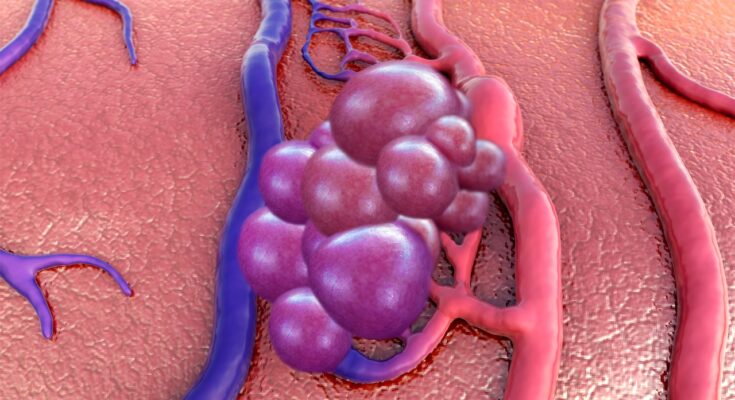
Cavernous Malformations Symptoms: Cavernous malformations, also known as cerebral cavernomas or cavernous angiomas, are vascular abnormalities in the brain or spinal cord that consist of small blood vessels that are dilated and irregular in structure.
These lesions can lead to various neurological symptoms and are a critical health topic requiring thorough understanding.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the symptoms and causes of cavernous malformations, aiming to provide valuable insights for those affected by this condition.
What is Cavernous Malformations?
Cavernous Malformations, also known as cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs), represent a type of vascular anomaly primarily found in the brain and spinal cord. These malformations are clusters of abnormal, thin-walled blood vessels. Unlike typical blood vessels, the ones in cavernous malformations are dilated and irregular, resembling a small berry. They can vary in size and number and have a tendency to bleed, leading to various neurological symptoms.
Prevalence and Demographics Affected
Cavernous malformations are relatively uncommon, with studies estimating that they affect approximately 0.5% of the population. However, this number could be higher as many cases are asymptomatic and go undiagnosed. They can occur in people of any age, but are most commonly diagnosed in adults between the ages of 20 and 40.
There’s a noted variation in prevalence based on ethnicity and genetics. For instance, certain genetic mutations linked to cavernous malformations are more prevalent in Hispanic populations, particularly those with a Mexican-American heritage. This genetic factor plays a significant role, as approximately 20% of individuals with cavernous malformations have a familial form of the condition, suggesting an inherited predisposition.
While both men and women can develop cavernous malformations, some studies suggest a slightly higher incidence in females. The reasons for this disparity are not fully understood and may be related to hormonal influences or genetic factors.
It’s important to note that the demographics affected by cavernous malformations can vary, and ongoing research continues to shed light on the intricacies of this condition. As such, understanding of the prevalence and demographics may evolve with new findings.
Symptoms of Cavernous Malformations
The symptoms of cavernous malformations vary depending on their location and size. Some individuals with cavernous malformations may remain asymptomatic, while others may experience a range of neurological symptoms, including:
Frequent Symptoms
The most common symptoms associated with cavernous malformations include:
- Headaches: Often the first sign, headaches linked to CCMs can vary in intensity and frequency.
- Seizures: Cavernous malformations can cause seizures, ranging from minor to severe, depending on their location in the brain.
- Neurological Deficits: These include issues like dizziness, difficulty with balance, and problems with speech and vision.
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: In some cases, these malformations can lead to bleeding in the brain, known as a hemorrhagic stroke, presenting sudden and severe symptoms.
Understanding Variability in Symptoms
The symptoms of cavernous malformations can significantly vary based on the malformation’s size and location:
- Size Factor: Larger malformations are more likely to cause noticeable symptoms compared to smaller ones.
- Location Specificity: Malformations in different parts of the brain or spinal cord can lead to various symptoms. For instance, a malformation in the brainstem may affect bodily functions and motor skills, while one in the cerebral cortex might be more likely to cause seizures.
Case Studies and Anecdotes
While clinical data provides a broad understanding, case studies and personal anecdotes offer valuable insights into the real-world impact of cavernous malformations. For example:
- A Patient’s Journey: One case involved a 35-year-old woman experiencing sudden severe headaches and visual disturbances. Medical examination revealed a large CCM in her occipital lobe, highlighting the connection between malformation location and symptom type.
- Living with CCM: Personal accounts from individuals living with cavernous malformations often emphasize the unpredictability of symptoms and the importance of regular monitoring and medical support.
However, understanding the symptoms of cavernous malformations is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. The variability in symptoms, influenced by the size and location of the malformations, underscores the need for individualized medical attention. Case studies and personal experiences further enrich our understanding of this complex condition, guiding both patients and healthcare providers in navigating its challenges.
Causes and Risk Factors of Cavernous Malformations
Cavernous malformations, a type of vascular abnormality in the brain or spinal cord, are influenced by various factors. Understanding these factors can aid in early detection and management. This article delves into the causes and risk factors, including genetic, environmental, and recent research findings.
Genetic Factors and Hereditary Patterns
- Genetic Mutations: Certain genetic mutations are known to increase the risk of developing cavernous malformations. These mutations can be inherited, making family history a significant risk factor.
- Hereditary Patterns: In families with a history of cavernous malformations, the condition can follow an autosomal dominant pattern. This means that a child has a 50% chance of inheriting the disorder if one parent carries the gene mutation.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
- Radiation Exposure: Exposure to ionizing radiation, such as from radiation therapy, has been linked to the development of cavernous malformations.
- Lifestyle Influences: While direct connections are less clear, overall health and lifestyle choices may influence the risk. Factors like high blood pressure and smoking, which affect vascular health, could potentially play a role.
Research Findings on Development
- Recent Studies: Ongoing research is crucial in understanding cavernous malformations. Recent studies have focused on the molecular and cellular mechanisms behind these malformations.
- Advancements in Understanding: Scientific advancements have shed light on how these malformations develop and progress, leading to better diagnostic and treatment methods.
Understanding the causes and risk factors of cavernous malformations is crucial for early detection and effective management. Continued research is essential for advancing our knowledge and improving patient outcomes. Stay informed about the latest developments to ensure comprehensive care and prevention strategies.
Diagnosis of Cavernous Malformations
Diagnosing cavernous malformations can be a nuanced process, primarily due to the asymptomatic nature of these lesions in many cases. This section delves into the common diagnostic procedures and the challenges faced in detecting CCMs.
Common Diagnostic Procedures
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI is the most effective tool for identifying cavernous malformations. It uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain and spinal cord, helping in detecting even small lesions that might be missed by other imaging techniques.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Although less sensitive than MRI, CT scans are sometimes used to diagnose cavernous malformations. They are particularly useful in emergency situations to quickly assess if a patient has had a hemorrhage.
- Genetic Testing: In cases where there is a family history of cavernous malformations, genetic testing might be recommended. This involves analyzing DNA to identify mutations that can lead to CCMs.
- Angiography: While cavernous malformations are typically not visible on angiography, this procedure might be conducted to rule out other vascular abnormalities. It involves injecting a contrast dye into the bloodstream and taking X-rays to visualize blood flow in the brain and spinal cord.
Challenges in Diagnosing Cavernous Malformations
The diagnosis of cavernous malformations presents several challenges, primarily because many individuals remain asymptomatic. These challenges include:
- Asymptomatic Nature: A significant proportion of people with cavernous malformations do not exhibit any symptoms. Such cases are often discovered incidentally during imaging for unrelated medical reasons.
- Variable Symptoms: When symptoms do occur, they can vary widely, ranging from headaches and seizures to more severe neurological deficits. This variability can lead to misdiagnosis or delays in correctly identifying the condition.
- Differential Diagnosis: Since the symptoms of cavernous malformations can mimic those of other neurological disorders, healthcare professionals must carefully differentiate between these conditions.
- Evolution Over Time: Cavernous malformations can change in size and number over time. Regular monitoring and repeated imaging may be required to understand the progression of the condition, adding complexity to the diagnosis and management.
However, diagnosing cavernous malformations requires a combination of advanced imaging techniques and careful clinical assessment. The asymptomatic nature of many cases and the variability in symptoms pose significant challenges, underscoring the need for awareness and expertise in handling this complex condition.
Treatment and Management of Cavernous Malformations
Managing and treating these malformations is crucial for reducing symptoms and preventing complications. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the treatment options, symptom management strategies, and lifestyle changes that can assist in dealing with cavernous malformations.
List of Treatment Options
- Surgical Removal: The most definitive treatment for accessible cavernous malformations is surgical removal. This option is typically considered when the malformation is in a location that can be reached safely, and when it has caused symptoms like bleeding or seizures.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery: For malformations that are difficult to access surgically, stereotactic radiosurgery, such as Gamma Knife surgery, can be an option. This non-invasive procedure uses focused radiation to reduce the size of the malformation and the risk of bleeding.
- Medication for Symptom Control: Medications can be used to manage symptoms associated with cavernous malformations. Antiepileptic drugs are often prescribed to control seizures, while pain relievers may be used to manage headache pain.
Discussion on the Management of Symptoms
Managing the symptoms of cavernous malformations is as important as treating the malformations themselves. The approach to symptom management typically depends on the specific symptoms experienced by the individual.
- Seizure Management: Seizures, a common symptom of cavernous malformations, can often be controlled with antiepileptic drugs. Regular monitoring and adjustments in medication may be necessary.
- Headache Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers can be effective for managing headaches. In some cases, your doctor may recommend preventive medication if headaches are frequent or severe.
- Neurological Observation: Regular neurological assessments are vital, especially for individuals with cavernous malformations that are not currently causing symptoms. These assessments help in early detection of changes that might require intervention.
Lifestyle Changes and Preventive Measures
In addition to medical treatment, certain lifestyle changes and preventive measures can be beneficial in managing cavernous malformations:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular exercise can improve overall health and well-being. However, it’s important to avoid contact sports or activities that pose a high risk of head injury.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support brain health and overall wellness.
- Avoiding Blood Thinners: It’s generally advisable for individuals with cavernous malformations to avoid medications that thin the blood, as they can increase the risk of bleeding.
- Stress Management: Since stress can exacerbate symptoms like headaches and seizures, adopting stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can be helpful.
- Regular Medical Checkups: Regular checkups with a healthcare provider are essential for monitoring the condition and making necessary adjustments in treatment.
- Stay Informed: Keeping informed about the latest research and treatment options for cavernous malformations can empower patients to make informed decisions about their health.
However, while cavernous malformations can pose significant challenges, a combination of appropriate medical treatment, symptom management, and lifestyle modifications can effectively manage the condition and enhance the quality of life for those affected. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare team to determine the best approach for individual needs.
Living with Cavernous Malformations
Living with cavernous malformations often involves managing a variety of symptoms and adjusting to the uncertainty and challenges they bring.
Common Experiences
Patients with cavernous malformations may experience a range of symptoms, including headaches, seizures, hemorrhages, neurological deficits, and in some cases, no symptoms at all. The variability and unpredictability of these symptoms can lead to significant stress and anxiety. Emotional and mental health issues are common among these patients, as they cope with the fear of potential hemorrhages and the impact on their daily lives.
Impact on Quality of Life
The quality of life for patients with cavernous malformations can vary greatly. Factors such as the location and size of the malformation, the frequency and severity of symptoms, and the patient’s overall health play a crucial role. Some individuals are able to maintain a relatively normal lifestyle, while others may face limitations in their physical abilities, work, and social interactions. It’s crucial for patients to have access to comprehensive care, including medical treatment, psychological support, and lifestyle counseling.
Support Systems and Resources for Cavernous Malformation Patients
Living with cavernous malformations is not only about managing medical symptoms but also about having the right support and resources. A robust support system and access to reliable resources can greatly enhance the quality of life for these patients.
Support Networks
- Healthcare Teams: A multidisciplinary healthcare team is essential. This team often includes neurologists, neurosurgeons, radiologists, and other specialists who understand the complexities of cavernous malformations.
- Support Groups: Many patients find solace and understanding in support groups. These groups provide a platform to share experiences, coping strategies, and emotional support.
- Family and Friends: The role of family and friends cannot be overstated. They provide emotional support, assist in navigating medical care, and help in maintaining a sense of normalcy.
Resources Available
- Educational Materials: Understanding the condition is vital. Hospitals, clinics, and patient advocacy groups often provide educational materials and resources.
- Online Platforms: Websites and online forums dedicated to cavernous malformations offer a wealth of information, including the latest research, treatment options, and patient stories.
- Financial and Legal Assistance: Managing a chronic condition can be costly. Access to financial and legal assistance programs can help alleviate some of these burdens.
Living with cavernous malformations presents unique challenges, but with the right support and resources, patients can lead fulfilling lives. Understanding patient experiences and providing comprehensive care and support systems are key to improving their quality of life. As awareness and knowledge about cavernous malformations grow, so does the hope for better treatments and outcomes for those affected by this condition.
Recent Research and Developments in Cavernous Malformations
Recent advancements in research and development have shed light on new findings and ongoing studies, offering hope for improved treatment and management strategies.
Summarizing the Latest Findings
- Genetic Discoveries: One of the most significant areas of recent research has focused on the genetic aspects of cavernous malformations. Studies have identified specific gene mutations responsible for CCMs, such as mutations in the CCM1, CCM2, and CCM3 genes. Understanding these genetic components has opened the door for targeted genetic therapies.
- Advances in Imaging Techniques: Improved imaging technologies, like high-resolution MRI, have made it easier to diagnose and monitor cavernous malformations. These advancements help in detecting smaller lesions and understanding the growth pattern of these malformations, crucial for treatment planning.
- Drug Development: Recent studies have explored various pharmacological approaches to treat or stabilize CCMs. For instance, research on drugs that can stabilize blood vessel walls or reduce leakage from these malformations is ongoing. These drugs aim to mitigate symptoms and prevent complications like hemorrhages.
- Surgical Techniques: Innovations in surgical techniques have also been a focus. Minimally invasive surgeries and advanced navigational tools have made the surgical removal of accessible lesions safer and more effective, reducing the risks associated with traditional open surgery.
Future Prospects in Treatment and Management
- Personalized Medicine: As we understand more about the genetic factors behind CCMs, personalized medicine becomes a promising prospect. Tailoring treatments based on individual genetic makeup could significantly improve outcomes.
- Stem Cell Research: Stem cell therapy is an emerging area of interest. The potential of stem cells to repair damaged blood vessels and restore normal blood flow in the affected areas could revolutionize treatment for cavernous malformations.
- Preventive Strategies: With advancements in genetic research, identifying individuals at risk of developing CCMs becomes feasible, leading to early interventions and preventive strategies.
- Collaborative Research Programs: Increased collaboration between research institutions worldwide is facilitating a more comprehensive understanding of CCMs. This collaboration is expected to accelerate the discovery of new treatments and management strategies.
- Public Awareness and Education: Enhancing public awareness and education about cavernous malformations is crucial. It ensures that individuals with CCMs receive timely diagnoses and access to the latest treatments, improving overall patient outcomes.
However, the field of cavernous malformations is witnessing significant progress, from genetic discoveries to surgical innovations. With ongoing research and future prospects focusing on personalized medicine, stem cell therapy, and preventive strategies, there is a hopeful outlook for individuals affected by this condition. The key lies in continued research, collaboration, and awareness to bring these advancements from the laboratory to clinical practice.
FAQ Section: Understanding Cavernous Malformations – Symptoms and Causes
1. What are cavernous malformations?
Cavernous malformations are abnormal blood vessels in the brain and spinal cord. They are sometimes referred to as cavernomas or cavernous angiomas. These malformations are characterized by clusters of dilated blood vessels that form lesions, which can vary in size and number.
2. What causes cavernous malformations?
The exact cause of cavernous malformations is not fully understood. They can be congenital (present at birth) or develop later in life. Genetic factors play a role in some cases, especially when multiple family members are affected. However, many cases occur sporadically with no clear genetic link.
3. What are the symptoms of cavernous malformations?
Symptoms vary depending on the size and location of the malformation. Common symptoms include headaches, seizures, stroke-like symptoms (such as weakness or numbness in limbs), vision problems, and bleeding in the brain (hemorrhage). However, some people with cavernous malformations may not experience any symptoms.
4. How are cavernous malformations diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests like MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) scans. These tests help in identifying the presence and extent of the malformations.
5. Can cavernous malformations lead to complications?
Yes, cavernous malformations can lead to complications, such as bleeding in the brain, neurological deficits, and increased risk of stroke. It’s important to monitor these malformations regularly to manage potential risks.
6. Are there treatments available for cavernous malformations?
Treatment options depend on the symptoms and risks associated with the malformation. In some cases, monitoring without immediate treatment is sufficient. Surgical removal may be considered for malformations that cause significant symptoms or have bled. Stereotactic radiosurgery is another treatment option for certain cases.
7. Can lifestyle changes help manage cavernous malformations?
While lifestyle changes cannot cure cavernous malformations, they can help manage symptoms and reduce risk factors for complications. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing blood pressure, and avoiding activities that increase the risk of head injury are advisable.
8. Is there a genetic test for cavernous malformations?
Genetic testing is available, especially for those with a family history of cavernous malformations. It can help in identifying the genetic mutation responsible and assist in family planning and risk assessment.
9. How common are cavernous malformations?
Cavernous malformations are relatively rare, affecting about 0.5% of the population. However, they can occur in any age group.
10. Can cavernous malformations recur after treatment?
There is a risk of recurrence, particularly in cases where the malformation was not completely removed during surgery. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is important for early detection and management of any recurrence.
Conclusion
With the complexity and variability of symptoms and causes, self-diagnosis is not advisable. This brings us to the most crucial point: the importance of consulting healthcare professionals. A medical expert can provide a thorough evaluation, accurate diagnosis, and a tailor-made treatment plan. Their guidance is invaluable, especially considering the potential complications associated with cavernous malformations, such as bleeding or neurological damage.
Remember, early detection and professional medical advice are your best defenses against the potential risks posed by cavernous malformations. By staying informed and proactive about your health, and seeking timely medical consultation, you can effectively manage or mitigate the impacts of this condition.
In conclusion, awareness and understanding of cavernous malformations are fundamental, but they are just the starting point. The next, and most crucial step, is to seek the guidance and expertise of healthcare professionals. They are your partners in ensuring a healthy and well-informed approach to managing any health concerns, including cavernous malformations. Stay aware, stay informed, and never hesitate to reach out for professional medical advice.