entire natural crown of the tooth. They can be made of gold, porcelain, resin, or other materials.
4. Root Canal Treatment
When decay reaches the inner material of your tooth (pulp), a root canal may be required. This procedure involves removing the damaged pulp, cleaning the inner chambers of the tooth, and sealing it to prevent further damage.
5. Tooth Extractions
In severe cases where the tooth is too damaged to be saved, extraction may be the only option. This involves removing the tooth entirely and can be followed by options like dental implants or bridges to replace the missing tooth.
6. Dental Implants
If a tooth is extracted due to decay, dental implants offer a durable replacement option. An implant is a metal post surgically inserted into the jawbone, and a false tooth (crown) is attached to it, closely mimicking a natural tooth.
7. Preventive Measures
In addition to these treatments, preventive measures such as regular brushing and flossing, using fluoride toothpaste, and having regular dental check-ups are vital in preventing cavities and tooth decay.
Early detection and treatment of cavities can prevent serious complications and preserve your oral health. If you suspect you have a cavity or tooth decay, consult your dentist promptly to determine the most appropriate treatment option for your situation.
Advanced Treatments and Technologies of Cavities and Tooth Decay
In the ever-evolving world of dental care, advancements in treatments and technologies are revolutionizing how we address cavities and tooth decay. This article delves into the innovative treatments for severe cases, explores the role of laser dentistry in treating cavities, and anticipates future advancements in cavity treatment.
Innovative Treatments for Severe Cases
For severe cases of tooth decay and cavities, traditional methods like fillings or crowns may not suffice. Here, cutting-edge treatments come to the rescue. One such innovation is the use of bioactive glass, a material that not only fills cavities but also helps in the regeneration of tooth minerals. This glass releases fluoride, calcium, and phosphate – elements crucial for tooth health – which actively combat decay and aid in the restoration of the tooth.
Another advanced technique involves the use of silver diamine fluoride (SDF). Unlike traditional treatments, SDF is a liquid solution that can be directly applied to the cavity, halting decay immediately. It’s a quick, non-invasive, and highly effective method, particularly for patients who have difficulty undergoing extensive dental procedures.
The Role of Laser Dentistry in Treating Cavities
Laser dentistry represents a significant leap in treating dental cavities. Lasers are used to precisely target and remove decayed tooth tissue, causing minimal discomfort and preserving more of the healthy tooth. This method is not only less invasive but also reduces the need for anesthesia, making it a preferred choice for many patients.
The accuracy of laser dentistry also allows dentists to detect cavities at an earlier stage than traditional methods. Early detection means less extensive treatment, preserving more of the natural tooth structure and ensuring a healthier dental future.
Future Advancements in Cavity Treatment
Looking towards the future, we can expect even more groundbreaking advancements in cavity treatment. One promising area is the development of smart fillings. These fillings are designed to release medication over time, helping to prevent further decay in the surrounding tooth area.
Another exciting development is the potential use of stem cells to regenerate tooth tissue. This could revolutionize dental care, allowing for the natural restoration of decayed teeth rather than relying on artificial materials.
In addition, research is ongoing into creating more effective fluoride delivery systems and developing materials that mimic tooth enamel, providing longer-lasting and more natural repairs for cavities.
However, the advancements in treatments and technologies for cavities and tooth decay are rapidly changing the landscape of dental care. From innovative treatments for severe cases to the integration of laser dentistry and the anticipation of future breakthroughs, dental health is moving towards more effective, less invasive, and patient-friendly approaches. As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise a brighter, healthier future for dental patients worldwide.
Prevention Strategies of Cavities and Tooth Decay
Maintaining a healthy mouth is crucial for overall wellbeing. Cavities and tooth decay are common dental issues that can lead to more serious health concerns if not addressed. However, you can effectively prevent these problems by adopting certain strategies. Here, we discuss key prevention methods, focusing on daily dental hygiene, dietary recommendations, and the importance of regular dental check-ups and cleanings.
Daily Dental Hygiene Practices
- Brushing Teeth Regularly: Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste is fundamental. Fluoride strengthens tooth enamel, making it more resistant to decay. Ensure you brush for at least two minutes, reaching all surfaces of your teeth.
- Flossing Daily: Flossing removes food particles and plaque from areas your toothbrush can’t reach. It’s recommended to floss once a day, ideally before bedtime, to reduce the risk of cavities and gum disease.
- Using Mouthwash: An antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce the levels of bacteria in your mouth. This not only freshens your breath but also helps in preventing tooth decay and gum problems.
Dietary Recommendations
- Limiting Sugary Foods and Drinks: Sugar is a leading cause of cavities. Bacteria in your mouth feed on sugar, producing acids that erode tooth enamel. Reducing your intake of sugary snacks and beverages can significantly lower your risk of tooth decay.
- Eating Teeth-friendly Foods: Incorporate foods that promote dental health. Dairy products like cheese and yogurt are high in calcium, which strengthens teeth. Crunchy fruits and vegetables stimulate saliva production, which helps in cleaning the mouth.
- Drinking Plenty of Water: Water is essential for overall health, including oral health. It helps wash away food particles and neutralize acids produced by bacteria in your mouth.
Regular Dental Check-ups and Cleanings
- Routine Dental Visits: Visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings is crucial. Dentists can spot early signs of decay and offer treatments before they become severe.
- Professional Cleanings: Dental hygienists remove plaque and tartar that can lead to cavities and gum disease during these visits. Professional cleanings are more thorough than regular brushing and flossing.
- Personalized Dental Advice: During these visits, your dentist can provide tailored advice based on your specific oral health needs. This might include recommendations for dental products or additional preventive measures.
However, preventing cavities and tooth decay involves a combination of good oral hygiene practices, a tooth-friendly diet, and regular dental visits. By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can maintain a healthy mouth and avoid the discomfort and expense of dental problems. Remember, a proactive approach to oral care is key to keeping your smile bright and healthy.
Complications of Untreated Cavities and Tooth Decay
Possible Health Implications of Untreated Cavities
Neglecting dental cavities can lead to a myriad of health issues, ranging from mild to severe. One of the primary consequences is the progression of the cavity into a deeper infection. This can affect not just the tooth, but also the surrounding gums and bone.
- Tooth Abscess: When a cavity is left untreated, it can lead to an abscessed tooth, which is an infection that spreads to the root and surrounding areas. This condition is not only painful but can also cause swelling and a range of systemic issues if the infection spreads further.
- Increased Sensitivity and Pain: As cavities grow, they expose more of the inner tooth, leading to heightened sensitivity and pain. This can impact daily activities like eating and drinking.
- Tooth Loss: In severe cases, the damage to the tooth can become so extensive that it becomes irreparable, leading to tooth loss. This not only affects your smile and confidence but also your ability to chew and speak properly.
- Gum Disease: Untreated cavities can contribute to gum disease, which can further lead to receding gums and loss of bone around the teeth.
- Effects on Overall Health: There is increasing evidence linking oral health to overall health. Untreated cavities and tooth decay can potentially exacerbate conditions like diabetes and heart disease, or lead to respiratory infections.
The Importance of Timely Treatment
Addressing cavities at an early stage is crucial for several reasons:
- Prevention of Further Decay: Early treatment stops the decay from progressing and spares the tooth from more extensive procedures.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Filling a small cavity is less expensive and less invasive than treating a large cavity or performing a root canal or extraction.
- Maintaining Overall Health: Good oral health is a vital component of overall well-being. Treating cavities promptly can help prevent related health issues.
- Preventing Pain and Discomfort: Early treatment of cavities can prevent the pain and discomfort associated with more advanced tooth decay.
- Preserving Natural Teeth: Prompt treatment helps to preserve the natural structure of the tooth, maintaining the integrity of your smile and oral function.
However, the timely treatment of cavities is not just essential for maintaining oral health but also plays a significant role in preserving overall health. Regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene, and addressing dental issues as soon as they arise are key to preventing the complications associated with untreated cavities and tooth decay.
Myths and Misconceptions about Cavities and Tooth Decay
Common Myths Debunked
Myth 1: Sugar is the Only Cause of Cavities
While it’s true that sugar plays a significant role in tooth decay, it’s not the only culprit. Cavities are caused by acid-producing bacteria that feed on carbohydrates in your mouth. These carbohydrates can come from sugary foods, but they can also come from starches, fruits, and even some vegetables. The key to preventing cavities is not just cutting down on sugar but maintaining good oral hygiene to reduce harmful bacteria.
Myth 2: Cavities are Only for Children
Many people believe that cavities are a childhood problem, but adults are equally at risk. As we age, our gums may recede, exposing the roots of our teeth to plaque and decay. Additionally, medications and certain health conditions can reduce saliva flow, which is critical in washing away food particles and neutralizing acids produced by bacteria.
Myth 3: If Your Tooth Doesn’t Hurt, You Don’t Have a Cavity
Tooth decay doesn’t always cause pain in its early stages. By the time you feel discomfort, the cavity may have already reached an advanced stage. Regular dental check-ups are essential for catching cavities early when they are easier to treat.
Myth 4: Fillings Last Forever
While fillings are an effective way to treat cavities, they don’t last forever. They typically last for several years but eventually need to be replaced due to wear and tear. Regular dental check-ups are crucial to monitor the condition of fillings.
Clarifying Misconceptions about Treatments
Misconception 1: Only Fillings Can Treat Cavities
Fillings are a common treatment for cavities, but they are not the only option. In cases of minor decay, fluoride treatments can sometimes reverse the damage. In more severe cases, crowns, root canals, or even tooth extractions may be necessary.
Misconception 2: Treating Cavities is Painful
Modern dentistry has made great strides in pain management. While the idea of getting a cavity filled might be intimidating, local anesthetics and sedation options can make the procedure comfortable and pain-free.
Misconception 3: Brushing Harder Prevents Cavities
Brushing with too much force can actually damage your enamel and gums, which can lead to tooth decay. It’s more effective to brush gently with a soft-bristled toothbrush and to use fluoride toothpaste to help protect your teeth from decay.
Misconception 4: Cavities Can Heal on Their Own
Once a tooth has decayed to the point of forming a cavity, it cannot heal on its own. Professional dental treatment is necessary to remove the decay and restore the tooth. Neglecting treatment can lead to more severe problems, including infection and tooth loss.
By debunking these common myths and misconceptions, you can take better care of your dental health and avoid the pitfalls of misinformation. Remember, the best way to prevent cavities and tooth decay is through regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene practices, and a balanced diet.
FAQs About Cavities and Tooth Decay Treatment
1. What causes cavities?
Cavities, also known as dental caries, are caused by the buildup of bacteria in the mouth. These bacteria produce acids that erode the tooth enamel, leading to decay. Factors contributing to cavities include poor oral hygiene, frequent snacking on sugary foods, and not getting enough fluoride.
2. How can I prevent cavities?
Preventing cavities involves maintaining good oral hygiene. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, eating a balanced diet with limited sugar, and regular dental check-ups.
3. What are the symptoms of tooth decay?
Symptoms of tooth decay include toothache, sensitivity to hot and cold, visible holes or pits in your teeth, brown, black, or white staining on any surface of a tooth, and pain when you bite down.
4. How are cavities treated?
Treatment depends on the severity of the cavity. Options include fluoride treatments, fillings, crowns, root canals, or in extreme cases, tooth extraction. Your dentist will recommend the most appropriate treatment for your situation.
5. Is cavity treatment painful?
Modern dental techniques and anesthesia make cavity treatment relatively painless. Your dentist will ensure you’re as comfortable as possible during the procedure.
6. How long does it take to recover from cavity treatment?
Recovery time varies depending on the treatment. For simple fillings, you might feel back to normal within a few hours. More extensive procedures like root canals might require a few days of recovery.
7. Can cavities come back after treatment?
Yes, new cavities can form around existing fillings or crowns if oral hygiene is neglected. Regular dental check-ups can help detect and prevent recurrent decay.
8. Are there any home remedies for cavities?
While home remedies can provide temporary relief from toothache, they cannot treat cavities. Professional dental treatment is necessary to address tooth decay.
9. Can children get cavities?
Yes, children are particularly susceptible to cavities, especially if they consume sugary foods and drinks and do not maintain good oral hygiene.
10. What is the difference between a cavity and tooth decay?
Tooth decay is the process that leads to the formation of cavities. A cavity is the actual hole that is created as a result of the decay process.
Conclusion:
We strongly encourage regular dental visits and preventive care. Regular dental check-ups play a pivotal role in early detection and management of tooth decay. These visits allow your dentist to monitor your oral health, offer professional cleanings to remove plaque buildup, and provide essential guidance on maintaining good oral hygiene. Preventive care, such as proper brushing, flossing, and using fluoride treatments, can significantly reduce the risk of cavities and tooth decay.
Remember, taking proactive steps in dental care not only ensures a healthy mouth but also contributes to your overall well-being. So, prioritize your dental health today. Schedule regular check-ups, embrace preventive care, and stay informed about the best practices for maintaining a cavity-free smile. Your teeth will thank you for it!